Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reflection
Reflection
Uploaded by
akber.kasamaliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Matriculation Physics (Geometrical Optics)Document99 pagesMatriculation Physics (Geometrical Optics)ridwan100% (9)
- Acoustic PresentationDocument17 pagesAcoustic Presentationarpanaroy179% (14)
- Mamdouh Gadalla ViejoDocument389 pagesMamdouh Gadalla ViejoAngie CamposNo ratings yet
- Light Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightDocument11 pagesLight Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument63 pagesReflection and Refraction of Lightzarish ziaNo ratings yet
- Light PuntlandDocument131 pagesLight PuntlandSaid Mohamed Mahad100% (1)
- S2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Document15 pagesS2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Kyaw Sit Nyein MaungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document185 pagesChapter 13farhanasikder123No ratings yet
- L8 G8 Reflection of LightDocument7 pagesL8 G8 Reflection of LightDina ThebianNo ratings yet
- Mirror'sDocument21 pagesMirror'sjanaicaackermanNo ratings yet
- 2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Document175 pages2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of ImagesDocument23 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Imagesmantilejoshua05No ratings yet
- Chapter 12: LightDocument9 pagesChapter 12: LightLi HongNo ratings yet
- Phy Quiz PDFDocument34 pagesPhy Quiz PDF202000123No ratings yet
- G10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesDocument98 pagesG10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesErika Mae Cordero100% (1)
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- P 13 Light 0625Document165 pagesP 13 Light 0625ravi.komaragiri76No ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and Refractionsalmasoma100% (1)
- HandPicked - Ray and Wave Optics by Aditya ParekhDocument16 pagesHandPicked - Ray and Wave Optics by Aditya Parekhadityaparekh705No ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument31 pagesLIGHT FinalyourmoNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 ReflectionDocument32 pagesCh.3 ReflectionPui Kwan LAINo ratings yet
- LightDocument15 pagesLightAfrina Asmi MINo ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument32 pagesLIGHT Finalehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light FeaturesDocument14 pagesChapter 7 - Light FeaturesMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Experiment No 1Document3 pagesLab Report - Experiment No 1Jawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Optical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesRay Optics Optical InstrumentsPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 LightDocument165 pagesUnit 6 LightBlop100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- SO OpticsDocument126 pagesSO OpticsHollyNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesLIGHT Power Point Presentationmuhammad umair100% (1)
- TERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightDocument22 pagesTERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightSolinaNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument19 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- C7 LightDocument40 pagesC7 LightKyle Miguel YcasianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Light - Reflection - and - RefractionDocument27 pagesChapter - 1 Light - Reflection - and - Refractionmadhavkaushik105No ratings yet
- Light - Free Exam AcademyDocument20 pagesLight - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Lecture UnacademyDocument57 pagesRay Optics Lecture UnacademyAbhishek Shukla100% (1)
- 3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3Document3 pages3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3NIMISH GARGNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- 05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pages05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Nikki NinjaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesDocument7 pagesLecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesparveezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryDocument3 pagesScience 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryAbigail CastroNo ratings yet
- Plane Mirrors: Score Date PerformedDocument4 pagesPlane Mirrors: Score Date PerformedGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 24898Document20 pagesReflection and Refraction 24898Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument27 pagesLIGHTInayaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument35 pagesReflection of Lightcharlesferrer718No ratings yet
- 12-Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument10 pages12-Reflection and Refraction of LightGIENo ratings yet
- Experiment Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759No ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Ray OpticsDocument12 pagesChapter 26 Ray OpticsKevin JiangNo ratings yet
- Wa0058.Document38 pagesWa0058.yadavdaksh986No ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and RefractionLily PlayzNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Physics 11Document16 pagesRay Optics: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3Document13 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Light - Strand 1Document17 pagesLight - Strand 1aaravNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics NotesDocument35 pagesRay Optics NotesNarenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - LightDocument56 pagesChapter 7 - LightMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light Till RefractionDocument49 pagesChapter 7 - Light Till RefractionMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Light For StudentsDocument70 pagesLight For StudentsVinu FelixNo ratings yet
- Light Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsDocument34 pagesLight Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsertugozNo ratings yet
- Light-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusDocument7 pagesLight-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Optics Part 1Document26 pagesLecture 20 - Optics Part 1Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Phong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionFrom EverandPhong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Oak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceDocument142 pagesOak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceГоар МкртичянNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Water PoollDocument14 pagesTutoria Water PoollahaaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics SyllabusDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics SyllabusAdarsh ThakareNo ratings yet
- Physics General ObjectivesDocument22 pagesPhysics General ObjectivesOlamide RokeebNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences 8Document39 pagesPhysical Sciences 8cyoung36No ratings yet
- Access To Success: Annual Examination-2013 Form One-Physics TIME:2:30HRS Name& SurnameDocument8 pagesAccess To Success: Annual Examination-2013 Form One-Physics TIME:2:30HRS Name& SurnameShani Ahmed SagiruNo ratings yet
- Buku Rujukan Fizik T4 KSSM Full - 158-191Document34 pagesBuku Rujukan Fizik T4 KSSM Full - 158-191Nathielly FuchsiaNo ratings yet
- Bijalwan 2020Document9 pagesBijalwan 2020Manisha ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Refraction QuestionsDocument18 pagesRefraction QuestionsSaransh Goyal100% (2)
- Slide Micro Teaching 5.3Document18 pagesSlide Micro Teaching 5.3Mastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- Waves and LightDocument21 pagesWaves and LightTheEinsteinofTomorrowNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument16 pagesLab ManualJhonny raunNo ratings yet
- 003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012Document28 pages003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012arian tejaratNo ratings yet
- Physics Crap SupermacyDocument16 pagesPhysics Crap SupermacyyourmoNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY of Physics 9-10Document44 pagesSUMMARY of Physics 9-10freeuser3No ratings yet
- 8 Critical Analysis of General ScienceDocument19 pages8 Critical Analysis of General ScienceMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionShubham Jain100% (1)
- Edexcel International AS Physics: Refraction, Re Ection & PolarisationDocument22 pagesEdexcel International AS Physics: Refraction, Re Ection & PolarisationAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Acoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCDocument14 pagesAcoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCKomal ChopadaNo ratings yet
- Ial Physics Unit 2 QP NoteDocument9 pagesIal Physics Unit 2 QP NoteNafisa NujhatNo ratings yet
- DPP-01 To 29Document145 pagesDPP-01 To 29Lisa JordanNo ratings yet
- Physics of Sound in JelloDocument2 pagesPhysics of Sound in JelloWyatt KesterNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics ReportDocument3 pagesDielectrics ReportFuckNo ratings yet
- FAST47 - 6 Optical FibreDocument7 pagesFAST47 - 6 Optical FibreSteveNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Document7 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Johnace_87No ratings yet
- LatihanDocument18 pagesLatihanAhmad DulfiNo ratings yet
- Dr.J.vinoth Kumar - Optical CommunicationDocument191 pagesDr.J.vinoth Kumar - Optical Communicationmech examNo ratings yet
Reflection
Reflection
Uploaded by
akber.kasamaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflection
Reflection
Uploaded by
akber.kasamaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflection of Light
It is the bouncing back of light rays in the same medium. If a ray of light strikes a plane
mirror and is bounced back on the same side, the process is called Reflection of Light.
Incident Ray:
It is the ray of light which strikes the surface.
Reflected Ray:
It is the ray of light which is bounced back after striking the surface.
Normal:
It is an imaginary 90° line drawn from the point of incidence of plane mirror.
Point of Incidence:
It is the point at which the ray of light strikes the surface.
Angle of incidence:
It is the angle between the incident ray and the normal (∠ i).
Angle of Reflection:
It is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (∠ r ).
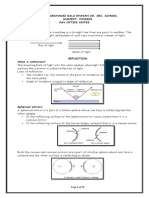
Laws of Reflection: Plane Mirror
Incident Ray
1. Angle of incidence is always equal to
the angle of reflection.
∠ i=∠ r
∠i
Normal
2. The incident ray, the reflected ray ∠r
Point of Incidence
and the normal all lie in the same
plane.
Reflected Ray
∠i =∠r
Experiment ⇨ To prove laws of reflection of light
Apparatus:
Wooden Board
Drawing Sheet
Plane Mirror
Common Pins
Thumb Pins
Protractor
Steps:
Fix the drawing sheet the wooden board with thumb pins and draw an outline of a
plane mirror in the middle of the sheet. From the midpoint of the outline, draw a
90° line (normal) and an angle of incidence (e.g. 40° to the normal). Fix two pins
on the incident ray line and look from the other side of the paper and fix two more
pins in such a manner that all 4 pins appear to be in a straight line. Draw the
reflected ray after removing the pins and measure the angle of reflection.
Observation:
Angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Keep in mind that due to human
error the angles might not be equal but very close.
Steps for Accuracy:
Thin lines are drawn for an accurate measurement.
While making the positions of the reflected ray pins we observe the bottom so
that the tilt of pins don’t affect.
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal must be more than 5cm long
as the radius of the protractor is 5cm.
Result:
The experiment proves the laws of reflection.
Image Formation by a Plane Mirror:
1. A plane mirror forms a virtual image; this image cannot be obtained on the
screen.
2. The size of the image in the plane mirror is equal to the size of the object.
3. The distance of the image in the mirror is equal to the distance of the object in
front of the mirror.
4. The image formed by a plane mirror is laterally inverted; it means that the right
hand side of the object comes to the left hand side of the image and vice versa.
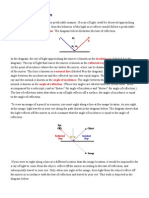
Ray Diagrams:
Place an object in front of a x cm x cm
plane mirror.
Construct the incident ray and
the reflected ray using the law Object Image
∠ i=∠ r .
Extend the reflected ray
backwards until the object ∠i
Normal
distance from the mirror is
∠r
the same as the image
distance from the mirror.
Object and image have to be
exactly opposite to each other.
Eye
END
You might also like
- Matriculation Physics (Geometrical Optics)Document99 pagesMatriculation Physics (Geometrical Optics)ridwan100% (9)
- Acoustic PresentationDocument17 pagesAcoustic Presentationarpanaroy179% (14)
- Mamdouh Gadalla ViejoDocument389 pagesMamdouh Gadalla ViejoAngie CamposNo ratings yet
- Light Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightDocument11 pagesLight Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument63 pagesReflection and Refraction of Lightzarish ziaNo ratings yet
- Light PuntlandDocument131 pagesLight PuntlandSaid Mohamed Mahad100% (1)
- S2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Document15 pagesS2-2nd Edit Unit-6 (6.1 Reflection)Kyaw Sit Nyein MaungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document185 pagesChapter 13farhanasikder123No ratings yet
- L8 G8 Reflection of LightDocument7 pagesL8 G8 Reflection of LightDina ThebianNo ratings yet
- Mirror'sDocument21 pagesMirror'sjanaicaackermanNo ratings yet
- 2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Document175 pages2e. 6091 Sec 4 Compiled Lesson Notes-1Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of ImagesDocument23 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Imagesmantilejoshua05No ratings yet
- Chapter 12: LightDocument9 pagesChapter 12: LightLi HongNo ratings yet
- Phy Quiz PDFDocument34 pagesPhy Quiz PDF202000123No ratings yet
- G10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesDocument98 pagesG10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesErika Mae Cordero100% (1)
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedDocument6 pagesQualitative Characteristics of Images: Absorbed Reflection Scatters TransmittedMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- P 13 Light 0625Document165 pagesP 13 Light 0625ravi.komaragiri76No ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and Refractionsalmasoma100% (1)
- HandPicked - Ray and Wave Optics by Aditya ParekhDocument16 pagesHandPicked - Ray and Wave Optics by Aditya Parekhadityaparekh705No ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument31 pagesLIGHT FinalyourmoNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 ReflectionDocument32 pagesCh.3 ReflectionPui Kwan LAINo ratings yet
- LightDocument15 pagesLightAfrina Asmi MINo ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument32 pagesLIGHT Finalehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light FeaturesDocument14 pagesChapter 7 - Light FeaturesMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Experiment No 1Document3 pagesLab Report - Experiment No 1Jawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Optical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesRay Optics Optical InstrumentsPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 LightDocument165 pagesUnit 6 LightBlop100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- SO OpticsDocument126 pagesSO OpticsHollyNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesLIGHT Power Point Presentationmuhammad umair100% (1)
- TERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightDocument22 pagesTERM+4+Ppt +Reflection+of+LightSolinaNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument19 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- C7 LightDocument40 pagesC7 LightKyle Miguel YcasianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Light - Reflection - and - RefractionDocument27 pagesChapter - 1 Light - Reflection - and - Refractionmadhavkaushik105No ratings yet
- Light - Free Exam AcademyDocument20 pagesLight - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Lecture UnacademyDocument57 pagesRay Optics Lecture UnacademyAbhishek Shukla100% (1)
- 3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3Document3 pages3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3NIMISH GARGNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesMuhammad Ahsan Ali KharalNo ratings yet
- 05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pages05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Nikki NinjaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesDocument7 pagesLecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesparveezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryDocument3 pagesScience 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryAbigail CastroNo ratings yet
- Plane Mirrors: Score Date PerformedDocument4 pagesPlane Mirrors: Score Date PerformedGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 24898Document20 pagesReflection and Refraction 24898Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument27 pagesLIGHTInayaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument35 pagesReflection of Lightcharlesferrer718No ratings yet
- 12-Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument10 pages12-Reflection and Refraction of LightGIENo ratings yet
- Experiment Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759No ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Ray OpticsDocument12 pagesChapter 26 Ray OpticsKevin JiangNo ratings yet
- Wa0058.Document38 pagesWa0058.yadavdaksh986No ratings yet
- Physics 18 - Reflection and RefractionDocument53 pagesPhysics 18 - Reflection and RefractionLily PlayzNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Physics 11Document16 pagesRay Optics: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3Document13 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Light - Strand 1Document17 pagesLight - Strand 1aaravNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics NotesDocument35 pagesRay Optics NotesNarenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - LightDocument56 pagesChapter 7 - LightMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light Till RefractionDocument49 pagesChapter 7 - Light Till RefractionMahmoud AltohamyNo ratings yet
- Light For StudentsDocument70 pagesLight For StudentsVinu FelixNo ratings yet
- Light Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsDocument34 pagesLight Waves: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in PhysicsertugozNo ratings yet
- Light-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusDocument7 pagesLight-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Optics Part 1Document26 pagesLecture 20 - Optics Part 1Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Phong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionFrom EverandPhong Reflection Model: Understanding Light Interactions in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Oak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceDocument142 pagesOak 2021 Secondary ks3 ks4 ScienceГоар МкртичянNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Water PoollDocument14 pagesTutoria Water PoollahaaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics SyllabusDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics SyllabusAdarsh ThakareNo ratings yet
- Physics General ObjectivesDocument22 pagesPhysics General ObjectivesOlamide RokeebNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences 8Document39 pagesPhysical Sciences 8cyoung36No ratings yet
- Access To Success: Annual Examination-2013 Form One-Physics TIME:2:30HRS Name& SurnameDocument8 pagesAccess To Success: Annual Examination-2013 Form One-Physics TIME:2:30HRS Name& SurnameShani Ahmed SagiruNo ratings yet
- Buku Rujukan Fizik T4 KSSM Full - 158-191Document34 pagesBuku Rujukan Fizik T4 KSSM Full - 158-191Nathielly FuchsiaNo ratings yet
- Bijalwan 2020Document9 pagesBijalwan 2020Manisha ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Refraction QuestionsDocument18 pagesRefraction QuestionsSaransh Goyal100% (2)
- Slide Micro Teaching 5.3Document18 pagesSlide Micro Teaching 5.3Mastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- Waves and LightDocument21 pagesWaves and LightTheEinsteinofTomorrowNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument16 pagesLab ManualJhonny raunNo ratings yet
- 003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012Document28 pages003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012arian tejaratNo ratings yet
- Physics Crap SupermacyDocument16 pagesPhysics Crap SupermacyyourmoNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY of Physics 9-10Document44 pagesSUMMARY of Physics 9-10freeuser3No ratings yet
- 8 Critical Analysis of General ScienceDocument19 pages8 Critical Analysis of General ScienceMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionShubham Jain100% (1)
- Edexcel International AS Physics: Refraction, Re Ection & PolarisationDocument22 pagesEdexcel International AS Physics: Refraction, Re Ection & PolarisationAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Acoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCDocument14 pagesAcoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCKomal ChopadaNo ratings yet
- Ial Physics Unit 2 QP NoteDocument9 pagesIal Physics Unit 2 QP NoteNafisa NujhatNo ratings yet
- DPP-01 To 29Document145 pagesDPP-01 To 29Lisa JordanNo ratings yet
- Physics of Sound in JelloDocument2 pagesPhysics of Sound in JelloWyatt KesterNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics ReportDocument3 pagesDielectrics ReportFuckNo ratings yet
- FAST47 - 6 Optical FibreDocument7 pagesFAST47 - 6 Optical FibreSteveNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Document7 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan School Grade Level IV Teacher Learning Area Science Date and Time Quarter 3Johnace_87No ratings yet
- LatihanDocument18 pagesLatihanAhmad DulfiNo ratings yet
- Dr.J.vinoth Kumar - Optical CommunicationDocument191 pagesDr.J.vinoth Kumar - Optical Communicationmech examNo ratings yet