Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability and Statistics Summary
Probability and Statistics Summary
Uploaded by
hernandezmaverick123Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Exam P FormulaDocument18 pagesExam P FormulaHông HoaNo ratings yet
- Issue Trees - The Definitive Guide (+in-Depth Examples) - Crafting CasesDocument147 pagesIssue Trees - The Definitive Guide (+in-Depth Examples) - Crafting CasesShubham Shah100% (1)
- Exam P Formula Sheet PDFDocument9 pagesExam P Formula Sheet PDFQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Technology (Casio)Document2 pagesProbability and Statistics Technology (Casio)paulNo ratings yet
- Calculating Probabilities Using Discrete Random Variables PDFDocument1 pageCalculating Probabilities Using Discrete Random Variables PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Statprob NotesDocument31 pagesStatprob NotesCatherine DitanNo ratings yet
- QBM101 FormulasDocument4 pagesQBM101 FormulasDeveshNo ratings yet
- Exam P: You Have What It Takes To PassDocument4 pagesExam P: You Have What It Takes To PassEllen HutagaolNo ratings yet
- BB113 Formula SheetDocument5 pagesBB113 Formula SheetmubbaahNo ratings yet
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDocument6 pagesList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNo ratings yet
- Mech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedDocument12 pagesMech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamFlávia PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamIsabel EirasNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument11 pagesAnalysisNISHANK KANSARANo ratings yet
- EC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesEC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFnormanNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument8 pagesFormula SheetLionel HectorNo ratings yet
- 课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalDocument2 pages课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalluoyifei1988No ratings yet
- Formula Help SheetDocument6 pagesFormula Help Sheetleah.efnNo ratings yet
- Statistic FormulasDocument4 pagesStatistic FormulasBasoko_LeaksNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Continuous Random VariablesDocument2 pagesStatistics of Continuous Random Variableshernandezmaverick123No ratings yet
- EDA - FormulaDocument2 pagesEDA - FormulaLyka Mae MancolNo ratings yet
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Document6 pagesCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401No ratings yet
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocument15 pagesCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyNo ratings yet
- Small Basin Is The: N.B. This Method Gives Good Results For Small Mountain BasinDocument9 pagesSmall Basin Is The: N.B. This Method Gives Good Results For Small Mountain BasinHubert MoforNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio Estati SticaDocument6 pagesFormula Rio Estati SticaGustavo MeloNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasMoshiurNo ratings yet
- GR22 Kapitel8 PEM PAMMDocument8 pagesGR22 Kapitel8 PEM PAMMFabian ScheiplNo ratings yet
- FormulaSheet Test 1Document6 pagesFormulaSheet Test 1bestreview7No ratings yet
- Exam FormulaSheetDocument1 pageExam FormulaSheetmqdghsxtrmNo ratings yet
- Inverse Normal Distribution (TI-nSpire)Document2 pagesInverse Normal Distribution (TI-nSpire)Shane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- SPFA01 6+Formula+SheetDocument3 pagesSPFA01 6+Formula+Sheettf9wgz2ysdNo ratings yet
- Stat 100 Formulas Probability TablesDocument6 pagesStat 100 Formulas Probability TablesApp CloudNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesModeling and Simulation Cheat SheetmaykelnawarNo ratings yet
- Formulas Tables 2021Document2 pagesFormulas Tables 2021bnvjNo ratings yet
- Discrete Uniform DistributionDocument7 pagesDiscrete Uniform DistributionRani GarginalNo ratings yet
- CLT Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCLT Cheat SheetAli BissenovNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsDocument7 pages1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsÖmer Faruk DemirNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet MTE23Document1 pageFormula Sheet MTE23Meera AlhefaityNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning FoundamentalDocument10 pagesMachine Learning Foundamentals_m_hosseini_ardaliNo ratings yet
- Beberapa Fungsi Distribusi Variabel Random DiskretDocument1 pageBeberapa Fungsi Distribusi Variabel Random DiskretNyoman WidiantiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statistics - Formula SheetDocument26 pagesFinancial Statistics - Formula Sheetale.ili.pauNo ratings yet
- COR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution TablesDocument2 pagesCOR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution Tables19Y6C11 MEAGAN TSENG MEI-ENNo ratings yet
- Mostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulasDocument10 pagesMostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulaskayNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBADocument5 pagesHoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBAeferrentiadcapNo ratings yet
- GB Academy Equation ListDocument16 pagesGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerchxrlslxrrenNo ratings yet
- Formulario PyEDocument1 pageFormulario PyESamantha Michelle Ontiveros FloresNo ratings yet
- Formulario PyEDocument1 pageFormulario PyEScorpion 1504No ratings yet
- CLT Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCLT Cheat SheethighkidarcNo ratings yet
- HW2 - Reliability Analysis: AnswerDocument6 pagesHW2 - Reliability Analysis: AnswerYen-Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz1 PDFyusufreviNo ratings yet
- Review 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesReview 2 Summarydinhbinhan19052005No ratings yet
- Rumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorDocument2 pagesRumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorAhmad Nur HadieNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFDocument7 pagesEstimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Solution SAS 2023 8Document2 pagesSolution SAS 2023 8PALANIAPPAN CNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic Transient Flow EquationDocument20 pages4 Basic Transient Flow EquationĐậu ChươngNo ratings yet
- Skew NessDocument13 pagesSkew NessBibek GaireNo ratings yet
- Statistic PartCDocument12 pagesStatistic PartCAnkit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- My First 10 Years ProjectDocument2 pagesMy First 10 Years ProjectahdyalNo ratings yet
- Nynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetDocument1 pageNynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetAnonymous S29FwnFNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2020) - 3Document2 pagesPractice Test (2020) - 3Duy HảiNo ratings yet
- Pontryagin's Maximum PrincipleDocument21 pagesPontryagin's Maximum PrincipleAhmed TalbiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6گل میوہNo ratings yet
- Building Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFDocument41 pagesBuilding Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFFgpeqwNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Deped Region 7 Poblacion, Talisay City, CebuDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Deped Region 7 Poblacion, Talisay City, CebuMarjorie Nervez Sarino Bongato50% (2)
- SkullDocument9 pagesSkullمحمد اینانلوNo ratings yet
- Material-Handler HydraForce 2015Document10 pagesMaterial-Handler HydraForce 2015yonggilNo ratings yet
- Business Plan-HCB MFGDocument18 pagesBusiness Plan-HCB MFGGenene asefa Debele75% (4)
- Community Involvement Output The Importance of Community Development ProjectsDocument7 pagesCommunity Involvement Output The Importance of Community Development ProjectsMark Angelo NasNo ratings yet
- Vietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListDocument9 pagesVietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListThe Cultural CommitteeNo ratings yet
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- Crowd Behavior, Crowd Control, and The Use of Non-Lethal WeaponsDocument48 pagesCrowd Behavior, Crowd Control, and The Use of Non-Lethal WeaponsHussainNo ratings yet
- A Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) Approach To Improve Overall Equipment EfficiencyDocument4 pagesA Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) Approach To Improve Overall Equipment EfficiencyIJMERNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Materials SelectionDocument2 pagesTutorial Materials SelectionSyahmiNo ratings yet
- ADT Service ManualDocument152 pagesADT Service ManualZakhele MpofuNo ratings yet
- Imperial Remnant Rules SheetDocument1 pageImperial Remnant Rules SheetJd DibrellNo ratings yet
- The Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFDocument25 pagesThe Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFmehedee129No ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and DesignDocument8 pagesObject-Oriented Systems Analysis and DesignAmar KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management: Chapter 4 Richards/Renandya Methodology in Language Teaching. (Marilyn Lewis)Document4 pagesClassroom Management: Chapter 4 Richards/Renandya Methodology in Language Teaching. (Marilyn Lewis)Florencia CorenaNo ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- Safety Matrix Master - Rev 1Document5 pagesSafety Matrix Master - Rev 1praagthishNo ratings yet
- SR Designworks: Head OfficeDocument15 pagesSR Designworks: Head Officeihameed4100% (1)
- Internship 2021Document25 pagesInternship 2021PRAGYA CHANSORIYANo ratings yet
- Chavan Avinash-Resume 2Document1 pageChavan Avinash-Resume 2Adinath Baliram ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Translator 文华在线教育 - Collaboration Agreement Bilingual TemplateDocument5 pagesTranslator 文华在线教育 - Collaboration Agreement Bilingual TemplateАлтер КацизнеNo ratings yet
- Ztable 2Document4 pagesZtable 2Yosua SiregarNo ratings yet
Probability and Statistics Summary
Probability and Statistics Summary
Uploaded by
hernandezmaverick123Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Statistics Summary
Probability and Statistics Summary
Uploaded by
hernandezmaverick123Copyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Statistics Summary
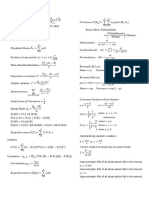
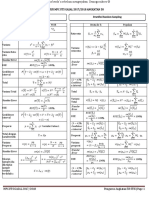
Conditional probability Addition rule
Pr(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) Pr(𝐴 ∪ 𝐵) = Pr(𝐴) + Pr(𝐵) − Pr(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵)
Pr(𝐴|𝐵) = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
Pr(𝐵)
Multiplication rule Law of total probability
Pr(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) = Pr(𝐵) × Pr(𝐴|𝐵) Pr(𝐴) = Pr(𝐵) × Pr(𝐴|𝐵) + Pr(𝐵 ) × Pr(𝐴|𝐵 )
Complement Combinations
Pr(𝐴 ) = 1 − Pr(𝐴) 𝑛 𝑛!
C = = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯, or Pascal's Triangle
𝑟 𝑟! (𝑛 − 𝑟)!
Tree diagram: use for sampling / conditional probability questions
Karnaugh map (table): use for intersection and union questions
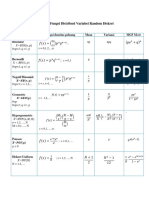
Discrete random variable
Probability density given by a table / graph / function
𝜇= 𝑥 Pr(𝑋 = 𝑥) , 𝜎 = (𝑥 − 𝜇) Pr(𝑋 = 𝑥) = 𝑥 Pr(𝑋 = 𝑥) − 𝜇
mean 𝜇 = E(𝑋) variance var(𝑋) = 𝜎 = E (𝑋 − 𝜇) = E(𝑋 ) − 𝜇
Binomial distribution Sample proportions
𝑋~Bi(𝑛, 𝑝), 𝑥 ∈ {0,1, … , 𝑛} 𝑋
𝑃 = ⎯⎯, 𝑋~Bi(𝑛, 𝑝)
𝑛
Pr(𝑋 = 𝑥) = C 𝑝 (1 − 𝑝)
Pr 𝑃 = 𝑝̂ = C 𝑝 (1 − 𝑝)
𝜇 = 𝑛𝑝, 𝜎 = 𝑛𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
𝜇 = 𝑝, 𝜎 = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
𝑛
Continuous random variable
Probability density given by function Pr(𝑎 ≤ 𝑋 ≤ 𝑏) = 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥
1
𝜇= 𝑥𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥 𝜎 = (𝑥 − 𝜇) 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥 − 𝜇 𝑓(𝑥)d𝑥 = ⎯⎯
2
Normal distribution Standard normal distribution Sample proportions
𝑋~N(𝜇, 𝜎) 𝑥−𝜇 ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
𝑍~N(0,1), 𝑧 = ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ 𝑝(1 − 𝑝)
CAS / 68-95-99.7% Rule 𝜎 𝑃~N 𝑝, ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
𝑛
Approximately 68% of the data lies within 1 standard deviation
Approximately 95% of the data lies within 2 standard deviations
Approximately 99.7% of the data lies within 3 standard deviations
Confidence interval
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
𝑝̂ (1 − 𝑝̂ ) 𝑝̂ (1 − 𝑝̂ ) for 90%, 𝑧 ≈ 1.64
𝑝̂ − 𝑧 ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯, 𝑝̂ + 𝑧 ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ , for 95%, 𝑧 ≈ 1.96 or 𝑧 ≈ 2
𝑛 𝑛 for 99%, 𝑧 ≈ 2.58
You might also like
- Exam P FormulaDocument18 pagesExam P FormulaHông HoaNo ratings yet
- Issue Trees - The Definitive Guide (+in-Depth Examples) - Crafting CasesDocument147 pagesIssue Trees - The Definitive Guide (+in-Depth Examples) - Crafting CasesShubham Shah100% (1)
- Exam P Formula Sheet PDFDocument9 pagesExam P Formula Sheet PDFQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Technology (Casio)Document2 pagesProbability and Statistics Technology (Casio)paulNo ratings yet
- Calculating Probabilities Using Discrete Random Variables PDFDocument1 pageCalculating Probabilities Using Discrete Random Variables PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Statprob NotesDocument31 pagesStatprob NotesCatherine DitanNo ratings yet
- QBM101 FormulasDocument4 pagesQBM101 FormulasDeveshNo ratings yet
- Exam P: You Have What It Takes To PassDocument4 pagesExam P: You Have What It Takes To PassEllen HutagaolNo ratings yet
- BB113 Formula SheetDocument5 pagesBB113 Formula SheetmubbaahNo ratings yet
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDocument6 pagesList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNo ratings yet
- Mech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedDocument12 pagesMech 430 Final Formula Sheet UpdatedSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamFlávia PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamIsabel EirasNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument11 pagesAnalysisNISHANK KANSARANo ratings yet
- EC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesEC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFnormanNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument8 pagesFormula SheetLionel HectorNo ratings yet
- 课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalDocument2 pages课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalluoyifei1988No ratings yet
- Formula Help SheetDocument6 pagesFormula Help Sheetleah.efnNo ratings yet
- Statistic FormulasDocument4 pagesStatistic FormulasBasoko_LeaksNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Continuous Random VariablesDocument2 pagesStatistics of Continuous Random Variableshernandezmaverick123No ratings yet
- EDA - FormulaDocument2 pagesEDA - FormulaLyka Mae MancolNo ratings yet
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Document6 pagesCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401No ratings yet
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocument15 pagesCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyNo ratings yet
- Small Basin Is The: N.B. This Method Gives Good Results For Small Mountain BasinDocument9 pagesSmall Basin Is The: N.B. This Method Gives Good Results For Small Mountain BasinHubert MoforNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio Estati SticaDocument6 pagesFormula Rio Estati SticaGustavo MeloNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasMoshiurNo ratings yet
- GR22 Kapitel8 PEM PAMMDocument8 pagesGR22 Kapitel8 PEM PAMMFabian ScheiplNo ratings yet
- FormulaSheet Test 1Document6 pagesFormulaSheet Test 1bestreview7No ratings yet
- Exam FormulaSheetDocument1 pageExam FormulaSheetmqdghsxtrmNo ratings yet
- Inverse Normal Distribution (TI-nSpire)Document2 pagesInverse Normal Distribution (TI-nSpire)Shane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- SPFA01 6+Formula+SheetDocument3 pagesSPFA01 6+Formula+Sheettf9wgz2ysdNo ratings yet
- Stat 100 Formulas Probability TablesDocument6 pagesStat 100 Formulas Probability TablesApp CloudNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesModeling and Simulation Cheat SheetmaykelnawarNo ratings yet
- Formulas Tables 2021Document2 pagesFormulas Tables 2021bnvjNo ratings yet
- Discrete Uniform DistributionDocument7 pagesDiscrete Uniform DistributionRani GarginalNo ratings yet
- CLT Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCLT Cheat SheetAli BissenovNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsDocument7 pages1.2 Discrete-Time Random Processes: 1.2.1 Sample Spaces and EventsÖmer Faruk DemirNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet MTE23Document1 pageFormula Sheet MTE23Meera AlhefaityNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning FoundamentalDocument10 pagesMachine Learning Foundamentals_m_hosseini_ardaliNo ratings yet
- Beberapa Fungsi Distribusi Variabel Random DiskretDocument1 pageBeberapa Fungsi Distribusi Variabel Random DiskretNyoman WidiantiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statistics - Formula SheetDocument26 pagesFinancial Statistics - Formula Sheetale.ili.pauNo ratings yet
- COR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution TablesDocument2 pagesCOR-STAT1202 Formula Sheet and Distribution Tables19Y6C11 MEAGAN TSENG MEI-ENNo ratings yet
- Mostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulasDocument10 pagesMostly Harmless Statistics Formula Packet: Chapter 3 FormulaskayNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBADocument5 pagesHoja de Formulas Primer Parcial2 (1) CANTONI UBAeferrentiadcapNo ratings yet
- GB Academy Equation ListDocument16 pagesGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerchxrlslxrrenNo ratings yet
- Formulario PyEDocument1 pageFormulario PyESamantha Michelle Ontiveros FloresNo ratings yet
- Formulario PyEDocument1 pageFormulario PyEScorpion 1504No ratings yet
- CLT Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCLT Cheat SheethighkidarcNo ratings yet
- HW2 - Reliability Analysis: AnswerDocument6 pagesHW2 - Reliability Analysis: AnswerYen-Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz1 PDFyusufreviNo ratings yet
- Review 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesReview 2 Summarydinhbinhan19052005No ratings yet
- Rumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorDocument2 pagesRumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorAhmad Nur HadieNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFDocument7 pagesEstimation of Mean Vector and Variance Covariance Matrix PDFMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- Solution SAS 2023 8Document2 pagesSolution SAS 2023 8PALANIAPPAN CNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic Transient Flow EquationDocument20 pages4 Basic Transient Flow EquationĐậu ChươngNo ratings yet
- Skew NessDocument13 pagesSkew NessBibek GaireNo ratings yet
- Statistic PartCDocument12 pagesStatistic PartCAnkit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- My First 10 Years ProjectDocument2 pagesMy First 10 Years ProjectahdyalNo ratings yet
- Nynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetDocument1 pageNynas Transformer Oil - Nytro 10GBN: Naphthenics Product Data SheetAnonymous S29FwnFNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2020) - 3Document2 pagesPractice Test (2020) - 3Duy HảiNo ratings yet
- Pontryagin's Maximum PrincipleDocument21 pagesPontryagin's Maximum PrincipleAhmed TalbiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document24 pagesChapter 6گل میوہNo ratings yet
- Building Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFDocument41 pagesBuilding Chatbots in Python Chapter2 PDFFgpeqwNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Deped Region 7 Poblacion, Talisay City, CebuDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Deped Region 7 Poblacion, Talisay City, CebuMarjorie Nervez Sarino Bongato50% (2)
- SkullDocument9 pagesSkullمحمد اینانلوNo ratings yet
- Material-Handler HydraForce 2015Document10 pagesMaterial-Handler HydraForce 2015yonggilNo ratings yet
- Business Plan-HCB MFGDocument18 pagesBusiness Plan-HCB MFGGenene asefa Debele75% (4)
- Community Involvement Output The Importance of Community Development ProjectsDocument7 pagesCommunity Involvement Output The Importance of Community Development ProjectsMark Angelo NasNo ratings yet
- Vietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListDocument9 pagesVietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListThe Cultural CommitteeNo ratings yet
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- Crowd Behavior, Crowd Control, and The Use of Non-Lethal WeaponsDocument48 pagesCrowd Behavior, Crowd Control, and The Use of Non-Lethal WeaponsHussainNo ratings yet
- A Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) Approach To Improve Overall Equipment EfficiencyDocument4 pagesA Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) Approach To Improve Overall Equipment EfficiencyIJMERNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Materials SelectionDocument2 pagesTutorial Materials SelectionSyahmiNo ratings yet
- ADT Service ManualDocument152 pagesADT Service ManualZakhele MpofuNo ratings yet
- Imperial Remnant Rules SheetDocument1 pageImperial Remnant Rules SheetJd DibrellNo ratings yet
- The Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFDocument25 pagesThe Microsoft-Nokia Strategic Alliance PDFmehedee129No ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and DesignDocument8 pagesObject-Oriented Systems Analysis and DesignAmar KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management: Chapter 4 Richards/Renandya Methodology in Language Teaching. (Marilyn Lewis)Document4 pagesClassroom Management: Chapter 4 Richards/Renandya Methodology in Language Teaching. (Marilyn Lewis)Florencia CorenaNo ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- Safety Matrix Master - Rev 1Document5 pagesSafety Matrix Master - Rev 1praagthishNo ratings yet
- SR Designworks: Head OfficeDocument15 pagesSR Designworks: Head Officeihameed4100% (1)
- Internship 2021Document25 pagesInternship 2021PRAGYA CHANSORIYANo ratings yet
- Chavan Avinash-Resume 2Document1 pageChavan Avinash-Resume 2Adinath Baliram ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Translator 文华在线教育 - Collaboration Agreement Bilingual TemplateDocument5 pagesTranslator 文华在线教育 - Collaboration Agreement Bilingual TemplateАлтер КацизнеNo ratings yet
- Ztable 2Document4 pagesZtable 2Yosua SiregarNo ratings yet