Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Uploaded by
Angel ZuñigaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- En Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsDocument15 pagesEn Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsshaheerNo ratings yet
- NCP For Gouty ArthritisDocument3 pagesNCP For Gouty ArthritisMolly HollyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Constipationbmrose3783% (12)
- 5 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without SurgeryDocument4 pages5 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without SurgeryYamini AnilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- Otc Advisor PainDocument24 pagesOtc Advisor Painfarzad100% (2)
- Technicalites of Health Insurance: Underwriting, Actuarial, Reinsurance, TPA and Claims For Order: Harish@Document4 pagesTechnicalites of Health Insurance: Underwriting, Actuarial, Reinsurance, TPA and Claims For Order: Harish@Harish SihareNo ratings yet
- 2011 Monitoring in Anesthesia and Perioperative CareDocument437 pages2011 Monitoring in Anesthesia and Perioperative CareOskar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Guide - Tail Lift Operators - A Simple GuideDocument8 pagesGuide - Tail Lift Operators - A Simple GuideMichailidis KonstantinosNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Joint Pain: Common Words, Phrases Used With Oa KneeDocument7 pagesMechanical Joint Pain: Common Words, Phrases Used With Oa KneePramestiningtyasNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Pain Exploring A Complex RelationshipDocument6 pagesExercise and Pain Exploring A Complex RelationshipPipsKhoor FxNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sosm Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation Guideline 11x8 - 5Document5 pagesFlyer Sosm Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation Guideline 11x8 - 5Pedro GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 - Durerea La Persoanele in Varsta Institutionalizate LTCDocument30 pagesCurs 3 - Durerea La Persoanele in Varsta Institutionalizate LTCPop AndreiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPHendy Hency YunusNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Physiotherapy Treatment PDFDocument10 pages4 Types of Physiotherapy Treatment PDFAshley D FrickNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Opioids SummariesDocument55 pagesPain Management Opioids SummariesPeter KhanhNo ratings yet
- Pain Management TechniquesDocument22 pagesPain Management Techniques9tmj9b22xvNo ratings yet
- Physiotheraphy Role in Pain ManagementDocument63 pagesPhysiotheraphy Role in Pain Management姐姐雯No ratings yet
- Jurnal William Flexion Exercise PDFDocument13 pagesJurnal William Flexion Exercise PDFRennyRay67% (3)
- Assessment NeuroDocument2 pagesAssessment NeurodhagallarteNo ratings yet
- Pain AssessmentDocument43 pagesPain AssessmentJalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- Gulseren Chronic PainDocument35 pagesGulseren Chronic PainneareastspineNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Acute Pain Management: A Guide To Multimodal Analgesia and Quality ImprovementDocument10 pagesOptimizing Acute Pain Management: A Guide To Multimodal Analgesia and Quality ImprovementAgus HendraNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Current Treatment Options in The Management of Severe Pain: William Campbell MD, PHD, Frca, Ffarcsi, FfpmrcaDocument10 pagesCurrent Treatment Options in The Management of Severe Pain: William Campbell MD, PHD, Frca, Ffarcsi, FfpmrcaJonathan TulipNo ratings yet
- Pain Sessment: Pain in The Cognitively ImpairedDocument43 pagesPain Sessment: Pain in The Cognitively Impairedalya1alya1No ratings yet
- College of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Care of Mother, Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Care of Mother, Child at Risk or With ProblemsDanica Yen PagalNo ratings yet
- Pain Rehabilitation: Husnul Mubarak, SP - KFRDocument32 pagesPain Rehabilitation: Husnul Mubarak, SP - KFRAhdiat Sang MantanNo ratings yet
- Managing Dystonia Through Exercise and PhysiotherapyDocument15 pagesManaging Dystonia Through Exercise and PhysiotherapyMohd AsadNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Implementing NICE GuidanceDocument19 pagesLow Back Pain: Implementing NICE GuidanceEsha Putriningtyas SetiawanNo ratings yet
- BARANDINO, Jia Laurice (Gouty Arthritis)Document18 pagesBARANDINO, Jia Laurice (Gouty Arthritis)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Sports InjuiresDocument18 pagesRehabilitation of Sports InjuiresSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAppendicitisjustinekaye diongsonNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice: SHS.423 Saba Nadeem DarDocument31 pagesEvidence Based Practice: SHS.423 Saba Nadeem DarFaheem MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ehc 65Document8 pagesEhc 65Faeyz OrabiNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Exercise As A Treatment For Chronic PainDocument5 pagesExercise As A Treatment For Chronic PainEvelyn MalaguttiNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Prescribing Opioids For Chronic Pain: When CONSIDERING Long-Term Opioid TherapyDocument1 pageChecklist For Prescribing Opioids For Chronic Pain: When CONSIDERING Long-Term Opioid TherapyMarcelo UGNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy and Artritis Information BookletDocument16 pagesPhysiotherapy and Artritis Information BookletFaheem ullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AssignmentDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Assignmentapi-576653292No ratings yet
- Physical Therapy BlogDocument4 pagesPhysical Therapy BlogZaira GonzálezNo ratings yet
- M1 Introduction To Manual TherapyDocument101 pagesM1 Introduction To Manual TherapySylvia LoongNo ratings yet
- Medical Policy: Title: Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger PointsDocument10 pagesMedical Policy: Title: Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger PointsRo KohnNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Touch For Health Kinesiology: The Art of Muscle MonitoringDocument2 pagesTouch For Health Kinesiology: The Art of Muscle MonitoringRukaphuongNo ratings yet
- Class 2 - Mental HealthDocument51 pagesClass 2 - Mental HealthAli RizwanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Aging WomenDocument52 pagesWeek 4 - Aging Womenmemoona kaleemNo ratings yet
- New Insights Into BED HandoutDocument6 pagesNew Insights Into BED HandoutjuanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Anorexia NervosaDocument20 pagesMental Health Anorexia NervosaregisterednurseNo ratings yet
- Terapi Rehabilitatif Pada Kondisi NyeriDocument32 pagesTerapi Rehabilitatif Pada Kondisi NyeriMutiara JihadNo ratings yet
- Schemes of ExercisesDocument12 pagesSchemes of Exercisesdnyanesh_23patilNo ratings yet
- painHEALTH Using A Pain TeamDocument4 pagespainHEALTH Using A Pain TeamMuhamad GumilangNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Delirium Screening PRISMEDocument1 pageDelirium Screening PRISMEWardah Fauziah El SofwanNo ratings yet
- SHURTLEFF - 9-22-16 WorkshopDocument21 pagesSHURTLEFF - 9-22-16 WorkshopMiguel TrillosNo ratings yet
- Therapy LIVE Ben CormackDocument23 pagesTherapy LIVE Ben Cormackgemichan26No ratings yet
- Pain Management Literature Review Poster by Megan Jones Kelsey Rising Cheyenne Singleton and Lauren SyersakDocument1 pagePain Management Literature Review Poster by Megan Jones Kelsey Rising Cheyenne Singleton and Lauren Syersakapi-663972838No ratings yet
- BB-NEDIC - Nutrition Care For Individuals With Eating Disorders - WEBDocument4 pagesBB-NEDIC - Nutrition Care For Individuals With Eating Disorders - WEBangela cabrejosNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11Document5 pagesFlyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11toaldoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravispsyNo ratings yet
- Medical Journal of Australia - 2023 - Langford - Clinical Practice Guideline For Deprescribing Opioid Analgesics SummaryDocument10 pagesMedical Journal of Australia - 2023 - Langford - Clinical Practice Guideline For Deprescribing Opioid Analgesics SummaryJuan Carlos Perez ParadaNo ratings yet
- What Interventions Are Effective To Taper Opioids in Patients With Chronic Pain?Document5 pagesWhat Interventions Are Effective To Taper Opioids in Patients With Chronic Pain?JoseA delgilNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach NotesDocument5 pagesBobath Approach NotesJuling Perales100% (3)
- Tongue Diagnosis Class PDFDocument157 pagesTongue Diagnosis Class PDFManea Laurentiu100% (13)
- Mapeh e - Class RecordDocument54 pagesMapeh e - Class RecordAnne Panlibuton TuanteNo ratings yet
- 05 Fiji Reproductive Health Policy MoH 2014Document36 pages05 Fiji Reproductive Health Policy MoH 2014Nawal KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Output: Abnormal PsychologyDocument5 pagesFinal Output: Abnormal PsychologyJobelle Cariño ResuelloNo ratings yet
- DR AnithaDocument24 pagesDR AnithaShivansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Icd CodingDocument58 pagesIcd CodingagnaveenanNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- College Wise BSC Nursing Vacant SeatsDocument8 pagesCollege Wise BSC Nursing Vacant SeatsBalu P NairNo ratings yet
- Management of Pneumonia in Intensive Care: Andrew Conway MorrisDocument17 pagesManagement of Pneumonia in Intensive Care: Andrew Conway MorrisWillian Palma GómezNo ratings yet
- NCP HomeworkDocument6 pagesNCP HomeworkAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- 5Document4 pages5Kelli BaldwinNo ratings yet
- Revised Madison City Schools 2021-2022 Reentry Plan - 8!2!21BDocument9 pagesRevised Madison City Schools 2021-2022 Reentry Plan - 8!2!21BKelsey DuncanNo ratings yet
- SMC CompiledDocument2 pagesSMC CompiledLovely De CastroNo ratings yet
- AneuScreen English EliDocument17 pagesAneuScreen English EliHaim EzerNo ratings yet
- DLL Hope1-W1Document5 pagesDLL Hope1-W1Patrick John Carmen100% (1)
- Orca Share Media1567258117004Document10 pagesOrca Share Media1567258117004Monique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Informed ApproachDocument111 pagesTrauma Informed Approachalejandra sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Wireless Biomedical Parameters Using Arm9Document8 pagesWireless Biomedical Parameters Using Arm919501A0475 NALLIBOYINA RAJESHNo ratings yet
- Advnce Directive ADocument14 pagesAdvnce Directive ACharlene GonzalesNo ratings yet
- How Depression Affects ChristiansDocument10 pagesHow Depression Affects ChristiansAdrian FurnicaNo ratings yet
- PlasmanateDocument4 pagesPlasmanateroelNo ratings yet
- Οδυσσέας Γκιλής. Propaganda. Θεσσαλονίκη 2016Document36 pagesΟδυσσέας Γκιλής. Propaganda. Θεσσαλονίκη 2016odysseas_gilisNo ratings yet
- Doctor List PDFDocument9 pagesDoctor List PDFVeronica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Relative Reinforcing Value of FoodDocument11 pagesRelative Reinforcing Value of FoodEnrique AlarconNo ratings yet
- Pt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangDocument17 pagesPt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangGhriya ReynathaNo ratings yet
- PTS Xi Sem 2 2020Document7 pagesPTS Xi Sem 2 2020KatarinaNo ratings yet
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Uploaded by
Angel ZuñigaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Visual-Summary-On-The-Management-Of Osteoarthritis
Uploaded by
Angel ZuñigaCopyright:
Available Formats
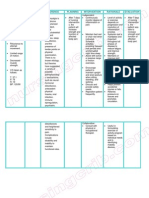
Management of osteoarthritis
Explain that:
Pharmacological management
• osteoarthritis is diagnosed clinically and usually does not need imaging to confirm diagnosis
• management is guided by symptoms and physical function If needed, use:
• the core treatments are therapeutic exercise and weight management, alongside information and support. • alongside non-pharmacological treatments and to
support therapeutic exercise
Exercise Weight management Information and support • the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible
time.
• For all people with osteoarthritis, • Tailor information to the person’s
offer therapeutic exercise tailored For people who are living with Review with the person whether to continue treatment.
overweight or obesity: individual needs and ensure it is Base frequency of reviews on clinical need.
to their needs (for example, local in an accessible format.
muscle strengthening, general • advise them that weight loss will
• Advise where people can find • Offer a topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
aerobic fitness). improve quality of life and physical
further information on: (NSAID) for knee osteoarthritis.
• Consider supervised therapeutic function, and reduce pain
o the condition and information • Consider a topical NSAID for other osteoarthritis-
exercise sessions. • support them to choose a weight
that challenges common affected joints.
• Advise people it may initially loss goal
• explain that any weight loss is likely misconceptions Consider an oral NSAID if topical medicines are
cause pain or discomfort but o specific types of exercise
long-term adherence to an exercise to be beneficial, but losing 10% is ineffective or unsuitable and offer
likely to be better than 5%. o managing their symptoms a gastroprotective treatment alongside.
plan will benefit the joints, reduce o how to access additional
pain and improve function. For guidance and information on information and support
• Consider combining therapeutic Do not offer:
weight management, including o benefits and limitations of
exercise with an education • paracetamol or weak opioids routinely, unless:
interventions for weight loss, see treatment.
programme or behaviour change o used infrequently for short-term pain relief
NICE’s topic page on obesity.
approaches in a structured o all other treatments are ineffective or unsuitable
treatment package. • glucosamine
• strong opioids
• intra-articular hyaluronan injections.
Do not offer:
Manual therapy Devices Consider intra-articular corticosteroid
• acupuncture or dry needling
Only consider for hip and knee Consider walking aids for lower injections for short-term relief when other
• electrotherapy treatments
osteoarthritis and alongside limb osteoarthritis. pharmacological treatments are ineffective or unsuitable
• insoles, braces, tape, splints or
therapeutic exercise. or to support therapeutic exercise.
supports routinely.
This is a summary of the recommendations on Referral for joint replacement
managing osteoarthritis in NICE’s guideline on
osteoarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management
Consider referring people with hip, knee or shoulder osteoarthritis for joint replacement if:
• joint symptoms are substantially impacting their quality of life and
• non-surgical management is ineffective or unsuitable.
Do not exclude people from referral for joint1replacement because of age, sex or gender, smoking, comorbidities, or overweight or obesity.
Published October 2022 © NICE 2022. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights.
You might also like
- En Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsDocument15 pagesEn Proefexamen VOL VCA QuestionsshaheerNo ratings yet
- NCP For Gouty ArthritisDocument3 pagesNCP For Gouty ArthritisMolly HollyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Constipationbmrose3783% (12)
- 5 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without SurgeryDocument4 pages5 Ways To Treat Chronic Back Pain Without SurgeryYamini AnilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- Otc Advisor PainDocument24 pagesOtc Advisor Painfarzad100% (2)
- Technicalites of Health Insurance: Underwriting, Actuarial, Reinsurance, TPA and Claims For Order: Harish@Document4 pagesTechnicalites of Health Insurance: Underwriting, Actuarial, Reinsurance, TPA and Claims For Order: Harish@Harish SihareNo ratings yet
- 2011 Monitoring in Anesthesia and Perioperative CareDocument437 pages2011 Monitoring in Anesthesia and Perioperative CareOskar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Guide - Tail Lift Operators - A Simple GuideDocument8 pagesGuide - Tail Lift Operators - A Simple GuideMichailidis KonstantinosNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Joint Pain: Common Words, Phrases Used With Oa KneeDocument7 pagesMechanical Joint Pain: Common Words, Phrases Used With Oa KneePramestiningtyasNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Pain Exploring A Complex RelationshipDocument6 pagesExercise and Pain Exploring A Complex RelationshipPipsKhoor FxNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sosm Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation Guideline 11x8 - 5Document5 pagesFlyer Sosm Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation Guideline 11x8 - 5Pedro GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 - Durerea La Persoanele in Varsta Institutionalizate LTCDocument30 pagesCurs 3 - Durerea La Persoanele in Varsta Institutionalizate LTCPop AndreiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPHendy Hency YunusNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Physiotherapy Treatment PDFDocument10 pages4 Types of Physiotherapy Treatment PDFAshley D FrickNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Opioids SummariesDocument55 pagesPain Management Opioids SummariesPeter KhanhNo ratings yet
- Pain Management TechniquesDocument22 pagesPain Management Techniques9tmj9b22xvNo ratings yet
- Physiotheraphy Role in Pain ManagementDocument63 pagesPhysiotheraphy Role in Pain Management姐姐雯No ratings yet
- Jurnal William Flexion Exercise PDFDocument13 pagesJurnal William Flexion Exercise PDFRennyRay67% (3)
- Assessment NeuroDocument2 pagesAssessment NeurodhagallarteNo ratings yet
- Pain AssessmentDocument43 pagesPain AssessmentJalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- Gulseren Chronic PainDocument35 pagesGulseren Chronic PainneareastspineNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Acute Pain Management: A Guide To Multimodal Analgesia and Quality ImprovementDocument10 pagesOptimizing Acute Pain Management: A Guide To Multimodal Analgesia and Quality ImprovementAgus HendraNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Current Treatment Options in The Management of Severe Pain: William Campbell MD, PHD, Frca, Ffarcsi, FfpmrcaDocument10 pagesCurrent Treatment Options in The Management of Severe Pain: William Campbell MD, PHD, Frca, Ffarcsi, FfpmrcaJonathan TulipNo ratings yet
- Pain Sessment: Pain in The Cognitively ImpairedDocument43 pagesPain Sessment: Pain in The Cognitively Impairedalya1alya1No ratings yet
- College of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Care of Mother, Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing Related Learning Experience Plan Course Title: NCM 109: Care of Mother, Child at Risk or With ProblemsDanica Yen PagalNo ratings yet
- Pain Rehabilitation: Husnul Mubarak, SP - KFRDocument32 pagesPain Rehabilitation: Husnul Mubarak, SP - KFRAhdiat Sang MantanNo ratings yet
- Managing Dystonia Through Exercise and PhysiotherapyDocument15 pagesManaging Dystonia Through Exercise and PhysiotherapyMohd AsadNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Implementing NICE GuidanceDocument19 pagesLow Back Pain: Implementing NICE GuidanceEsha Putriningtyas SetiawanNo ratings yet
- BARANDINO, Jia Laurice (Gouty Arthritis)Document18 pagesBARANDINO, Jia Laurice (Gouty Arthritis)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Sports InjuiresDocument18 pagesRehabilitation of Sports InjuiresSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAppendicitisjustinekaye diongsonNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice: SHS.423 Saba Nadeem DarDocument31 pagesEvidence Based Practice: SHS.423 Saba Nadeem DarFaheem MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ehc 65Document8 pagesEhc 65Faeyz OrabiNo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Exercise As A Treatment For Chronic PainDocument5 pagesExercise As A Treatment For Chronic PainEvelyn MalaguttiNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Prescribing Opioids For Chronic Pain: When CONSIDERING Long-Term Opioid TherapyDocument1 pageChecklist For Prescribing Opioids For Chronic Pain: When CONSIDERING Long-Term Opioid TherapyMarcelo UGNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy and Artritis Information BookletDocument16 pagesPhysiotherapy and Artritis Information BookletFaheem ullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AssignmentDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Assignmentapi-576653292No ratings yet
- Physical Therapy BlogDocument4 pagesPhysical Therapy BlogZaira GonzálezNo ratings yet
- M1 Introduction To Manual TherapyDocument101 pagesM1 Introduction To Manual TherapySylvia LoongNo ratings yet
- Medical Policy: Title: Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger PointsDocument10 pagesMedical Policy: Title: Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger PointsRo KohnNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Touch For Health Kinesiology: The Art of Muscle MonitoringDocument2 pagesTouch For Health Kinesiology: The Art of Muscle MonitoringRukaphuongNo ratings yet
- Class 2 - Mental HealthDocument51 pagesClass 2 - Mental HealthAli RizwanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Aging WomenDocument52 pagesWeek 4 - Aging Womenmemoona kaleemNo ratings yet
- New Insights Into BED HandoutDocument6 pagesNew Insights Into BED HandoutjuanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Anorexia NervosaDocument20 pagesMental Health Anorexia NervosaregisterednurseNo ratings yet
- Terapi Rehabilitatif Pada Kondisi NyeriDocument32 pagesTerapi Rehabilitatif Pada Kondisi NyeriMutiara JihadNo ratings yet
- Schemes of ExercisesDocument12 pagesSchemes of Exercisesdnyanesh_23patilNo ratings yet
- painHEALTH Using A Pain TeamDocument4 pagespainHEALTH Using A Pain TeamMuhamad GumilangNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Delirium Screening PRISMEDocument1 pageDelirium Screening PRISMEWardah Fauziah El SofwanNo ratings yet
- SHURTLEFF - 9-22-16 WorkshopDocument21 pagesSHURTLEFF - 9-22-16 WorkshopMiguel TrillosNo ratings yet
- Therapy LIVE Ben CormackDocument23 pagesTherapy LIVE Ben Cormackgemichan26No ratings yet
- Pain Management Literature Review Poster by Megan Jones Kelsey Rising Cheyenne Singleton and Lauren SyersakDocument1 pagePain Management Literature Review Poster by Megan Jones Kelsey Rising Cheyenne Singleton and Lauren Syersakapi-663972838No ratings yet
- BB-NEDIC - Nutrition Care For Individuals With Eating Disorders - WEBDocument4 pagesBB-NEDIC - Nutrition Care For Individuals With Eating Disorders - WEBangela cabrejosNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11Document5 pagesFlyer Sosm Stress Fracture Rehab Guideline 8 - 5x11toaldoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravispsyNo ratings yet
- Medical Journal of Australia - 2023 - Langford - Clinical Practice Guideline For Deprescribing Opioid Analgesics SummaryDocument10 pagesMedical Journal of Australia - 2023 - Langford - Clinical Practice Guideline For Deprescribing Opioid Analgesics SummaryJuan Carlos Perez ParadaNo ratings yet
- What Interventions Are Effective To Taper Opioids in Patients With Chronic Pain?Document5 pagesWhat Interventions Are Effective To Taper Opioids in Patients With Chronic Pain?JoseA delgilNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach NotesDocument5 pagesBobath Approach NotesJuling Perales100% (3)
- Tongue Diagnosis Class PDFDocument157 pagesTongue Diagnosis Class PDFManea Laurentiu100% (13)
- Mapeh e - Class RecordDocument54 pagesMapeh e - Class RecordAnne Panlibuton TuanteNo ratings yet
- 05 Fiji Reproductive Health Policy MoH 2014Document36 pages05 Fiji Reproductive Health Policy MoH 2014Nawal KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Output: Abnormal PsychologyDocument5 pagesFinal Output: Abnormal PsychologyJobelle Cariño ResuelloNo ratings yet
- DR AnithaDocument24 pagesDR AnithaShivansh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Icd CodingDocument58 pagesIcd CodingagnaveenanNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- College Wise BSC Nursing Vacant SeatsDocument8 pagesCollege Wise BSC Nursing Vacant SeatsBalu P NairNo ratings yet
- Management of Pneumonia in Intensive Care: Andrew Conway MorrisDocument17 pagesManagement of Pneumonia in Intensive Care: Andrew Conway MorrisWillian Palma GómezNo ratings yet
- NCP HomeworkDocument6 pagesNCP HomeworkAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- 5Document4 pages5Kelli BaldwinNo ratings yet
- Revised Madison City Schools 2021-2022 Reentry Plan - 8!2!21BDocument9 pagesRevised Madison City Schools 2021-2022 Reentry Plan - 8!2!21BKelsey DuncanNo ratings yet
- SMC CompiledDocument2 pagesSMC CompiledLovely De CastroNo ratings yet
- AneuScreen English EliDocument17 pagesAneuScreen English EliHaim EzerNo ratings yet
- DLL Hope1-W1Document5 pagesDLL Hope1-W1Patrick John Carmen100% (1)
- Orca Share Media1567258117004Document10 pagesOrca Share Media1567258117004Monique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Informed ApproachDocument111 pagesTrauma Informed Approachalejandra sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Wireless Biomedical Parameters Using Arm9Document8 pagesWireless Biomedical Parameters Using Arm919501A0475 NALLIBOYINA RAJESHNo ratings yet
- Advnce Directive ADocument14 pagesAdvnce Directive ACharlene GonzalesNo ratings yet
- How Depression Affects ChristiansDocument10 pagesHow Depression Affects ChristiansAdrian FurnicaNo ratings yet
- PlasmanateDocument4 pagesPlasmanateroelNo ratings yet
- Οδυσσέας Γκιλής. Propaganda. Θεσσαλονίκη 2016Document36 pagesΟδυσσέας Γκιλής. Propaganda. Θεσσαλονίκη 2016odysseas_gilisNo ratings yet
- Doctor List PDFDocument9 pagesDoctor List PDFVeronica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Relative Reinforcing Value of FoodDocument11 pagesRelative Reinforcing Value of FoodEnrique AlarconNo ratings yet
- Pt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangDocument17 pagesPt. Restu Cahaya Sejahtera Farma: Daftar Harga Jual BarangGhriya ReynathaNo ratings yet
- PTS Xi Sem 2 2020Document7 pagesPTS Xi Sem 2 2020KatarinaNo ratings yet