Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RAC Unit6 (6.5)
RAC Unit6 (6.5)
Uploaded by
rhaertrober0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
RAC Unit6(6.5)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageRAC Unit6 (6.5)
RAC Unit6 (6.5)
Uploaded by
rhaertroberCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
RAC Unit-6
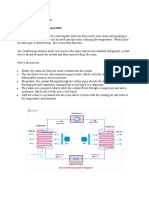
Flow Diagram and Working Principle of Air Washer(6.5)
Working Principle
Air Intake:
Ambient air is drawn into the air washer through the air inlet. This air can contain dust, pollutants,
and other particulates.
Pre-Filtration:
The air passes through pre-filters that capture larger particles, such as dust and debris. This helps in
reducing the load on the subsequent stages of filtration and humidification.
Water Spray Chamber:
The pre-filtered air enters the spray chamber, where water is sprayed into the air stream using
nozzles. The water spray captures finer particles, pollutants, and impurities present in the air. This
process is known as wet scrubbing.
Humidification:
The interaction between the water droplets and air increases the humidity level of the air. This is
particularly useful in dry environments where humidification is needed .
Baffles/Drift Eliminators:
After the air passes through the spray chamber, it encounters baffles or drift eliminators. These
components remove any water droplets from the air to ensure that only clean and humidified air
proceeds further.
Cooling (Optional):
If the air washer is equipped with a cooling coil, the air passes over the cooling coil, where its
temperature is reduced. This helps in providing a cooling effect, making the air more comfortable in
hot conditions.
Air Distribution:
The blower or fan moves the cleaned, humidified, and optionally cooled air out of the air washer
and distributes it into the indoor space through the air outlet .
You might also like
- Conditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirDocument19 pagesConditioning and Distribution of Compressed AirKCNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesLab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningSayam AliNo ratings yet
- HVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Document18 pagesHVAC Services in Buildings: Ar. Antara Nandy Assistant Professor Rani Rashmoni College of Architecture, Durgapur (W.B)Archi PinuNo ratings yet
- Sterile Products 2023 Part DDocument63 pagesSterile Products 2023 Part DSHAHIQNo ratings yet
- Report of DehumidificationDocument5 pagesReport of DehumidificationMahmoud MerdanNo ratings yet
- Piping - Bag FiltersDocument5 pagesPiping - Bag FiltersSathiyamoorthy TNo ratings yet
- B.S 13TH WEEK LEC 1Document10 pagesB.S 13TH WEEK LEC 1yumsNo ratings yet
- Air Washer PDFDocument6 pagesAir Washer PDForganicspolybondNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document61 pagesChapter 6Dayang Azraa AfeefaaNo ratings yet
- Types of Humidifier: AC and RefrigerationDocument7 pagesTypes of Humidifier: AC and RefrigerationBenNo ratings yet
- Desiccant Wheel Dehumidification 2Document19 pagesDesiccant Wheel Dehumidification 2ovidiu73No ratings yet
- PneumaticDocument8 pagesPneumaticMohamad HarithNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreDocument20 pagesDepartment of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreEman FatimaNo ratings yet
- Dryer-Operation 1Document1 pageDryer-Operation 1GamalpageNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System NoteDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning System NoteSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Air Generation & Distribution SystemDocument46 pagesAir Generation & Distribution SystemHuzai AzmanNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge Process (ASP)Document14 pagesActivated Sludge Process (ASP)ShabanaNo ratings yet
- Fan Coil Unit 1) Box EnclosureDocument2 pagesFan Coil Unit 1) Box EnclosureRUSHALI SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument12 pagesAir ConditioningSNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Dust CollectorDocument31 pagesDust CollectorKaran Sharma100% (2)
- Chapter 7 - Air and Hydraulic Filters, Air Dryers and LubricatorsDocument15 pagesChapter 7 - Air and Hydraulic Filters, Air Dryers and LubricatorsDedi Setiono100% (1)
- Industrial VentilationDocument14 pagesIndustrial VentilationARULSELVAN MURUGESANNo ratings yet
- Contamination Removal Filters&dryersDocument94 pagesContamination Removal Filters&dryersfredyNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control EquipmentDocument3 pagesAir Pollution Control EquipmentSamantha SwiftNo ratings yet
- Admapn016en 0905Document8 pagesAdmapn016en 0905Angel Daniel GarciajoyaNo ratings yet
- Instrument AirDocument6 pagesInstrument Airasarobin1989No ratings yet
- Dilution VentilationDocument4 pagesDilution VentilationUthman OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Drying PDFDocument29 pagesCompressed Air Drying PDFmaddukuri jagadeesh babu100% (2)
- Screw Type of CompressorDocument9 pagesScrew Type of CompressorAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- VPHB s3 PDFDocument16 pagesVPHB s3 PDFshekhusatavNo ratings yet
- Design Equipment To Dry and Clean AirDocument8 pagesDesign Equipment To Dry and Clean Airدنيا ثامر حاجي عبدNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument56 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- PWR1836Document37 pagesPWR1836Elroy LeeNo ratings yet
- Air Condationing FinalDocument40 pagesAir Condationing FinalPeterson muchiriNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Air-ConditioningDocument93 pagesVentilation and Air-ConditioningEmmanuel P Dube100% (2)
- 03 Preparation of Compressed AirDocument3 pages03 Preparation of Compressed AirNatsuko KayamaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Positive Displacement CompressorsDocument5 pagesFigure 1: Positive Displacement CompressorsendoparasiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Compressed Air PreparationDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Compressed Air PreparationerickaNo ratings yet
- Air Separators: Pumps and Water Distribution 191Document2 pagesAir Separators: Pumps and Water Distribution 191Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- Membrane DryerDocument4 pagesMembrane DryerMuhammad SaifNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Dryer - WikipediaDocument49 pagesCompressed Air Dryer - WikipediaNicko PilonNo ratings yet
- Draw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling UnitDocument23 pagesDraw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling Unityousuff0% (1)
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchDocument5 pagesAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Part 1Document25 pagesUnit 4 - Part 1akhilkrrish143No ratings yet
- CD Ad BD tcm795-3534350Document12 pagesCD Ad BD tcm795-3534350glizamabNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- Air Conditioning On ShipsDocument5 pagesAir Conditioning On ShipsjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Equipment: Moisture Holding Capacity of Air According To TemperatureDocument16 pagesAuxiliary Equipment: Moisture Holding Capacity of Air According To TemperatureCharles RobiansyahNo ratings yet
- Drying of AirDocument5 pagesDrying of AirHalima LAARARINo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument8 pagesAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Mondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Document2 pagesMondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Cristian MondragonNo ratings yet
- M&E Assignment 3Document12 pagesM&E Assignment 3han0701No ratings yet
- Source - Wiki: Edit EditDocument5 pagesSource - Wiki: Edit EditWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- Air Purifier BE Project 2Document13 pagesAir Purifier BE Project 2raja maneNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet