Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Resistance Jour
Chemical Resistance Jour
Uploaded by
mb.pipingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Resistance Jour
Chemical Resistance Jour
Uploaded by
mb.pipingCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical resistance PEEK and other polymers
general reference
Chemical resistance of PEEK Chemical characteristics of PEEK®
at high temperature PEEK exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of
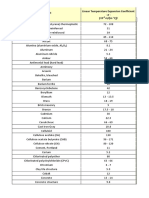
Chemical °C °F Rating
organic and inorganic chemicals. The compatibility
of PEEK with many chemicals at 20°C (68°F) has been
Acetic acid 200 420
investigated and the results for unreinforced grades are
Ammonia gas 200 420 given in the table below.
Carbon monoxide gas 200 420
PEEK is compatible with almost any of the solvents used
Ethylene glycol 200 420
in HPLC. The only solvents which will attack PEEK are
Ethylene glycol (50%) 140 284 concentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acids. However,
Hydrogen sulphide gas 200 420 PEEK tubing can safely withstand 20-30% nitric acid
Liquid ammonia 200 420 when passivating a system.
Methane 200 420 Methylene chloride, DMSO, and THF may cause swelling
Methylethylketone 200 420 in PEEK. The highest temperature we recommend
for PEEK is 100°C. The tubing will maintain the stated
Nitrobenzene 200 420
pressure rating up to this temperature.
Phosphoric acid (50%) 200 420
Sodium hydroxide solution 200 420
Sulphuric acid (50%) 200 420
Sulphur dioxide gas 200 420
Chemical resistance of PEEK and other polymers
A
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Acetaldehyde – – – – –
Acetic acid (20 %)
Acetic acid (80 %) – – –
Acetic acid (glacial)
Acetone
Acetonitrile – –
Acrylic acid – – – – – – –
Ammonia, anhydrous – – – – – –
Ammonia (10 %) – –
Ammonia (Liquid) – – – – – –
Ammonium hydroxide – – –
Aqua regia – – – –
Aromatic hydrocarbons – – – – –
B
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Benzene – –
Benzoic acid – – – – – – –
Benzaldehyde – – – – – – –
Bromine/dibromoethane – – – – – – –
legend
Bromine (dry) – – – – – – –
Suitable
Bromine (wet) – – – –
Marginal; dependent
Boric acid – – – – – – – on application
Butanol – – – Not recommended
– No data available
96 | www.vici-jour.com| VICI AG International
Chemical resistance PEEK and other polymers
general reference
C
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Calcium hydroxide – – – – – – –
Carbon tetrachloride – – – – – – –
Chlorine (gas) – – – –
Chlorine (liquid) – – – – – –
Chloroacetic acid – – –
Chlorobenzene – – – – – –
Chloroform – –
Cyclohexane – –
Cyclohexanone
D
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Diethylamine – – – –
Diethylether – – – – – –
Diethylformamide
Dioxane – – – – –
E
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Ethanol
Ether – –
Ethyl acetate
Ethylene chloride – – –
Ethlene glycol
H
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Heptane
Hexane – –
Hydrobromic acid (100%) – – – –
Hydrobromic acid (20%) – – – –
Hydrochloric acid (100%) – – – –
Hydrochloric acid (20%) – – –
Hydrofluoric acid (100%) – – – –
Hydrofluoric acid (20%) – – – –
Hydrogen peroxide (100%) – – – –
Hydrogen peroxide (50%) – – – –
Hydrogen peroxide (10%) – – –
I
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Iso-octane – – – – –
Isopropanol –
Isopropyl ether – – – – –
K
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Ketones – – – –
VICI AG International | www.vici-jour.com | 97
Chemical resistance PEEK and other polymers
general reference
M
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Methanol
Methyl dichloride – – – – – – –
Methyl ethylketone – –
Methlyene chloride
N
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Nitric acid (100%) – – –
Nitric acid (20%) – – –
P
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Pentane – – – – –
Perchloric acid – – – – –
Phenol (dilute) – – – – – – –
Phenol (concentrated) – – – – – – –
Phosphoric acid (100%) – – –
Phosphoric acid (40%) – – –
Potassium hydroxide (dilute) – – – – – – –
Potassium hydroxide (70%) – – – – – – –
Propanol – – – – –
Pyridine – – –
S
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Sodium hydroxide (80%) – – –
Sodium hydroxide (20%) – –
Sulfuric acid (100%) – –
Sulfuric acid (75%) – –
Sulfuric acid (40%) – –
T
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Tetrahydrofuran – –
Toluene – –
Trichloroacetic acid – –
Trichloroethane – – – – –
Trichloroethylene – – – – – –
Triethylamine – – – – –
W
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM
Water
Water (distilled) – – –
legend
X Suitable
Resistance at 20°C PEEK PA PE PP PPS FEP ETFE PFA PTFE NBR EPDM Marginal; dependent
on application
Xylene – – – – – – –
Not recommended
– No data available
98 | www.vici-jour.com| VICI AG International
Properties of polymers
general reference
Properties of polymers
CTFE PEEK™
Chlorotrifluoroethylene, is the generic name Considered relatively inert and biocompatible,
for the material produced as Kel-F®. It is very polyetheretherketone tubing can withstand
resistant to all chemicals except THF and some temperatures up to 100°C. Under the right
halogenated solvents, and is resistant to all circumstances, .005” - .020” ID tubing can be
inorganic corrosive liquids, including oxidizing used up to 5000 psi for a limited time, and
acids. CTFE can be used at temperatures up to 0.030” to 3000 psi. Larger IDs are typically good
100°C. Swells in ketones. to 500 psi. These limits will be substantially
reduced at elevated temperatures and in
EPDM contact with some solvents or acids.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. Ethylene-
propylene synthetic rubbers offer excellent Its mechanical properties allow PEEK to be used
heat resistance as well as resistance to aging instead of stainless in many situations and in
from oxidation, ozone, and weather due to some environments where stainless would be
their stable, saturated polymer backbone too reactive. However, PEEK can be somewhat
structure. As non-polar elastomers, they have absorptive of solvents and analytes, notably
good electrical resistivity as well as resistance methylene chloride, DMSO, THF, and high
to polar solvents such as water, acids, alkanes, concentrations of sulfuric and nitric acid. This
phosphates, esters, and many ketones and tubing is highly prone to “kinking”, or sealing off,
alcohols. if held in a sharp bend over time.
ETFE PFA
Ethyltrifluoroethylene is the generic name for Perfluoroalkoxy is a fluorocarbon with chemical
the material such as Tefzel®. A fluoropolymer and mechanical properties similar to FEP. More
used for sealing surfaces, it is resistant to most rigid than either PTFE or FEP. Commonly used
chemical attack; however, some chlorinated for injection molded parts.
chemicals will cause a physical swelling of ETFE PPS
tubing. Polyphenylene sulphide is the generic name
for the material produced as Fortron®, Ryton®,
FEP
and Techtron®. It is very resistant to all solvents,
Fluorinated ethylene propylene is another
acids, and bases.
member of the fluorocarbon family with similar
chemical properties. It is generally more rigid PTFE
than PTFE, with somewhat increased tensile Polytetrafluoroethylene is the generic name for
strength. It is typically more transparent than the class of materials such as Teflon®. It offers
PTFE, slightly less porous, and less permeable superior chemical resistance but is limited in
to oxygen. FEP is not as subject to compressive pressure and temperature capabilities. Because
creep at room temperature as PTFE, and it’s so easy to handle, it is often used in low
because of its slightly higher coefficient of pressure situations where stainless steel might
friction is easier to retain in a compression cause adsorption. PTFE tubing is relatively
fitting. porous, and compounds of low molecular
weight can diffuse through the tubing wall.
FFKM
FFKM (perfluorinated rubber) is a Polyacetal
perfluoroelastomer, a class of materials such Polyacetal or polyoxymethylene (POM) is the
as Kalrez®. It is chemically resistant to polar generic name for the material produced as
solvents, organic solvents, inorganic and Delrin®. It is an engineering polymer with high
organic acids and bases, fuels, oils, lubricants, mechanical strength and rigidity, excellent
inorganic salts, aldehydes, metal halogen dimensional stability and excellent resistance
compounds, chlorine, sodium hydroxide, to moisture and solvents. It has a wide useful
aromatics, alcohols, steam, and strong oxidizing temperature range in air of -50°C to +90°C.
agents. The normal temperature service It is not suitable for use with acids, alkalis, or
range is -40°C to 315°C, with up to 343°C in oxidizing agents, and has limited resistance to
intermittent service. dichloromethane and methyl ethyl ketone.
Continued, next page.
VICI AG International | www.vici-jour.com | 99
Properties of materials Polymers and metals
general reference
Polyamide Polypropylene
Polyamide is a thermoplastic polymer also Widely used polymer for non-wetted parts.
known as nylon. Nylon has very good physical Attacked by strong oxidizers as well as aromatic
properties, but moisture can have a significant and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
effect. It exhibits very good heat resistance and
excellent chemical and wear resistance. PVDF
PVDF, or polyvinylidene fluoride, has excellent
Polyethylene resistance to most mineral and organic acids,
Polyethylene is a semi-crystalline material aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, and
with excellent chemical resistance, plus good halogenated solvents. Poor resistance to
fatigue and wear resistance. Polyethylenes acetone, MEK, THF, and potassium and sodium
provide good resistance to organic solvents hydroxide. Often supplied as Kynar®.
and staining, and have low moisture absorption
rates.
Properties of metals
Stainless steel, Type 316 Titanium
This is the standard tubing material for Although it is more difficult to machine than
chromatography, suitable for a wide variety common alloys containing aluminum and
of applications. It is cold drawn seamless, not vanadium, VICI uses Grade 2 pure titanium in
welded, with close tolerances held on both ID order to avoid possible contamination of the
and OD. We neither recommend nor offer Type sample stream with these metals. Good for
304 stainless steel for analytical applications. organic and inorganic salts except aluminum
and calcium chlorides, and all alkalis except
Austenitic stainless steels may be used for
boiling concentrated potassium hydroxide.
most chromatographic applications. Type 316
is most commonly used for HPLC because of its Good with dilute, low temperature formic,
superior chloride ion resistance. lactic, sulfuric, hydrochloric, and phosphoric
acids, but rapidly attacked by hydrofluoric
Stainless steel, Type 303 acid. Good with dilute nitric acid at low
Recommended for GC use and general temperatures; corrodes at high concentrations
purpose connections, combining excellent and temperatures. Can ignite with fuming nitric
machining characteristics with good resistance acid. Attacked by oxalic acid, concentrated
to corrosion and high temperature oxidation. phosphoric acid, hot trichloroacetic acid, and
Susceptible to attach by chlorides, iodides, and zinc chloride.
bromides.
100 | www.vici-jour.com| VICI AG International
You might also like
- Cassava Starch Processing Project PDFDocument38 pagesCassava Starch Processing Project PDFAnouar MohamadouNo ratings yet
- 00 Saip 74Document8 pages00 Saip 74balajiNo ratings yet
- Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers (Amendments-Supplements To ISO 15547-1-2005)Document16 pagesPlate and Frame Heat Exchangers (Amendments-Supplements To ISO 15547-1-2005)Jacob PhilipNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Chemical Compatibility: Inspired by ChallengeDocument16 pagesTechnical Information Chemical Compatibility: Inspired by Challengeyrdna nawaiteosNo ratings yet
- Bard - TechnicoatDocument2 pagesBard - TechnicoatGabriel Ortiz MNo ratings yet
- PT Orindo Eratec Catalogue - 02272023Document40 pagesPT Orindo Eratec Catalogue - 02272023Teknik produksi wikonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistances MaterialDocument4 pagesChemical Resistances MaterialCecep AtmegaNo ratings yet
- PT Orindo Eratec All Catalogue - BATCH 1 - 4MBDocument54 pagesPT Orindo Eratec All Catalogue - BATCH 1 - 4MBWulanNo ratings yet
- BECKOPOX VEH 2188w 55WA - EN - A4Document2 pagesBECKOPOX VEH 2188w 55WA - EN - A4NganNo ratings yet
- Core Range - Industrial Formulators PDFDocument18 pagesCore Range - Industrial Formulators PDFAniket Patel100% (1)
- Bandeja Portacable de Fibra de Vidrio PDFDocument52 pagesBandeja Portacable de Fibra de Vidrio PDFcarlos_sagitarioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatability GuideDocument4 pagesChemical Compatability GuideRene Canello GalliNo ratings yet
- Vendor BandejaDocument50 pagesVendor BandejagimacoNo ratings yet
- Trico Bond EpDocument2 pagesTrico Bond EpBrandon TrocNo ratings yet
- Beständigkeitsliste - Kunststoffe - Valvecenter UKDocument24 pagesBeständigkeitsliste - Kunststoffe - Valvecenter UKVelibor StokicNo ratings yet
- Production of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On A Petrochemical BasisDocument8 pagesProduction of Aromatic Hydrocarbons On A Petrochemical Basisstephanie lazarteNo ratings yet
- M02 - Product Specification PDFDocument8 pagesM02 - Product Specification PDFResaPrihtianaSatriaNo ratings yet
- Arkema MP Chemical Process Industry Market PresentationDocument17 pagesArkema MP Chemical Process Industry Market PresentationMarcelo PerettiNo ratings yet
- Fiberglass Catalogo CharolaDocument52 pagesFiberglass Catalogo Charolaoscar rdzNo ratings yet
- Cooper FiberglassDocument52 pagesCooper FiberglassOzan AtıcıNo ratings yet
- Catalog OritecDocument20 pagesCatalog OritecHSE Wana Dirga NusantaraNo ratings yet
- Carbon BLK SpecificationDocument2 pagesCarbon BLK Specificationmohsen siahpooshNo ratings yet
- Compound Selection and Conversion ChartsDocument6 pagesCompound Selection and Conversion ChartsRolando DoderoNo ratings yet
- Resistance of Wefapress Plastics To Chemicals and Other Media!Document20 pagesResistance of Wefapress Plastics To Chemicals and Other Media!Pedro Henriques RamosNo ratings yet
- Cement Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDocument27 pagesCement Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingjaymarNo ratings yet
- Castrol Product Training: It'S More Than Just Oil. It'S Liquid EngineeringDocument106 pagesCastrol Product Training: It'S More Than Just Oil. It'S Liquid EngineeringFerry Marketing SekafuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance of The Materials: AquaforceDocument2 pagesChemical Resistance of The Materials: AquaforceFadi Mohd ShaherNo ratings yet
- Copeland Refrigeration OilsDocument2 pagesCopeland Refrigeration Oilsjose antonioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility TableDocument28 pagesChemical Compatibility TableBea LubaoNo ratings yet
- Coating SDocument60 pagesCoating SAllel HamdacheNo ratings yet
- E02 - GpsaDocument6 pagesE02 - GpsaJorge Luis Guerra FlorezNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Acido Citrico RZBC ChinaDocument2 pagesFicha Tecnica Acido Citrico RZBC ChinaEmanuel Pajares JuárezNo ratings yet
- H FameDocument30 pagesH FameM Rasyid RidhoNo ratings yet
- Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene Copolymer (ABS) : Eco-Profiles of The European Plastics IndustryDocument14 pagesAcrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene Copolymer (ABS) : Eco-Profiles of The European Plastics IndustryMary Grace VelitarioNo ratings yet
- Coef Dilatare LiniaraDocument5 pagesCoef Dilatare LiniaraDan SabadusNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance of PlasticsDocument4 pagesChemical Resistance of PlasticsBedoor BuallayNo ratings yet
- FPD - Pipes ChartDocument1 pageFPD - Pipes ChartAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Gpsa 2Document6 pagesGpsa 2David Cortez PeraltaNo ratings yet
- AkzoNobel MEA PIS Tcm53-24552Document1 pageAkzoNobel MEA PIS Tcm53-24552Desi Apriyanti RahayuNo ratings yet
- F34b-Chemical Resistance GuideDocument6 pagesF34b-Chemical Resistance GuideDenison Dutra ChavesNo ratings yet
- 2 Cement For Engineering Construction: 2.1 GeneralDocument12 pages2 Cement For Engineering Construction: 2.1 GeneralIMJ JNo ratings yet
- Chemicals For Substitution of Hazardous ChemicalsDocument6 pagesChemicals For Substitution of Hazardous ChemicalsFatima AnwarNo ratings yet
- PDS Perkadox BM 50 RDocument4 pagesPDS Perkadox BM 50 RscabugueiraNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications: Section 2Document6 pagesProduct Specifications: Section 2sebas guzNo ratings yet
- Arnite Chemical Resistance v1 1Document13 pagesArnite Chemical Resistance v1 1tomasykNo ratings yet
- 20060525baker Petrolite PDFDocument35 pages20060525baker Petrolite PDFizzybjNo ratings yet
- Organic CoatingsDocument32 pagesOrganic CoatingsSreekumar RajendrababuNo ratings yet
- High Performance Epoxy Tile GroutDocument3 pagesHigh Performance Epoxy Tile GroutShaik J MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lubricantes Aprobados Por CopelandDocument1 pageLubricantes Aprobados Por Copelandfreeddy navarroNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Map Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesConceptual Map Functional GroupsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance GuideDocument20 pagesChemical Resistance GuidepunkassbobNo ratings yet
- Cationic Flotation of Iron Ores AmineDocument5 pagesCationic Flotation of Iron Ores AmineBismark SarpongNo ratings yet
- 1-A-4-Small-Combustion-Factori Emisie PDFDocument119 pages1-A-4-Small-Combustion-Factori Emisie PDFelena_ene1025No ratings yet
- EPDM CHEMICAL RESISTANCE 12him - Stoikost.uplotnitelDocument14 pagesEPDM CHEMICAL RESISTANCE 12him - Stoikost.uplotnitelScenic777No ratings yet
- Inver Powderpaint SpecirficationsDocument2 pagesInver Powderpaint SpecirficationsArun PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Application of Cationic Softeners PDFDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Application of Cationic Softeners PDFHuseini PatanwalaNo ratings yet
- PR-1772 Class B Low Weight Fuselage SealantDocument2 pagesPR-1772 Class B Low Weight Fuselage SealantLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Codan Chemical Resistance 2015Document4 pagesCodan Chemical Resistance 2015Gokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- The Chlorine Envelope: Phenol Bisphenol A CumeneDocument1 pageThe Chlorine Envelope: Phenol Bisphenol A CumenetotpityiNo ratings yet
- FGS Line Pipe-OverviewDocument45 pagesFGS Line Pipe-OverviewTaras ByloNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 1Document2 pagesPage 1 of 1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- MESC Description 772041.904.1Document2 pagesMESC Description 772041.904.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Mesc Text For 77.00.35.008.1Document2 pagesMesc Text For 77.00.35.008.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- GEG 206-1 Rev.0Document63 pagesGEG 206-1 Rev.0mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 0Document1 pagePage 1 of 0mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Mesc 771334.009.1Document2 pagesMesc 771334.009.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Mesc 766579.210.1Document1 pageMesc 766579.210.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 1Document2 pagesPage 1 of 1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Mesc 766510.316.1Document1 pageMesc 766510.316.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- MESC Description 76.31.39.208.1Document1 pageMESC Description 76.31.39.208.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 0Document1 pagePage 1 of 0mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- MESC Description 771033.005.1Document2 pagesMESC Description 771033.005.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- MESC Description 76.65.80.404.1Document1 pageMESC Description 76.65.80.404.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- MESC Description 76.65.79.208.1Document1 pageMESC Description 76.65.79.208.1mb.pipingNo ratings yet
- CF Catalog PDFDocument15 pagesCF Catalog PDFHIDRAULICA MANSE SERVICIO TECNICONo ratings yet
- Sample Entry Test (Listening & Use of English)Document5 pagesSample Entry Test (Listening & Use of English)heoquay193100% (2)
- Stainless Steel Tanks For Biogas Production: Publication P412Document20 pagesStainless Steel Tanks For Biogas Production: Publication P4124MT17ME160 VIGHNESHNo ratings yet
- Annealing of Cold-Worked Austenitic Stainless Steels: ReviewDocument9 pagesAnnealing of Cold-Worked Austenitic Stainless Steels: ReviewstaedtlerpNo ratings yet
- Daniel Series 700 - Model V707: Spring Loaded Back Pressure ValveDocument8 pagesDaniel Series 700 - Model V707: Spring Loaded Back Pressure ValveMarcelo PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Coatings and Overlays For Critical Valve ApplicationsDocument12 pagesCoatings and Overlays For Critical Valve Applicationsnavar001No ratings yet
- NEO Steel Chimney DesignDocument8 pagesNEO Steel Chimney DesignAnil Pradeep100% (1)
- Materials For Ultra Supercritical Fossil Power Plants by R. ViswanathanDocument66 pagesMaterials For Ultra Supercritical Fossil Power Plants by R. ViswanathanHASAN IZHAR KHANNo ratings yet
- Dezurik Eccentric Plug Valves Pec Pef 4 Larger Pec Eccentric Plug Valves Technical 12 - 001dDocument24 pagesDezurik Eccentric Plug Valves Pec Pef 4 Larger Pec Eccentric Plug Valves Technical 12 - 001dRahmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 01-SAMSS-046 2018 Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy PipesDocument13 pages01-SAMSS-046 2018 Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy PipesWHWENNo ratings yet
- Dolphy India Private LimitedDocument25 pagesDolphy India Private LimitedSudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Cutouts and Cutout-Arrester Combinations: (Standard, Linkbreak & Loadbreak)Document20 pagesCutouts and Cutout-Arrester Combinations: (Standard, Linkbreak & Loadbreak)Marko SanzNo ratings yet
- Sleeve CatalogueDocument32 pagesSleeve CatalogueMohd Khairi Mohd NorzianNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Testing Procedure For Mechanical EquipmentDocument39 pagesPneumatic Testing Procedure For Mechanical EquipmentCepi Sindang KamulanNo ratings yet
- Catalogo S20Document25 pagesCatalogo S20Jaime Zzaa100% (1)
- QIRT 2020 Renil - Detection of Dis Bond Between Honeycomb and Composite Facesheet of An Inner Fixed Structure Bond Panel of A Jet Engine Nacelle Using InfraredDocument16 pagesQIRT 2020 Renil - Detection of Dis Bond Between Honeycomb and Composite Facesheet of An Inner Fixed Structure Bond Panel of A Jet Engine Nacelle Using InfraredKrishnan BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- For Public Comment: Draft Malaysian StandardDocument60 pagesFor Public Comment: Draft Malaysian StandardKeith ChooNo ratings yet
- List of Profitable Projects On Pipe & Tubes ProductionDocument74 pagesList of Profitable Projects On Pipe & Tubes ProductionTube10 rNo ratings yet
- WelDocument4 pagesWelShaikhan NadzemiNo ratings yet
- Granulating Machine, Granulators Granulator Machines, Granulators For Pharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical Injection Moulding Machines, Mumbai, IndiaDocument3 pagesGranulating Machine, Granulators Granulator Machines, Granulators For Pharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical Injection Moulding Machines, Mumbai, Indiagreenlite16No ratings yet
- Astm A313 2003Document7 pagesAstm A313 2003ArefkhanNo ratings yet
- SP Product Guide GrundfosDocument106 pagesSP Product Guide GrundfosManuel VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Ads High Flow Compressed Air Couplings Staubli enDocument8 pagesAds High Flow Compressed Air Couplings Staubli enTonči KosorNo ratings yet
- (Ed01-2019) Plunger Flow Control Valves (Complete)Document28 pages(Ed01-2019) Plunger Flow Control Valves (Complete)Sandeepan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Blagdon: Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpDocument2 pagesBlagdon: Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpGagan Deep AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Flomax Catalog 2021 Hi ResDocument42 pagesFlomax Catalog 2021 Hi ResdobolanNo ratings yet
- 1.2210 Datasheet, 1.2210 Property, 1.2210 Standard Specification, 1Document3 pages1.2210 Datasheet, 1.2210 Property, 1.2210 Standard Specification, 1adaNo ratings yet