Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RAC Unit-6.3
RAC Unit-6.3
Uploaded by
rhaertroberCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesLab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningSayam AliNo ratings yet
- RAC Unit-6.4Document1 pageRAC Unit-6.4rhaertroberNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument29 pagesRefrigeration CycleShyam WanaskarNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Air ConditioningDocument12 pagesAir ConditioningSNo ratings yet
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Cooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationDocument1 pageCooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationSushant MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning BasicsDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning BasicsLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- Hvac 2Document3 pagesHvac 2emumerr69No ratings yet
- Types of Air ConditioningDocument9 pagesTypes of Air ConditioningENVERNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument7 pagesRefrigerationCatfishNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of VRF SystemDocument11 pagesWorking Principle of VRF Systemghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning SystemannNo ratings yet
- Air Condationing FinalDocument40 pagesAir Condationing FinalPeterson muchiriNo ratings yet
- How It Works?Document2 pagesHow It Works?saimunNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiDocument5 pagesWorking Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiSNEHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument3 pagesRefrigeration CycleJaime Alava MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Major Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsDocument8 pagesMajor Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsXahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Report.Document15 pagesAir Conditioning Report.Ethan XavierNo ratings yet
- Mondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Document2 pagesMondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Cristian MondragonNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of A Split Type Air Conditioning SystemDocument15 pagesPerformance Evaluation of A Split Type Air Conditioning SystemWiZofFaTeNo ratings yet
- Thermo (Mini Project)Document2 pagesThermo (Mini Project)nisasoberiNo ratings yet
- Principle of VRFDocument5 pagesPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning-Window Air Conditioner: Building Services-VIDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning-Window Air Conditioner: Building Services-VINitin GrewalNo ratings yet
- Geometry/Structure:: Main Functional Requirement: Design ParameterDocument1 pageGeometry/Structure:: Main Functional Requirement: Design ParameterVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism and PrincipleDocument2 pagesBasic Mechanism and PrinciplesahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- How Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkSaad jamilNo ratings yet
- Refregeration CycleDocument6 pagesRefregeration CycleFinito TheEndNo ratings yet
- Bs Group Case Study Shopping ComplexDocument31 pagesBs Group Case Study Shopping Complexasmita shilNo ratings yet
- ComponentDocument2 pagesComponentSri Harsha BNo ratings yet
- The Refrigeration CycleDocument2 pagesThe Refrigeration CycleIvy Pearl TabagNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document2 pagesQuestion 2MUHAMMAD FARIS IQBAL BIN RIDUANNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument56 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet
- Dasar Teori PendinginDocument64 pagesDasar Teori PendinginsuhandywNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump TrainerDocument6 pagesHeat Pump TrainerAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- WAC and VCRSDocument8 pagesWAC and VCRSShubham MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 Hvac-Refrigeration CycleDocument5 pages1 Hvac-Refrigeration CycleAkshaye VaidNo ratings yet
- Group-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and The Concept of ZoningDocument37 pagesGroup-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and The Concept of ZoningVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Hvac LabDocument20 pagesHvac LabMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6Document11 pagesHvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6AliNo ratings yet
- Ac How It WorksDocument4 pagesAc How It Workshassanain_100No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning EditDocument64 pagesAir Conditioning EditQuratul AiniNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesCentral Air ConditioningHashim MuhammedNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Principles of The CoolingDocument10 pages4.2 Principles of The CoolingAdam AlexNo ratings yet
- AC Plant Includes The CompressorDocument3 pagesAC Plant Includes The CompressorsidhumoosewalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 04: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 04: ObjectiveAhsen NasimNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HVACDocument66 pagesUnit 2 HVACJaya SubhaNo ratings yet
RAC Unit-6.3
RAC Unit-6.3
Uploaded by
rhaertroberCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RAC Unit-6.3
RAC Unit-6.3
Uploaded by
rhaertroberCopyright:
Available Formats
RAC Unit-6
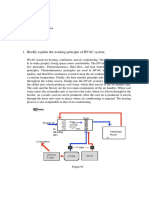
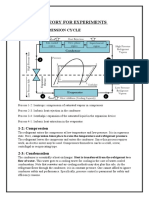
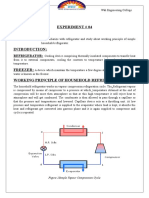
Flow Diagram and Working Principle of a Split-Type Room Air Conditioner(6.3)
Working Principle:-
A split-type air conditioner operates based on the principles of refrigeration. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of its
working:
Evaporator Coil (Indoor Unit):
Air Intake: Warm air from the room is drawn into the indoor unit through an air inlet.
Filtration: The air passes through a filter that removes dust and other particles.
Cooling Process: The filtered air then passes over the evaporator coil, which contains cold refrigerant. As the air
flows over the coil, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, cooling it down.
Fan and Louvers: The cooled air is then circulated back into the room by a fan. Adjustable louvers direct the flow of
cooled air.
Compressor (Outdoor Unit):
Compression: The refrigerant, now warm and in a gaseous state after absorbing heat from the indoor air, is
pumped to the outdoor unit where the compressor is located. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, raising its
temperature even further.
Condenser Coil (Outdoor Unit):
Heat Release: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas flows through the condenser coil. A fan blows
outdoor air over the coil, causing the refrigerant to release its heat to the outside environment. As it loses heat, the
refrigerant condenses back into a liquid state.
Expansion Valve:
Pressure Reduction: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then flows through an expansion valve where its pressure
and temperature drop significantly.
Cycle Repeats:
Cooling Cycle: The low-pressure, low-temperature liquid refrigerant returns to the evaporator coil in the indoor unit
to absorb more heat from the room air, and the cycle repeats.
Key Components and Functions
Evaporator Coil: Absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it down.
Compressor: Pressurizes the refrigerant, increasing its temperature.
Condenser Coil: Releases absorbed heat from the refrigerant to the outside air.
Expansion Valve: Reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
Fan: Circulates air over the evaporator coil inside and the condenser coil outside.
Filter: Removes dust and particles from the air before it is cooled.
Air Direction Louvers: Control the direction of the cooled air flow.
You might also like
- Lab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesLab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningSayam AliNo ratings yet
- RAC Unit-6.4Document1 pageRAC Unit-6.4rhaertroberNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument29 pagesRefrigeration CycleShyam WanaskarNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Air ConditioningDocument12 pagesAir ConditioningSNo ratings yet
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Cooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationDocument1 pageCooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationSushant MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning BasicsDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning BasicsLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- Hvac 2Document3 pagesHvac 2emumerr69No ratings yet
- Types of Air ConditioningDocument9 pagesTypes of Air ConditioningENVERNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument7 pagesRefrigerationCatfishNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of VRF SystemDocument11 pagesWorking Principle of VRF Systemghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning SystemannNo ratings yet
- Air Condationing FinalDocument40 pagesAir Condationing FinalPeterson muchiriNo ratings yet
- How It Works?Document2 pagesHow It Works?saimunNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiDocument5 pagesWorking Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiSNEHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument3 pagesRefrigeration CycleJaime Alava MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Major Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsDocument8 pagesMajor Elements of Refrigeration System and Their FunctionsXahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Report.Document15 pagesAir Conditioning Report.Ethan XavierNo ratings yet
- Mondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Document2 pagesMondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Cristian MondragonNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of A Split Type Air Conditioning SystemDocument15 pagesPerformance Evaluation of A Split Type Air Conditioning SystemWiZofFaTeNo ratings yet
- Thermo (Mini Project)Document2 pagesThermo (Mini Project)nisasoberiNo ratings yet
- Principle of VRFDocument5 pagesPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning-Window Air Conditioner: Building Services-VIDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning-Window Air Conditioner: Building Services-VINitin GrewalNo ratings yet
- Geometry/Structure:: Main Functional Requirement: Design ParameterDocument1 pageGeometry/Structure:: Main Functional Requirement: Design ParameterVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism and PrincipleDocument2 pagesBasic Mechanism and PrinciplesahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- How Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does A Cooling System of A Generator WorkSaad jamilNo ratings yet
- Refregeration CycleDocument6 pagesRefregeration CycleFinito TheEndNo ratings yet
- Bs Group Case Study Shopping ComplexDocument31 pagesBs Group Case Study Shopping Complexasmita shilNo ratings yet
- ComponentDocument2 pagesComponentSri Harsha BNo ratings yet
- The Refrigeration CycleDocument2 pagesThe Refrigeration CycleIvy Pearl TabagNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document2 pagesQuestion 2MUHAMMAD FARIS IQBAL BIN RIDUANNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument56 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet
- Dasar Teori PendinginDocument64 pagesDasar Teori PendinginsuhandywNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump TrainerDocument6 pagesHeat Pump TrainerAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- WAC and VCRSDocument8 pagesWAC and VCRSShubham MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 Hvac-Refrigeration CycleDocument5 pages1 Hvac-Refrigeration CycleAkshaye VaidNo ratings yet
- Group-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and The Concept of ZoningDocument37 pagesGroup-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and The Concept of ZoningVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Hvac LabDocument20 pagesHvac LabMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6Document11 pagesHvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6AliNo ratings yet
- Ac How It WorksDocument4 pagesAc How It Workshassanain_100No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning EditDocument64 pagesAir Conditioning EditQuratul AiniNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesCentral Air ConditioningHashim MuhammedNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Principles of The CoolingDocument10 pages4.2 Principles of The CoolingAdam AlexNo ratings yet
- AC Plant Includes The CompressorDocument3 pagesAC Plant Includes The CompressorsidhumoosewalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 04: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment # 04: ObjectiveAhsen NasimNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HVACDocument66 pagesUnit 2 HVACJaya SubhaNo ratings yet