Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y7P2 Sound KO
Y7P2 Sound KO
Uploaded by
theodora.deering0Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Y7P2 Sound KO
Y7P2 Sound KO
Uploaded by
theodora.deering0Copyright:
Available Formats
Year 7 Physics Loudness Pitch
Chapter 2: Sound
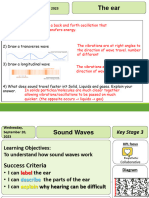
Transverse waves occur when LARGE AMPLITUDE→ LOUD SOUND High frequency → High pitch
the oscillations (vibrations)
are perpendicular (at 90
degrees) to the direction of
the wave.
SNALL AMPLITUDE → QUIET SOUND
Low frequency → low pitch
Longitudinal waves occur when
Frequency is the number of waves passing a point per
the oscillations (vibrations) are
second
parallel to the direction of the
wave.
Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz)
3) The vibrations are passed onto tiny bones called
1) The pinna
the ossicles that amplify the sound
A vibration produces a sound wave. Sound waves spread by causing directs the
particles in a medium (solid, liquid or gas) to vibrate. sound into your
auditory canal 4) The vibrations are
In a vacuum there are no particles so no sound can be produced or passed on to liquid in
spread the cochlea which
contains tiny hairs.
As the liquid moves,
2) The sound the hairs move and
wave causes produces electrical
your ear drum signals.
to vibrate
5) The electrical signals travel down the auditory
Speed of sound decreases nerve to your brain
Retrieval Practice
Question Answer
1. Define frequency The number of waves passing a point per second
2. Name the type of waves where the oscillations are perpendicular to Transverse
the direction of the wave.
3. State what produces sound waves Vibrations
4. Name the tiny bones in the ear that amplify sound Ossicles
5. Describe a longitudinal wave When the oscillations are parallel to the direction of the wave.
6. Describe the volume of a sound wave with a large amplitude Loud (high volume)
7. Name the state of matter where sound travels the fastest. Solids
8. State the part of the ear that contains a liquid with tiny hairs and Cochlea
produces electrical signals.
9. State the unit of frequency Hz (Hertz)
10. Explain why no sound waves can travel in a vacuum. There are no particles.
You might also like
- TGCF Extras 245-252Document102 pagesTGCF Extras 245-252Farrah Seville95% (137)
- Virtual General Assembly - ScriptDocument1 pageVirtual General Assembly - ScriptVictoria Angela Castro100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Champion 4500 Owner's ManualDocument56 pagesChampion 4500 Owner's ManualHobart Welding ProductsNo ratings yet
- Gnossienne 3Document2 pagesGnossienne 3wil7ver100% (16)
- Waves and SoundDocument17 pagesWaves and SoundMUHAMMAD DANIYAL KANDANo ratings yet
- Physics Fast Revision NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics Fast Revision NotesdivyanshagrawalbsNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Diana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- 9ps Ko ArbDocument1 page9ps Ko ArbsanNo ratings yet
- 7 Vy Sou TLQ QZXMe SGZFR 3Document11 pages7 Vy Sou TLQ QZXMe SGZFR 3Aradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument3 pagesMind MapsGiannaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument16 pagesSoundRSNo ratings yet
- Module-4 SummaryDocument34 pagesModule-4 SummaryChristian Paul SorianoNo ratings yet
- Good Vibrations: The Science Behind The ShowDocument2 pagesGood Vibrations: The Science Behind The ShowKristyne OliciaNo ratings yet
- Light and SoundDocument1 pageLight and SoundlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Study Material Chapter 12Document16 pagesClass 9 Science Study Material Chapter 12Aryaman OfficialNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Sound and Hearing: Sound Is Very Important To UsDocument24 pagesUnit 14 Sound and Hearing: Sound Is Very Important To UsVienna LaoNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves: By: British Bunnies/Group 3Document7 pagesSound Waves: By: British Bunnies/Group 3milesNo ratings yet
- Physics 14 - Sound 0625Document106 pagesPhysics 14 - Sound 0625ravi.komaragiri76No ratings yet
- Sound PresentationDocument10 pagesSound PresentationFeliciaNo ratings yet
- 2 (2) 5olasaDocument11 pages2 (2) 5olasaolosschool123No ratings yet
- 2016 SoundDocument69 pages2016 Soundryancasal959No ratings yet
- 3 - Sound Waves and The EarDocument24 pages3 - Sound Waves and The EarMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- KS3 Sound Waves Differentiated Homework Worksheet LADocument8 pagesKS3 Sound Waves Differentiated Homework Worksheet LARamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Traveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Document7 pagesTraveling Waves and Sound: Physics 11Trishla VermaNo ratings yet
- Physics (Waves, Light)Document6 pagesPhysics (Waves, Light)mvfrances17No ratings yet
- 01b Fund AcousticsDocument56 pages01b Fund AcousticsKanad Kumar GhoshNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Sound and LightDocument68 pagesWeek 8 - Sound and LightGenel Yutuc100% (1)
- Physics CH 05 Sound Notes Hany Elgezawy Pre Igcse Y8Document13 pagesPhysics CH 05 Sound Notes Hany Elgezawy Pre Igcse Y8maxprime558No ratings yet
- Physics Portfolio 29-9-23Document16 pagesPhysics Portfolio 29-9-23saanvicodingNo ratings yet
- Architectural AccousticsDocument25 pagesArchitectural AccousticsJOTHINo ratings yet
- Activity Lesson Science Grade 8 Sound 2 4Document6 pagesActivity Lesson Science Grade 8 Sound 2 4brenda marie ralutoNo ratings yet
- 1 - SoundDocument26 pages1 - SoundOSHIN BALASINGHNo ratings yet
- Hearing.: NameDocument3 pagesHearing.: NameDuyBùiNo ratings yet
- 29sound: What I Should Know: What I Should Be Able To DoDocument1 page29sound: What I Should Know: What I Should Be Able To DovarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument36 pagesSound Wavesmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- C10 Sound WavesDocument3 pagesC10 Sound WavesONG JUN YAO MoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1Document23 pagesLecture-12 Sound Waves, Zaheer Rizvi1fourtechmediadmeagentsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sound NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 10 Sound NotesAzaanNo ratings yet
- 9 Phy Together CH 9 SoundDocument19 pages9 Phy Together CH 9 Soundjhbhatt1603No ratings yet
- Sound Chapter Question AnswerDocument4 pagesSound Chapter Question Answersultan29074No ratings yet
- Ripple On A Pond Wave On A StringDocument4 pagesRipple On A Pond Wave On A StringEllaine Kate RoquenNo ratings yet
- Sound Space - PresentationDocument68 pagesSound Space - PresentationVic ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument460 pagesUnit VNisarga JNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument82 pagesUnit INisarga JNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument6 pagesWave NotesVittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument30 pagesSound WavesRidwan Pratama YudhaNo ratings yet
- DhwaniDocument11 pagesDhwaniShreyansh DuggarNo ratings yet
- Resonancesoundear NotesDocument25 pagesResonancesoundear NotesMihnea TurcuNo ratings yet
- 14 Sound and Wave Model VDocument19 pages14 Sound and Wave Model Vbha0052No ratings yet
- Sound - FrequencyDocument1 pageSound - Frequencyreymart.pucolangasNo ratings yet
- Physics of WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics of WavesMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingSam AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 WavesDocument28 pagesNota Padat Fizik F5 Wavesslokkro98% (102)
- Adventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandAdventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Sound: Profound Experiences with Chanting, Toning, Music, and Healing FrequenciesFrom EverandSound: Profound Experiences with Chanting, Toning, Music, and Healing FrequenciesNo ratings yet
- Drainage Department Surat Municipal Corporation Update of Renue Licence & New Licence Plumber List 2020-21Document3 pagesDrainage Department Surat Municipal Corporation Update of Renue Licence & New Licence Plumber List 2020-21drNo ratings yet
- Yamaha ENG Spring11 rx-v71Document8 pagesYamaha ENG Spring11 rx-v71tranganilloNo ratings yet
- Dance, The Movement of The Body in A Rhythmic Way, Usually To Music andDocument5 pagesDance, The Movement of The Body in A Rhythmic Way, Usually To Music andJake BarriosNo ratings yet
- Challenges 3 Test 1Document4 pagesChallenges 3 Test 1NedNo ratings yet
- My First Piano Adventure For The Young Beginner (TEACHER EDITION)Document20 pagesMy First Piano Adventure For The Young Beginner (TEACHER EDITION)TEAM EVOS RAJANo ratings yet
- Agnus Dei-Partitura e PartesDocument6 pagesAgnus Dei-Partitura e PartesJean CosaNo ratings yet
- Teach Music SyllabusDocument8 pagesTeach Music SyllabusCherry lyn EnadNo ratings yet
- Dunkin DonutsDocument12 pagesDunkin DonutsMelanie Kirin100% (1)
- 2) Cant Help Falling in Love (Partitura Violín)Document2 pages2) Cant Help Falling in Love (Partitura Violín)Piero Vittori LocatelliNo ratings yet
- Philippine Popular Culture Final Exam Answer KeyDocument16 pagesPhilippine Popular Culture Final Exam Answer KeyTobias FateNo ratings yet
- Psalm-95 ChordsDocument1 pagePsalm-95 ChordsIvan MascarenasNo ratings yet
- Roosevelt Island Art History 7 Sir Edward Burne-JonesDocument3 pagesRoosevelt Island Art History 7 Sir Edward Burne-JonesrooseveltislanderNo ratings yet
- DLL MAPEH7 - 3rd QuarterDocument73 pagesDLL MAPEH7 - 3rd QuarterEleuterio MontaNo ratings yet
- M83 Bass Chorus Deluxe: 92503013529 RevbDocument2 pagesM83 Bass Chorus Deluxe: 92503013529 RevbDaniel DekkerNo ratings yet
- (Free Scores - Com) - Kondo Koji Mario Bros Theme Song Clarinet 32398Document2 pages(Free Scores - Com) - Kondo Koji Mario Bros Theme Song Clarinet 32398Grecia PasaperaNo ratings yet
- Module in Music,, SIR BERJADocument21 pagesModule in Music,, SIR BERJAShainna BaloteNo ratings yet
- FM600 Revision ADocument107 pagesFM600 Revision ADeleste BroacastNo ratings yet
- Message Passing-Based Joint Cfo and Channel Estimation in Mmwave Systems With One-Bit AdcsDocument14 pagesMessage Passing-Based Joint Cfo and Channel Estimation in Mmwave Systems With One-Bit Adcsluuvuduc81No ratings yet
- The Cambridge Guide To Orchestration - (Chapter 2 Wind Instruments)Document68 pagesThe Cambridge Guide To Orchestration - (Chapter 2 Wind Instruments)Paulo LopezNo ratings yet
- Weebly Cite Work CitedDocument2 pagesWeebly Cite Work Citedapi-551134819No ratings yet
- Alesis Spitfire 15 Owners Manual 163368 PDFDocument16 pagesAlesis Spitfire 15 Owners Manual 163368 PDFGonzalo Andres Hormazabal NuñezNo ratings yet
- EN - 02 Satellite Reception 06 2018 - ScreenDocument140 pagesEN - 02 Satellite Reception 06 2018 - Screennihilistu12No ratings yet
- Marshall MG15CD MG15CDR MG15DFX Users ManualDocument8 pagesMarshall MG15CD MG15CDR MG15DFX Users Manualb0beiii100% (1)
- Ennio Morricone - The Professional by Marco SavelliDocument4 pagesEnnio Morricone - The Professional by Marco SavellicanamenseNo ratings yet
- Bts SongsDocument6 pagesBts Songskim jeonNo ratings yet
- 3000 Most Common Words in English - EF - Global SiteDocument77 pages3000 Most Common Words in English - EF - Global SiteAkibNo ratings yet