Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Uploaded by
mccano99Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Uploaded by
mccano99Copyright:
Available Formats
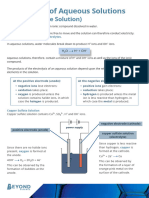
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions
Aqueous solutions are dissolved in IT
water. So in addition to the ions from
the salt, the ions from the water molecules also have to be considered.
Water molecules ionise (or split) to form hydrogen ions (H + ) and hydroxide
ions (OH - ). -
H 2O 7-
H + + OH
During the electrolysis of aqueous solutions the fate of these ions also
needs to be considered.
-
1 -
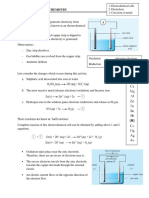
Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution i
Sodium chloride ionises in water to form positive sodium ions (Na+ ) and
-
negative chloride ions (Cl ).
-
NaCl (aq) → Na + + Cl
There are four ions in the aqueous solution. The two positive ions will be
attracted to the negative electrode (cathode). These are H + and Na+.
The two negative ions will be attracted to the positive electrode (anode).
These are OH - and Cl -.
t
④
if¥*
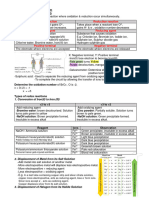
The reactivity series is used to work out which ion -
H
sodium
will react at the electrode. magnesium
carbon
t
Hydrogen will be produced at the negative electrode zinc
(cathode) if the ee
metal is more reactive than hydrogen. iron
hydrogen
I
Sodium is more reactive than TL
hydrogen, so hydrogen will copper
be produced at the negative electrode (cathode).
If the aqueous solution contains halide ions (e.g. F,- Cl -, Br - or I - ), then
1-11-1
-
the halogen will be produced at the 1-1
-
positive electrode (anode).
As a result, chlorine will be produced at the positive electrode.
H
I
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions...
-
1 -
Half equations for electrolysis of sodium chloride
reduction
At the negative electrode (cathode): 2H + + 2e - -
H2
- - oxidation
At the positive electrode (anode): 2Cl - 2e -
Cl 2
-
1 -
Electrolysis of copper sulfate solution i
Copper sulfate ionises in water to form positive copper ions (Cu2+) and
negative sulfate ions (SO4 2- ).
l l
CuSO4(aq) →
Cu 2++ SO 42-
There are four ions in the aqueous solution. The two positive ions will be
attracted to the negative electrode (cathode). These are H + and Cu 2+.
The two negative ions will be attracted to the positive electrode (anode).
These are OH - and SO4 2- .
Platinum is often used as inert
F- a
(unreactive) electrodes
so:
-
I sina.t
The reactivity series is used to work out which ion -
H
sodium
will react at the electrode. magnesium
carbon
'=
Hydrogen will be produced at the negative electrode zinc
(cathode) if the #
metal is more reactive than hydrogen. iron
hydrogen
Copper is I
less reactive than I
hydrogen, so copper will be copper
produced at the negative electrode (cathode).
If the aqueous solution does not contain halide ions then oxygen will be
-
produced at the positive electrode by the OH ions.
-
1 -
Half equations for electrolysis of copper sulfate
2+ - reduction
At the negative electrode: Cu + 2e -
Cu
- - →
oxidation
: :
At the positive electrode: 4OH - 4e O 2 + 2H 2O
#¥;.
watch video
You might also like
- Salt and Water Powered Lamp For Santa Clara Ilaya Batangs CityDocument14 pagesSalt and Water Powered Lamp For Santa Clara Ilaya Batangs CityKarl Anthonni Miguel GuicoNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsCherry EmbateNo ratings yet
- Previews AWS A5 12M A5 12 2009 PreDocument12 pagesPreviews AWS A5 12M A5 12 2009 PreMani Vannan100% (1)
- NTU FYP PresentationDocument46 pagesNTU FYP PresentationchingkeatNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesElectrolysis Cheat Sheet: by Viaaziz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Ol Notes 2Document7 pagesElectrochemistry Ol Notes 2Ahmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument16 pagesElectrochemistry NotesHE HUA YIPNo ratings yet
- ElectroDocument48 pagesElectroMang friesNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument31 pagesElectrolysisVasavi VaasuNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in MaterialsDocument16 pagesCorrosion in MaterialsARYAN PIRTANo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesElectrochemistryShannon Smith100% (1)
- Electrolysis OL NotesDocument11 pagesElectrolysis OL Notesshlaibat13No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument54 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAkash Roy67% (6)
- 1.4 BI CompleteDocument9 pages1.4 BI CompleteRawid GoshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesChapter-8 ElectrolysisOhi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Ch13 ElectrolysisDocument35 pagesCh13 ElectrolysishahaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) PosterDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Aqeous Solutions (Copper Sulfate) Posternnilam1308No ratings yet
- Electrochemical ProcessesDocument19 pagesElectrochemical Processeshrishikeshdeka18No ratings yet
- A Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectDocument10 pagesA Chemistry Electrolysis ProjectLij WynterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesChapter 15 - ElectrolysisKayla WNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Document33 pagesELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaNo ratings yet
- s.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Document9 pagess.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Ronald RomNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- BatteriesDocument6 pagesBatteriesAbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- 7 +Electrolytic+CellsDocument17 pages7 +Electrolytic+Cellsadairyoung946No ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument28 pagesElectricity and ChemistryPUTRI DEWI SARTIKANo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesElectrolysisapi-381901280% (5)
- C12 Electrochemistry IgcseDocument33 pagesC12 Electrochemistry IgcseAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes OLDocument13 pagesElectrolysis Notes OLHooria AminNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- CHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long Questionssomerakhan2023No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - EnglishDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry - Englishchamath p.s.a.d amakaraNo ratings yet
- Voltaic CellDocument32 pagesVoltaic CellMahijar Jarullhayati Hassan50% (2)
- Chm221 Chapter 5Document42 pagesChm221 Chapter 5Badrudin JundailiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document13 pagesChapter 4Pyae Sone Kyaw100% (2)
- Electrochem - SimplifiedDocument13 pagesElectrochem - Simplifiedilias1973No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesElectrolysisMahmudul Hassan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Redox EquilibriumDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Redox EquilibriumjunzNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSISDocument18 pagesELECTROLYSISboipelomajagaNo ratings yet
- (Aq) 3 (Aq) 2 4 (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) 4 (Aq) 3 2 (Aq)Document19 pages(Aq) 3 (Aq) 2 4 (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) 4 (Aq) 3 2 (Aq)Tunde DabiriNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument22 pagesElectrolysisDebbie BerriesNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Document3 pagesELECTROLYSIS Notes Condensed 2Diya ShahNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS STDocument11 pagesREDOX REACTIONS STirehan.saiyedNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and DegradationDocument25 pagesCorrosion and Degradationnoahshredx13No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 1Document14 pagesElectrolysis 1cleohambiraNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemical ChangeDocument20 pagesElectricity & Chemical ChangeGautam DayalNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis LessonDocument21 pagesElectrolysis LessonShenaya HewaNo ratings yet
- Summary - ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSummary - ElectrolysisKeertana SNNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis SummaryDocument1 pageElectrolysis SummaryrgblackmanNo ratings yet
- 3b Battery MCDasDocument18 pages3b Battery MCDasAbhisar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument46 pagesKimiaErvina RetnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis O LevelDocument17 pagesElectrolysis O LevelInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- The Electrolytic CellDocument11 pagesThe Electrolytic CellTeandraNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument9 pagesElectricity and ChemistryFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- ElectrolyisDocument5 pagesElectrolyisMukeshNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectrochemistryDocument36 pagesBasics of ElectrochemistryNaveed JanjuaNo ratings yet
- New Electrolysis 1Document18 pagesNew Electrolysis 1Rethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transport NumberDocument15 pagesTransport NumberSURESHNo ratings yet
- The Effects of System Grounding Bus Insulation and Probability On Arc Flash Hazard Reduction Part 2 TestingDocument15 pagesThe Effects of System Grounding Bus Insulation and Probability On Arc Flash Hazard Reduction Part 2 TestingLaurence MichaelNo ratings yet
- Ais 048Document21 pagesAis 048hermantoNo ratings yet
- NA3 AND NA4 - Troubleshooting Guide (IM278TS SEPT 2006)Document32 pagesNA3 AND NA4 - Troubleshooting Guide (IM278TS SEPT 2006)Julio BacilioNo ratings yet
- ALDI Workzone Welder 140amp (Mma140)Document28 pagesALDI Workzone Welder 140amp (Mma140)Jonathan McDonaldNo ratings yet
- VW-AUDI SSP 499 EngDocument68 pagesVW-AUDI SSP 499 EnggeorgescuriosNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Document33 pagesCaie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Aditya Drolia100% (1)
- Modeling The Lithium-Ion BatteryDocument10 pagesModeling The Lithium-Ion BatterymavericksailorNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Lithium-Ion Battery Cell ComponentsDocument29 pagesManufacturing of Lithium-Ion Battery Cell ComponentsMDRNo ratings yet
- Lec06 04 LVDocument4 pagesLec06 04 LVgiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Sensors Volume 1: Fundamentals of Sensing Material: General ApproachesDocument74 pagesChemical Sensors Volume 1: Fundamentals of Sensing Material: General ApproachesMomentum Press0% (1)
- Lecturer-II /I Electrochemical Cells and Its Types. Electrode Potential - Origin - Oxidation and Reduction PotentialDocument43 pagesLecturer-II /I Electrochemical Cells and Its Types. Electrode Potential - Origin - Oxidation and Reduction PotentialThingnam Jotin SinghNo ratings yet
- PDF The Physics of Solar Energy Conversion Perovskites Organics and Photovoltaic Fundamentals 1St Edition Juan Bisquert Ebook Full ChapterDocument54 pagesPDF The Physics of Solar Energy Conversion Perovskites Organics and Photovoltaic Fundamentals 1St Edition Juan Bisquert Ebook Full Chapterjulie.barnett539100% (2)
- Design of Copper Electrowinning Circuit Using Conventional CellsDocument59 pagesDesign of Copper Electrowinning Circuit Using Conventional Cellsjoseph kafumbila95% (20)
- Thermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalDocument27 pagesThermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalThejasjayadeepNo ratings yet
- An Ec 008 PDFDocument3 pagesAn Ec 008 PDFIsidoro OlveraNo ratings yet
- Measuring InsstrumentsDocument11 pagesMeasuring Insstrumentsamit singhNo ratings yet
- ButlerDocument3 pagesButlerAravindan B BabuNo ratings yet
- Using Cyanex 923 For Selective Extraction in A High Concentration Chloride Medium-Part II-LarssonDocument8 pagesUsing Cyanex 923 For Selective Extraction in A High Concentration Chloride Medium-Part II-LarssonDaiana NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Sully Direct CurrentDocument20 pagesSully Direct Currentpraveenpv7No ratings yet
- 9 and 19 MCQDocument18 pages9 and 19 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- Electrochlorination Basic Process TrainingDocument40 pagesElectrochlorination Basic Process Trainingraghuvarma50% (2)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Projectom dahale93% (27)
- 10 1016@j Chemosphere 2019 05 233Document8 pages10 1016@j Chemosphere 2019 05 233Azzeddine MustaphaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Introduction Presentation (Chapter 1)Document32 pages4 - Introduction Presentation (Chapter 1)Dung TranNo ratings yet
- Vivek Paper Battery OkDocument21 pagesVivek Paper Battery OkShi BiliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current - Class 8 - Notes - PANTOMATHDocument9 pagesChemical Effects of Electric Current - Class 8 - Notes - PANTOMATHsourav9823No ratings yet