Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System - Lecture
Nervous System - Lecture
Uploaded by
kissesjazzy falcojCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aligner Orthodontics and Orofacial OrthopedicsDocument1,091 pagesAligner Orthodontics and Orofacial OrthopedicsovanayaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors WorksheetDocument12 pagesSensory Receptors WorksheetAlexis CastellanosNo ratings yet
- HES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesDocument4 pagesHES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesLAGUERTA, JOHN MICHAEL A.No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ANAPHY TransesDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 9 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Special Senses UnitDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Special Senses UnitjosephNo ratings yet
- Transes - SensesDocument6 pagesTranses - SensesKyla Trina De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- General SensesDocument66 pagesGeneral SensesOnecho Angelo GabineteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Finals Reviewer (Chap 9-14)Document43 pagesAnaphy Lec Finals Reviewer (Chap 9-14)Janine AlintanaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DesignDocument28 pagesUntitled DesignChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document11 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Sensory ReceptorsDocument20 pagesTypes and Functions of Sensory ReceptorspashaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: General & Special Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman Anatomy: General & Special Sensory OrgansLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Stimuli AND ResponseDocument57 pagesStimuli AND Responseaniszainuddin77No ratings yet
- Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeDocument10 pagesTheme: Management and Continuity of LifeAnonymous 7pn3HEbYLNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsDocument62 pagesSensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Psychology Presentation: B.A. L.L.B. (Hons.) Semester-1Document10 pagesWelcome To Psychology Presentation: B.A. L.L.B. (Hons.) Semester-1ADITI YADAVNo ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Document12 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Study SheetDocument3 pagesNervous System Study SheetMarym ElsayedNo ratings yet
- 9 SensesDocument4 pages9 SensesMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Summary and Activities - Unit 4 Interaction Function - 2024Document8 pagesSummary and Activities - Unit 4 Interaction Function - 2024adrodo33siunnNo ratings yet
- Resumen Science 2 TrimestreDocument5 pagesResumen Science 2 TrimestreHazel Brenes PochetNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument77 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiSiti Nur HalizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter#4Document14 pagesChapter#4Tania kumariNo ratings yet
- Anatomi SensasiDocument59 pagesAnatomi SensasiCredo AriefNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Basis of PsychologyDocument62 pagesNeurobiological Basis of PsychologyJovelyn Morales JosolNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument8 pagesSensation and PerceptionJessa TanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - SensesDocument4 pagesAnaphy - SensesAthena LeeNo ratings yet
- SensationDocument6 pagesSensationIzhar KhanNo ratings yet
- Ana - ReviewerDocument5 pagesAna - ReviewerAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Ansci Lec ReviewerDocument15 pagesAnsci Lec ReviewerKarla CarbonelNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument4 pagesSensesDiana CabreraNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument51 pagesSensation and Perceptionmelissa quanNo ratings yet
- Sensory ReceptorsDocument26 pagesSensory ReceptorsEmmanuel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Sensation & PerceptionDocument55 pagesSensation & PerceptionMary James100% (1)
- Special SensesDocument73 pagesSpecial SensesErnie SyarinaNo ratings yet
- Mine AnkdsjcsDocument2 pagesMine AnkdsjcsKarl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- I.Psy - Module 2Document40 pagesI.Psy - Module 2vennelaNo ratings yet
- BLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDocument35 pagesBLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDineth GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Amiey SehokNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument6 pagesSensesNicole FinuliarNo ratings yet
- 658fdb5a7f835b001893b25c - ## - Revision 02 - Control and Coordination - Class NotesDocument68 pages658fdb5a7f835b001893b25c - ## - Revision 02 - Control and Coordination - Class Notesshifabelim70No ratings yet
- PNS and Special Online To Post For StudentsDocument15 pagesPNS and Special Online To Post For Studentspham vanNo ratings yet
- Psych 205 Review 1Document12 pagesPsych 205 Review 1James Yu100% (1)
- Itcp Mid pt2Document9 pagesItcp Mid pt2EISHA SHAYKHNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Document5 pagesCH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Olivia DoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument44 pagesChapter IIJESPER BAYAUANo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses NotesataraxialliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Anaphy TransesDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Anaphy TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- p12-13 Touch and PainDocument41 pagesp12-13 Touch and PainBob SmithNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lec - Sense OrganDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Sense OrganReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: Psychology 1Document28 pagesSensation and Perception: Psychology 1Vincent OrianaNo ratings yet
- SENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Document6 pagesSENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Karl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument69 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiShabrina MaharaniNo ratings yet
- CH 9 SensesDocument6 pagesCH 9 SensesJERIKO EGBALIC CABREZOSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document69 pagesLecture 4mudassirali7711No ratings yet
- Sensory PhysiologyDocument35 pagesSensory PhysiologyMansooreh NamiNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument2 pagesSensation and PerceptionBagi Racelis0% (1)
- Psychology: Sensing The EnvironmentDocument48 pagesPsychology: Sensing The EnvironmentyoshiNo ratings yet
- Faradic CurrentDocument4 pagesFaradic CurrentNamrathaThalatoti ywSSAmHsULNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesVertebral Column Lesson PlanlataduttajgmNo ratings yet
- A. Multiple Choice. Answer TheDocument1 pageA. Multiple Choice. Answer TheJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Midterm Examination: 2225124@slu - Edu.PhDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab Midterm Examination: 2225124@slu - Edu.PhDimmuyog, Krizel AnnNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Signal Processing and ControlDocument7 pagesBiomedical Signal Processing and Controlbornich glegleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document60 pagesChapter 8enewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Lobe FunctionsDocument77 pagesLobe FunctionsAnanya100% (1)
- JageshwarDocument1 pageJageshwarrajeshsaloaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Control Neuronal de La Resistencia A InsulinaDocument12 pages8 - Control Neuronal de La Resistencia A InsulinaValery Alexandra Silva CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC210206017Document3 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC210206017Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Concentration Level: Level of Goal AccomplishmentDocument1 pageConcentration Level: Level of Goal AccomplishmentMinh Quân KhổngNo ratings yet
- BIO621 Chapter 2Document135 pagesBIO621 Chapter 2MizahNo ratings yet
- ADHD and The BrainDocument1 pageADHD and The Brain111No ratings yet
- SNR and Speech IntelligibilityDocument7 pagesSNR and Speech IntelligibilityRaphael ChristantoNo ratings yet
- 11 +Muscle+TissueDocument58 pages11 +Muscle+Tissuegabbs_123No ratings yet
- An Overview of The Physiology of Pain For The VeterinarianDocument5 pagesAn Overview of The Physiology of Pain For The VeterinarianMr. questionNo ratings yet
- Shah 2015 - Myofacial Trigger Points Then and Now - A Historical and Scientific PerspectiveDocument16 pagesShah 2015 - Myofacial Trigger Points Then and Now - A Historical and Scientific PerspectiveParvathi PatilNo ratings yet
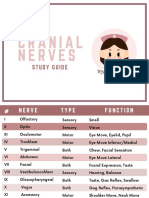
- Cranial NervesDocument6 pagesCranial Nervesvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Pudendal Nerve BlockDocument2 pagesPudendal Nerve BlockLauraNo ratings yet
- Daseb 010323Document9 pagesDaseb 010323Shifa ShiblyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2Document10 pagesReviewer 2Bailey EtormaNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Ragina AguilaDocument55 pagesRabies: Ragina AguilaCharles Lester AdalimNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolAdrian DionisioNo ratings yet
- Module 14: Anatomy & Physiology Case Study #4: Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesModule 14: Anatomy & Physiology Case Study #4: Nervous SystemRafaelaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 1109 Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Course Plan 2023Document30 pagesNurs 1109 Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Course Plan 2023Sidney BowenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3ADocument28 pagesChapter 3AjNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesIngrid GomesNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System Topic TestDocument5 pagesHuman Nervous System Topic TestSthockzin EntNo ratings yet
Nervous System - Lecture
Nervous System - Lecture
Uploaded by
kissesjazzy falcojOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System - Lecture
Nervous System - Lecture
Uploaded by
kissesjazzy falcojCopyright:
Available Formats
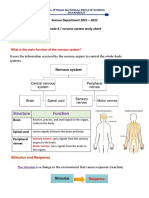
The Nervous System
Exteroreceptor
– located near external environment (skin)
Synesthesia
Perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation Interoreceptor
of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to – interprets stimuli from internal organs
automatic
Involuntary experiences in a second sensory Proprioreceptor
or cognitive pathway. – located near moving body parts, interprets position
Ideasthesia Functional Receptor Types
– Letters and numbers evoke colors
Chemoreceptor – chemicals, mostly found in
General Senses = receptors found throughout the nose/mouth
body, Including joints and organs Osmoreceptor – respond to solutes in body fluids
Thermoreceptor – temperature
Special senses = specialized receptors found in the Mechanoreceptor – pressure, vibration, body position
head (eyes, ears, mouth) Nocireceptor – pain (chemicals released when tissue
is damaged)
Sensation = feeling that occurs when a brain
interprets a sensory nerve Impulse Sense of Pain
Projection = the brain causes a feeling to stem from a Visceral Pain – occurs in visceral tissues such as heart,
source lungs, intestine
Referred pain – feels as though it is coming from a
Sensory adaptation = sensory Receptors stop sending different part (heart pain may be felt as pain in arm or
signals when they are repeatedly stimulated shoulder)
Acute Pain – originates from skin, usually stops when
Sensory Deprivation stimulus stops (needle prick)
A technique initially used by neuro- Chronic Pain – dull aching sensation
psychiatrists designed to deliberately reduce
or completely remove stimuli from one or all An overview of how opioids work to block pain and
of the senses. why they become less effective the longer you use
them.
Receptor cells in the PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Are activated by stimuli in the environment 1. Nerve sends signal
2. Opioids slow/block signal
Receptor cells classified into 3 different types 3. Limbic system (emotions) and reward pathway
are stimulated
Cell type, position, and function
Special Senses
Free Nerve Endings
– Dendrites embedded in tissue as receiver Olfactory (smell)
respond to pain and temperature Gustatory (taste)
Hearing & Equilibrium
Encapsulated Sight
– embedded in connective tissue to increase
sensitivity (pressure and touch) Sense of Smell (Olfactory)
Specialized Odor Receptor Cell Olfactory bulb Olfactory
– receptors in the retina of the eye Tract
LIMBIC SYSTEM
Location-Based Receptor Types
Papillae = taste buds
Umami – a savory taste, is one of the five basic tastes,
Sense of Hearing
External Ear
Auricle (pinna) – outer ear auditory Canal
(external auditory meatus)
- Opening to the eardrum
Auriculares
- Group of muscles called the are responsible for
this movement.
Ear wiggling is considered a
VESTIGIAL trait
– a trait that no longer functions but is part of our
evolutionary past.
Middle Ear (tympanic cavity)
Eardrum (tympanum)
Auditory Ossicles
– malleus, incus, stapes
– transmit vibrations and amplify the signal
Auditory Tube (eustachian tube)
– connects the middle
Ear to the throat
– helps maintain air pressure
You might also like
- Aligner Orthodontics and Orofacial OrthopedicsDocument1,091 pagesAligner Orthodontics and Orofacial OrthopedicsovanayaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors WorksheetDocument12 pagesSensory Receptors WorksheetAlexis CastellanosNo ratings yet
- HES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesDocument4 pagesHES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesLAGUERTA, JOHN MICHAEL A.No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ANAPHY TransesDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 9 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Special Senses UnitDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Special Senses UnitjosephNo ratings yet
- Transes - SensesDocument6 pagesTranses - SensesKyla Trina De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- General SensesDocument66 pagesGeneral SensesOnecho Angelo GabineteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Finals Reviewer (Chap 9-14)Document43 pagesAnaphy Lec Finals Reviewer (Chap 9-14)Janine AlintanaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DesignDocument28 pagesUntitled DesignChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document11 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #11 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Sensory ReceptorsDocument20 pagesTypes and Functions of Sensory ReceptorspashaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: General & Special Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman Anatomy: General & Special Sensory OrgansLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Stimuli AND ResponseDocument57 pagesStimuli AND Responseaniszainuddin77No ratings yet
- Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeDocument10 pagesTheme: Management and Continuity of LifeAnonymous 7pn3HEbYLNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsDocument62 pagesSensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Psychology Presentation: B.A. L.L.B. (Hons.) Semester-1Document10 pagesWelcome To Psychology Presentation: B.A. L.L.B. (Hons.) Semester-1ADITI YADAVNo ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Document12 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Study SheetDocument3 pagesNervous System Study SheetMarym ElsayedNo ratings yet
- 9 SensesDocument4 pages9 SensesMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Summary and Activities - Unit 4 Interaction Function - 2024Document8 pagesSummary and Activities - Unit 4 Interaction Function - 2024adrodo33siunnNo ratings yet
- Resumen Science 2 TrimestreDocument5 pagesResumen Science 2 TrimestreHazel Brenes PochetNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument77 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiSiti Nur HalizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter#4Document14 pagesChapter#4Tania kumariNo ratings yet
- Anatomi SensasiDocument59 pagesAnatomi SensasiCredo AriefNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Basis of PsychologyDocument62 pagesNeurobiological Basis of PsychologyJovelyn Morales JosolNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument8 pagesSensation and PerceptionJessa TanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - SensesDocument4 pagesAnaphy - SensesAthena LeeNo ratings yet
- SensationDocument6 pagesSensationIzhar KhanNo ratings yet
- Ana - ReviewerDocument5 pagesAna - ReviewerAngelica CruzNo ratings yet
- Ansci Lec ReviewerDocument15 pagesAnsci Lec ReviewerKarla CarbonelNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument4 pagesSensesDiana CabreraNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument51 pagesSensation and Perceptionmelissa quanNo ratings yet
- Sensory ReceptorsDocument26 pagesSensory ReceptorsEmmanuel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Sensation & PerceptionDocument55 pagesSensation & PerceptionMary James100% (1)
- Special SensesDocument73 pagesSpecial SensesErnie SyarinaNo ratings yet
- Mine AnkdsjcsDocument2 pagesMine AnkdsjcsKarl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- I.Psy - Module 2Document40 pagesI.Psy - Module 2vennelaNo ratings yet
- BLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDocument35 pagesBLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDineth GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Amiey SehokNo ratings yet
- SensesDocument6 pagesSensesNicole FinuliarNo ratings yet
- 658fdb5a7f835b001893b25c - ## - Revision 02 - Control and Coordination - Class NotesDocument68 pages658fdb5a7f835b001893b25c - ## - Revision 02 - Control and Coordination - Class Notesshifabelim70No ratings yet
- PNS and Special Online To Post For StudentsDocument15 pagesPNS and Special Online To Post For Studentspham vanNo ratings yet
- Psych 205 Review 1Document12 pagesPsych 205 Review 1James Yu100% (1)
- Itcp Mid pt2Document9 pagesItcp Mid pt2EISHA SHAYKHNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Document5 pagesCH 14 Sensory Perception (Notes)Olivia DoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument44 pagesChapter IIJESPER BAYAUANo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses NotesataraxialliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Anaphy TransesDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Anaphy TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- p12-13 Touch and PainDocument41 pagesp12-13 Touch and PainBob SmithNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lec - Sense OrganDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Sense OrganReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: Psychology 1Document28 pagesSensation and Perception: Psychology 1Vincent OrianaNo ratings yet
- SENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Document6 pagesSENSORY SYSTEM (Draft) Group 5Karl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument69 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiShabrina MaharaniNo ratings yet
- CH 9 SensesDocument6 pagesCH 9 SensesJERIKO EGBALIC CABREZOSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document69 pagesLecture 4mudassirali7711No ratings yet
- Sensory PhysiologyDocument35 pagesSensory PhysiologyMansooreh NamiNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument2 pagesSensation and PerceptionBagi Racelis0% (1)
- Psychology: Sensing The EnvironmentDocument48 pagesPsychology: Sensing The EnvironmentyoshiNo ratings yet
- Faradic CurrentDocument4 pagesFaradic CurrentNamrathaThalatoti ywSSAmHsULNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesVertebral Column Lesson PlanlataduttajgmNo ratings yet
- A. Multiple Choice. Answer TheDocument1 pageA. Multiple Choice. Answer TheJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Midterm Examination: 2225124@slu - Edu.PhDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab Midterm Examination: 2225124@slu - Edu.PhDimmuyog, Krizel AnnNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Signal Processing and ControlDocument7 pagesBiomedical Signal Processing and Controlbornich glegleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document60 pagesChapter 8enewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Lobe FunctionsDocument77 pagesLobe FunctionsAnanya100% (1)
- JageshwarDocument1 pageJageshwarrajeshsaloaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Control Neuronal de La Resistencia A InsulinaDocument12 pages8 - Control Neuronal de La Resistencia A InsulinaValery Alexandra Silva CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC210206017Document3 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC210206017Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Concentration Level: Level of Goal AccomplishmentDocument1 pageConcentration Level: Level of Goal AccomplishmentMinh Quân KhổngNo ratings yet
- BIO621 Chapter 2Document135 pagesBIO621 Chapter 2MizahNo ratings yet
- ADHD and The BrainDocument1 pageADHD and The Brain111No ratings yet
- SNR and Speech IntelligibilityDocument7 pagesSNR and Speech IntelligibilityRaphael ChristantoNo ratings yet
- 11 +Muscle+TissueDocument58 pages11 +Muscle+Tissuegabbs_123No ratings yet
- An Overview of The Physiology of Pain For The VeterinarianDocument5 pagesAn Overview of The Physiology of Pain For The VeterinarianMr. questionNo ratings yet
- Shah 2015 - Myofacial Trigger Points Then and Now - A Historical and Scientific PerspectiveDocument16 pagesShah 2015 - Myofacial Trigger Points Then and Now - A Historical and Scientific PerspectiveParvathi PatilNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument6 pagesCranial Nervesvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Pudendal Nerve BlockDocument2 pagesPudendal Nerve BlockLauraNo ratings yet
- Daseb 010323Document9 pagesDaseb 010323Shifa ShiblyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2Document10 pagesReviewer 2Bailey EtormaNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Ragina AguilaDocument55 pagesRabies: Ragina AguilaCharles Lester AdalimNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 10 Science Nerve Cell: Mariano Ponce National High SchoolAdrian DionisioNo ratings yet
- Module 14: Anatomy & Physiology Case Study #4: Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesModule 14: Anatomy & Physiology Case Study #4: Nervous SystemRafaelaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 1109 Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Course Plan 2023Document30 pagesNurs 1109 Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Course Plan 2023Sidney BowenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3ADocument28 pagesChapter 3AjNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Nerve Conduction StudiesIngrid GomesNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System Topic TestDocument5 pagesHuman Nervous System Topic TestSthockzin EntNo ratings yet