Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science - Sequence of Content
Science - Sequence of Content
Uploaded by
Thị Như Quỳnh Hoàng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesOriginal Title
science_-_sequence_of_content
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesScience - Sequence of Content
Science - Sequence of Content
Uploaded by
Thị Như Quỳnh HoàngCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
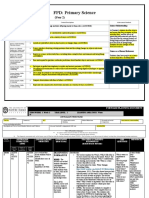
Science: Sequence of content F-6 Strand: Science understanding
Sub-strand Foundation Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
Biological Living things have Living things have Living things grow, Living things can Living things have life Living things have The growth and
sciences basic needs, including a variety of external change and have be grouped on the cycles (ACSSU072) structural features survival of living
food and water features (ACSSU017) offspring similar basis of observable Living things depend and adaptations that things are affected by
(ACSSU002) Living things live in to themselves features and can be on each other and help them to survive physical conditions
different places where (ACSSU030) distinguished from the environment to in their environment of their environment
their needs are met non-living things survive (ACSSU073) (ACSSU043) (ACSSU094)
(ACSSU211) (ACSSU044)
Chemical Objects are made of Everyday materials Different materials A change of state Natural and Solids, liquids and Changes to materials
sciences materials that have can be physically can be combined for between solid and processed materials gases have different can be reversible
observable properties changed in a variety a particular purpose liquid can be caused have a range of observable properties or irreversible
(ACSSU003) of ways (ACSSU018) (ACSSU031) by adding or removing physical properties and behave in (ACSSU095)
heat (ACSSU046) that can influence different ways
their use (ACSSU074) (ACSSU077)
Earth and Daily and seasonal Observable changes Earth’s resources are Earth’s rotation on its Earth’s surface The Earth is part of Sudden geological
space changes in our occur in the sky used in a variety of axis causes regular changes over time a system of planets changes and extreme
sciences environment affect and landscape ways (ACSSU032) changes, including as a result of natural orbiting around a star weather events can
everyday life (ACSSU019) night and day processes and human (the sun) (ACSSU078) affect Earth’s surface
(ACSSU004) (ACSSU048) activity (ACSSU075) (ACSSU096)
Physical The way objects move Light and sound are A push or a pull Heat can be produced Forces can be exerted Light from a source Electrical energy
sciences depends on a variety produced by a range affects how an object in many ways and by one object on forms shadows and can be transferred
of factors, including of sources and can be moves or changes can move from one another through direct can be absorbed, and transformed in
their size and shape sensed (ACSSU020) shape (ACSSU033) object to another contact or from a reflected and electrical circuits and
(ACSSU005) (ACSSU049) distance (ACSSU076) refracted (ACSSU080) can be generated
from a range of
sources (ACSSU097)
v8.1 Australian Curriculum www.australiancurriculum.com.au December 2015 Page 1
Science: Sequence of content: F-6 Strand: Science as a human endeavour
Sub-strand Foundation Year 1-2 Year 3-4 Year 5-6
Nature and Science involves observing, asking Science involves observing, asking Science involves making predictions and Science involves testing predictions
development questions about, and describing questions about, and describing describing patterns and relationships by gathering data and using evidence
of science changes in, objects and events changes in, objects and events (ACSHE050) & (ACSHE061) to develop explanations of events and
(ACSHE013) (ACSHE021) & (ACSHE034) phenomena and reflects historical and
cultural contributions (ACSHE081) &
(ACSHE098)
Use and People use science in their daily Science knowledge helps people to Scientific knowledge is used to solve
influence of lives, including when caring for understand the effect of their actions problems and inform personal and
science their environment and living things (ACSHE051) & (ACSHE062) community decisions (ACSHE083) &
(ACSHE022) & (ACSHE035) (ACSHE100)
v8.1 Australian Curriculum www.australiancurriculum.com.au December 2015 Page 2
Science: Sequence of content: F-6 Strand: Science inquiry skills
Sub-strand Foundation Year 1-2 Year 3-4 Year 5-6
Questioning Pose and respond to questions about Pose and respond to questions, and With guidance, identify questions With guidance, pose clarifying questions
and predicting familiar objects and events (ACSIS014) make predictions about familiar objects in familiar contexts that can be and make predictions about scientific
and events (ACSIS024) & (ACSIS037) investigated scientifically and make investigations (ACSIS231) & (ACSIS232)
predictions based on prior knowledge
(ACSIS053) & (ACSIS064)
Planning and Participate in guided investigations and Participate in guided investigations With guidance, plan and conduct Identify, plan and apply the elements
conducting make observations using the senses to explore and answer questions scientific investigations to find answers of scientific investigations to answer
(ACSIS011) (ACSIS025) & (ACSIS038) to questions, considering the safe use questions and solve problems using
of appropriate materials and equipment equipment and materials safely and
Use informal measurements to collect
(ACSIS054) & (ACSIS065) identifying potential risks (ACSIS086) &
and record observations, using digital
(ACSIS103)
technologies as appropriate (ACSIS026) Consider the elements of fair tests and
& (ACSIS039) use formal measurements and digital Decide variables to be changed and
technologies as appropriate, to make measured in fair tests, and observe
and record observations accurately measure and record data with accuracy
(ACSIS055) & (ACSIS066) using digital technologies as appropriate
(ACSIS087) & (ACSIS104)
Processing Engage in discussions about Use a range of methods to sort Use a range of methods including tables Construct and use a range of
and analysing observations and represent ideas information, including drawings and and simple column graphs to represent representations, including tables and
data and (ACSIS233) provided tables through discussion, data and to identify patterns and trends graphs, to represent and describe
information compare observations with predictions (ACSIS057) & (ACSIS068) observations, patterns or relationships
(ACSIS027) & (ACSIS040) Compare results with predictions, in data using digital technologies as
suggesting possible reasons for findings appropriate (ACSIS090) & (ACSIS107)
(ACSIS215) & (ACSIS216) Compare data with predictions and use
as evidence in developing explanations
(ACSIS218) & (ACSIS221)
Evaluating Compare observations with those of Reflect on investigations, including Reflect on and suggest improvements
others (ACSIS213) & (ACSIS041) whether a test was fair or not to scientific investigations (ACSIS091) &
(ACSIS058) & (ACSIS069) (ACSIS108)
Communicating Share observations and ideas Represent and communicate Represent and communicate Communicate ideas, explanations
(ACSIS012) observations and ideas in a variety of observations, ideas and findings using and processes using scientific
ways (ACSIS029) & (ACSIS042) formal and informal representations representations in a variety of ways,
(ACSIS060) & (ACSIS071) including multi-modal texts (ACSIS093)
& (ACSIS110)
v8.1 Australian Curriculum www.australiancurriculum.com.au December 2015 Page 3
Science: Sequence of content: 7-10 Strand: Science understanding
Sub-strand Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10
Biological Classification helps organise the diverse Cells are the basic units of living things;
Multi-cellular organisms rely on Transmission of heritable characteristics
sciences group of organisms (ACSSU111) they have specialised structures and coordinated and interdependent internal from one generation to the next involves
functions (ACSSU149) systems to respond to changes to their DNA and genes (ACSSU184)
Interactions between organisms,
including the effects of human activities Multi-cellular organisms contain systems environment (ACSSU175) The theory of evolution by natural
can be represented by food chains and of organs carrying out specialised Ecosystems consist of communities of selection explains the diversity of living
food webs (ACSSU112) functions that enable them to survive interdependent organisms and abiotic things and is supported by a range of
and reproduce (ACSSU150) components of the environment; matter scientific evidence (ACSSU185)
and energy flow through these systems
(ACSSU176)
Chemical Mixtures, including solutions, contain Properties of the different states of All matter is made of atoms that are The atomic structure and properties of
sciences a combination of pure substances that matter can be explained in terms of the composed of protons, neutrons and elements are used to organise them in
can be separated using a range of motion and arrangement of particles electrons; natural radioactivity arises the Periodic Table (ACSSU186)
techniques (ACSSU113) (ACSSU151) from the decay of nuclei in atoms Different types of chemical reactions are
Differences between elements, (ACSSU177) used to produce a range of products
compounds and mixtures can be Chemical reactions involve rearranging and can occur at different rates
described at a particle level (ACSSU152) atoms to form new substances; during a (ACSSU187)
Chemical change involves substances chemical reaction mass is not created or
reacting to form new substances destroyed (ACSSU178)
(ACSSU225)
Chemical reactions, including
combustion and the reactions of acids,
are important in both non-living and
living systems and involve energy
transfer (ACSSU179)
Earth and Predictable phenomena on Earth, Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic The theory of plate tectonics explains The universe contains features including
space including seasons and eclipses, are rocks contain minerals and are formed global patterns of geological activity and galaxies, stars and solar systems,
sciences caused by the relative positions of the by processes that occur within Earth continental movement (ACSSU180) and the Big Bang theory can be used
sun, Earth and the moon (ACSSU115) over a variety of timescales (ACSSU153) to explain the origin of the universe
Some of Earth’s resources are (ACSSU188)
renewable, including water that cycles Global systems, including the carbon
through the environment, but others are cycle, rely on interactions involving the
non-renewable (ACSSU116) biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and
atmosphere (ACSSU189)
Physical Change to an object’s motion is caused Energy appears in different forms, Energy transfer through different Energy conservation in a system can be
sciences by unbalanced forces, including Earth’s including movement (kinetic energy), mediums can be explained using wave explained by describing energy transfers
gravitational attraction, acting on the heat and potential energy, and energy and particle models (ACSSU182) and transformations (ACSSU190)
object (ACSSU117) transformations and transfers cause The motion of objects can be described
change within systems (ACSSU155) and predicted using the laws of physics
(ACSSU229)
v8.1 Australian Curriculum www.australiancurriculum.com.au December 2015 Page 4
Science: Sequence of content: 7-10 Strand: Science as a human endeavour
Sub-strand Year 7-8 Year 9-10
Nature and Scientific knowledge has changed peoples’ understanding of the world and is Scientific understanding, including models and theories, is contestable and
development refined as new evidence becomes available (ACSHE119) & (ACSHE134) is refined over time through a process of review by the scientific community
of science (ACSHE157) & (ACSHE191)
Science knowledge can develop through collaboration across the disciplines of
science and the contributions of people from a range of cultures (ACSHE223) & Advances in scientific understanding often rely on technological advances and are
(ACSHE226) often linked to scientific discoveries (ACSHE158) & (ACSHE192)
Use and Solutions to contemporary issues that are found using science and technology, People use scientific knowledge to evaluate whether they accept claims,
influence of may impact on other areas of society and may involve ethical considerations explanations or predictions, and advances in science can affect people’s lives,
science (ACSHE120) & (ACSHE135) including generating new career opportunities (ACSHE160) & (ACSHE194) and
(ACSHE161) & (ACSHE195)
People use science understanding and skills in their occupations and these have
influenced the development of practices in areas of human activity (ACSHE121) & Values and needs of contemporary society can influence the focus of scientific
(ACSHE136) research (ACSHE228) & (ACSHE230)
Science: Sequence of content: 7-10 Strand: Science inquiry skills
Sub-strand Year 7-8 Year 9-10
Questioning Identify questions and problems that can be investigated scientifically and make Formulate questions or hypotheses that can be investigated scientifically
and predicting predictions based on scientific knowledge (ACSIS124) & (ACSIS139) (ACSIS164) & (ACSIS198)
Planning and Collaboratively and individually plan and conduct a range of investigation types, Plan, select and use appropriate investigation types, including field work and
conducting including fieldwork and experiments, ensuring safety and ethical guidelines are laboratory experimentation, to collect reliable data; assess risk and address ethical
followed (ACSIS125) & (ACSIS140) issues associated with these methods (ACSIS165) & (ACSIS199)
Measure and control variables, select equipment appropriate to the task and Select and use appropriate equipment, including digital technologies, to collect and
collect data with accuracy (ACSIS126) & (ACSIS141) record data systematically and accurately (ACSIS166) & (ACSIS200)
Processing Construct and use a range of representations, including graphs, keys and models Analyse patterns and trends in data, including describing relationships between
and analysing to represent and analyse patterns or relationships in data using digital technologies variables and identifying inconsistencies (ACSIS169) & (ACSIS203)
data and as appropriate (ACSIS129) & (ACSIS144) Use knowledge of scientific concepts to draw conclusions that are consistent with
information evidence (ACSIS170) & (ACSIS204)
Summarise data, from students’ own investigations and secondary sources, and
use scientific understanding to identify relationships and draw conclusions based
on evidence (ACSIS130) & (ACSIS145)
Evaluating Reflect on scientific investigations including evaluating the quality of the data Evaluate conclusions, including identifying sources of uncertainty and possible
collected, and identifying improvements (ACSIS131) & (ACSIS146) alternative explanations, and describe specific ways to improve the quality of the
data (ACSIS171) & (ACSIS205)
Use scientific knowledge and findings from investigations to evaluate claims based
on evidence (ACSIS132) & (ACSIS234) Critically analyse the validity of information in primary and secondary sources and
evaluate the approaches used to solve problems (ACSIS172) & (ACSIS206)
Communicating Communicate ideas, findings and evidence based solutions to problems using Communicate scientific ideas and information for a particular purpose, including
scientific language, and representations, using digital technologies as appropriate constructing evidence-based arguments and using appropriate scientific language,
(ACSIS133) & (ACSIS148) conventions and representations (ACSIS174) & (ACSIS208)
v8.1 Australian Curriculum www.australiancurriculum.com.au December 2015 Page 6
You might also like
- Science Forward Planning DocumentDocument18 pagesScience Forward Planning Documentapi-451266317No ratings yet
- Curriculum LinksDocument4 pagesCurriculum Linksapi-391216982No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD 5esDocument15 pagesPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-398069738No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD 5esDocument13 pagesPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-409145936No ratings yet
- Curric AssDocument2 pagesCurric Assapi-389638207No ratings yet
- Science: Planning Document University of Notre DameDocument15 pagesScience: Planning Document University of Notre Dameapi-319889786No ratings yet
- Final FPDDocument14 pagesFinal FPDapi-389638207No ratings yet
- Australian Curriculum: Science (Foundation) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement StandardDocument16 pagesAustralian Curriculum: Science (Foundation) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement Standardapi-451196897No ratings yet
- Sciencefpd 2Document12 pagesSciencefpd 2api-397568836No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPDDocument20 pagesPrimary Science FPDapi-398083288No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPDDocument11 pagesPrimary Science FPDapi-503017745No ratings yet
- Niamh Tosh Biology Year 2 FPDDocument8 pagesNiamh Tosh Biology Year 2 FPDapi-458783343No ratings yet
- Earth Space Science-Fpd DwesterhoutfinalDocument15 pagesEarth Space Science-Fpd Dwesterhoutfinalapi-347389851No ratings yet
- Year 5 Science-2Document1 pageYear 5 Science-2api-431986153No ratings yet
- Year 6Document1 pageYear 6api-450945881No ratings yet
- Australian CurriculumDocument2 pagesAustralian Curriculumapi-409534192No ratings yet
- Science-Fpd - AdaptationsDocument21 pagesScience-Fpd - Adaptationsapi-395538019No ratings yet
- Science PresentationDocument5 pagesScience Presentationapi-451081553No ratings yet
- Australian Curriculum - Year 3Document1 pageAustralian Curriculum - Year 3api-391225671No ratings yet
- Forward Planning DocumentDocument11 pagesForward Planning Documentapi-458392513No ratings yet
- Science Curriculum DocumentDocument2 pagesScience Curriculum Documentapi-360143529No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)Document12 pagesPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)api-479877445No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5)Document2 pagesPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5)api-391230274No ratings yet
- Year 6 Overview-2Document2 pagesYear 6 Overview-2api-350585868No ratings yet
- Australian CurriculumDocument2 pagesAustralian Curriculumapi-427927675No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)Document7 pagesPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)api-393907299No ratings yet
- Science FPDDocument11 pagesScience FPDapi-479604636No ratings yet
- Adaptations FPDDocument16 pagesAdaptations FPDapi-357270342No ratings yet
- FPD Yr3Document8 pagesFPD Yr3api-430863841No ratings yet
- My FPD PDFDocument7 pagesMy FPD PDFapi-430999432No ratings yet
- Australian CurriculumDocument2 pagesAustralian Curriculumapi-450861338No ratings yet
- Year 1Document2 pagesYear 1api-398695607No ratings yet
- FPD With 5esDocument19 pagesFPD With 5esapi-397898275No ratings yet
- Year 6 Science FPDDocument10 pagesYear 6 Science FPDapi-390074616No ratings yet
- Year 5 Science UnitDocument13 pagesYear 5 Science Unitapi-359063455No ratings yet
- Science FPDDocument15 pagesScience FPDapi-431314968No ratings yet
- Forward Planning Document - Year 4Document12 pagesForward Planning Document - Year 4api-476445675No ratings yet
- Unit OverviewDocument2 pagesUnit Overviewapi-451107029No ratings yet
- Primary Science FPD 5esDocument11 pagesPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-525582472No ratings yet
- Science CurriculumDocument2 pagesScience Curriculumapi-451039239No ratings yet
- Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2) : English MathsDocument15 pagesAustralian Curriculum: Science (Year 2) : English Mathsapi-545623990No ratings yet
- Curriculum OverviewDocument2 pagesCurriculum Overviewapi-524115360No ratings yet
- Aus CurricDocument3 pagesAus Curricapi-408957435No ratings yet
- FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)Document14 pagesFPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)api-397553972100% (1)
- Primary Science FPD 5esDocument34 pagesPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-451203309No ratings yet
- FPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)Document17 pagesFPD: Primary Science: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 2)api-475676181No ratings yet
- Science FPDDocument9 pagesScience FPDapi-282280430No ratings yet
- Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 5) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement StandardDocument2 pagesAustralian Curriculum: Science (Year 5) : Sub-Strands Content Descriptions Achievement Standardapi-483241012No ratings yet
- Adaptations FPD - Year 5 Biological SciencesDocument12 pagesAdaptations FPD - Year 5 Biological Sciencesapi-395840685No ratings yet
- Science Forward Planning Document 2Document8 pagesScience Forward Planning Document 2api-398148089No ratings yet
- Cover Page ScsaDocument1 pageCover Page Scsaapi-409530934No ratings yet
- Science FPDDocument13 pagesScience FPDapi-391256129No ratings yet
- FPD Science PDFDocument22 pagesFPD Science PDFapi-397550706No ratings yet
- Science Planning Document Primary & Secondary University ofDocument10 pagesScience Planning Document Primary & Secondary University ofapi-443327549No ratings yet
- Year 4 OverviewDocument3 pagesYear 4 Overviewapi-395537862No ratings yet
- Biological Science Year 1 FPDDocument17 pagesBiological Science Year 1 FPDapi-398688270No ratings yet
- Science-Forward-Planning-Document-2 1Document11 pagesScience-Forward-Planning-Document-2 1api-397513560No ratings yet
- FPD Science 2019Document10 pagesFPD Science 2019api-479357785No ratings yet
- Australian Curriculum Year 3Document2 pagesAustralian Curriculum Year 3api-432911874No ratings yet
- Mt Stromlo Observatory: From Bush Observatory to the Nobel PrizeFrom EverandMt Stromlo Observatory: From Bush Observatory to the Nobel PrizeNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Aerated Lagoons & Secondary Clarifier (Compatibility Mode)Document7 pagesLec 4 - Aerated Lagoons & Secondary Clarifier (Compatibility Mode)Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Thermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)Document1 pageThermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)brunizzaNo ratings yet
- Chiral Symmetry Breaking by A Magnetic Field in GrapheneDocument38 pagesChiral Symmetry Breaking by A Magnetic Field in GrapheneKadhim JabbarNo ratings yet
- Sorbead R: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesSorbead R: Product Data Sheetpmfg847633No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Isothermal CSTR Design (Conversion)Document11 pagesLecture 8 Isothermal CSTR Design (Conversion)Mhmad E. HerzallahNo ratings yet
- Circle Seal ControlsDocument34 pagesCircle Seal Controls朱向斌No ratings yet
- Cooling Curve Shape Analysis Can Help Evaluate Quenchants: by M.E. Dakins, G E. Totten and R.W. HeinsDocument2 pagesCooling Curve Shape Analysis Can Help Evaluate Quenchants: by M.E. Dakins, G E. Totten and R.W. Heinsmayin007mixNo ratings yet
- CHB302P Viscometer 3rd Sem SSahaDocument3 pagesCHB302P Viscometer 3rd Sem SSahajoandalilis7316No ratings yet
- Primary TreatmentDocument22 pagesPrimary TreatmentEmil AbdoNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Martensitic NiTi Files A Systematic ReviewDocument13 pagesMetallurgy and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Martensitic NiTi Files A Systematic ReviewNani TioNo ratings yet
- Approval Sheet: Customer ManufacturerDocument7 pagesApproval Sheet: Customer ManufacturerypadillaNo ratings yet
- ATS 10 Foamed Concrete AdmixturesDocument3 pagesATS 10 Foamed Concrete AdmixturesBadshah AkhilNo ratings yet
- Pipe Insulation - Finding The Optimal ThicknessDocument5 pagesPipe Insulation - Finding The Optimal ThicknessmbsahgNo ratings yet
- Labsheet DJJ30113 Heat Treatment PDFDocument3 pagesLabsheet DJJ30113 Heat Treatment PDFkarim100% (1)
- Nanostructural Reorganization of Bacterial Cellulose by Ultrasonic TreatmentDocument8 pagesNanostructural Reorganization of Bacterial Cellulose by Ultrasonic Treatmentdhy182No ratings yet
- Fluid Bed ProcessorDocument16 pagesFluid Bed ProcessorjavierbravoantonNo ratings yet
- Monod Equation ProblemDocument7 pagesMonod Equation Problemeiddnew100% (1)
- Global Warm: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionDocument16 pagesGlobal Warm: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionsixemNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Lorama Polysaccharide ResinDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet: Lorama Polysaccharide ResinSatish Chipkar100% (1)
- Diagrama Cu-S-H2ODocument10 pagesDiagrama Cu-S-H2Ocasa.dezac19No ratings yet
- NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsDocument26 pagesNCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsKelsey Macaraig100% (3)
- Process Modeling: Flavio Manenti, CMIC "Giulio Natta" DeptDocument32 pagesProcess Modeling: Flavio Manenti, CMIC "Giulio Natta" DeptsagarsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Principles, Operational Challenges, and Perspectives in Boiler Feedwater Treatment ProcessDocument11 pagesPrinciples, Operational Challenges, and Perspectives in Boiler Feedwater Treatment ProcessNguyễn Quốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Innovation - Guide - 2011 Isp PDFDocument60 pagesInnovation - Guide - 2011 Isp PDFgabriel oliveira monteiroNo ratings yet
- CLEANER Conforms to ANSI Z400.1-2010 Standard - HCS 2012 SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking 1.1 Product identifier - Protective Clothing General Hazard DOTDocument10 pagesCLEANER Conforms to ANSI Z400.1-2010 Standard - HCS 2012 SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking 1.1 Product identifier - Protective Clothing General Hazard DOTFreddy Carl FredricksenNo ratings yet
- MOM II - Module 1Document10 pagesMOM II - Module 1Wolf LordNo ratings yet
- 2018 06 Waters TA Roadshow DMADocument45 pages2018 06 Waters TA Roadshow DMAAbd BaghadNo ratings yet
- Distillation Ch4 ReboilerDocument27 pagesDistillation Ch4 Reboilerkphk1979No ratings yet
- Vacuum: For 10mev 50Kw AcceleratorDocument27 pagesVacuum: For 10mev 50Kw AcceleratorrendydunNo ratings yet
- TricoDocument103 pagesTricoEzequiel100% (1)