Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Uploaded by
Andrea MayorCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument19 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseRiza Indelible Sibullas80% (5)
- Handouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesHandouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH Quarternicole balgumaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESDocument6 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESRowan Yñigo TamayoNo ratings yet
- PEH Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument7 pagesPEH Causes of Sports InjuriesFaye TiuNo ratings yet
- Elm Grade 11 (Peh)Document28 pagesElm Grade 11 (Peh)Kimberly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseMr. CRAFTNo ratings yet
- PEH2 Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesPEH2 Finals ReviewerPedro HampaslupaNo ratings yet
- SLM PE 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesSLM PE 4th QuarterRichmond LeeNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sport InjuriesDocument12 pagesCauses of Sport Injuriesyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Ligaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainDocument5 pagesLigaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainKyla Patricia ZabalaNo ratings yet
- PE and HealthDocument3 pagesPE and HealthRia Ellaine Cornelio LachicaNo ratings yet
- SHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument10 pagesSHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseKylie CadenasNo ratings yet
- Sports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, ActivityDocument9 pagesSports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, Activitywelcome homeNo ratings yet
- Pe Ni Ms NicaDocument2 pagesPe Ni Ms NicaLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument4 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Managementchristine mae picocNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices And: Sports InjuryDocument27 pagesSafety Practices And: Sports InjuryRaeven FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument9 pagesSport InjurieswriterseinnaaaoNo ratings yet
- Health 11 3rdqDocument7 pagesHealth 11 3rdqflbshyneNo ratings yet
- PE & HealthDocument2 pagesPE & Healthshoti lahNo ratings yet
- 1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFDocument44 pages1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFMark Anthony Nazareth100% (2)
- Eapp StrainDocument6 pagesEapp StrainHanes ArthurNo ratings yet
- Q2 Grade 4 Lesson - 4 Major Organs (Muscles and Bones)Document18 pagesQ2 Grade 4 Lesson - 4 Major Organs (Muscles and Bones)Marcus Sayson DabonNo ratings yet
- Mapeh WuizDocument1 pageMapeh WuizBriana Doriane NebrejaNo ratings yet
- 7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument25 pages7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseFirst GhostNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument15 pagesCauses of Sports InjuriesMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- G11 - Pe 2 - Module 1Document7 pagesG11 - Pe 2 - Module 1John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument18 pagesSports InjuriesIntan AqilaNo ratings yet
- SPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofDocument7 pagesSPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofPriyanshu KanojiaNo ratings yet
- 2 Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument34 pages2 Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementGajete, Dnvr Cliedzray L.No ratings yet
- INJURYDocument4 pagesINJURYjessell bonifacioNo ratings yet
- Safety Practice in Sports and ExerciseDocument32 pagesSafety Practice in Sports and ExercisePrincess Reiann LopezNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument38 pagesFinalKeanna Marie MarfilNo ratings yet
- Sports Related InjuriesDocument3 pagesSports Related Injuriessalabsabhga0529No ratings yet
- CH-7 Class 12Document54 pagesCH-7 Class 12Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Anat 112 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesAnat 112 Assignmentsmedoos19052005No ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument23 pagesOrthopedic Nursinggabrielle magdaraog100% (1)
- Are You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsFrom EverandAre You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsNo ratings yet
- Pe Bblan AssignmentDocument2 pagesPe Bblan AssignmentOrlando Sanchez RimaNo ratings yet
- MSN 303fractureDocument10 pagesMSN 303fractureFryam BellsNo ratings yet
- P eDocument2 pagesP eMia KhufraNo ratings yet
- First Aid FractureDocument2 pagesFirst Aid FractureJudea Drizzle BaguidudolNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationEuan Marlee F. SampeloNo ratings yet
- Recognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingDocument4 pagesRecognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingJake GarciaNo ratings yet
- Injury Manag Ement: Ms. Mercy Mae P. Miaral Adamson University Senior High SchoolDocument26 pagesInjury Manag Ement: Ms. Mercy Mae P. Miaral Adamson University Senior High SchoolbAddy's gAmbinoNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - 09Document18 pagesModule 7 - 09john frits gerard mombayNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument33 pagesFractureJinu George100% (2)
- Lesson-11-Water SafetyDocument3 pagesLesson-11-Water SafetyKrystal GailNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument51 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseKenn Almazan100% (1)
- PEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Document3 pagesPEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Ally OcbianNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument3 pagesSports InjuriesMario MurilloNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Sprain and StrainDocument4 pagesDifference Between Sprain and StrainTayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Pe Health q2 Week 1 2Document12 pagesPe Health q2 Week 1 2Arlene MangaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesMuscular SystemJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- PE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2Document15 pagesPE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2nhoj eiram Rodavlas50% (2)
- Q4 - PE - Common Injuries Involve in RecreationDocument21 pagesQ4 - PE - Common Injuries Involve in RecreationDemise LANo ratings yet
- Fracturesgoutosteosprain 2Document199 pagesFracturesgoutosteosprain 2Rose Cristille Yeso JocsonNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument10 pagesPe ReviewerLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- Green and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000Document4 pagesGreen and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000alcuirezjane2No ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument7 pagesSport InjuriesChelsea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Surgery WorkDocument9 pagesSurgery WorkHigh TechNo ratings yet
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Uploaded by
Andrea MayorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Chapter 7 Safe Wps Office
Uploaded by
Andrea MayorCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 7: SAFETY PRACTICES IN SPORTS AND EXERCISE
LESSON 14 : CAUSES OF COMMON SPORTS INJURY
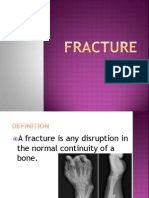
Injuries are damaged tissues or organs which occurs when it encounters trauma or physical force
that is greater than what it can resist or absorb.
The Musculoskeletal Structures
1. Ligaments - stabilized joints
2. Tendons - attachment muscles to bones
3. Muscles - creates movements
4. Bones - anchor for muscles
5. Joints - fulcrum for movements
Direction of Force Applied to Musculoskeletal Structures
1.Compressive Forces- impact the center causing to bend or fold
2.Tensile Forces - are those that act away from the center of the structure causing a pull or
stretch.
3.Shear Forces - are opposing forces toward the different ends of structure causing it to twist.
2 Types of Sport Injuries
1.Acute Injuries
2.Chronic Injuries
Acute Injuries - have sign and symptoms ( ex. pain,swelling ) that manifest immediately after
force application.
Examples:
Sprains - an overstretch ligaments
Strain - caused by excessive stretching that causes tears in the muscle- tendon unit.
Fractures - are breaks in the continuity of the bone.
Dislocations - are bones that are pushed out from their joint capsules
Chronic / Overuse Injuries - usually result from overuse of one area of the body and develop
gradually over time.
Examples:
Stress fractures - tiny cracks in a bone
Tendinophaty - any tendon condition that causes pain and swelling
Osteoarthritis - degenerative joint condition
Bursitis - inflammation of the bursae.
You might also like
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument19 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseRiza Indelible Sibullas80% (5)
- Handouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesHandouts Topic 1 CS15 2 4TH Quarternicole balgumaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESDocument6 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 5 SPORTS INJURIESRowan Yñigo TamayoNo ratings yet
- PEH Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument7 pagesPEH Causes of Sports InjuriesFaye TiuNo ratings yet
- Elm Grade 11 (Peh)Document28 pagesElm Grade 11 (Peh)Kimberly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseMr. CRAFTNo ratings yet
- PEH2 Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesPEH2 Finals ReviewerPedro HampaslupaNo ratings yet
- SLM PE 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesSLM PE 4th QuarterRichmond LeeNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sport InjuriesDocument12 pagesCauses of Sport Injuriesyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Ligaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainDocument5 pagesLigaments Stabilize Joints Sprain Tendons Attaches Muscles To Bones StrainKyla Patricia ZabalaNo ratings yet
- PE and HealthDocument3 pagesPE and HealthRia Ellaine Cornelio LachicaNo ratings yet
- SHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument10 pagesSHS Lesson 10 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseKylie CadenasNo ratings yet
- Sports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, ActivityDocument9 pagesSports Injury: Organs Through Any Sport Equipment, Activitywelcome homeNo ratings yet
- Pe Ni Ms NicaDocument2 pagesPe Ni Ms NicaLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument4 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury Managementchristine mae picocNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices And: Sports InjuryDocument27 pagesSafety Practices And: Sports InjuryRaeven FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument9 pagesSport InjurieswriterseinnaaaoNo ratings yet
- Health 11 3rdqDocument7 pagesHealth 11 3rdqflbshyneNo ratings yet
- PE & HealthDocument2 pagesPE & Healthshoti lahNo ratings yet
- 1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFDocument44 pages1 Safety Practices in Sports and Exercise PDFMark Anthony Nazareth100% (2)
- Eapp StrainDocument6 pagesEapp StrainHanes ArthurNo ratings yet
- Q2 Grade 4 Lesson - 4 Major Organs (Muscles and Bones)Document18 pagesQ2 Grade 4 Lesson - 4 Major Organs (Muscles and Bones)Marcus Sayson DabonNo ratings yet
- Mapeh WuizDocument1 pageMapeh WuizBriana Doriane NebrejaNo ratings yet
- 7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument25 pages7 Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseFirst GhostNo ratings yet
- Causes of Sports InjuriesDocument15 pagesCauses of Sports InjuriesMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- G11 - Pe 2 - Module 1Document7 pagesG11 - Pe 2 - Module 1John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument18 pagesSports InjuriesIntan AqilaNo ratings yet
- SPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofDocument7 pagesSPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofPriyanshu KanojiaNo ratings yet
- 2 Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument34 pages2 Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementGajete, Dnvr Cliedzray L.No ratings yet
- INJURYDocument4 pagesINJURYjessell bonifacioNo ratings yet
- Safety Practice in Sports and ExerciseDocument32 pagesSafety Practice in Sports and ExercisePrincess Reiann LopezNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument38 pagesFinalKeanna Marie MarfilNo ratings yet
- Sports Related InjuriesDocument3 pagesSports Related Injuriessalabsabhga0529No ratings yet
- CH-7 Class 12Document54 pagesCH-7 Class 12Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Anat 112 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesAnat 112 Assignmentsmedoos19052005No ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument23 pagesOrthopedic Nursinggabrielle magdaraog100% (1)
- Are You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsFrom EverandAre You Okay? Sports Injuries: Causes, Types and Treatment - Sports Book 4th Grade | Children's Sports & OutdoorsNo ratings yet
- Pe Bblan AssignmentDocument2 pagesPe Bblan AssignmentOrlando Sanchez RimaNo ratings yet
- MSN 303fractureDocument10 pagesMSN 303fractureFryam BellsNo ratings yet
- P eDocument2 pagesP eMia KhufraNo ratings yet
- First Aid FractureDocument2 pagesFirst Aid FractureJudea Drizzle BaguidudolNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationEuan Marlee F. SampeloNo ratings yet
- Recognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingDocument4 pagesRecognising and Classifying Injuries 9c Injuries Recognising ClassifyingJake GarciaNo ratings yet
- Injury Manag Ement: Ms. Mercy Mae P. Miaral Adamson University Senior High SchoolDocument26 pagesInjury Manag Ement: Ms. Mercy Mae P. Miaral Adamson University Senior High SchoolbAddy's gAmbinoNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - 09Document18 pagesModule 7 - 09john frits gerard mombayNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument33 pagesFractureJinu George100% (2)
- Lesson-11-Water SafetyDocument3 pagesLesson-11-Water SafetyKrystal GailNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices in Sports and ExerciseDocument51 pagesSafety Practices in Sports and ExerciseKenn Almazan100% (1)
- PEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Document3 pagesPEH REVIEWER (Final Exam)Ally OcbianNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument3 pagesSports InjuriesMario MurilloNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Sprain and StrainDocument4 pagesDifference Between Sprain and StrainTayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Pe Health q2 Week 1 2Document12 pagesPe Health q2 Week 1 2Arlene MangaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesMuscular SystemJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- PE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2Document15 pagesPE11 Q4 Module4a Weeks1and2nhoj eiram Rodavlas50% (2)
- Q4 - PE - Common Injuries Involve in RecreationDocument21 pagesQ4 - PE - Common Injuries Involve in RecreationDemise LANo ratings yet
- Fracturesgoutosteosprain 2Document199 pagesFracturesgoutosteosprain 2Rose Cristille Yeso JocsonNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument10 pagesPe ReviewerLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- Green and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000Document4 pagesGreen and Brown UI Frame Style Types of Bullying Poster - 20240414 - 141003 - 0000alcuirezjane2No ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument7 pagesSport InjuriesChelsea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Surgery WorkDocument9 pagesSurgery WorkHigh TechNo ratings yet