Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Atom Notes
The Atom Notes
Uploaded by
jakhurabushra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOriginal Title
The atom notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThe Atom Notes
The Atom Notes
Uploaded by
jakhurabushraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
The Atom Notes Close
Notes - The Atom
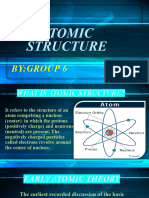
The Atom
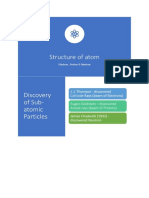
Some of the scientists who have contributed
to the theory of the atom include J.J.
Thomson (discovery of the electron, which
led to the Plum Pudding Model of the
atom), Marie and Pierre Curie (work on
radiation), Ernest Rutherford (discovery that
positive charge is concentrated in the center
of the atom) and Niels Bohr (the arrangement
of electrons around the nucleus in energy
levels).
•Because of the very small mass of atoms,
their mass is measured in atomic mass
units (u) 1 u = 66×10−24 g.
•The relative atomic mass of an element is
the average mass of all the naturally
occurring isotopes of that element. The units
for relative atomic mass are atomic mass
units. The relative atomic mass is written
under the elements' symbol on the periodic
:
under the elements' symbol on the periodic
table.
The Atom
•An atom is made up of a
central nucleus (containing protons and neutron
s), surrounded by electrons. Most of the atom is
empty space.
•The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons
in an atom.
•The atomic mass number (A) is the number of
protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
•The standard notation that is used to write an
element, is where X is the element symbol, A is the atomic
mass number and Z is the atomic number.
•The isotope of a particular element is made
up of atoms which have the same number of
protons as the atoms in the original element,
but a different number of neutrons. This
means that not all atoms of an element will
have the same atomic mass.
•Within each energy level, an electron may
move within a particular shape of orbital.
An orbital defines the space in which an
electron is most likely to be found.
•The electron configuration is the
:
arrangement of electrons in an atom,
molecule or other physical structure.
•Energy diagrams such as Aufbau
diagrams are used to show the electron
configuration of atoms.
•The electron configuration of an atom can
be given using spectroscopic notation.
•Different orbitals have different shapes: s
orbitals are spherically shaped and p
orbitals are dumbbell shaped.
•The electrons in the outermost energy level
are called valence electrons.
•The electrons in an atom that are not
valence electrons are called core
electrons.
•Atoms whose outermost energy level is
full, are less chemically reactive and
therefore more stable, than those atoms
whose outermost energy level is not full.
:
You might also like
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology 8th Edition Abbas Test BankDocument34 pagesCellular and Molecular Immunology 8th Edition Abbas Test Bankpoorly.germuleo6bv97% (31)
- DRYPIX Smart Reference GuideDocument80 pagesDRYPIX Smart Reference GuideHugo79% (33)
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlop100% (1)
- D6ca B Truck DTC PDFDocument725 pagesD6ca B Truck DTC PDFhexxa300093% (15)
- What Is A PsychopathDocument30 pagesWhat Is A Psychopathmarinel june100% (1)
- CHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)Document22 pagesCHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)ogedengbed28No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic StructureFelix LiandaNo ratings yet
- Module As Level ChemistryDocument407 pagesModule As Level ChemistryBank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Description of An AtomDocument32 pagesSession 2-Description of An Atomvalerianphotunatus2002No ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Goals: Principles of Imaging Science IDocument13 pagesGoals: Principles of Imaging Science INeeraj JangidNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesAtomic Structurerajesh.pandey9870606No ratings yet
- General Chemistry PresentationDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistry PresentationJohn Adrian MalunesNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Atom Grade11Document36 pagesPhysics of The Atom Grade11Jodell CampbellNo ratings yet
- Atoms & The Periodic TableDocument36 pagesAtoms & The Periodic TableJovenill Granton VIINo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Theory 20-28Document9 pagesAtomic Structure - Theory 20-28tc2brmg4mkNo ratings yet
- 1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Document38 pages1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Simon McCabeNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument33 pagesAtomic Structureshikshyapokhrel3003No ratings yet
- Atoms: According To DaltonDocument5 pagesAtoms: According To DaltonSahnaz Mela SandyNo ratings yet
- Inside The AtomsDocument21 pagesInside The AtomskashishhagarwalNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1Document64 pagesInorganic Chem 1Habtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- 3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsDocument41 pages3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsFranchesca De los SantosNo ratings yet
- 08 The Atom SlidesDocument26 pages08 The Atom Slidesjackoread28No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1695 Converted 1 77Document9 pagesAtomic Structure 1695 Converted 1 77Sanjana DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- 6-Understanding AtomDocument42 pages6-Understanding AtomEmma Angelica ValeraNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument27 pagesAtomKyle CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1 Atomic StructureDocument97 pages1 Atomic StructurecccNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesDocument32 pagesAtoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- Chem Assignment 4Document7 pagesChem Assignment 4ttamNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Molecules: BIO 103-L2Document29 pagesThe Nature of Molecules: BIO 103-L2Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Composition of MatterDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Composition of Matterjhontayson12No ratings yet
- Chemistry For PhysiciansDocument14 pagesChemistry For PhysiciansenzlibraryNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument16 pagesChemistrySarika JadhavNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument6 pagesAtomsshreyaNo ratings yet
- EE2317-Course-Atomic Structures and Interatomic BondingDocument94 pagesEE2317-Course-Atomic Structures and Interatomic BondingJOSEPH BENEDICT PRIMNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Electron, Proton & NeutronDocument11 pagesStructure of Atom: Electron, Proton & NeutronAarav AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1Imperial PlayzNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDocument51 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical ReactionsDavid PhilemonNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument29 pagesChem ProjectMohammad Osama anasas aliNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument10 pagesAtomalishaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Atoms and The Periodic Table. DistributionDocument41 pagesWeek 1-Atoms and The Periodic Table. DistributionKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor BasicsDocument94 pagesSemiconductor BasicsArindam SenNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules 2Document50 pagesAtoms and Molecules 2Bank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsKristin HernaisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Note-1Document27 pagesChemistry Note-1mematugoldahmunu21No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of The Atom NotesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of The Atom Notesraunakranamohapatra24No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Notes - LectureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure Notes - LecturealexandremoutonNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureAnabella MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Mohammad Akter Hossain Lecturer, Dept. of MNS Brac UniversityDocument66 pagesStructure of Atom: Mohammad Akter Hossain Lecturer, Dept. of MNS Brac UniversityNafiz AhmedNo ratings yet
- 8TH Atomic StructureDocument65 pages8TH Atomic StructureAnna Maria DominicNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Atom:Atoms Are The Smallest Particle of Element That ContainDocument12 pagesAtomic Structure: Atom:Atoms Are The Smallest Particle of Element That ContainAbdul AwalNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Promote Nutrion Song GROUP 1Document35 pagesMAPEH Promote Nutrion Song GROUP 1sauvarizziNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document8 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Almira MejoradaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistryanyone1018ghoshNo ratings yet
- Module 4.1Document16 pagesModule 4.1RainNo ratings yet
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Volvo S80 Owners Manual MY10 en Tp10946Document306 pagesVolvo S80 Owners Manual MY10 en Tp10946rees1098No ratings yet
- Individual Practice With Peer EvaluationDocument1 pageIndividual Practice With Peer EvaluationFatima TreviñoNo ratings yet
- S.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDocument695 pagesS.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDixit JariwalaNo ratings yet
- DX 350 User Manual Multi LanguageDocument22 pagesDX 350 User Manual Multi LanguageDulce Martinez TolentinoNo ratings yet
- J of Cosmetic Dermatology - 2021 - Segurado - An Expert Consensus Report On The Clinical Use of The Vycross HyaluronicDocument10 pagesJ of Cosmetic Dermatology - 2021 - Segurado - An Expert Consensus Report On The Clinical Use of The Vycross HyaluronicHong Nhung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Financing The National Capital Integrated Coastal Development (NCICD) Project in Jakarta (Indonesia) With The Private SectorDocument7 pagesFinancing The National Capital Integrated Coastal Development (NCICD) Project in Jakarta (Indonesia) With The Private SectorRicardo RicardoNo ratings yet
- RFB ManualDocument22 pagesRFB Manualstormtrooper1015No ratings yet
- 30 Day SELTrackerDocument3 pages30 Day SELTrackerLiz Harrison PooleNo ratings yet
- Safety Inspection Vs Safety AuditDocument10 pagesSafety Inspection Vs Safety Auditاحمد عبداللاNo ratings yet
- Carti Scrise de Pema ChodronDocument38 pagesCarti Scrise de Pema ChodronSpiridon Andrei CristianNo ratings yet
- Kode Error Honda Pre ObdDocument11 pagesKode Error Honda Pre ObdSabri Bprf HuarrNo ratings yet
- FTIRDocument9 pagesFTIRAnila AftabNo ratings yet
- 52369.Đề ôn thi lớp 10Document5 pages52369.Đề ôn thi lớp 10Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- Diffusion ProcessDocument19 pagesDiffusion Processtalk2ankur2006No ratings yet
- HUAWEI DataDocument10 pagesHUAWEI DataMinhazul IslamNo ratings yet
- PROJECTDocument13 pagesPROJECTWOLVERINEffNo ratings yet
- K K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalDocument6 pagesK K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalSelly MonicaNo ratings yet
- Kalas BK DP SGR UlDocument2 pagesKalas BK DP SGR Ulmatthew_edwards_49No ratings yet
- StyrofoamDocument9 pagesStyrofoamapi-353356333No ratings yet
- New Hanover County School Service Animal Policy 2012-2019Document2 pagesNew Hanover County School Service Animal Policy 2012-2019Ben SchachtmanNo ratings yet
- Documment Number (Rev.) Comments: Project: PETROBRAS 78 (P-78)Document4 pagesDocumment Number (Rev.) Comments: Project: PETROBRAS 78 (P-78)Sumit MishraNo ratings yet
- List of Headings: CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesList of Headings: Carbohydratessneh1509No ratings yet
- Séptimo Ingles 21Document6 pagesSéptimo Ingles 21Nadi Salamandra UrregoNo ratings yet
- Food AdulterationDocument20 pagesFood AdulterationMahanth ThoraviNo ratings yet
- GBH 2 20 D Professional Manual 162121Document167 pagesGBH 2 20 D Professional Manual 162121Gomez GomezNo ratings yet
- EIA Envt Impact Assessment Report On Myitsone Dam BurmeseDocument13 pagesEIA Envt Impact Assessment Report On Myitsone Dam BurmesePugh JuttaNo ratings yet