Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2 Exercise2
Module 2 Exercise2
Uploaded by
saulgdm076Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Games Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadDocument18 pagesGames Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadAmyBrightdqjm100% (36)
- Study Guide Questions For Edogawa Rampo's "Human Chair" (1925)Document6 pagesStudy Guide Questions For Edogawa Rampo's "Human Chair" (1925)BeholdmyswarthyfaceNo ratings yet
- 서울대 게임이론 중간Document10 pages서울대 게임이론 중간유준우No ratings yet
- Test - Game TheoryDocument4 pagesTest - Game TheoryAmmi Julian100% (1)
- Appendix 5 - Geometrical Analysis of Consumer EquilibriumDocument8 pagesAppendix 5 - Geometrical Analysis of Consumer EquilibriumStevenRJClarkeNo ratings yet
- Class Test-I Intermediate Microeconomics-II Time: 1 Hour Maximum Marks: 25Document2 pagesClass Test-I Intermediate Microeconomics-II Time: 1 Hour Maximum Marks: 25amrat meenaNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet1 NewDocument2 pagesProblemSet1 Newsamx9950No ratings yet
- Game Theory Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesGame Theory Exam QuestionsPaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Game Theory Problem Set #1: Jörgen WeibullDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Game Theory Problem Set #1: Jörgen WeibullŞimal KöseoğluNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Rohan Lansakara0% (1)
- Problem Set OligopolyDocument3 pagesProblem Set Oligopolyasmitamittal1998No ratings yet
- Problems Repeated and Bayesian Game PDFDocument6 pagesProblems Repeated and Bayesian Game PDFvictorginer8No ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 (2022)Document1 pageProblem Set 3 (2022)AnneNo ratings yet
- ProblemBank203 2Document86 pagesProblemBank203 2canerNo ratings yet
- GCT 2015-16 - Final Exam - 2015-12-18 - SolutionDocument9 pagesGCT 2015-16 - Final Exam - 2015-12-18 - SolutionpadrefloNo ratings yet
- Monopoly SolutionsDocument2 pagesMonopoly SolutionszamirNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Oligopoly: Supergames 1Document42 pagesDynamic Oligopoly: Supergames 1Akash BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesFinal Exam SolutionsMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Markets and StrategyDocument4 pagesProblem Set 1 Markets and StrategyRick HeunisNo ratings yet
- 04 RepetitionDocument12 pages04 Repetitionbawar98947No ratings yet
- EMO 2020-2021 Final QuestionsDocument8 pagesEMO 2020-2021 Final QuestionsBobNo ratings yet
- GT Homework 1 PDFDocument5 pagesGT Homework 1 PDFAnonymous TbKiHGZgrNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 8Document3 pagesProblem Set 8Le MoustierNo ratings yet
- Exam M2O 2023Document4 pagesExam M2O 2023Sarah WajsbrotNo ratings yet
- Exercises Set BiaDocument17 pagesExercises Set BiadavopastorcarmenNo ratings yet
- GT Homework 6Document4 pagesGT Homework 6Anonymous TbKiHGZgrNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Merged PDFDocument50 pagesProblem Sets Merged PDFraspberryoriannaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microeconomics III: Game Theory Problem Set 1: Spring Term 2019Document4 pagesAdvanced Microeconomics III: Game Theory Problem Set 1: Spring Term 2019Marcelo Rodrigo RiffoNo ratings yet
- Test - Game Theory PDFDocument4 pagesTest - Game Theory PDFAmmi Julian100% (1)
- Econ 2022.2022.23. Assignment 1.WoADocument2 pagesEcon 2022.2022.23. Assignment 1.WoABereket AdamssegedNo ratings yet
- 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pages1 Multiple ChoicesanthoshNo ratings yet
- MGEBJ21-1 - End Term Question PaperDocument3 pagesMGEBJ21-1 - End Term Question PapermikeNo ratings yet
- XET 301-CEC 305 October-Jan 2022 ExaminantionDocument5 pagesXET 301-CEC 305 October-Jan 2022 ExaminantionABDULLAHI MUSA MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- HS 123 22Document12 pagesHS 123 22Pujan ShahNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2dianazokhrabekova100% (1)
- EC2066Document49 pagesEC2066Josiah KhorNo ratings yet
- Freq2 11jan12Document7 pagesFreq2 11jan12crod123456No ratings yet
- Computational Game Theory LCTN - Yishay MansourDocument150 pagesComputational Game Theory LCTN - Yishay MansourBay RazNo ratings yet
- Game Theory: Normal Form Games: Michael Levet June 23, 2016Document12 pagesGame Theory: Normal Form Games: Michael Levet June 23, 2016Dalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Assignment Help: ProblemsDocument7 pagesComputer Network Assignment Help: ProblemsComputer Network Assignment Help100% (1)
- Infinitely Repeated Games: U S UsDocument14 pagesInfinitely Repeated Games: U S Usswapneel_gen9599No ratings yet
- Chap 1: Normal Form Games: Step 1: Each Player Simultaneously and Independently Chooses An ActionDocument6 pagesChap 1: Normal Form Games: Step 1: Each Player Simultaneously and Independently Chooses An ActionFayçal SinaceurNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela End - Term Examination, 2017Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Rourkela End - Term Examination, 2017AbinashNo ratings yet
- Micro EconomicsDocument20 pagesMicro EconomicsLal ChhuanmawiaNo ratings yet
- Sagarika Game' 1Document43 pagesSagarika Game' 1Sandeep PramanikNo ratings yet
- MATH 308 - Assignment 5Document3 pagesMATH 308 - Assignment 5ThịnhNguyễnTrườngNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1Luka JanjalashviliNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lecture 5Document5 pagesModule 2 Lecture 5Swapan Kumar SahaNo ratings yet
- Mitschrift ExcerciseDocument18 pagesMitschrift ExcerciseJuKaschu0% (1)
- Home Test - 1: Exercise 1Document4 pagesHome Test - 1: Exercise 1Cindy LeeNo ratings yet
- Tha 3Document4 pagesTha 3hridai madhukarNo ratings yet
- Chap 010Document69 pagesChap 010hihi427No ratings yet
- Problem 1Document2 pagesProblem 1Velichka DimitrovaNo ratings yet
- Tha 5Document3 pagesTha 5Abhinash BorahNo ratings yet
- Problems Static Games PDFDocument9 pagesProblems Static Games PDFvictorginer8No ratings yet
- Pset 4Document3 pagesPset 4Amirreza TaheriNo ratings yet
- EBC2023 Managerial Economics - T01discussionDocument3 pagesEBC2023 Managerial Economics - T01discussionSuat NaneNo ratings yet
- Pset 4Document6 pagesPset 4Parminder SinghNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document2 pagesProblem Set 2Mar ConchaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT For Weekend Stu.Document2 pagesASSIGNMENT For Weekend Stu.yimerNo ratings yet
- Msc. in Economics Games & Contract Theory: Correct Answers: 0.5 Pts. Wrong Answers: - 0.25 Pts. (Document11 pagesMsc. in Economics Games & Contract Theory: Correct Answers: 0.5 Pts. Wrong Answers: - 0.25 Pts. (padrefloNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Take Home PDFDocument8 pagesGame Theory Take Home PDFDiego MontañaNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics CHP 5678Document24 pagesMicro Economics CHP 5678Imran farhathNo ratings yet
- Krishna Kanta Handiqui State Open University: (Only For The January 2021 Batch and in Lieu of MCQ Tests)Document4 pagesKrishna Kanta Handiqui State Open University: (Only For The January 2021 Batch and in Lieu of MCQ Tests)avatar sudarsanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandRulojyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument6 pagesElasticity of DemandVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- PVF, PVAF, CVF, CVAF Tables For Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesPVF, PVAF, CVF, CVAF Tables For Financial ManagementManish Kumar0% (1)
- Attribute Theory of Demand: by Dr. Biswabhusan Bhuyan (PH.D)Document9 pagesAttribute Theory of Demand: by Dr. Biswabhusan Bhuyan (PH.D)Shakthi BharatheeNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics 2.: Demand, Supply and Market EquilibriumDocument36 pagesManagerial Economics 2.: Demand, Supply and Market EquilibriumhenNo ratings yet
- Topical MCQs - A2 Economics - 2.1 - Consumer EquilibriumDocument24 pagesTopical MCQs - A2 Economics - 2.1 - Consumer EquilibriumidkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EcoDocument19 pagesChapter 4 EcoAfifah HananiNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Economics 6th Edition Bade Test BankDocument25 pagesFoundations of Economics 6th Edition Bade Test BankJenniferDiazqmfsi100% (59)
- Installment ExamplesDocument3 pagesInstallment ExamplesMohib HaqueNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand-3Document25 pagesElasticity of Demand-3vismayNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument53 pagesChapter ThreeshimelisNo ratings yet
- Bits f314 Mids QDocument2 pagesBits f314 Mids QArshdeep Singh KochharNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Economics For Managers 3 e 3rd Edition Paul G FarnhamDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Economics For Managers 3 e 3rd Edition Paul G Farnhamacraspedalucchesezsl3q100% (17)
- GT Homework 1Document5 pagesGT Homework 1John HunNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesExercises 1 - SolutionsbatuhanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics NVM Lec 2 PrefrencesDocument67 pagesMicroeconomics NVM Lec 2 Prefrencessatyam91No ratings yet
- CFO11e Micro Ch05Document28 pagesCFO11e Micro Ch05Ersin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Eco Project Pal Ak Class 11Document17 pagesEco Project Pal Ak Class 11astrobhavikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Demand Analysis & ForecastingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Demand Analysis & ForecastingAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- w4 Topic 3.consumer ChoiceDocument23 pagesw4 Topic 3.consumer Choice刘家亨No ratings yet
- Investment FunctionDocument17 pagesInvestment Functionapi-3757629No ratings yet
- ECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Document2 pagesECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeDocument6 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeBella AdrianaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12th MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12th MicroeconomicssubhashreeNo ratings yet
- Economics - Lecture 02: Prepared By: Cams GandaDocument25 pagesEconomics - Lecture 02: Prepared By: Cams GandaGladymae MaggayNo ratings yet
Module 2 Exercise2
Module 2 Exercise2
Uploaded by
saulgdm076Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2 Exercise2
Module 2 Exercise2
Uploaded by
saulgdm076Copyright:
Available Formats
ECO400: Decisions, Strategy and Information
Exercise sheet II.2
Strategic interaction II
Exercise 1: Consider a repeated game in which the following simultaneous-move game
is played twice:
-
b1 b2 b3
a1 11, 11 1, 12 0, 13
a2 12, 1 5, 5 0, 0
a3 13, 0 0, 0 2, 2
Prior to the second play of the game, the players observe the actions chosen in the first
play of the game. Suppose the players do not discount future payo↵s. What are the
pure strategy subgame perfect Nash equilibria of this game?
Exercise 2: There are two firms that produce a homogeneous good and each firm’s
marginal production cost is c (there are no fixed costs). Firms compete for customers by
setting prices simultaneously. Suppose that a firm can attract all customers whenever
its price is below the competitor’s price, i.e. there are no capacity constraints. When
the firms’ prices are equivalent, each firm serves half of the demand. Hence,
8
>
> D(pi ) if pi < pj
>
<
Di (p1 , p2 ) = 12 D(pj ) if pi = pj
>
>
>
:0 if pi > pj
a) What is the Nash equilibrium if the firms interact only once?
b) What is the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium if firms repeat the game for T
periods?
c) Suppose the game is infinitely repeated and firms discount future profits with
the discount factor . Under which condition is it possible for firms to sustain
monopoly profits in each period as a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium?
!
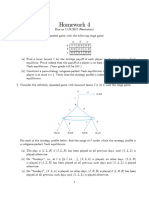
u1
Exercise 3: Consider the following game in extensive form where are the re-
u2
spective payo↵s of the two players:
Mohammed Mardan and Justin Valasek NHH
ECO400: Decisions, Strategy and Information
a) What are the strategies of players 1 and 2?
b) What is the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium of the game?
c) Represent the dynamic game in the normal form.
d) Determine all Nash equilibria in pure strategies. Are all Nash equilibria plausible?
Mohammed Mardan and Justin Valasek NHH
You might also like
- Games Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadDocument18 pagesGames Strategies and Decision Making 2nd Edition Harrington Solutions Manual DownloadAmyBrightdqjm100% (36)
- Study Guide Questions For Edogawa Rampo's "Human Chair" (1925)Document6 pagesStudy Guide Questions For Edogawa Rampo's "Human Chair" (1925)BeholdmyswarthyfaceNo ratings yet
- 서울대 게임이론 중간Document10 pages서울대 게임이론 중간유준우No ratings yet
- Test - Game TheoryDocument4 pagesTest - Game TheoryAmmi Julian100% (1)
- Appendix 5 - Geometrical Analysis of Consumer EquilibriumDocument8 pagesAppendix 5 - Geometrical Analysis of Consumer EquilibriumStevenRJClarkeNo ratings yet
- Class Test-I Intermediate Microeconomics-II Time: 1 Hour Maximum Marks: 25Document2 pagesClass Test-I Intermediate Microeconomics-II Time: 1 Hour Maximum Marks: 25amrat meenaNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet1 NewDocument2 pagesProblemSet1 Newsamx9950No ratings yet
- Game Theory Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesGame Theory Exam QuestionsPaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Game Theory Problem Set #1: Jörgen WeibullDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Game Theory Problem Set #1: Jörgen WeibullŞimal KöseoğluNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Rohan Lansakara0% (1)
- Problem Set OligopolyDocument3 pagesProblem Set Oligopolyasmitamittal1998No ratings yet
- Problems Repeated and Bayesian Game PDFDocument6 pagesProblems Repeated and Bayesian Game PDFvictorginer8No ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 (2022)Document1 pageProblem Set 3 (2022)AnneNo ratings yet
- ProblemBank203 2Document86 pagesProblemBank203 2canerNo ratings yet
- GCT 2015-16 - Final Exam - 2015-12-18 - SolutionDocument9 pagesGCT 2015-16 - Final Exam - 2015-12-18 - SolutionpadrefloNo ratings yet
- Monopoly SolutionsDocument2 pagesMonopoly SolutionszamirNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Oligopoly: Supergames 1Document42 pagesDynamic Oligopoly: Supergames 1Akash BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesFinal Exam SolutionsMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Markets and StrategyDocument4 pagesProblem Set 1 Markets and StrategyRick HeunisNo ratings yet
- 04 RepetitionDocument12 pages04 Repetitionbawar98947No ratings yet
- EMO 2020-2021 Final QuestionsDocument8 pagesEMO 2020-2021 Final QuestionsBobNo ratings yet
- GT Homework 1 PDFDocument5 pagesGT Homework 1 PDFAnonymous TbKiHGZgrNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 8Document3 pagesProblem Set 8Le MoustierNo ratings yet
- Exam M2O 2023Document4 pagesExam M2O 2023Sarah WajsbrotNo ratings yet
- Exercises Set BiaDocument17 pagesExercises Set BiadavopastorcarmenNo ratings yet
- GT Homework 6Document4 pagesGT Homework 6Anonymous TbKiHGZgrNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Merged PDFDocument50 pagesProblem Sets Merged PDFraspberryoriannaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microeconomics III: Game Theory Problem Set 1: Spring Term 2019Document4 pagesAdvanced Microeconomics III: Game Theory Problem Set 1: Spring Term 2019Marcelo Rodrigo RiffoNo ratings yet
- Test - Game Theory PDFDocument4 pagesTest - Game Theory PDFAmmi Julian100% (1)
- Econ 2022.2022.23. Assignment 1.WoADocument2 pagesEcon 2022.2022.23. Assignment 1.WoABereket AdamssegedNo ratings yet
- 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pages1 Multiple ChoicesanthoshNo ratings yet
- MGEBJ21-1 - End Term Question PaperDocument3 pagesMGEBJ21-1 - End Term Question PapermikeNo ratings yet
- XET 301-CEC 305 October-Jan 2022 ExaminantionDocument5 pagesXET 301-CEC 305 October-Jan 2022 ExaminantionABDULLAHI MUSA MOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- HS 123 22Document12 pagesHS 123 22Pujan ShahNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2dianazokhrabekova100% (1)
- EC2066Document49 pagesEC2066Josiah KhorNo ratings yet
- Freq2 11jan12Document7 pagesFreq2 11jan12crod123456No ratings yet
- Computational Game Theory LCTN - Yishay MansourDocument150 pagesComputational Game Theory LCTN - Yishay MansourBay RazNo ratings yet
- Game Theory: Normal Form Games: Michael Levet June 23, 2016Document12 pagesGame Theory: Normal Form Games: Michael Levet June 23, 2016Dalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Assignment Help: ProblemsDocument7 pagesComputer Network Assignment Help: ProblemsComputer Network Assignment Help100% (1)
- Infinitely Repeated Games: U S UsDocument14 pagesInfinitely Repeated Games: U S Usswapneel_gen9599No ratings yet
- Chap 1: Normal Form Games: Step 1: Each Player Simultaneously and Independently Chooses An ActionDocument6 pagesChap 1: Normal Form Games: Step 1: Each Player Simultaneously and Independently Chooses An ActionFayçal SinaceurNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela End - Term Examination, 2017Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Rourkela End - Term Examination, 2017AbinashNo ratings yet
- Micro EconomicsDocument20 pagesMicro EconomicsLal ChhuanmawiaNo ratings yet
- Sagarika Game' 1Document43 pagesSagarika Game' 1Sandeep PramanikNo ratings yet
- MATH 308 - Assignment 5Document3 pagesMATH 308 - Assignment 5ThịnhNguyễnTrườngNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1Luka JanjalashviliNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lecture 5Document5 pagesModule 2 Lecture 5Swapan Kumar SahaNo ratings yet
- Mitschrift ExcerciseDocument18 pagesMitschrift ExcerciseJuKaschu0% (1)
- Home Test - 1: Exercise 1Document4 pagesHome Test - 1: Exercise 1Cindy LeeNo ratings yet
- Tha 3Document4 pagesTha 3hridai madhukarNo ratings yet
- Chap 010Document69 pagesChap 010hihi427No ratings yet
- Problem 1Document2 pagesProblem 1Velichka DimitrovaNo ratings yet
- Tha 5Document3 pagesTha 5Abhinash BorahNo ratings yet
- Problems Static Games PDFDocument9 pagesProblems Static Games PDFvictorginer8No ratings yet
- Pset 4Document3 pagesPset 4Amirreza TaheriNo ratings yet
- EBC2023 Managerial Economics - T01discussionDocument3 pagesEBC2023 Managerial Economics - T01discussionSuat NaneNo ratings yet
- Pset 4Document6 pagesPset 4Parminder SinghNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document2 pagesProblem Set 2Mar ConchaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT For Weekend Stu.Document2 pagesASSIGNMENT For Weekend Stu.yimerNo ratings yet
- Msc. in Economics Games & Contract Theory: Correct Answers: 0.5 Pts. Wrong Answers: - 0.25 Pts. (Document11 pagesMsc. in Economics Games & Contract Theory: Correct Answers: 0.5 Pts. Wrong Answers: - 0.25 Pts. (padrefloNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Take Home PDFDocument8 pagesGame Theory Take Home PDFDiego MontañaNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics CHP 5678Document24 pagesMicro Economics CHP 5678Imran farhathNo ratings yet
- Krishna Kanta Handiqui State Open University: (Only For The January 2021 Batch and in Lieu of MCQ Tests)Document4 pagesKrishna Kanta Handiqui State Open University: (Only For The January 2021 Batch and in Lieu of MCQ Tests)avatar sudarsanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandRulojyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument6 pagesElasticity of DemandVaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- PVF, PVAF, CVF, CVAF Tables For Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesPVF, PVAF, CVF, CVAF Tables For Financial ManagementManish Kumar0% (1)
- Attribute Theory of Demand: by Dr. Biswabhusan Bhuyan (PH.D)Document9 pagesAttribute Theory of Demand: by Dr. Biswabhusan Bhuyan (PH.D)Shakthi BharatheeNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics 2.: Demand, Supply and Market EquilibriumDocument36 pagesManagerial Economics 2.: Demand, Supply and Market EquilibriumhenNo ratings yet
- Topical MCQs - A2 Economics - 2.1 - Consumer EquilibriumDocument24 pagesTopical MCQs - A2 Economics - 2.1 - Consumer EquilibriumidkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EcoDocument19 pagesChapter 4 EcoAfifah HananiNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Economics 6th Edition Bade Test BankDocument25 pagesFoundations of Economics 6th Edition Bade Test BankJenniferDiazqmfsi100% (59)
- Installment ExamplesDocument3 pagesInstallment ExamplesMohib HaqueNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand-3Document25 pagesElasticity of Demand-3vismayNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument53 pagesChapter ThreeshimelisNo ratings yet
- Bits f314 Mids QDocument2 pagesBits f314 Mids QArshdeep Singh KochharNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Economics For Managers 3 e 3rd Edition Paul G FarnhamDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Economics For Managers 3 e 3rd Edition Paul G Farnhamacraspedalucchesezsl3q100% (17)
- GT Homework 1Document5 pagesGT Homework 1John HunNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesExercises 1 - SolutionsbatuhanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics NVM Lec 2 PrefrencesDocument67 pagesMicroeconomics NVM Lec 2 Prefrencessatyam91No ratings yet
- CFO11e Micro Ch05Document28 pagesCFO11e Micro Ch05Ersin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Eco Project Pal Ak Class 11Document17 pagesEco Project Pal Ak Class 11astrobhavikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Demand Analysis & ForecastingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Demand Analysis & ForecastingAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- w4 Topic 3.consumer ChoiceDocument23 pagesw4 Topic 3.consumer Choice刘家亨No ratings yet
- Investment FunctionDocument17 pagesInvestment Functionapi-3757629No ratings yet
- ECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Document2 pagesECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeDocument6 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeBella AdrianaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12th MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12th MicroeconomicssubhashreeNo ratings yet
- Economics - Lecture 02: Prepared By: Cams GandaDocument25 pagesEconomics - Lecture 02: Prepared By: Cams GandaGladymae MaggayNo ratings yet