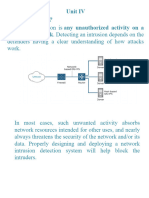
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antivirus
Antivirus
Uploaded by
Kamma VidyaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Synthesis Essay Revised - On Cyber Security BESTDocument11 pagesSynthesis Essay Revised - On Cyber Security BESTklm klmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Solution Manual Accounting Information SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Solution Manual Accounting Information SystemsMahmoud AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Are Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Intrusion Detection SystemsAbirami SekarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System - WikipediaDocument15 pagesIntrusion Detection System - WikipediaHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053Document7 pagesAssignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053KashifNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Info SecuDocument8 pagesUnit-4 Info Secuworkwithasr04No ratings yet
- Case Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesCase Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemAnonymous tIi0h0100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument12 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemNew ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Terminology: TypesDocument4 pagesTerminology: TypesAbhiteja AbhiNo ratings yet
- 08-Class - Cont. Network Security II - Information SecurityDocument28 pages08-Class - Cont. Network Security II - Information SecuritySyeda Insharah RiazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Ids/IpsDocument7 pagesIds/Ipszaiby41No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-IDocument27 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-Idsa dsaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Module-1: Information Security DevicesDocument52 pagesModule-1: Information Security DevicessendhilksNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument4 pagesIntrusion DetectionSolomon AkpanNo ratings yet
- IntrudersDocument25 pagesIntruderskaushalnishant64No ratings yet
- Module 5Document19 pagesModule 5anandkumarshaw79923No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument2 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemGopi Chand reddyNo ratings yet
- Is Unit5Document43 pagesIs Unit5Sudharsan BalaNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3cnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument48 pagesUnit IVYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- How To Use Snort in KaliDocument9 pagesHow To Use Snort in Kaliabdullah0No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.Document16 pagesIntrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.preetam a rare dragonNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument13 pagesIntrusion DetectionSharmila100% (1)
- An Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSDocument41 pagesAn Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSTigerHATSNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness - 2017Document21 pagesCyber Security Awareness - 2017nileshNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401Document4 pagesInformation Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument3 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemR. P. VermaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- IDSDocument36 pagesIDSshreeyanalla45No ratings yet
- Slides Set 11Document33 pagesSlides Set 11Muhammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationscatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- White Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventionDocument5 pagesWhite Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventiongynxNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument13 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemMohamed Abdirahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Document10 pagesIntrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Vaishali KodwalNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Document7 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Sonia Sultana100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemArchana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Seminar On IdsDocument17 pagesSeminar On IdsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Weaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument11 pagesWeaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsijcsesNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityDocument30 pagesIntrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityKillerbeeNo ratings yet
- FirewallDocument1 pageFirewallAnurag RaiNo ratings yet
- Data Security Mid SolveDocument2 pagesData Security Mid SolveHuzair NadeemNo ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsZak RyderNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument23 pagesIntrusion Detection Systemabhijitkakati100% (1)
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5Jil Poraskumar Bhatti -No ratings yet
- Network Security DesignDocument5 pagesNetwork Security DesignMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Endpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Document10 pagesEndpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Playing PurposesNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Surveillance"Document9 pagesNtroduction: Surveillance"aliov mezherNo ratings yet
- Host Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Document23 pagesHost Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Shaban MahekulaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 IDS AC & Other Sec ToolsDocument46 pagesCH 7 IDS AC & Other Sec ToolsNishanth KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument16 pagesIntrusion DetectionShubhada WavaleNo ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2013 08 31 083Document8 pagesIjaiem 2013 08 31 083International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Evading IDS Firewall and Honeypots - 12Document22 pagesEvading IDS Firewall and Honeypots - 12victor phiriNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5From EverandCISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Mike Meyers Comptia Security Certification Passport Exam Sy0 501 Dawn Dunkerley Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pages(Download PDF) Mike Meyers Comptia Security Certification Passport Exam Sy0 501 Dawn Dunkerley Full Chapter PDFtsenaerajawy8100% (8)
- Case Study-Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities in Industrial Control SystemDocument3 pagesCase Study-Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities in Industrial Control SystemAnkitaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Legal Cybersecurity Arctic WolfDocument9 pagesLegal Cybersecurity Arctic WolfPio BarbagelataNo ratings yet
- Updated List of Senior Citizens: NOT LATER THAN MARCH 24, 2021 (12:00 NN)Document4 pagesUpdated List of Senior Citizens: NOT LATER THAN MARCH 24, 2021 (12:00 NN)Ylaine NavaltaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To Penetration TestingDocument4 pagesA Complete Guide To Penetration Testingraghunandhan.cvNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking: Technical Seminar ReportDocument26 pagesEthical Hacking: Technical Seminar ReportMaliha Fatima18-57No ratings yet
- Cyber Security NotesDocument2 pagesCyber Security NotesFed NeseeNo ratings yet
- Script Project 1-3, Gabrielle LinkherzDocument2 pagesScript Project 1-3, Gabrielle LinkherzGabrielle_LinkherzNo ratings yet
- Sophos Firewall SBDocument1 pageSophos Firewall SBxmangakaxNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Various Cyber Attacks and Their ClassificationDocument7 pagesA Survey On Various Cyber Attacks and Their Classificationrajvaibhav nimbalkarNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Security SolutionsDocument10 pagesCyber Security Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Security SolutionsFasika TegegnNo ratings yet
- BTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)Document90 pagesBTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)svvv ganduNo ratings yet
- 1 English For Information Technology Elementa-51-60Document10 pages1 English For Information Technology Elementa-51-60HERRERANo ratings yet
- GISEC ListDocument33 pagesGISEC Listgaju619No ratings yet
- Eti 2510 Cat 2Document1 pageEti 2510 Cat 2paulkorirNo ratings yet
- Trend Micro Web Security Data SheetDocument2 pagesTrend Micro Web Security Data SheetWalter PurezaNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Fortiwifi 90g SeriesDocument10 pagesFortigate Fortiwifi 90g Seriesnurcahyo teguh PermadiNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Cyber Threats To Small Businesses.Document8 pagesTop 10 Cyber Threats To Small Businesses.infosectrain04No ratings yet
- Mobile App Security PDFDocument3 pagesMobile App Security PDFAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.22 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Hacking Concepts Part 2Document44 pages1.22 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Hacking Concepts Part 2Giang LeNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Data Economy: The Marketplace For Stolen Digital InformationDocument15 pagesThe Hidden Data Economy: The Marketplace For Stolen Digital InformationLía Serrano MiquelNo ratings yet
- Eset 2Document2 pagesEset 2Dicky ChristianNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cyber SecurityDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Cyber SecurityDr-Samson ChepuriNo ratings yet
- Internet Security Solved MCQs (Set-1)Document6 pagesInternet Security Solved MCQs (Set-1)AnkitNo ratings yet
- Application Hacking PPT-1Document23 pagesApplication Hacking PPT-1ShivaniNo ratings yet
- CSS - 05-Week 14 - Module 14 - Security Firewall and VPNDocument5 pagesCSS - 05-Week 14 - Module 14 - Security Firewall and VPNElixa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Introduction and Security Trends NotesDocument69 pagesChapter-1-Introduction and Security Trends NotesVrushaliNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security (R20a6202)Document75 pagesCyber Security (R20a6202)Anacademy FreeNo ratings yet
Antivirus
Antivirus
Uploaded by
Kamma VidyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antivirus
Antivirus
Uploaded by
Kamma VidyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Firewalls, antivirus solutions, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential
components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, each serving distinct
purposes in safeguarding computer systems and networks. Here are the key
differences among them:
1. Firewalls:
Purpose:
Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted
external networks, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on
predetermined security rules.
Functionality:
Firewalls operate at the network layer (Layer 3) and, to some extent, the transport
layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model.
Traffic Filtering:
Firewalls examine packets and filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and
protocols. They can block or allow traffic based on predefined rules.
Use Cases:
Commonly used to prevent unauthorized access, protect against network-based
attacks, and define access policies for specific services.
2. Antivirus Solutions:
Purpose:
Antivirus solutions are designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software,
including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and other types of malware.
Functionality:
Antivirus software operates at the endpoint (individual devices) and examines files
and activities on those devices.
Detection Methods:
Antivirus solutions use signature-based detection (matching known malware
signatures) and heuristic analysis (detecting suspicious behavior) to identify and
quarantine or remove threats.
Use Cases:
Essential for protecting endpoints (computers, servers, mobile devices) from
malware infections and ensuring the integrity of files and applications.
3. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
Purpose:
IDS monitors network or system activities for signs of unauthorized or malicious
behavior and generates alerts or takes actions to mitigate potential threats.
Functionality:
IDS can operate at the network or host level. Network-based IDS (NIDS) examines
network traffic, while host-based IDS (HIDS) monitors activities on individual
devices.
Detection Methods:
IDS uses signature-based detection, anomaly detection (detecting deviations from
normal behavior), or a combination of both.
Use Cases:
Effective for detecting and responding to suspicious activities, such as intrusion
attempts, unauthorized access, or unusual patterns of behavior within a network or
on a specific device.
Key Differences:
Scope:
Firewalls focus on managing network traffic and controlling access between
networks.
Antivirus solutions concentrate on identifying and eliminating malware on
individual devices.
IDS monitors and analyzes activities for signs of malicious behavior within a
network or on specific devices.
Layer of Operation:
Firewalls operate at the network and transport layers.
Antivirus solutions operate at the endpoint (application and file layers).
IDS can operate at the network or host layers.
Detection Methods:
Firewalls use rules to filter traffic based on addresses, ports, and protocols.
Antivirus solutions use signatures and heuristic analysis to identify known and
potential threats.
IDS uses signature-based detection, anomaly detection, or a combination to identify
malicious behavior.
Focus:
Firewalls focus on preventing unauthorized access and protecting the network
perimeter.
Antivirus solutions focus on detecting and removing malware on individual devices.
IDS focuses on detecting and responding to suspicious activities within a network.
In practice, a robust cybersecurity strategy often involves the deployment of all
three components—firewalls, antivirus solutions, and intrusion detection systems—to
create a layered defense against a wide range of cyber threats.
You might also like
- Synthesis Essay Revised - On Cyber Security BESTDocument11 pagesSynthesis Essay Revised - On Cyber Security BESTklm klmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Solution Manual Accounting Information SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Solution Manual Accounting Information SystemsMahmoud AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Are Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Intrusion Detection SystemsAbirami SekarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System - WikipediaDocument15 pagesIntrusion Detection System - WikipediaHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053Document7 pagesAssignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053KashifNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Info SecuDocument8 pagesUnit-4 Info Secuworkwithasr04No ratings yet
- Case Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesCase Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemAnonymous tIi0h0100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument12 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemNew ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Terminology: TypesDocument4 pagesTerminology: TypesAbhiteja AbhiNo ratings yet
- 08-Class - Cont. Network Security II - Information SecurityDocument28 pages08-Class - Cont. Network Security II - Information SecuritySyeda Insharah RiazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Ids/IpsDocument7 pagesIds/Ipszaiby41No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-IDocument27 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-Idsa dsaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Module-1: Information Security DevicesDocument52 pagesModule-1: Information Security DevicessendhilksNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument4 pagesIntrusion DetectionSolomon AkpanNo ratings yet
- IntrudersDocument25 pagesIntruderskaushalnishant64No ratings yet
- Module 5Document19 pagesModule 5anandkumarshaw79923No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument2 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemGopi Chand reddyNo ratings yet
- Is Unit5Document43 pagesIs Unit5Sudharsan BalaNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3cnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument48 pagesUnit IVYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- How To Use Snort in KaliDocument9 pagesHow To Use Snort in Kaliabdullah0No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.Document16 pagesIntrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.preetam a rare dragonNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument13 pagesIntrusion DetectionSharmila100% (1)
- An Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSDocument41 pagesAn Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSTigerHATSNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness - 2017Document21 pagesCyber Security Awareness - 2017nileshNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401Document4 pagesInformation Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument3 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemR. P. VermaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- IDSDocument36 pagesIDSshreeyanalla45No ratings yet
- Slides Set 11Document33 pagesSlides Set 11Muhammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationscatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- White Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventionDocument5 pagesWhite Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventiongynxNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument13 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemMohamed Abdirahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Document10 pagesIntrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Vaishali KodwalNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Document7 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Sonia Sultana100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemArchana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Seminar On IdsDocument17 pagesSeminar On IdsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Weaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument11 pagesWeaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsijcsesNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityDocument30 pagesIntrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityKillerbeeNo ratings yet
- FirewallDocument1 pageFirewallAnurag RaiNo ratings yet
- Data Security Mid SolveDocument2 pagesData Security Mid SolveHuzair NadeemNo ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsZak RyderNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument23 pagesIntrusion Detection Systemabhijitkakati100% (1)
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5Jil Poraskumar Bhatti -No ratings yet
- Network Security DesignDocument5 pagesNetwork Security DesignMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Endpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Document10 pagesEndpoint Security and Analysis: Common Type Found in 2016Playing PurposesNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Surveillance"Document9 pagesNtroduction: Surveillance"aliov mezherNo ratings yet
- Host Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Document23 pagesHost Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Shaban MahekulaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 IDS AC & Other Sec ToolsDocument46 pagesCH 7 IDS AC & Other Sec ToolsNishanth KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument16 pagesIntrusion DetectionShubhada WavaleNo ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2013 08 31 083Document8 pagesIjaiem 2013 08 31 083International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Evading IDS Firewall and Honeypots - 12Document22 pagesEvading IDS Firewall and Honeypots - 12victor phiriNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5From EverandCISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Mike Meyers Comptia Security Certification Passport Exam Sy0 501 Dawn Dunkerley Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pages(Download PDF) Mike Meyers Comptia Security Certification Passport Exam Sy0 501 Dawn Dunkerley Full Chapter PDFtsenaerajawy8100% (8)
- Case Study-Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities in Industrial Control SystemDocument3 pagesCase Study-Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities in Industrial Control SystemAnkitaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Legal Cybersecurity Arctic WolfDocument9 pagesLegal Cybersecurity Arctic WolfPio BarbagelataNo ratings yet
- Updated List of Senior Citizens: NOT LATER THAN MARCH 24, 2021 (12:00 NN)Document4 pagesUpdated List of Senior Citizens: NOT LATER THAN MARCH 24, 2021 (12:00 NN)Ylaine NavaltaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To Penetration TestingDocument4 pagesA Complete Guide To Penetration Testingraghunandhan.cvNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking: Technical Seminar ReportDocument26 pagesEthical Hacking: Technical Seminar ReportMaliha Fatima18-57No ratings yet
- Cyber Security NotesDocument2 pagesCyber Security NotesFed NeseeNo ratings yet
- Script Project 1-3, Gabrielle LinkherzDocument2 pagesScript Project 1-3, Gabrielle LinkherzGabrielle_LinkherzNo ratings yet
- Sophos Firewall SBDocument1 pageSophos Firewall SBxmangakaxNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Various Cyber Attacks and Their ClassificationDocument7 pagesA Survey On Various Cyber Attacks and Their Classificationrajvaibhav nimbalkarNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Security SolutionsDocument10 pagesCyber Security Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Security SolutionsFasika TegegnNo ratings yet
- BTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)Document90 pagesBTICS501 Network Security & Cryptography (Unit-1 To 5)svvv ganduNo ratings yet
- 1 English For Information Technology Elementa-51-60Document10 pages1 English For Information Technology Elementa-51-60HERRERANo ratings yet
- GISEC ListDocument33 pagesGISEC Listgaju619No ratings yet
- Eti 2510 Cat 2Document1 pageEti 2510 Cat 2paulkorirNo ratings yet
- Trend Micro Web Security Data SheetDocument2 pagesTrend Micro Web Security Data SheetWalter PurezaNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Fortiwifi 90g SeriesDocument10 pagesFortigate Fortiwifi 90g Seriesnurcahyo teguh PermadiNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Cyber Threats To Small Businesses.Document8 pagesTop 10 Cyber Threats To Small Businesses.infosectrain04No ratings yet
- Mobile App Security PDFDocument3 pagesMobile App Security PDFAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.22 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Hacking Concepts Part 2Document44 pages1.22 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Hacking Concepts Part 2Giang LeNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Data Economy: The Marketplace For Stolen Digital InformationDocument15 pagesThe Hidden Data Economy: The Marketplace For Stolen Digital InformationLía Serrano MiquelNo ratings yet
- Eset 2Document2 pagesEset 2Dicky ChristianNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cyber SecurityDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Cyber SecurityDr-Samson ChepuriNo ratings yet
- Internet Security Solved MCQs (Set-1)Document6 pagesInternet Security Solved MCQs (Set-1)AnkitNo ratings yet
- Application Hacking PPT-1Document23 pagesApplication Hacking PPT-1ShivaniNo ratings yet
- CSS - 05-Week 14 - Module 14 - Security Firewall and VPNDocument5 pagesCSS - 05-Week 14 - Module 14 - Security Firewall and VPNElixa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Introduction and Security Trends NotesDocument69 pagesChapter-1-Introduction and Security Trends NotesVrushaliNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security (R20a6202)Document75 pagesCyber Security (R20a6202)Anacademy FreeNo ratings yet