Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beeby Map ch05
Beeby Map ch05
Uploaded by
Koushikci Kanjilal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
beeby_map_ch05
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageBeeby Map ch05
Beeby Map ch05
Uploaded by
Koushikci KanjilalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
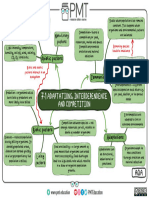
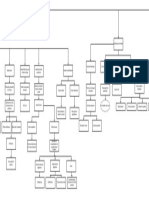
SPECIES INTERACTIONS
principally driven by resource acquisition
Interaction Competition Consumption Cooperation
Cost/benefit Cost to both species Benefit to consumer Benefit to both
cost to consumed or at least no cost to one
Type Herbivory Predation Parasitism/ Symbiosis Commensalism
Pathogens (facilitation)
Model Lotka-Volterra Tilman Lotka- SI Models
Volterra of infectious disease
Principal Interspecific > Each species Plant defences Periodic Size of S
Indication Intraspecific limited by a solution relative to
for different resource threshold
Secondary
competitive allows density (ST)
plant
exclusion coexistence
metabolites
Compensation
Missing Effect of other species Effect of other prey, predators;
Detail (predators, parasites), time; Numerical and functional responses
Cannot explain prevalence of –satiation, handling times.
coexistence in some ecosystems Animal defences.
Realized and fundamental niches Optimal foraging theory
character displacement
All examples of co-evolution
© Oxford University Press, 2012. All rights reserved.
Ch. 5 Interactions between Species
You might also like
- Science Notebook Answer Key Mendelian GeneticsDocument5 pagesScience Notebook Answer Key Mendelian GeneticsBasma Ahmed0% (1)
- Essentials of Physical Anthropology 3rd Edition Clark Test BankDocument10 pagesEssentials of Physical Anthropology 3rd Edition Clark Test BankTravisChristensenfteir100% (15)
- Elements of Ecology, 9e (Smith) Chapter 5 Adaptation and Natural SelectionDocument15 pagesElements of Ecology, 9e (Smith) Chapter 5 Adaptation and Natural SelectionChinNo ratings yet
- Modeling System ConceptDocument6 pagesModeling System ConceptMichael CorselloNo ratings yet
- ENVI SCI Lecture 5ADocument4 pagesENVI SCI Lecture 5AMary Rose SioNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u Population Dynamics - Part IVDocument4 pagesSbi4u Population Dynamics - Part IVmarNo ratings yet
- Wa0000Document10 pagesWa0000Eduardo AramayoNo ratings yet
- Mind Map ch7Document1 pageMind Map ch7hazel loyNo ratings yet
- SYMBIOSISDocument3 pagesSYMBIOSISJot BuenaNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology-: Communities Habitat Species BiodiversityDocument24 pagesCommunity Ecology-: Communities Habitat Species BiodiversityPercival DomingoNo ratings yet
- LIMITING FACTORS and INTERACTIONDocument39 pagesLIMITING FACTORS and INTERACTIONJayson Maesa BaisaNo ratings yet
- B7 Part 1 Mind Map TREBLESDocument1 pageB7 Part 1 Mind Map TREBLESkrishp06No ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship and Its TypesDocument33 pagesSymbiotic Relationship and Its TypesMayuri Vohra0% (1)
- 2018 Aljbory Chen Indirect Defense Against HerbivoreDocument22 pages2018 Aljbory Chen Indirect Defense Against HerbivorePriscila MezzomoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Ecological RelationshipsDocument35 pagesChapter 3 - Ecological RelationshipsJudy Ann SibayanNo ratings yet
- PSB 7 1306Document15 pagesPSB 7 1306zahra07No ratings yet
- The Evolutionnaryecology of Insect Chemicals To Plant Chemicals 2007Document11 pagesThe Evolutionnaryecology of Insect Chemicals To Plant Chemicals 2007Ng Kin HoongNo ratings yet
- Bioscience, Biotechnology, and BiochemistryDocument14 pagesBioscience, Biotechnology, and BiochemistryCARLOS ALBERTO OSORIO MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Final)Document13 pagesChapter 1 (Final)Jessa SelimNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test: Terms in This SetDocument5 pagesFlashcards Learn Write Spell Test: Terms in This SetBon AppleteaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of The EcosystemDocument15 pagesThe Basic Principles of The EcosystemMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 1-PagerDocument1 pageChapter 24 1-Pagerapi-522847737No ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human SocietyDocument4 pagesScience, Technology, and Society Lecture 5: Biodiversity and Human Societyjennylyn karunungan100% (1)
- 4 Agroecology IPMDocument16 pages4 Agroecology IPMZahara AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Relationships 1Document12 pagesEcological Relationships 1api-512405061No ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument1 pageResistanceisamat07No ratings yet
- Defense Mechanisms A. Mellifera (2015)Document12 pagesDefense Mechanisms A. Mellifera (2015)Felipe BecerraNo ratings yet
- Ahmed 1994Document7 pagesAhmed 1994Pacheco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document65 pagesGroup 1025wilmelNo ratings yet
- Crop Weed CompetetionDocument6 pagesCrop Weed CompetetionSendo SegundoNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test: Terms in This SetDocument7 pagesFlashcards Learn Write Spell Test: Terms in This SetBon AppleteaNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology & Species InteractionDocument7 pagesCommunity Ecology & Species InteractionWinsleth DizonNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Interactions Between Multiple Insecticide Resistance LociDocument6 pagesA Review of The Interactions Between Multiple Insecticide Resistance LociVictor Lauro Perez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Plant-Mediated Interactions Between Whiteflies, Herbivores, and Natural EnemiesDocument20 pagesPlant-Mediated Interactions Between Whiteflies, Herbivores, and Natural EnemieshwlsfgjodxtlcrquqyNo ratings yet
- Scienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFDocument12 pagesScienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFnaliniNo ratings yet
- Physical Interaction: Symbiotic Relationship SymbiosisDocument9 pagesPhysical Interaction: Symbiotic Relationship SymbiosisSanchi GargNo ratings yet
- FRAC - Fungicide - Mode of Action (以真菌life cycle角度) GOOOOOOOODDocument54 pagesFRAC - Fungicide - Mode of Action (以真菌life cycle角度) GOOOOOOOODCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Y9 Keywords CommDocument5 pagesY9 Keywords CommfugzieNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Inmunidad Mediada Por Efectores-2017-2018Document65 pages3.3. Inmunidad Mediada Por Efectores-2017-2018Sergio IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Fungicide Formulation and Mode of Action 1710748609Document11 pagesFungicide Formulation and Mode of Action 1710748609Raj ChandirasekaranNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Variation On Tree Tops 2018 LamkeDocument12 pagesPhytochemical Variation On Tree Tops 2018 LamkeClaude MenodzNo ratings yet
- Guerrieri 2008Document11 pagesGuerrieri 2008Edith TapiaNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument14 pagesUntitled NotebookPanda ProductionsNo ratings yet
- UGEB2360-7 Community EcologyDocument39 pagesUGEB2360-7 Community Ecologyhochungtang28No ratings yet
- Microbial EcologyDocument2 pagesMicrobial Ecologycheskhadomingo33No ratings yet
- Defense Mechanisms of Plants To Insect Pests: From Morphological To Biochemical ApproachDocument10 pagesDefense Mechanisms of Plants To Insect Pests: From Morphological To Biochemical ApproachDayanaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Ecology SlideDocument16 pagesBio 1 - Ecology SlideMatthew LimboNo ratings yet
- Periodontal War - Bs and InmunutyDocument65 pagesPeriodontal War - Bs and InmunutyAlejandra.ignacia20No ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Chain: Infectious AgentDocument1 pageCommunicable Disease Chain: Infectious AgentEmmanuel OpiyoNo ratings yet
- Y9glossary CommDocument5 pagesY9glossary CommfugzieNo ratings yet
- Inter Specific InteractionDocument7 pagesInter Specific InteractionSandeep kumar SathuaNo ratings yet
- 2020-Natural Variation and Resistance DurabilityDocument10 pages2020-Natural Variation and Resistance DurabilityJay Prakash MauryaNo ratings yet
- Population: What Are Some Ecological Interactions?Document11 pagesPopulation: What Are Some Ecological Interactions?Aldren Pagui-en BonaobraNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology & Species Interaction: ZGE 4301-Environmental Sciences Dept of Biological Sciences UE - ManilaDocument39 pagesCommunity Ecology & Species Interaction: ZGE 4301-Environmental Sciences Dept of Biological Sciences UE - ManilaMark ChouNo ratings yet
- Ir Section 14 2Document3 pagesIr Section 14 2Valeria RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Additive Genes Definition and Examples - Biology Online DictionaryDocument3 pagesAdditive Genes Definition and Examples - Biology Online DictionaryAzima SalisNo ratings yet
- Binder1 (1) - Part1Document1 pageBinder1 (1) - Part1MAURO CASTRO SALINASNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes TemplateDocument4 pagesCornell Notes Templateshehnaz akhtarNo ratings yet
- Mobilidade de FungicidasDocument5 pagesMobilidade de FungicidasCelismarNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Ecology - WikipediaDocument12 pagesBehavioral Ecology - WikipediadpolsekNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Interactions: Predation Competition IsDocument23 pagesPositive and Negative Interactions: Predation Competition IsRe HanaNo ratings yet
- Option C Full NotesDocument21 pagesOption C Full NotesIrksomeApple788 GamerNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Feb 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Feb 2023Koushikci KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11 Oct 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 11 Oct 2023Koushikci KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Biology Question PaperDocument15 pagesBiology Question PaperKoushikci KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Biology Test XXXXIIDocument5 pagesBiology Test XXXXIIKoushikci KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Molecular Systematic Lecture 1Document57 pagesMolecular Systematic Lecture 1hudaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approaches To Phylogeny)Document26 pagesSystematic Approaches To Phylogeny)Mhi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Isolating Mechanisms-2Document20 pagesIsolating Mechanisms-2Rupali GuravNo ratings yet
- Polygenic Traits ActivityDocument3 pagesPolygenic Traits ActivityAlveena ZehraNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology P3 Specimen PaperDocument3 pagesA Level Biology P3 Specimen PaperPrudence MasimbeNo ratings yet
- Notes On BiogeoraphyDocument1 pageNotes On BiogeoraphyHasin Ishrakh Shovon (191011066)No ratings yet
- 16.2 AnswersDocument2 pages16.2 AnswersMadison EilandNo ratings yet
- Homology (Biology)Document7 pagesHomology (Biology)Valentin MateiNo ratings yet
- Cecca F. & Alii 2006 - Evolution of The Tithonian Ammonite SemiformicerasDocument12 pagesCecca F. & Alii 2006 - Evolution of The Tithonian Ammonite Semiformiceraschin dasNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Natural SelectionDocument7 pagesEvolution and Natural SelectionMichelleneChenTadleNo ratings yet
- 45 Genetic AlgorithmsDocument20 pages45 Genetic AlgorithmsSachin A GaragNo ratings yet
- Mendoza WebquestDocument3 pagesMendoza Webquestapi-267645354No ratings yet
- ReebopsDocument2 pagesReebopschabriesNo ratings yet
- Bio Forum 8Document4 pagesBio Forum 8Daphne Khoo Xin EeNo ratings yet
- Els LT Adm 27Document6 pagesEls LT Adm 27KristineNo ratings yet
- Bio2581 Syllabus 2018Document6 pagesBio2581 Syllabus 2018api-389173677No ratings yet
- DLL FrontDocument4 pagesDLL FrontAnafemolyn NingascaNo ratings yet
- Bio 105: Genetics Practice Problems: Elizabeth DominguezDocument4 pagesBio 105: Genetics Practice Problems: Elizabeth Dominguezemily121602No ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Mark V. LomolinoDocument8 pagesFourth Edition: Mark V. LomolinoTapan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Bio Geography of EvolutionDocument34 pagesBio Geography of EvolutionMeylinNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument6 pagesHuman EvolutionblahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document15 pagesChapter 23nfnf otupyooorefnNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MechanismsDocument15 pagesEvolution of MechanismsJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- A Reflection Paper On "Tim Berra's Darwin's Paradigm Shift"Document3 pagesA Reflection Paper On "Tim Berra's Darwin's Paradigm Shift"Renren50% (2)
- Darwin's Theory of Natural SelectionDocument3 pagesDarwin's Theory of Natural SelectionSteve SmithNo ratings yet
- EVOLALALALABDocument7 pagesEVOLALALALABGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Multiple AllelesDocument8 pagesIncomplete Multiple AllelesMarc RusselNo ratings yet