Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 - Elements and Chemical Bonds
Chapter 8 - Elements and Chemical Bonds
Uploaded by
María Isabel Gramajo CuéllarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 - Elements and Chemical Bonds
Chapter 8 - Elements and Chemical Bonds
Uploaded by
María Isabel Gramajo CuéllarCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1 Electrons and Energy Levels
Scan Lesson 1. Record three questions you have about electrons and energy levels in your
Science Journal. Try to answer your questions as you read.
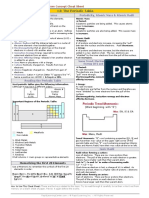
The Periodic Table Describe characteristics of the periodic table.
Characteristic Description
I found this on page .
Atomic number
Atomic mass
Period
Group
I found this on page .
Metals
Metalloids
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Nonmetals
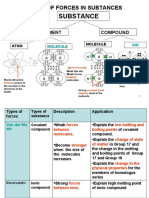
Atoms Bond Describe compounds.
I found this on page .
I found this on page . Summarize the relationship between an electron’s energy
level and its location in an atom. Circle the word that makes each
statement true.
The closer to the nucleus, the The farther from the nucleus, the
lower / higher lower / higher
an electron’s energy level. an electron’s energy level.
74 Elements and Chemical Bonds
Lesson 1 | Electrons and Energy Levels (continued)
I found this on page . Model the structure of an atom. Use the labels listed below
to indicate the location of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Draw
lines from the labels to indicate the position of the nucleus, the
lowest energy level, and the highest energy level.
6 protons (label “+”)
6 neutrons (label “n”)
6 electrons (label “–”)
nucleus
lowest energy level
highest energy level
I found this on page . Analyze details about valence electrons.
farthest from weakest
attraction to
involved in
Valence
most energy
Electrons
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
same number for all elements in
(with the exception of )
I found this on page . Sequence the steps in constructing and interpreting an electron
dot diagram.
1 Identify the element’s .
2 Identify the number of , which is the
same as the of the .
3 Place dot at a time on each of the
. Pair up the dots until all are used.
4 Identify an atom as if all are .
5 Count the to determine how many
an unstable atom can form.
Elements and Chemical Bonds 75
Lesson 1 | Electrons and Energy Levels (continued)
I found this on page . Explain why noble gases are stable.
I found this on page . Complete the flowchart about the behavior of atoms with
unpaired valence electrons.
An atom has unpaired valence electrons.
The atom is chemically .
The atom must , , or
unpaired .
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
The atom forms with
When an atom’s become
, the atom becomes .
Use what you have learned in Lesson 1 to explain why elements are
rarely found in their pure forms.
76 Elements and Chemical Bonds
Lesson 2 Compounds, Chemical Formulas, and Covalent Bonds
Predict three facts that will be discussed in Lesson 2 after reading the headings. Record your
predictions in your Science Journal.
From Elements Recall information about elements and compounds. Read
to Compounds each statement. If it is true, write T in the center column. If it is
false, write F in the center column and rewrite the underlined words
to make the statement true.
Statement T or F Correction
I found this on page . Compounds are chemical
combinations of elements.
I found this on page . Compounds usually have the
same properties as the bonds
they are made from.
I found this on page . Atoms form bonds by sharing
physical properties.
Covalent Bonds— Define covalent bond.
Electron Sharing
I found this on page .
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Describe types of covalent bonds.
Description of Comment on the
Covalent Valence Electron Strength of the
Bond Sharing Bond
I found this on page . Single
I found this on page . Double
I found this on page . Triple
Elements and Chemical Bonds 77
Lesson 2 | Compounds, Chemical Formulas, and Covalent Bonds (continued)
Covalent Compounds Identify 4 common properties of covalent compounds.
I found this on page .
1.
2.
3.
4.
I found this on page . Complete the analogy.
Atom is to element as is to compound.
I found this on page . Summarize the structure of polar molecules.
a partial
sharing of polar
and a partial molecule
results in
I found this on page . Explain why water is a polar molecule.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
I found this on page . Differentiate polar and nonpolar molecules with regard to
shared electrons.
Polar Molecules Nonpolar Molecules
I found this on page . Relate the saying “like dissolves like” to the ability of compounds
to dissolve one another.
78 Elements and Chemical Bonds
Lesson 2 | Compounds, Chemical Formulas, and Covalent Bonds (continued)
I found this on page . Define chemical formula.
I found this on page . Explain the chemical formula for a molecule of water. Describe
what each symbol represents.
H2O
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
I found this on page . Identify four types of molecular models.
Molecular
Models
Explain why there are many more covalent compounds than there are
pure elements.
Elements and Chemical Bonds 79
Lesson 3 Ionic and Metallic Bonds
Scan Lesson 3. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts
you discovered about ionic and metallic bonds. Record your facts in your Science Journal.
Understanding Ions Organize information about ions.
I found this on page .
Overall charge becomes
An atom gains an
electron
Overall charge becomes
An atom loses an
electron
I found this on page . Analyze what happens to sodium and chlorine atoms in the
formation of the compound sodium chloride.
Na (sodium) Cl (chlorine)
Type of element
Atomic number
Number of valence
electrons
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Stable or unstable?
Electron transfer
Description after
transfer
Type of ion
Ionic Bonds—Electron Complete the diagram of an ionic bond.
Transferring
I found this on page .
+ –
Ionic Bond
Explanation:
80 Elements and Chemical Bonds
Lesson 3 | Ionic and Metallic Bonds (continued)
Ionic Compounds Identify five common properties of ionic compounds.
I found this on page .
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Metallic Bonds—Electron Explain how a metallic bond forms.
Pooling
I found this on page .
I found this on page . Describe three properties of metallic compounds.
Properties of Metallic Compounds
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
I found this on page . Contrast 3 ways atoms can bond and become stable.
Electron Electron Electron
Process Pooling Transfer Sharing
Type of
chemical
bond
Description
Explain the difference between a neutral atom and a stable atom.
Elements and Chemical Bonds 81
Review Elements and Chemical Bonds
Chapter Wrap-Up
Now that you have read the chapter, think about what you have learned.
Use this checklist to help you study.
Complete your Foldables® Chapter Project.
Study your Science Notebook on this chapter.
Study the definitions of vocabulary words.
Reread the chapter, and review the charts, graphs, and illustrations.
Review the Understanding Key Concepts at the end of each lesson.
Look over the Chapter Review at the end of the chapter.
Reread the chapter Big Idea and the lesson Key Concepts. Use
what you have learned to describe why it is important in the modern world to
understand the types of chemical bonds and the properties of types of compounds.
Give at least one example.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Challenge Research the uses of noble gases in technological devices. Why do the properties of the
gases make them useful? Summarize your discoveries in your Science Journal.
82 Elements and Chemical Bonds
You might also like
- HW2 Fall09 SolutionsDocument3 pagesHW2 Fall09 Solutionsmxg091000No ratings yet
- IGCSE Unit Planner Physics Radioactivity Chapter 5Document5 pagesIGCSE Unit Planner Physics Radioactivity Chapter 5shwetha100% (2)
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesElectricity and Magnetismosama100% (1)
- Electricity & Magnetism: Topic OutlineDocument21 pagesElectricity & Magnetism: Topic OutlinePrathmesh Sinha100% (2)
- Chemistry Unit 1 Review SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Unit 1 Review Sheetapi-330460747No ratings yet
- Dokumen PDF 13Document1 pageDokumen PDF 13Farhan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument69 pagesPhysical Chemistrym.waseemNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2NDDocument4 pagesGen Chem 2NDrenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- Electrics Level 3 Rev PDFDocument243 pagesElectrics Level 3 Rev PDFEghie RahardiNo ratings yet
- Eng SciDocument1 pageEng SciAzaa anuarNo ratings yet
- L03 Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument20 pagesL03 Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Bond Revisited - Ed063p660Document5 pagesThe Chemical Bond Revisited - Ed063p660Akef AfanehNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Nature of ElectricityDocument5 pages1.2. Nature of ElectricityKATE ARBIE LACDO-ONo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 (.2) - The Particle ZooDocument19 pagesLesson 7 (.2) - The Particle Zooharold hargridNo ratings yet
- 01 - Atoms and Periodic TableDocument21 pages01 - Atoms and Periodic Table04 Nguyễn Việt Bảo 12A3No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (A)Document63 pagesLecture 2 (A)Yingqi SuNo ratings yet
- Type of Forces 1 Notes 2010Document26 pagesType of Forces 1 Notes 2010Mohd Iruan JanalNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Super Teacher WorksheetsDocument2 pagesStatic Electricity: Super Teacher WorksheetsmaryannnucejayahoocomNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations LessonDocument19 pagesElectron Configurations LessonWARREN ESCAPENo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Reviewer QRT2Document9 pagesGen Chem Reviewer QRT2limits.fireNo ratings yet
- Sat Sat Chemistry Theory v2Document22 pagesSat Sat Chemistry Theory v2tawiekayyNo ratings yet
- Physics: Earning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesPhysics: Earning Objectivesiron hulkNo ratings yet
- Physics in Materials Science: Roland V. SarmagoDocument23 pagesPhysics in Materials Science: Roland V. SarmagoReinna MicaellaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry: Your Definitions!Document5 pagesBasic Chemistry: Your Definitions!Alea ManetNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.4Document4 pagesLecture 1.4wemata7962No ratings yet
- Notebook L3Document5 pagesNotebook L3Somaya HussienNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- CIVE 205 - Spring2017 - Week3Document62 pagesCIVE 205 - Spring2017 - Week3haloNo ratings yet
- 1 - X Live Class Slides Atomic Structure and PropertiesDocument52 pages1 - X Live Class Slides Atomic Structure and Properties5796fpdfmrNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document18 pagesGeneral Physics 2Nea Faith L. LEMERICNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1Document35 pagesAtomic Structure 1Jeprox Martinez0% (1)
- ATOMDocument40 pagesATOMveronica lunaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer Final ExamDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer Final ExamNikolai Gwyneth ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Biochemlec Mod 1 6Document50 pagesBiochemlec Mod 1 6Sean Michael ComprendioNo ratings yet
- Why Doesn T The Electron Fall Into The NucleusDocument3 pagesWhy Doesn T The Electron Fall Into The NucleusVanessaLassoNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheets COMBDocument20 pagesRevision Sheets COMBJessica DaiNo ratings yet
- Polarization 1Document25 pagesPolarization 1OwimarkNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument56 pagesIonic BondingAiza TullabangNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 UNIT 1 ScienceDocument3 pagesGrade 9 UNIT 1 ScienceFrancesca Irah MapaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument20 pagesElectricityJürgen GeermanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure NotesDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure NotesArti DeviNo ratings yet
- D0597179 CHEM12 C0500 SWBT Mig PDFDocument12 pagesD0597179 CHEM12 C0500 SWBT Mig PDFMr: Mohamed BesharaNo ratings yet
- 14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic RadiiDocument1 page14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic Radiibooty holeNo ratings yet
- Demonstrate Electrostatic PhenomenaDocument71 pagesDemonstrate Electrostatic PhenomenajolieprincesseishimweNo ratings yet
- MYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsDocument31 pagesMYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsAref Dahabrah100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Atomic StructureDocument66 pagesLecture 3 Atomic StructureDaniel QuarteyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: 2.1 The AtomDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: 2.1 The AtomMelanny Johemy Jordán VásquezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Sheet IU2Document14 pagesChemistry Study Sheet IU2Shien EgNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FullDocument16 pagesChemistry FullmiomodgNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2Document2 pagesWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2oscarbecNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument5 pagesQuiz LetFarihah FazimNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology-Chapter 2: Terms in This SetDocument2 pagesCampbell Biology-Chapter 2: Terms in This SetAngelene PelayoNo ratings yet
- Element Mo'S: What Motivates AtomsDocument4 pagesElement Mo'S: What Motivates AtomsjnfurstNo ratings yet
- RM 1 - ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesRM 1 - Electrostaticsibdeveterbo.nhcsNo ratings yet
- Radproduction Chapter 2-9Document276 pagesRadproduction Chapter 2-9Christian DioNo ratings yet
- Activity On Periodic Property and Behavior of Valence Electrons ActivityDocument2 pagesActivity On Periodic Property and Behavior of Valence Electrons ActivityMarkNo ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument51 pagesElectron AffinityS K MishraNo ratings yet
- Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)Document3 pagesReviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)HelloNo ratings yet
- NucChem Week 1Document13 pagesNucChem Week 1Angel Akiko AlbertoNo ratings yet
- The History of The Development of The Atomic ModelDocument25 pagesThe History of The Development of The Atomic ModelNaomi Chávez HernándezNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document3 pagesChem 1chin.rochinnyNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Ncert ChapterDocument26 pages11 Physics Ncert ChapterBhumika DNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table & PropertiesDocument16 pagesPeriodic Table & PropertiesAYUSH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quantum NumbersDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quantum NumbersVienie Ramirez BadangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 The Development of Atomic Theory, Atomic Structure and Atomic ModelsDocument11 pagesLesson 3.1 The Development of Atomic Theory, Atomic Structure and Atomic ModelsMary Jane YepesNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91164Document2 pagesLearning Objectives As91164api-252561013No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Instruments For Optical SpectrosDocument19 pagesLecture 2 - Instruments For Optical SpectrosBelay HaileNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year 9 Course BookDocument63 pagesChemistry Year 9 Course BookArham KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of Atomic Abso R Pti N Spectroscopy AlfredDocument62 pagesPrinciples and Applications of Atomic Abso R Pti N Spectroscopy AlfredSazNo ratings yet
- FUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2Document27 pagesFUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2shabanaNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Test BankDocument26 pagesIntroductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Test BankStephanieMckayeqwr100% (57)
- Assignment Periodic Table JH Sir-3575Document30 pagesAssignment Periodic Table JH Sir-3575aachuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Angular MomentumDocument8 pagesNuclear Angular Momentumfirthosh banuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsDocument11 pagesChapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsswatkoolNo ratings yet
- I.E. Irodov - Problems in Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument263 pagesI.E. Irodov - Problems in Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsGianniNicheli100% (1)
- Struttura Della MateriaDocument131 pagesStruttura Della MateriaGomblotto BotNo ratings yet
- SS2 Chemistry 1st Term Lesson Note PDFDocument73 pagesSS2 Chemistry 1st Term Lesson Note PDFAugustine AmaechiNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesStructure of AtomSumit PatilNo ratings yet
- Gamma Ray SpectrometryDocument27 pagesGamma Ray SpectrometryAlvin Peñonal AballeNo ratings yet
- Systematic Variation of The Raman Spectra ofDocument6 pagesSystematic Variation of The Raman Spectra ofDev ApenisaNo ratings yet
- Nagyvary Nature PageDocument1 pageNagyvary Nature PageEd McManusNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument72 pagesLecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsKEMPNo ratings yet
- FISMODDocument5 pagesFISMODSiti SyarahNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument34 pagesChemistryrishank guptasNo ratings yet
- Element-T-shirt ProjectDocument2 pagesElement-T-shirt ProjectRemzy LenonNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Packet KeyDocument21 pagesUnit 8 Packet KeyHiddenNo ratings yet
- The Atom Exam 2 Review - ANSWER KEYDocument2 pagesThe Atom Exam 2 Review - ANSWER KEYjeerawat promajuntNo ratings yet
- Rutherfordium: Rutherfordium Is A Synthetic ChemicalDocument46 pagesRutherfordium: Rutherfordium Is A Synthetic ChemicalAnonymous gUjimJKNo ratings yet