Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decancit SR
Decancit SR
Uploaded by
ahmedagoz444Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decancit SR
Decancit SR
Uploaded by
ahmedagoz444Copyright:
Available Formats
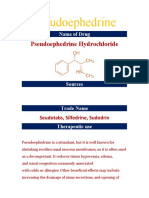
Decancit SR tablets:
5 mg Cetirizine hydrochloride + 120 mg Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride
DRUG DESCRIPTION: Decancit SR tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) Extended Release Tablets for oral administration contain
5 mg of cetirizine hydrochloride for immediate release and 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride for extended release. Cetirizine hydrochloride, one of the two active components of
Decancit SR tablets, is an orally active and selective H1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (+/-)- [2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid,
dihydrochloride. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a racemic compound with an empirical formula of C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a white,
crystalline powder and is water-soluble. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, the other active ingredient of Decancit SR tablets, is an adrenergic (vasoconstrictor) agent with the chemical
name (1S.2S)-2-methylamino-1-phenyl-1-propanol hydrochloride. The molecular weight is 201.70. The molecular formula is C10H15NO•HCl. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride occurs as
fine, white to off-white crystals or powder, having a faint characteristic odor. It is very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, and sparingly soluble in chloroform.
Active Ingredients:
Active ingredient (in each extended release tablet). Purpose
Cetirizine HCl 5 mg. Antihistamine
Pseudoephedrine HCl 120 mg. Nasal decongestant
Inactive Ingredients: Lactose monohydrate, dibasic calcium phosphate, methocel K-15, povidon K-90, anhydrous colloidal silica, magnesium stearate ,methocel E-5, ethyl
cellulose N-50, PEG 6000, talc, titanium dioxide.
INDICATIONS: Decancit SR tablets should be administered when both the antihistaminic properties of cetirizine hydrochloride and the nasal decongestant properties of
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride are desired.
Decancit SR tablets are indicated for the relief of nasal and non-nasal symptoms associated with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children 12 years of age and older.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Do not break or chew tablet; swallow tablet whole. Adults and Children 12 Years and over: take 1 tablet every 12 hours; do not
take more than 2 tablets in 24 hours
Adults 65 years and over: Ask a doctor.
Children under 12 years of age: Ask a doctor.
Consumers with liver or kidney disease: Ask a doctor.
• Decancit SR tablets may be given with or without food.
HOW SUPPLIED: Decancit SR tablets: are white, round, biconvex, tablets containing 5 mg cetirizine hydrochloride and 120 mg pseudoephedrine hydrochloride.
SIDE EFFECTS: Autonomic Nervous System: anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine,
myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
Gastrointestinal: abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal
hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
Genitourinary: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
Hearing and Vestibular: deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
Metabolic/Nutritional: dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
Psychiatric: abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia,
nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
Respiratory System: bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
Reproductive: dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
Reticuloendothelial: lymphadenopathy.
Skin: acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating,
maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
Special Senses: parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
Vision: blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
Body as a Whole: accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema,
malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors. Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred
during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine has been reported. In foreign marketing
experience or experience in the post market period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: anaphylaxis, cholestasis,
glomerulonephritis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, thrombocytopenia, aggressive reaction and convulsions.
PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE: Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride may cause mild CNS stimulation in hypersensitive patients. Nervousness,
excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness, or insomnia may occur. Headache, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, palpitation, pressor activity, and cardiac arrhythmias have
been reported. Sympathomimetic drugs have also been associated with other untoward effects such as fear, anxiety, tenseness, tremor, hallucinations, seizures, pallor,
respiratory difficulty, dysuria, and cardiovascular collapse.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride do not influence the pharmacokinetics of each other when administered concomitantly.
No clinically significant drug interactions have been found with cetirizine and theophylline at a low dose, azithromycin, ketoconazole, or erythromycin. There was a small
decrease in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline; it is possible that larger theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
Due to the pseudoephedrine component, Decancit SR tablets are contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and for 14 days after stopping use of
an MAO inhibitor. Concomitant use with antihypertensive drugs that interfere with sympathetic activity (e.g., methyldopa, mecamylamine, and reserpine) may reduce their
antihypertensive effects. Increased ectopic pacemaker activity can occur when pseudoephedrine is used concomitantly with digitalis. Care should be taken in the administration
of Decancit SR tablets concomitantly with other sympathomimetic amines because combined effects on the cardiovascular system may be harmful to the patient.
WARNINGS: Sympathomimetic amines should be used judiciously and sparingly in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased
intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy. Sympathomimetic amines may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions
or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension. The elderly are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetic amines.
PRECAUTIONS: Due to its pseudoephedrine component, Decancit SR tablets should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic
heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy. Patients with decreased renal function should be given a lower initial
dose (one tablet per day) because they have reduced elimination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine.
Activities Requiring Mental Alertness: In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking cetirizine or Decancit SR tablets; due caution
should therefore be exercised when driving a car or operating potentially dangerous machinery after taking Decancit SR tablets. Concurrent use of Decancit SR tablets with
alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur.
Because cetirizine and pseudoephedrine are excreted in milk , use of Decancit SR tablets in nursing mothers is not recommended.
Pregnancy Category C: Decancit SR tablets: Tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers: Because cetirizine and pseudoephedrine are excreted in milk, use of Decancit SR tablets in nursing mothers is not recommended.
Pediatric Use: Decancit SR tablets contain 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in an extended release formulation. This dose of pseudoephedrine exceeds the
recommended dose for pediatric patients under 12 years of age. Therefore, clinical trials have not been conducted in patients under 12 years of age.
OVERDOSE: Information regarding acute overdosage is limited to experience with cetirizine alone and the marketing history of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride. Overdosage has been
reported with cetirizine. In one adult patient who took 150 mg of cetirizine, the patient was somnolent but did not display any other clinical signs or abnormal blood chemistry or hematology
results. In an 18-month-old pediatric patient who took an overdose of cetirizine (approximately 180 mg), restlessness and irritability were observed initially; this was followed by
drowsiness. Should overdose occur, treatment should be symptomatic or supportive, taking into account any concomitantly ingested medications. There is no known specific antidote to
cetirizine. Cetirizine is not effectively removed by dialysis, and dialysis will be ineffective unless a dialyzable agent has been concomitantly ingested. The acute minimal lethal oral doses
in mice and rats were 237 and 562 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 95 and 460 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). In rodents, the target of
acute toxicity was the central nervous system, and the target of multiple-dose toxicity was the liver. In large doses, sympathomimetics may give rise to giddiness, headache, nausea,
vomiting, sweating, thirst, tachycardia, precordial pain, palpitations, difficulty in micturition, muscular weakness and tenseness, anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Many patients can
present a toxic psychosis with delusions and hallucinations. Some may develop cardiac arrhythmias, circulatory collapse, convulsions, coma and respiratory failure.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Decancit SR tablets are contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients or to hydroxyzine.
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, Decancit SR tablets are contraindicated in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention, and in patients receiving
monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy or within fourteen (14) days of stopping such treatment (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions section). It is also contraindicated
in patients with severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease, and in those who have shown hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to its components, to adrenergic agents,
or to other drugs of similar chemical structures. Manifestations of patient idiosyncrasy to adrenergic agents include insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, or arrhythmias.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Mechanisms of Action: Cetirizine, a metabolite of hydroxyzine, is an antihistamine; its principal effects are mediated via selective inhibition
of H1 receptors. The antihistaminic activity of cetirizine has been clearly documented in a variety of animal and human models. In vivo and Ex vivo animal models have shown negligible
anticholinergic and antiserotonergic activity. In clinical trials, however, dry mouth was more common with cetirizine than with placebo. In vitro receptor binding studies have shown no
measurable affinity for other than H1 receptors. Autoradiographic studies with radiolabeled cetirizine in the rat have shown negligible penetration into the brain. Ex vivo experiments in the
mouse have shown that systemically administered cetirizine does not significantly occupy cerebral H1 receptors. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is an orally active sympathomimetic amine
and exerts a decongestant action on the nasal mucosa. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is recognized as an effective agent for the relief of nasal congestion due to allergic rhinitis.
Pseudoephedrine produces peripheral effects similar to those of ephedrine and central effects similar to, but less intense than, amphetamines. It has the potential for excitatory side effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS: Absorption: The bioavailability of cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride from Decancit SR tablets is not significantly
different from that achieved with separate administration of a cetirizine 5 mg tablet and a pseudoephedrine 120 mg extended release tablets. Co-administration of cetirizine and
pseudoephedrine does not significantly affect the bioavailability of either component. Following a single dose of the Decancit SR tablets, a mean peak plasma concentration
(Cmax) of 114 ng/mL at a time (Tmax) of 2.2 hours postdose was observed for cetirizine and a mean Cmax of 309 ng/mL at a Tmax of 4.4 hours postdose was observed for
pseudoephedrine. Food had no significant effect on the extent of cetirizine absorption (AUC), but Tmax was delayed by 1.8 hours and Cmax was decreased by 30%. Food had
no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine. Decancit SR tablets may be given with or without food.
Distribution: The mean plasma protein binding of cetirizine is 93% , independent of concentration in the range of 25-1000 ng/mL, which includes the therapeutic plasma levels
observed. The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of pseudoephedrine has been reported to be 2.6-3.3 L/kg. No plasma protein binding data in humans are available.
Metabolism: Cetirizine is metabolized to a limited extent by oxidative O-dealkylation to a metabolite with negligible antihistaminic activity. The enzyme or enzymes responsible for this
metabolism have not been identified. One to seven percent of the pseudoephedrine dose appeared to be metabolized to norpseudoephedrine by N-demethylation after a single dose.
Elimination: After administration of the Decancit SR tablets, the mean elimination half-life of cetirizine was 7.9 hours and the mean elimination half-life of pseudoephedrine was 6.0 hours.
The pattern of the relative milk/plasma drug concentration profile showed that pseudoephedrine concentrations in milk were 2- to 3-fold higher than those in plasma.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Pharmacokinetic interaction trials with cetirizine in adults were conducted with pseudoephedrine, antipyrine, ketoconazole, erythromycin and
azithromycin. No interactions were observed. In a multiple dose study of theophylline (400 mg once daily for 3 days) and cetirizine (20 mg once daily for 3 days), a 16% decrease
in the clearance of cetirizine was observed. The disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
Special Populations: Pediatrics: Although cetirizine pharmacokinetics have been studied in children, Decancit SR tablets are not recommended for patients under 12 years of age.
Geriatrics: The decrease in cetirizine clearance in these elderly volunteers may be related to decreased renal function.
The pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine have not been adequately studied in geriatric subjects.
Gender: The effect of gender on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Race: The effect of race on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Renal Impairment: Moderately impaired patients had a 3-fold increase in half-life and a 70% decrease in clearance compared to normal volunteers. Less than 10% of the
administered dose was removed during the single dialysis session. About 55-75% of an administered dose of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is excreted unchanged in the urine;
the remainder is apparently metabolized in the liver. Therefore, pseudoephedrine may accumulate in patients with renal insufficiency. Dosing adjustment is necessary in patients
with moderate or severe renal impairment and in patients on dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment: The effect of hepatic impairment on pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics is unknown. Dosing adjustment may be necessary in patients with hepatic impairment.
Pharmacodynamics: There was no significant increase in QTc with cetirizine alone or in combination with azithromycin.
PACKAGE AND STORAGE: Carton box contains 1,2,3 PVC/Alu each of 10 tablets + insert leaflet. Store in a dry place at temperature not exceeding 30˚ C.
Keep All Medicine Out of Reach of Children
Manufactured by: Apex Pharma - S.A.E - Badr City- Egypt.
3200000311
3085011102
You might also like
- Top 100 OTCDocument4 pagesTop 100 OTCBen Thomas Moore92% (12)
- One Pot (Shake & Bake) Methamphetamine Labs: PresentationDocument0 pagesOne Pot (Shake & Bake) Methamphetamine Labs: PresentationAbdullah S. Abdullah63% (8)
- The Ammonicarb Operation Book Format 4 PDF FreeDocument149 pagesThe Ammonicarb Operation Book Format 4 PDF FreePantelis Krintz100% (1)
- Clandestine InfoDocument115 pagesClandestine Infoxathrid369100% (6)
- Contents DrugDocument6 pagesContents Drugwestcoastaromatics0% (1)
- Meth ExtractionarticleDocument5 pagesMeth Extractionarticleburhan2875% (4)
- Drug Cards (PDF Library)Document5 pagesDrug Cards (PDF Library)Jim Stewart0% (2)
- Conversation Pharmacy AssistantsDocument6 pagesConversation Pharmacy Assistantsami yuningsihNo ratings yet
- Zyrtec: Tablet Core: Tablet CoatingDocument5 pagesZyrtec: Tablet Core: Tablet CoatingDwi WirastomoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Pseudo EphedrineDocument3 pagesPseudo Ephedrineapi-37979410% (1)
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTDocument14 pagesPharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- DisulfiramDocument3 pagesDisulfiramapi-3797941100% (1)
- File1 146 1714383Document366 pagesFile1 146 1714383Mutiara SazkiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument16 pagesDrug Study For End Stage Renal DiseaselenecarglbnNo ratings yet
- Sinarest SyrupDocument9 pagesSinarest SyrupYidiv VidiyNo ratings yet
- Clarinase Repetabs Leaflet (Eng) - CCDS 122013-2014-06-26Document2 pagesClarinase Repetabs Leaflet (Eng) - CCDS 122013-2014-06-26Andrew LienataNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of Drug私 シャーロット100% (1)
- Loratadine 5mg + Pseudoephedrine 120mg (Clarinase Repetabs)Document9 pagesLoratadine 5mg + Pseudoephedrine 120mg (Clarinase Repetabs)ddandan_2No ratings yet
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study - Diazepammarengbib100% (1)
- LicenseSPC PA0007-008-007 12052016140038Document7 pagesLicenseSPC PA0007-008-007 12052016140038willyco.g77No ratings yet
- Zyprexa: Generic Name: OlanzapineDocument3 pagesZyprexa: Generic Name: Olanzapinenasir khanNo ratings yet
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Xavier University-Ateneo de Cagayan College of NursingDocument14 pagesXavier University-Ateneo de Cagayan College of NursingSheila_Mae_Fai_5510No ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Injection, USP: H H CL C O CH CH N (CH)Document2 pagesDiphenhydramine Hydrochloride Injection, USP: H H CL C O CH CH N (CH)Erikson TobingNo ratings yet
- GravolDocument5 pagesGravoldrugcardrefNo ratings yet
- Generic Name LasixDocument4 pagesGeneric Name LasixSabita PaudelNo ratings yet
- Drug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects NSG Responsibilities Acetazolamide 250mg/tab 1 Tab Now Then TIDDocument8 pagesDrug Name General Action Specific Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects NSG Responsibilities Acetazolamide 250mg/tab 1 Tab Now Then TIDimthebossNo ratings yet
- Zyrtec: New Zealand DatasheetDocument15 pagesZyrtec: New Zealand DatasheetbobsyauncleNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDocument6 pagesDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsSarah Carretero0% (1)
- Dekinet Tablets: Use in PregnancyDocument3 pagesDekinet Tablets: Use in Pregnancyddandan_2No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykristen_ramos_3No ratings yet
- Dipyridamole (Cardoxin Forte)Document6 pagesDipyridamole (Cardoxin Forte)asdwasdNo ratings yet
- New Hope Hospital Drug Formulary: First EditionDocument17 pagesNew Hope Hospital Drug Formulary: First EditionBrunette CesaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet For Dd1 AssgmntDocument2 pagesLeaflet For Dd1 AssgmntayuNo ratings yet
- Buffered Aspirin ProductsDocument7 pagesBuffered Aspirin ProductsKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CCUDocument5 pagesDrug Study CCUKrishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Diphendryl Expectorant: PresentationDocument2 pagesDiphendryl Expectorant: PresentationFarhah RahimanNo ratings yet
- Deca DurabolinDocument6 pagesDeca DurabolinJohn C HaleNo ratings yet
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument65 pagesAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsMikro BatomouroNo ratings yet
- De PURADocument1 pageDe PURARasikapriya Shyam DasNo ratings yet
- Zine Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesZine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Product Monograph: Pyridium®Document17 pagesProduct Monograph: Pyridium®Chon ChiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ShenDocument12 pagesDrug Study ShenLass KazeNo ratings yet
- Drugs GRP!!Document89 pagesDrugs GRP!!Joanne SandovalNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Fluphenazine Drug Study!Document3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study!EmJay Balansag100% (3)
- Deca Durabolin Product InformationDocument7 pagesDeca Durabolin Product Informationenc2011No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsDocument6 pagesNifedipine Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsXICMENNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument18 pagesDrugsdantacNo ratings yet
- SUDAFED 60mgDocument1 pageSUDAFED 60mga.klimasara228No ratings yet
- Decadron Uses, Side Effects & WarningsDocument5 pagesDecadron Uses, Side Effects & WarningspatgarettNo ratings yet
- gddrg0012 25974 63375Document5 pagesgddrg0012 25974 63375DijattxNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On EpinephrineDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On EpinephrineMaesy Garcia LorenaNo ratings yet
- What Is Dexamethasone and How Is It Used?Document17 pagesWhat Is Dexamethasone and How Is It Used?Madx VNo ratings yet
- Sildenafil Citrate or ViagraDocument3 pagesSildenafil Citrate or ViagraKat ZNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Tata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALDocument27 pagesTata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALNikko Khairul DafaNo ratings yet
- Wong ChemicalDocument36 pagesWong Chemicalerikia100% (1)
- Fexet D Tab Leaflet EXP GADocument2 pagesFexet D Tab Leaflet EXP GASaghir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 6.5 MCC Oxymetazoline SubmissionDocument20 pages6.5 MCC Oxymetazoline SubmissionAmit DwivediNo ratings yet
- Cough N Cold Medicine List PDFDocument7 pagesCough N Cold Medicine List PDFDonna DominnoNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride TabletsDocument2 pagesPseudoephedrine Hydrochloride TabletsK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaNo ratings yet
- Asthmanefrin Sales Sheet SeptemberDocument2 pagesAsthmanefrin Sales Sheet Septembermerc2No ratings yet
- Panadol SinusDocument4 pagesPanadol SinusNy Ade HanifNo ratings yet
- Black Market Report On Ephedrine PDFDocument26 pagesBlack Market Report On Ephedrine PDFshane charltonNo ratings yet
- A Novel RP-HPLC Method For Analysis of Paracetamol Pseudo Ephedrine, Caffeine andDocument3 pagesA Novel RP-HPLC Method For Analysis of Paracetamol Pseudo Ephedrine, Caffeine andDr. Varaprasad Bobbarala100% (1)
- Acetaminophen Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Doxylamine Succinate and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Oral SolutionDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Doxylamine Succinate and Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Oral SolutionMaximiliano OjedaNo ratings yet
- ChloroephedrineDocument9 pagesChloroephedrineTyanNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Phenylephrine With New Info Which Says Iodine Can Be Used Instead Od Hydroiodic AcidDocument10 pagesReduction of Phenylephrine With New Info Which Says Iodine Can Be Used Instead Od Hydroiodic Acidloulouqwerty123100% (1)
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Appalachia: High Intensity Drug Trafficking Area Drug Market AnalysisDocument12 pagesAppalachia: High Intensity Drug Trafficking Area Drug Market Analysislosangeles100% (3)
- 1Document8 pages1Lizzy Roger Ojeda100% (2)
- The Common Cold GuideDocument27 pagesThe Common Cold Guidehappyscottlee3438No ratings yet
- Ohio State Board of Pharmacy: EphedrineDocument28 pagesOhio State Board of Pharmacy: EphedrinePascu Vasile-GeluNo ratings yet
- Drugs Interactions PDFDocument2 pagesDrugs Interactions PDFArne BorgerNo ratings yet
- 7a Extent of Licit Trade in Precursors 2017 PDFDocument25 pages7a Extent of Licit Trade in Precursors 2017 PDFDragan AntulovNo ratings yet
- Backgrounder FDADocument89 pagesBackgrounder FDAWilliams PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Alexandra Doddridge, Michael Collins and Helen SalourosDocument26 pagesAlexandra Doddridge, Michael Collins and Helen SalourosDoc Martenz100% (1)
- Methamphetamine From Ephedrine Tablets - Breaking BadDocument10 pagesMethamphetamine From Ephedrine Tablets - Breaking BadIgnacio BeltránNo ratings yet