Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ScheduledTest Question Ans PDF Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15 Answers Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15
ScheduledTest Question Ans PDF Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15 Answers Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15
Uploaded by
shivaysinghrajputofficialCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ScheduledTest Question Ans PDF Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15 Answers Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15
ScheduledTest Question Ans PDF Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15 Answers Test15 Pyq Phase1 2023 23042024 15
Uploaded by
shivaysinghrajputofficialCopyright:
Available Formats
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
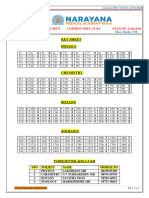
ANSWER KEY
1- 2 41- 4 81- 3 121- 2 161- 1
2- 2 42- 3 82- 3 122- 4 162- 1
3- 4 43- 1 83- 3 123- 3 163- 3
4- 4 44- 3 84- 3 124- 4 164- 4
5- 1 45- 4 85- 4 125- 1 165- 1
6- 4 46- 4 86- 3 126- 4 166- 2
7- 2 47- 2 87- 4 127- 4 167- 2
8- 1 48- 4 88- 4 128- 2 168- 4
9- 2 49- 4 89- 3 129- 4 169- 1
10- 4 50- 1 90- 2 130- 2 170- 2
11- 4 51- 4 91- 4 131- 2 171- 4
12- 3 52- 1 92- 4 132- 4 172- 2
13- 3 53- 3 93- 4 133- 1 173- 1
14- 4 54- 3 94- 1 134- 3 174- 1
15- 4 55- 1 95- 4 135- 1 175- 1
16- 4 56- 2 96- 1 136- 2 176- 4
17- 1 57- 4 97- 1 137- 1 177- 3
18- 1 58- 4 98- 2 138- 4 178- 1
19- 2 59- 2 99- 4 139- 2 179- 1
20- 4 60- 2 100- 3 140- 1 180- 3
21- 3 61- 2 101- 2 141- 2 181- 4
22- 1 62- 2 102- 3 142- 2 182- 1
23- 4 63- 1 103- 4 143- 2 183- 1
24- 2 64- 4 104- 1 144- 1 184- 1
25- 2 65- 1 105- 1 145- 4 185- 2
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
26- 4 66- 4 106- 1 146- 4 186- 1
27- 1 67- 4 107- 1 147- 4 187- 1
28- 3 68- 2 108- 2 148- 3 188- 1
29- 2 69- 4 109- 2 149- 4 189- 3
30- 1 70- 4 110- 2 150- 4 190- 3
31- 3 71- 4 111- 4 151- 3 191- 4
32- 1 72- 2 112- 1 152- 3 192- 2
33- 3 73- 2 113- 4 153- 4 193- 1
34- 3 74- 4 114- 3 154- 3 194- 1
35- 4 75- 4 115- 1 155- 1 195- 2
36- 2 76- 4 116- 4 156- 4 196- 2
37- 1 77- 1 117- 1 157- 4 197- 4
38- 4 78- 1 118- 4 158- 4 198- 2
39- 3 79- 3 119- 4 159- 4 199- 2
40- 4 80- 1 120- 1 160- 4 200- 1
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
PHYSICS Surface energy of bubble = 2 ×
SECTION-A change in surface area × surface
1. (2) tension
Radius of gyration of a solid sphere, = 8πr2×T = 8 × 3.142 × 4 × 10-4 ×
MKs2 =
2
MR2 3 × 10-2 J = 3.01 × 10-4 J.
5
2
(Mechanical properties of
Ks = R
5 fluids, Surface tension)
Radius of gyration of hollow sphere, 4. (4)
2 2 2
MK H = 3
MR R = 22 × 103 ± 5%
2 First band = Red
KH = 3
R
2nd band = Red
*In actual neet paper the answer
3rd band = Orange (Multiplier)
was incorrect so bonus was given
4th band = Gold (Tolerance)
to all who attempted
(Current electricity, Resistance
(System of particles and
bands)
rotational motion)
5. (1)
2. (2)
For resonance frequency
Incident energy = 2.20 eV
XL = Xc
If (work function) ϕ < 2.20 eV 1
⇒ωL =
electron will emit. ω𝐶
1 1
ϕ > 2.20 eV No electron emission ω= = =
𝐿𝐶 −3
10 × 10 × 1 × 10
−6
Only caesium will emit electron. 1
= 104 rad/s
(Dual nature of matter and
−8
10
4
radiation, Einstein’s ω
f = ( 2π ) =
10
= 1.59 kHz.
2π
photoelectric equation) (Alternating current,
3. (4) resonance frequency)
According to question, surface 6. (4)
-1
tension = T = 0.03 Nm 𝐸
As c = 𝐵
Radius of soap bubble = r = 2cm =
Here, E is the amplitude of electric
2 × 10-2
field and B is the amplitude of
magnetic field, c is the speed of
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
𝐸 48
light. So, B = = = 16 ×
𝐶 3×10
8
through a closed surface. If ∮𝐸.𝑑𝑆 =
-8 -7
10 = 1.6 × 10 T. 𝑠
0, then it signifies that the number
(Electromagnetic waves and its
of electric flux lines entering the
characteristics)
surface must be equal to the
7. (2)
number of flux lines leaving the
Photovoltaic devices can convert
surface,
optical radiation into electricity.
(Electric charges and fields,
The basic example of such a device
Gauss’s Law)
is solar photovoltaic system which
10. (4)
converts solar energy directly into
No current through ‘G’
electrical energy.
So, potential difference across R is
Zener diode is heavily doped p-n
2V,
junction diode operating in reverse
8
biased condition in breakdown So, current i = 400
A
2
region. Now Resistance (R) = ( 8 ×400) =
(Semiconductor electronics, 100 Ω.
devices) (Current Electricity) (Basic
8. (1) concept)
As the factors controlling 11. (4)
temperature and voltage supply are Capacitive reactance = XC =
1
ω𝐶
beyond prediction and control so
(say)
the error occurred due to
on decreasing the operating
unpredictable fluctuations of
frequency ω reduces
temperature and voltage would be
As Xc is inversely proportional to
random errors.
ω the value of Xc increase
(Units and measurements)
∴ IC = ID (displacement current)
(Theoretical) 𝑉𝑂
9. (2) = 𝑋𝐶
Thus, as XC increases, displacement
According to Gauss’s law, ∮𝐸.𝑑𝑆
𝑠 current decreases.
represents total electric flux passing
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Alternating current, (∆ρ/ρ)×100 = (∆M/M)×100 + 2×(∆
displacement current) r/r)×100+(∆L/L)×100
12. (3) ⇒
0.002 0.001
×100 + 2× 0.3 ×100 +
0.4
eV = Energy of electron 0.02
5
×100 = 0.5 + 0.67 + 0.4 =
for minimum wavelength, maximum
1.57% or 1.6%.
loss of energy
ℎ𝑐
(Units and measurement, error
eV = λ in measurement)
1
Thus, λα 𝑉
. 16. (4)
(Atoms) (Conceptual) As angular separation of fringes ∆θ
13. (3) =
λ
𝑑
Venturi-meter is a device used to So, angular separation does not
measure the flow speed of depend on the distance between
incompressible fluid, It works on screen and plane. Thus, statement I
Bernoulli's principle. is correct.
(Mechanical properties of As, θαλ
fluids) (Theoretical) If a monochromatic source is
14. (4) replaced by another
Capacitor in parallel removes the ac monochromatic source of larger
ripple from the rectified output. wavelength, then angular separation
(Semiconductor electronics) of fringes increases. Hence,
(Theoretical) statement II is incorrect.
15. (4) (Wave optics, Young’s double
We have mass M = (0.4 ± 0.002) g, slit experiment)
radius R = (0.3 ± 0.001) mm, length 17. (1)
L = (5 ± 0.02) cm Potential energy stored in the
Now, we know that density of the 1
spring = 2
kx2
2
wire is calculated as ρ = (M)/(πr L) 1
Now k(2)2 = U
Maximum percentage error in the 2
2𝑈 𝑈
measurement of density of wire is So, k = 4
= 2
found as; When x = 8 cm, let potential
energy = U’
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
=
1
×
𝑈
(8)2 = 16U 20. (4)
2 2
(Work, energy and power) Initial velocity of the football player
(Basic concept) = -v𝑗
18. (1) Final velocity of the football player
Speed of light in air is = v𝑖
𝑥
C= 𝑡1
Speed of light in another denser
medium
10𝑥
C2 = 𝑡2
𝐶
Now refractive index μ = 𝐶2
=
𝑥 𝑡 𝑡2
𝑡1
× 10𝑥
= 10𝑡1
So, the change in velocity = v 𝑖 - (-v
Since for total internal reflection,
10𝑡1
𝑗 ) = v( 𝑖 + 𝑗 )
1
sinic = =
μ 𝑡2 Momentum gain is along 𝑖 + 𝑗
−1 10𝑡
Critical angle ic = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 ( 𝑡 1 ). So, force experienced is along 𝑖 + 𝑗
2
That is the North-East direction.
(Ray optics and optical
(Laws of motion, Conservation
instruments, refraction)
of momentum)
19. (2)
21. (3)
According to question,
The circuit can be redrawn as an
VS = 12 V
equivalent circuit given below:
Now, for a transformer
𝑖𝑝 𝑉𝑠 𝑁𝑝
𝑖𝑠
= 𝑉𝑝
= 𝑁𝑠
- (a)
iS = 60/12 = 5 A
Putting this in equation a and VP =
220 V, we get,
𝑖𝑝 12 3
= = = 0.27 A.
5 220 11
Now, according to Ohm’s Law,
(Alternating current,
Transformer)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
V = iR {where V is the voltage, i is equal to the number of field lines
the current and R is the resistance
entering the surface or, ∮𝐵.𝑑𝐴 = 0.
in the circuit} 𝑆
5 = i × 10 (Magnetism and matter,
⇒i=
5
= 0.5 A from B to A Gauss’s law in magnetism)
10
through E. 25. (2)
(Current electricity, Ohm’s In the above figure, two 3 μF are in
law) parallel,
22. (1) ⇒ Ceq = 3 + 3 = 6 μF
The angular acceleration direction Now, this will be in series with the
is given along angular velocity or 3 μF capacitor,
opposite to angular velocity
depending upon whether angular
velocity magnitude is increasing or 1 1
So, Cfinal = + 6 = 2 μF.
decreasing and this direction 3
(Electrostatics potential and
remains along the axis of circular
capacitance, arrangement of
motion.
capacitors)
(Motion in a plane)
26. (4)
(Conceptual)
Time taken for vehicle to cover first
23. (4)
𝑠/2 𝑠
Maximum height attained by the half, t1 = 𝑣
= 2𝑣
2 2
𝑢 𝑠𝑖𝑛 θ
2 2
(280) 𝑠𝑖𝑛 30
0
Time taken by vehicle to cover
bullet: hmax = 2𝑔
= 2×9.8 𝑠/2 𝑠
second half, t2 = =
= 1000 m. 2𝑣 4𝑣
(Motion in a plane) (Basic Therefore, Average speed = vavg =
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑑 𝑠/2+𝑠/2
concept) 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑡𝑎𝑘𝑒𝑛
= 𝑡1+𝑡2
=
24. (2) 𝑠 4𝑣
𝑠/2𝑣+𝑠/4𝑣
= 3
.
Net magnetic flux through a closed
(Motion in a straight line,
surface is zero because the number
average speed)
of field lines leaving the surface are
27. (1)
As T1/2 = 20 minutes,
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
According to question,
𝑁
=
1
= Magnetic energy stored in an
𝑁𝑂 16
1
1 1/T1/2 inductor = LI2
( 2
) 2
Here, L is the inductance and I is
t = 4T1/2 = 20 × 4 = 80 minutes.
the current
(Nuclei, half life) −6 2
1
28. (3) = 2
× 4 × 10 × (2) = 8 μJ.
Initial temperature of gas, Ti = (Electromagnetic induction)
-50oC (Basic concept)
= -50+273 = 223 K 31. (3)
We know that vrms ∝ 𝑇 Longitudinal stress = F/A = T/A =
𝑊
As vrms is increased by 3 times, Weight/Area = 𝐴
.
So, (vrms)f = 4(vrms)initial (Mechanical properties of solid,
= Tf = 16 Ti Longitudinal stress)
= 16 × 223 = 3568 K 32. (1)
o
To convert in C, 3568-273 = The dipole moment and electric
3295oC field have an angle of 300 between
(Kinetic theory of gases, RMS each other,
velocity)
29. (2)
as efficiency of carnot engine = η =
𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑘
1- 𝑇𝑠𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑐𝑒
= 0.5 (Given)
𝑇𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑘
So, 0.5 = Torque = τ = 𝑃×𝐸
𝑇𝑠𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑐𝑒
1
Where P is the dipole moment and
⇒Tsink = ×(327+273)K
2 E is the electric field
1
= 2
×600 = 300K |τ| = PESinθ
Or 300-273 = 27°C {as K = °C + ⇒ 4 = q × 2a × E sin 30o {2a is the
273} length of the dipole}
(Thermodynamics, Carnot’s Charge (q) = −2
4
5 1
=2
(2×10 )×2×10 × 2
engine)
× 10-3 C = 2mC.
30. (1)
(Electric charges and fields,
Electric dipole)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
33. (3)
In hydrogen spectrum,
1 1 1
λ
= R( 2
− 2
)
𝑛2 𝑛1
For shortest wavelength in the Let the gravitational field is zero at
Balmer series, a distance x from the mass m.
n1 = 2, n2 = ∞ 𝐺𝑚 𝐺9𝑚
2 = 2
1 1 1 𝑥 (𝑅−𝑥)
So, = R( − )
λ 2
2 ∞
2
⇒R - x = 3x or x = R/4
⇒λ =
4 Now, Gravitational potential at R/4
𝑅
is:
Now for the shortest wavelength of
𝐺𝑚 𝐺9𝑚 4𝐺𝑚 12𝐺𝑚
Brackett series, n1 = 4, n2 = ∞ =- 𝑅 - 3𝑅 =- 𝑅
- 𝑅
=-
4 4
1 1 1
λ𝐵
= R( 2
− 2
) 16𝐺𝑚
.
4 ∞ 𝑅
16 (Gravitation, Gravitational
Thus, λB = = 4λ.
𝑅
potential)
(Atoms, Hydrogen spectra)
SECTION-B
34. (3)
36. (2)
Fundamental harmonic frequency
Using work energy theorem,
open pipe
Kf - Ki = W
𝑣
= = fo 1 𝑢 1
2𝐿 = 2
m( 3 )2 - 2
mu2 = -FR × 24
Fundamental harmonic frequency of 1
Also, 0 - mu2 = -FR × d
closed pipe 2
𝑣 Now, we divide both equations,
= 4𝐿
= fc 1 2
𝑚𝑢 𝑑
𝑣 2
2 = 24
So, the required ratio = fo/fc = =
2𝐿 1 8
2
𝑚𝑢 × 9
𝑣
4𝐿 9
d = 24 × = 27 cm.
2:1. 8
(Waves) (Basic concept) (Work, energy and power)
35. (4) (Conceptual)
The given information is shown 37. (1)
below: Radius of innermost orbit of
H-atom
ro = 5.3 × 10-11 m
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
So, radius of third allowed orbit of In terms of series combination Req
H-atom, (equivalent) = R/10
r3 = ron2 = ro(3)2 = 9ro So, IP =
10𝐸
𝑅
𝑜
= 9×5.3 × 10-11 = 4.77 𝐴 As, IP = n × IS
(Atoms) (Basic concept) ⇒
10𝐸
=n×
𝐸
𝑅 10𝑅
38. (4)
⇒ n = 100.
(Current electricity,
Combination of resistors)
40. (4)
Let height of bridge = h
Displacement of ball, S = –h
Using newton’s equation of motion
As N = mg for free fall,
And f = ma S = ut + (½)at2
So, if f ≤ friction force then only car -h = 4 × 4 + (½)(-10)(4)2 {a = g =
will remain stationary 9.8 m/s2}
f ≤ µN So, -h = 16 - 80
I.e., a≤µg h = 64 m.
-2
⇒ a≤1.5 ms (Motion in a straight line, free
-2
Or amax = 1.5 ms . fall)
(Motion in a straight line) 41. (4)
(Conceptual) as angular frequency ω = 2πf
39. (3) Here, f is the frequency = 50 Hz
When 10 resistors each of So, ω = 2π×50 = 100π
resistance R is connected in series, Now, impedance of a L-C-R circuit
then equivalent resistance, Rt = is found as: Z =
R+R+R+.... 10 times 2 2
𝑅 + (𝑋𝐿 − 𝑋𝐶)
= 10 R
Now, current drawn from battery = = 10
2
+ (ω𝐿 −
1 2
)
ω𝐶
𝐸
IS = 10𝑅 50 −3 1 2
100 + (100 × π
× 10 − 10
3
−6
)
100π× π
×10
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
2
= 100 + (5 − 10)
= Z = 5 5Ω.
(Alternating current) (Basic
concept)
42. (3)
Time period of satellite T = 2π
𝑅
3 y=
𝐺𝑀 =A+B
Here, M is the mass of the earth
and R is radius of earth,
3
𝑅
= 2π 4 3
𝐺𝑑 3 π𝑅
3π
⇒T= 𝐺𝑑
3π
So, 𝐺𝑑
= T2 (Semiconductor electronics,
(Gravitation, Motion of logic gates)
satellite) 45. (4)
43. (1) The magnetic field at P point would
Focal length of convex lens = fconvex be due to upper wire, semi-circle
= +f wire and lower wire,
Focal length of concave lens = fconcave
𝐵P = 𝐵upper-wire⊗ + 𝐵semi-circle +𝐵
= -f
lower-wire⊗
When both lenses are in contact µ𝑖 µ𝑜𝑖 µ𝑜𝑖
= - 4π𝑅
𝑜
+ -
then equivalent focal length (F)is: 4𝑅 4π𝑅
µ𝑜𝑖 2
1
𝐹
=
1
𝑓𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑥
+
1
𝑓𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑐𝑎𝑣𝑒
=
1
𝑓
-
1
𝑓
=0 = 4𝑅
[1- π ] pointing away from the
So, F = ∞. page.
(Ray optics and optical (Moving charges and
instruments, Lenses) magnetism) (Conceptual)
44. (3-c) 46. (4)
The output of the logic circuit is: R = Ro(1 + α∆𝑇)
Where Ro is the resistance at 0oC
and α is the temperature coefficient
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
and ∆𝑇 is the change in (Ray optics and optical
temperature instruments, Lens maker’s
⇒ 6.8 = 2(1 + α(80 − 0) formula)
⇒α=
3.4−1
= 0.03 = 3 × 10-2 oC-1 49. (4)
80
(Current electricity) (Basic Magnetic force on a wire is the
concept) cross product of Length of wire and
47. (2) magnetic field B multiplied by
The electric potential at P is due to current I,
+q and -q charges, |𝐹| = | I(𝐿×𝐵) |
So, VP = Vq + V-q = | I[L 𝑖 × (2 𝑖 +3 𝑗 -4𝑘)] |
=(
𝐾𝑞
+
−𝐾𝑞
)×102 = 5IL.
5−3 5+3
𝑘𝑞 𝑘𝑞 (Moving charges and
=( 2
− 8
)×102
magnetism, Magnetic force on
= (3/8)Kq×102
charged particle in magnetic
(Electrostatics potential and
field)
capacitance, Electrostatic
50. (1)
potential)
From x-t graph,
48. (4)
Amplitude (A) = 1m, Time period =
For a plano-convex lens, the focal
8 sec
length is calculated as: 2π π
1 1 1 Angular frequency = ω = =
𝑓
= (µ-1)( ∞
- )
𝑅
𝑇 4
Now, at t = 2, x = 1
So, for lens L1, Acceleration a = -ω2x
1 1 1 −3
= (1. 6-1)( - )= π
2
π
2
𝑓1 ∞ 20 100 ⇒ a = - 16 ×1 = - 16 ms-2
For lens L2, (Oscillations, Simple harmonic
1
𝑓2
= (1.5-1)( 20 - −20 ) =
1 1 1
20
motion)
CHEMISTRY
Now, focal length F of the
SECTION-A
combination is,
51. (2)
1 1 1 1 −3 1 3
𝐹
= 𝑓1
+ 𝑓2
+ 𝑓3
= 100
+ 20
- 100
−1 The stability of Cu2+(aq) is more than
= 100 Cu+(aq) is due to the much more
Or F = -100 cm. negative ΔhydH° of Cu2+(aq) than
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Cu+(aq), which more than (States of Matter)
compensates for second ionization
54. (3)
enthalpy of Cu.
● Few reactions can have zero
2+ –1
ΔhydH°of Cu (aq) = –2121 kJ mol activation energy for example
ΔHo1 of Cu = +745 kJ mol–1 radical reactions.
● Activation energy is defined
o –1
ΔH of Cu = +1960 kJ mol
2
as the minimum amount of
(The d-and f-Block Elements)
52. ( 3) extra energy absorbed by
Combination of N2 and H2 to form NH3 in reactants to achieve threshold
presence of finely divided Fe is an example energy.
of heterogeneous catalysis.
(Chemical Kinetics)
55. (1)
Other examples of homogeneous catalysis. In case, nitrogen and sulfur both are
present in organic compounds,
sodium thiocyanate is formed. It gives
blood red color and no Prussian blue
(Surface Chemistry) since there are no free cyanide ions.
53. (3) Na + C + N + S ——→ NaSCN
According to Boyle’s law
Fe3+ + SCN– ——→[Fe(SCN)]2+ (Blood Red)
PV=nRT
P=nRT(1/V) (Organic Chemistry-Some Basic
P versus 1/V gives a straight line graph with Principles and Techniques)
slope nRT
56. (2)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
● Graphite is very soft and
slippery. Hence, it is used as a
dry lubricant in machines
running at high temperature.
(The p-Block Elements)
59. (2)
➔ All enzymes that utilize ATP in
(Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)
phosphate transfer require Mg as
57. (4)
the cofactor.
➔ Bone in the human body is not
Rate (r) = k[A]2[B]
an inert and unchanging
When concentration of A is tripled tripled
[A’] =[3A] substance but is continuously
New rate r’ = k[A’]2[B] = k[3A]2[B] = being solubilised and
9k[A]2[B]
redeposited.
r’ =9r
➔ Ca plays an important role in
(Chemical Kinetics)
58. ( 4) neuromuscular function,
interneuronal transmission,
● Coke is largely used as a reducing cell membrane integrity and
agent in metallurgy.
blood coagulation.
● In diamond, each carbon atom
undergoes sp3 hybridisation and ➔ The daily requirement of Mg
linked to four other carbon atoms and Ca in the human body is
by using hybridized orbitals in
estimated to be 200 - 300 mg
tetrahedral fashion
● Buckminsterfullerene contains (0.2 - 0.3 g).
six membered and five (The s-Block Elements)
membered rings and hence is 60. ( 2)
a cage-like molecule.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Number of atoms of element B = N As we move down the group, due to poor
Number of atoms of element A =⅓ x 2N shielding effect of intervening d and f
The formula of the compound = A ⅔ N B N orbitals, the increased effective nuclear
=A2B3 charge holds ns electrons tightly and
So, x = 2 therefore restricts their participation in
y=3 bonding. So, the relative stability of +1 O.S
x+y=5 increases for heavier elements.
E° for In3+ |In+ 0.16 V
(The Solid State)
E° for Tl3+|Tl + = +1.6 V
61. (2)
Hence, TII is more stable than TII3
(The p-Block Elements)
➔ Complexes in which a metal is bound 64. (4)
to only one kind of donor groups are
Helium is used as a diluent for oxygen in
called as homoleptic complexes
modern diving apparatus because of its
➔ Potassium trioxalatoaluminate very low solubility in blood.
(III) K3[Al(ox)3].It is a Gases diffuse easily with each other.
homoleptic complex (Solutions)
65. (1)
(Coordination Compounds)
Atoms consist of three fundamental
62. ( 2) particles : Electrons, protons and neutrons
For molecules like B2, C2, N2 etc. the The mass of the electron is 9.10939 ×
increasing order of energies of various 10–31 kg
molecular orbitals is
All the isotopes of a given element show
σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s < σ*2s < (π2px = π2py) the same chemical properties.
< σ2pz < (π*2px = π*2py) < σ*2pz
Protons and neutrons present in the
(Chemical Bonding and Molecular nucleus are collectively called nucleons.
Structure)
63. ( 1) Dalton’s atomic theory, regarded the atom
as the ultimate particle of matter .
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
So, the correct statements are B, C, E only
(Structure of Atom) Conductivity = conductance × cell constant
66. (4) k = G G*
Statement A, B, C are correct K =(1/R) G*
G* = k × R = 0.0210 × 60 = 1.26 cm–1
(D) H – H bond dissociation energy
is maximum as compared to a single (Electrochemistry)
70. (4)
bond between two atoms of any
Lewis acids are the one which accepts lone
element. pairs of electrons due to presence of
(E) Hydrogen reduces oxides of metal that vacant orbital in outermost shell.
are less active than iron.
(Hydrogen)
67. ( 4)
α-carbon is sp3 carbon which is right next
(The p-Block Elements (Group 15 to
to =C=C=
18))
This α-position is known as allylic position
71. (4)
.Hence the above mentioned compound is
allylic halide
A unit formed by the attachment of a base
(Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)
to 1’ position of sugar is known as
68. (2)
nucleoside. In nucleosides, the sugar
This reaction is Clemmensen reduction carbons are numbered as 1’, 2’, 3’, etc. in
order to distinguish these from the bases
(Fig a). When nucleoside is linked to
phosphoric acid at 5 -position of sugar
moiety, we get a nucleotide (Fig b).
(Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Acids)
69. (4)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Fig : Structure of (a) a nucleoside and (b) a Intermolecular forces are the forces
nucleotide
of attraction and repulsion between
(Biomolecules)
interacting molecules. This term does
72. ( 2)
not include covalent bonds as
nm = 2L + 1
covalent bonds hold atoms of a
L=(nm-1)/2
molecule together.
As there are (2L + 1) number of
Hence, dipole - dipole forces, dipole -
permissible values of magnetic quantum
induced dipole forces, hydrogen
number.
bonding and dispersion forces are
(Structure of Atom)
intermolecular forces.
73. (2)
(Chemical Bonding and
Molecular Structure)
AlCl3, BeCl2 and PCl5 do not obey octet
rule. 75. (4)
AlCl3 and BeCl2 both are electron-deficient
On dissolving alkali metal (sodium) in
species having six electrons in the valence
liquid ammonia, a deep blue solution
shell of the central atom whereas PCl5 has is developed due to an ammoniated
ten electrons in the valence shell of electron which absorbs energy in
phosphorus. visible regions of light and imparts
The structures are : blue color. Due to unpaired
electrons, the solution is
paramagnetic.
M + (x + y)NH3 → [M(NH3)x]+ +
[e(NH3)y]–
So, the assertion statement is correct but
the reason is incorrect.
(The s-Block Elements)
76. (4)
(Chemical Bonding and Molecular
Structure) Among isoelectronic monoatomic species,
74. (4) size is inversely proportional to atomic
number.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Hence among isoelectronic species Na+,
O2–, N3–, F– (having
nearest noble gas configuration); (Polymers)
Order of size is Na+ < F– < O2– < N3– 80. (1)
N3– has the least atomic number hence
largest size.
(Classification of Elements and
Periodicity in Properties)
77. (1)
The value of rG depends on n value as per
the equation (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
ΔrG = –nFEcell Acids)
Where E is the emf of the cell 81. ( 3)
nF is the amount of charge passed.
So, assertion statement is correct This reaction is called soda lime
Ecell is an intensive property while rG is an decarboxylation
extensive thermodynamic property
So, reason is correct but not explaining the
assertion
(Electrochemistry)
Molar mass of CH4 = 16 g/mol Weight of 2
78. ( 1) moles of CH4 = 16 × 2 =32
Veronal is the derivative of Barbituric acid (Hydrocarbons)
and considered as barbiturate.
82. ( 3)
Meprobamate, valium and chlordiazepoxide
are other tranquilizers.
79. (3)
Chloroprene is the monomer of
neoprene.Neoprene is formed by free
radical polymerisation of chloroprene.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Amines) Correct relation between change in
83. (3) enthalpy and change in internal energy is
ΔH = ΔU + ΔngRT
20 g of 20% CaCO3 = 20*20/100 = 4g
CaCO3 (Thermodynamics)
87. (4)
Reaction follows SN1 pathway involving
According to the reaction Benzylic carbocation
100 g of CaCO3 → 44 g of CO2
4g CaCO3 →( 4*44)/100 g of CO2
=1.76 g of CO2
(Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry)
84. ( 3) Mechanism
(Amines) (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers)
85. (4) 88. ( 4)
The highest oxidation number
corresponding to the group number in
transition metal oxides is attained in Sc2O3
to Mn2O7.
No of σ bonds =11 CrO is basic but Cr2O3 is amphoteric.
No of π bonds =3 Note:
No of lone pair of e-=1
All the transition metals except scandium
(Chemical Bonding and form MO oxides which are ionic (Only for
Molecular Structure) 3d series, this statement is true)
Hence, (A), (C) and (D) are incorrect. But
SECTION-B not given in the options.
86. ( 3) (The d-and f-Block Elements)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
89. (3) Ammoniacal silver nitrate solution is
Tollens’ reagent. Tollens’ reagent can be
used to distinguish aldehyde & ketone as
aldehyde upon warming with Tollens’
reagent produces a silver mirror due to
Formation of Conjugated diene in option 3 formation of silver metal in alkaline
makes the given reactant most reactive medium. Aldehyde is oxidized to
towards dehydration in acidic conditions. corresponding carboxylate anion
Mechanism
(Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Acids)
92. (4)
(Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers) One edge of a cube is common to four
90. (2) unit cells. Hence One edge center
octahedral void contributes ¼ to one
At 900-1500K (higher temperature range
unit cell.
in the blast furnace)
The total number of octahedral voids in
Reaction which take place:- FCC are four Octahedral voids in FCC =
C+CO2 → 2CO Edge centers + Body center
FeO +CO → Fe + CO2 The contribution of edge center = 1/4
CaO +SiO2 →CaSiO3 (Slag formation) Fraction of one edge centered octahedral
Fe2O3 + CO →2FeO + CO2 [This takes void in one unit cell of FCC = ¼
place at 500-800 K] (The Solid State)
(General Principles and Processes of 93. ( 4)
Isolation of Elements) Keq =[A] [B]/[C][D]
91. ( 4) Keq = (10 x6 )/ (2x 3)
Tollen’s reagent oxidize aldehydes into ΔG0 = –2.303 R T log Keq. =
carboxylate ion whereas ketone is not –2.303(2)(300)(log10)
oxidized by tollen’s reagent = –1381.8 cal (⸪ R = 2 cal/mol k)
(Equilibrium)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
94. (1) (Redox Reactions)
Acc. to Huckel rule, A compound/molecule
97. (1 )
is said to be aromatic if it have cyclic
conjugate and [4n + 2]p electron system Eutrophication occurs when the water
Molecule must be sp2 hybridised body becomes overly enriched with
Molecule must be planar nutrients.
Eutrophication leads to decrease in the
level of dissolved oxygen (DO) in water
bodies
All these are aromatic species acc. to
(Environmental Chemistry)
Huckel rule.
98. (2)
(Hydrocarbons)
95. ( 4)
Ethylene diamine, en is bidentate, chelating
ligand.
Chelating ligands increase stability due to
higher entropy stability LiAlH4 used for reduction of carbonyl
(Coordination Compounds) group into alcohol
96. (1 ) H2SO4 used for dehydration of alcohol.
Alkenes react with hydrogen bromide in
Reduction half reaction. the cold. The double bond breaks and a
Cr2 O72- +14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr+3 + 7H2 O hydrogen atom ends up attached to one of
Oxidation half reaction the carbons and a bromine atom to the
2- 2- -
SO + H2O → SO 4 + 2e ]x 3 other. In the case of ethene, bromoethane
Oxygen is balanced by adding water and is formed.
hydrogen is balanced by adding H+ and the
99. (4)
charge is balanced by electrons.
Pumice stone is an example of solid sol. In
Add(eq. (i)) + (3 × eq. (ii))
this type of colloid, the dispersion
Cr2O72- + 3SO32- + 8H+ → 2Cr+3 + 3SO2- + medium is solid and the dispersion phase
4H2O is gas.
a=1 b=3 c=8 (Surface Chemistry)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Plant growth and
100. (3) development, Plant Hormone
Ethylene)
102. (3)
Sol. Movement and accumulation of
ions across a membrane against
their concentration gradient can be
explained by active transport. It
uses energy to transport molecules
from lower concentration to a
higher concentration.
Osmosis (option 4) is the
movement of water across a
(The p-Block Elements (Group 15 to selectively permeable membrane
18)) from an area of lower solute
concentration to an area of higher
solute concentration. Facilitated
diffusion (option 1) and passive
BIOLOGY
transport (option 2) involve the
SECTION-A movement of substances down
101. (2) their concentration gradient
Ethylene is a plant hormone that without the input of energy.
plays a significant role in promoting (Transport in Plant, Movement
internode and petiole elongation, of water, gases and nutrient)
especially in deep water rice. When
rice plants sense flooding or
submergence, they produce
increased levels of ethylene, which
stimulates elongation growth to
help the plant reach the water's
surface for gas exchange. 103. (4)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Large, colourful, fragrant flowers phenomenon may be called as
with nectar attract biotic dedifferentiation.
pollinators (insects), thus, they are Dedifferentiation is a phenomenon
seen in insect pollinated plants. by which the living differentiated
These characteristics serve to plant cells, that by now have lost
attract insects such as bees, the capacity to divide, can regain
butterflies, and beetles, which play a the capacity of division under
key role in pollinating the flowers certain conditions.
while seeking nectar as a food Senescence is the process of aging
source. Bird-pollinated plants or deterioration in cells, tissues, or
(option 1) may have brightly whole organisms. Differentiation
colored flowers but typically lack is the process by which cells
strong fragrances, as birds have a become specialized into distinct cell
less acute sense of smell. types with specific functions.
Bat-pollinated plants (option 2) may (Plant growth and
have large, showy flowers, but they development,
are often nocturnal and produce Dedifferentiation)
strong odors rather than colorful 105. (1)
displays. Wind-pollinated plants Sol. The Convention on Biological
(option 3) usually have Diversity (CBD), established during
inconspicuous flowers without the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro
colorful petals or strong fragrances, in 1992, urged all nations to adopt
as they rely on the wind to carry measures for the conservation of
pollen from one flower to another. biodiversity and the sustainable use
(Sexual reproduction in of its resources.
flowering plants, Pollination (Biodiversity and conservation,
type) Conventions on Biological
104. (1) Diversity)
Sol. In tissue culture experiments, 106. (1)
leaf mesophyll cells are put in a Sol. Option (1) is the correct
culture medium to form callus. This answer as, during isolation of the
genetic material, purified DNA
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
ultimately precipitates out after the
addition of chilled ethanol. RNA is
less soluble in cold ethanol
compared to DNA, histones, and
polysaccharides, allowing it to
separate and form a visible pellet,
leaving the desired DNA intact in
solution.
Option (2) is not the answer as
proteins can be removed by
treatment with proteases. Option (Respiration, Calvin cycle)
(4) is not the answer as RNA can 108. (2)
be removed by treatment with Sol. In the equation where GPP
ribonuclease. represents Gross Primary
(Principles and process of Productivity and NPP stands for
biotechnology, Isolation of Net Primary Productivity, R
DNA) typically represents (2) Respiratory
107. (1) loss. This term accounts for the
Sol. For every CO2 molecule energy lost by plants through
entering the Calvin cycle, 3 respiration during the process of
molecules of ATP and 2 of converting the fixed carbon into
NADPH2 are required. energy for cellular activities.
To make one molecule of glucose, 6 (Ecosystem, productivity and
turns of the cycle are required. decomposition)
Thus, ATP and NADPH2 molecules 109. (2)
required for synthesis of one Option 2 is the correct answer
molecule of Glucose during because the gene gun method
Calvin cycle will be involves the utilization of
6 * 3 ATP = 18 ATP and microparticles made of tungsten or
6 * 2 NADPH = 12 NADPH gold. These materials are chosen
because of their inert nature,
ensuring they do not change the
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
chemical composition of cells. production of cells with smaller
Therefore, they serve as suitable diameters.
carriers for delivering genetic
material into target cells without The reason given (R) explains why
causing any unwanted alterations. late wood has fewer xylary
(Principles and process of elements with narrow vessels. The
biotechnology, Genetic decrease in cambium activity during
engineering) winters leads to the formation of
110. (2) narrower vessels and fewer xylary
Sol. The phenomenon of elements during late wood
pleiotropism refers to (2) A single formation in the subsequent
gene affecting multiple phenotypic summer season.
expressions. This occurs when a
(Anatomy of flowering plants,
single gene has multiple effects on
Cambium activity)
the phenotype of an organism.
112. (1)
These effects can manifest in
Sol. Replication of DNA takes place
various traits or characteristics,
in S-phase of cell cycle in
sometimes seemingly unrelated to
eukaryotes.
each other, due to the complex
G1 phase (Gap 1 phase): In this
interactions within biological
phase, the cell grows in size,
systems.
synthesizes proteins, and carries
(Heredity and variation,
out its normal metabolic functions.
Pleiotropy)
It is a period of preparation for
111. (4)
DNA replication.
Sol. Late wood, also known as
G2 phase (Gap 2 phase): During
autumn wood, typically has fewer
the G2 phase, the cell continues to
xylary elements with narrower
grow and prepare for cell division. It
vessels compared to early wood
synthesizes additional proteins and
(springwood). This is because
organelles necessary for mitosis and
during the summer, when late wood
cytokinesis.
is formed, the cambium activity
decreases, resulting in the
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
M phase (Mitotic phase): The M
phase is where cell division occurs
and consists of two main stages:
mitosis and cytokinesis.
(Morphology of flowering plant, floral
diagram)
114. (3)
Sol. In axile placentation, the ovules are
attached to a central column or axis within
(Cell division, Cell cycle) the ovary. China rose, Tomato, Petunia and
Lemon show axile placentation.
113. (4) In free central the ovules are attached
Sol. The characteristic specific to family directly to the central axis, and they
Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or develop freely without any partitions.
Liliaceae is (4) Diadelphous and Dianthus and Primrose show free central
Dithecous anthers. placentation. In marginal placentation, the
placenta is located along the margin or
In the Fabaceae family, the stamens are edge of the ovary. Pea, Lupin and Beans
often arranged in two groups show marginal placentation.
(diadelphous), with nine stamens fused In parietal placentation, the ovules are
together to form a tube, while one stamen attached to the inner wall or periphery of
is separate. Additionally, the anthers the ovary. Cucumber and mustard show
typically have two locules (dithecous), parietal placentation.
meaning they consist of two pollen sacs.
These characteristics are unique to
Fabaceae and distinguish it from Solanaceae
and Liliaceae.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Morphology of flowering Sol. The tassels on the corn cob represent
plant,Placentation) the stigma and style, which sway in the
wind to capture pollen grains.
115. (1)
Sol. In heterosporous pteridophytes, there
are two types of spores produced:
microspores and megaspores. Selaginella
and Salvinia are heterosporous
pteridophytes.
In homosporous pteridophytes, a single
type of spore is produced.Psilotum,
Lycopodium and Equisetum are
homosporous pteridophytes.
(Sexual reproduction in flowering
plants, Pollination)
(Plant kingdom, Pteridophytes) 118. (4)
Sol. The predominant stage of the life cycle
116. (4) of a moss is the gametophyte which
Sol. The thickness of the ozone in a consists of two stages. The first stage is the
column of air from the ground to the top protonema stage, which develops directly
of the atmosphere is measured in terms of from a spore. Capsule of the sporophyte
Dobson units (DU). Noise is measured in contains spore which gives rise to
decibels. protonema. Thus, reason correctly explains
(Environmental issues, Ozone the assertion.
depletion)
117. (1)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Alfred Sturtevant used the frequency
of recombination between gene pairs on
the same chromosome as a measure of the
distance between genes and ‘mapped’ their
position on the chromosome.
Sutton and Boveri proposed chromosomal
theory of inheritance which suggests that
(Plant kingdom, Life cycle of Mosses) genes, which carry hereditary information,
119. (4) are located on chromosomes and are
Sol. Statement I is correct as transmitted through the process of
measurements reveal that the forces chromosome segregation and assortment
generated by transpiration can create during cell division. Henking discovered
pressures sufficient to lift a xylem sized X-chromosome.
column of water up to 130 meters high. Thomas Hunt Morgan proved
Statement II is also correct as transpiration chromosomal theory of inheritance and
cools leaf surfaces, sometimes 10 to 15 proposed the concept of linkage.
degrees, by evaporative cooling. (Heredity and variation,
(Transport in plants, Transpiration) Chromosome theory of inheritance)
120. (1) 122. (4)
Sol. Gibberellic acid is a plant hormone Sol. All the genes that are expressed as
that promotes growth and development. RNA are referred to as Expressed
When sprayed on juvenile conifers, it can Sequence Tags (ESTs). Expressed Sequence
hasten the maturity period, leading to early Tags (ESTs) are short, single-pass
seed production. Gibberellic acid stimulates sequences generated from the expressed
cell elongation and division, which can regions of a genome, particularly from the
accelerate the growth and reproductive messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts.
processes in plants. (Molecular basis of inheritance, DNA
(Plant growth and development, Fingerprinting)
Gibberellin)
123. (3)
121. (2)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Option (3) is the correct answer
because in recombinant DNA technology
the separated DNA fragments can be
visualised only after staining the DNA with
a substance known as ethidium bromide
followed by exposure to U.V. radiation.
Bright orange coloured bands of DNA can
be seen in an ethidium bromide stained gel
exposed to U.V. light.
(Principles and process of
biotechnology, Genetic engineering)
(Respiration, Glycolysis)
124. (4)
Sol. Assertion A states that ATP is used at 125. (1)
two steps in glycolysis, which is true. Sol. The unequivocal proof that DNA is the
genetic material came from the experiment
Reason R provides the correct explanation
of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase. They
for Assertion A by detailing the two steps
conducted the famous Hershey-Chase
where ATP is used: the conversion of
experiment in 1952, which further
glucose to glucose-6-phosphate and the
supported the idea that DNA, not protein,
conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to
was the genetic material
fructose-1,6-diphosphate.The reason of the
Avery, Macleoid and McCarty gave the
utilisation of ATP is for phosphorylation
biochemical characterisation of
the substrates.
Transforming Principle. They conducted
experiments in 1944 demonstrating that
Both statements are true and Reason R
DNA extracted from a pathogenic strain of
appropriately explains Assertion A.
bacteria could transform a non-pathogenic
strain into a pathogenic one.The
transformation experiments by using
Pneumococcus was conducted by
Frederick Griffith. Wilkins and Franklin
produced X-ray diffraction data of DNA.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Molecular basis of inheritance, (Photosynthesis, Pigments involved in
Search for genetic material and DNA Photosynthesis)
as genetic material)
128. (2)
126. (4) Sol. Synergids are the cells of gametophyte
Sol. Humus is a dark, organic material that and hence these are haploid.
forms as a result of the decomposition of The zygote is formed by the fusion of the
plant and animal matter by detritivores and other sperm cell with the egg cell in the
decomposers.During mineralization, the embryo sac. The zygote is diploid (2n) and
microbes break down the humus into develops into the embryo, which eventually
simpler inorganic compounds, releasing forms the new plant.
nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and After fertilization, the primary endosperm
potassium back into the soil. The detritus nucleus, which is triploid (3n), is formed by
food chain begins with detritus that is dead the fusion of one sperm cell with two polar
organic matter. nuclei in the central cell of the embryo sac.
Leaching is a process by which This triploid nucleus gives rise to the
water-soluble inorganic nutrients, such as endosperm, which provides nourishment
nitrates and phosphates, are washed down to the developing embryo.
from the topsoil into deeper layers of the
soil or even into groundwater. This can
occur due to excessive rainfall or irrigation,
which carries the nutrients downward.
The saprotrophic bacteria and fungi
breakdown detritus into simpler inorganic
substances by a process called catabolism.
(Ecosystem, Decomposition) (Sexual reproduction in flowering
plants, Development of endosperm
127. (4) and embryo)
Sol. In PS-I, the reaction centre chlorophyll
a has an absorption peak at 700 nm, while 129. (4)
in PS-II, reaction centre has an absorption
maxima at 680 nm.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Manganese plays a major role in the doesn't form the complex helices required
splitting of water to liberate oxygen during to interact with iodine molecules, unlike
photosynthesis. starch which does form such helices and
Copper is essential for the overall reacts with iodine to produce a blue color.
metabolism in plants. Molybdenum is Therefore, cellulose does not exhibit a blue
included in nitrogen metabolism. color when treated with iodine.Option (1),
Magnesium activates several enzymes (3) and (4) are not correct as cellulose is a
involved in photosynthesis and respiration. polysaccharide.
(Mineral Nutrition, Role of minerals)
130. (2)
Sol. During Anaphase II of meiosis, the
centromeres split, and the sister
chromatids are pulled apart towards
opposite poles of the cell. This is when the
division of the centromere occurs, leading
to the separation of chromatids. During
Metaphase I and II, chromosomes align at (Biomolecules, Polysaccharide)
the equator. During telophase,
chromosomes reach the respective poles. 132. (4)
Sol. Habitat loss and fragmentation is the
most important cause driving animals and
plants to extinction.
Habitat Loss: This refers to the process by
which natural habitats are destroyed or
(Cell Cycle and Cell Division, Stages
significantly altered, leading to a decrease in
of meiosis)
the overall quality and quantity of suitable
habitat for various species. Habitat loss can
131. (2)
occur due to a variety of human activities,
Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer.
including urbanization, deforestation,
Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of
agriculture, mining, and infrastructure
glucose monomers, and its structure
development.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Habitat Fragmentation: Habitat Sol. Endarch and exarch are the terms
fragmentation occurs when large, often used for describing the position of
continuous areas of habitat are divided into primary xylem in the plant body.
smaller, isolated patches or fragments, Primary xylem is of two types protoxylem
often as a result of human activities such as and metaxylem. On the basis of relative
road construction, agriculture, and urban position of protoxylem and metaxylem in
expansion. the organ the arrangement of primary
(Biodiversity and Conservation, Loss xylem can be endarch or exarch.
of biodiversity) Exarch type of primary xylem is seen in
roots. Therefore, Statement I is false and
133. (1) Statement II is true.
Sol. In eukaryotes there are three major
types of RNA polymerases.
RNA polymerase I transcribes : 5.8S, 18S,
28S rRNAs
RNA polymerase II transcribes : hnRNAs
(precurssor of mRNA)
RNA polymerase III transcribes : tRNAs, (Anatomy of plants, Xylem)
ScRNA, 5S rRNA and snRNA
RNA polymerase III is responsible for 135. (1)
transcribing small, specialized RNAs Sol. The process of recombination occurs
including transfer RNA (tRNA), 5S at Pachytene stage of prophase I. This stage
ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and some small is characterised by the appearance of
nuclear RNAs (snRNA) in eukaryotic cells. recombination nodules. Zygoteneis
These RNAs are essential for various characterized by the pairing of homologous
cellular processes such as protein synthesis chromosomes, a process known as
and RNA processing. synapsis. The synaptonemal complex begins
(Molecular basis of inheritance, to disassemble, although chiasmata remain
Transcription) visible, marking sites of genetic exchange
during diplotene.
134. (3)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, they do not
improve water quality and can have
detrimental effects on fisheries.
The other statements are correct.
(Environmental issues, Water
pollution)
138. (4)
(Cell Cycle and Cell Division, Sol. Chemiosmosis is a process that occurs
Prophase 1) in both cellular respiration and
SECTION-B photosynthesis. It involves the movement
of protons (H⁺ ions) across a membrane,
136. (2) typically the inner mitochondrial
Sol. Assertion is correct but reason is false membrane in cellular respiration or the
as in gymnosperms the pollen grains are thylakoid membrane in photosynthesis.
released from the microsporangium and This movement of protons creates a
they are carried in air currents. They come proton gradient, which is then utilized by
in contact with the opening of the ovules ATP synthase to produce ATP. Therefore, a
borne on megasporophylls. The pollen tube membrane, proton pump (to pump
carrying the male gametes grows towards protons across the membrane), proton
archegonia in the ovules and discharge gradient (formed by the accumulation of
their contents near the mouth of the protons on one side of the membrane),
archegonia. and ATP synthase (to utilize the proton
(Plant kingdom, Gymnosperm) gradient to produce ATP) are all necessary
components for chemiosmosis.
137. (1)
Sol. Algal blooms caused by an excess of
organic matter in water can lead to
eutrophication, which often results in a
decrease in water quality due to the
depletion of oxygen in the water, leading to
fish kills and other negative impacts on
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(+, 0) Commensalism : Commensalism is a
type of symbiotic relationship in which one
species benefits while the other species is
neither harmed nor benefited.
(–, 0) Amensalism : Neither species is
benefitted. One remains unharmed and the
other is harmed.
(+, –) Parasitism : Parasitism is a type of
(Respiration, Chemiosmosis) symbiotic relationship in which one
organism, the parasite, benefits at the
139. (2) expense of the other organism, the host.
Sol. M phase or mitosis is the phase where (Organisms and environment,
the actual cell division occurs. Mitosis is Population Interaction)
also called equational division.
During G2 phase DNA synthesis stops but 141. (2)
cell synthesis RNA, proteins, etc. for next Sol. Statement I refers to Gause's
phase. Quiescent stage is inactive phase in Competitive Exclusion Principle, which
which non-dividing cells enters. indeed states that two species competing
G1 phase is the interval between mitosis for the same resources cannot coexist
and initiation of DNA replication. indefinitely, and eventually, one will
Therefore, option (2) is correct. outcompete the other leading to
( Cell cycle and division, Stages of cell elimination.
cycle) Statement II is incorrect as in general,
herbivores and plants appear to be more
140. (1) adversely affected by competition than
Sol. (+, +) Mutualism : Mutualism is a type carnivores.
of symbiotic relationship in which both (Organisms and environment,
species involved benefit from the Gause's Competitive Exclusion
interaction. Both organisms receive some Principle)
form of advantage, such as food,
protection, or other resources. 142. (2)
Sol. Iron activates catalase enzyme.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Zinc plays a crucial role in the production are specialized pores or openings in the
of auxin. bark of woody plants, particularly in stems
Boron is essential for both cell elongation and branches, that allow for the exchange
and cell differentiation. of gases.
Molybdenum is component of nitrogenase Bark refers to periderm and secondary
and nitrate reductase enzyme. Therefore, phloem. Bark is a technical term that
option (2) is correct. encompasses all tissues exterior to the
(Mineral Nutrition, Role of minerals) vascular cambium in woody plants. This
includes the periderm, which is the outer
143. (2) protective tissue formed by the cork
Sol. Klinefelter's syndrome is caused due to cambium (phellogen), as well as the
the presence of an additional copy of secondary phloem, which is the tissue
X-chromosome resulting into a karyotype responsible for transporting sugars and
of 47, XXY. Such an individual has overall other nutrients produced by the leaves to
masculine development, however, the other parts of the plant.
feminine development is also expressed. Bark that is formed early in the season is
Such individuals are sterile. Thus, called early or soft bark. Towards the end
statement B and E are correct regarding of the season late or hard bark is formed.
Klinefelter's syndrome. Phellogen is couple of layers thick
Statement A, C and D are incorrect w.r.t. Therefore, only statement A and D are
Klinefelter’s syndrome as they are correct.
associated with Down’s syndrome. Down
syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a
genetic condition caused by the presence
of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
(Principles of Inheritance and
Variation, Chromosomal disorders in
humans)
144. (1)
Sol. Lenticels are the lens-shaped openings
permitting the exchange of gases. Lenticels
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Anatomy of plants, Secondary structure. Competitive inhibitors are often
growth) used in the control of bacterial pathogens.
(Respiration, TCA cycle)
145. (4)
Sol. The ribosome, which is the cellular 147. (4)
machinery responsible for protein Sol. Cohesion involves the mutual
synthesis, is composed of both ribosomal attraction among water molecules.
RNA (rRNA) and proteins.The ribosome Adhesion involves the attraction of water
consists of structural RNAs and about 80 molecules to other substances, particularly
different proteins. polar surfaces.
(Molecular basis of inheritance, Surface tension is the property of liquids
Translation) resulting from the cohesive forces between
molecules at the surface.
146. (4) Guttation is the process of water loss from
Sol. Option (4) is the correct answer to the leaves of plants in liquid form.
this question because malonate is a Thus, option (4) is correct.
competitive inhibitor of enzyme succinate (Transport in plants, Long distance
dehydrogenase. transport of water)
Succinic dehydrogenase is an enzyme
involved in the citric acid cycle (also known 148. (3)
as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid Sol. Pyruvate, which is formed by the
cycle) which occurs in the mitochondria of glycolytic catabolism of carbohydrates in
cells. This enzyme plays a crucial role in the the cytosol, after it enters mitochondrial
oxidation of succinate to fumarate, while matrix undergoes oxidative
simultaneously reducing ubiquinone to decarboxylation by a complex set of
ubiquinol. This step is important for the reactions catalyzed by pyruvate
generation of energy in the form of dehydrogenase.
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through The scheme of glycolysis was given by
oxidative phosphorylation. Gustav Embden, Otto Meyrhof and J.
Inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by Parnas, and is often referred to as the EMP
malonate occurs due to close resemblance pathway.
of malonate with substrate succinate in
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
In electron transport system, the energy of a plasmid) are both cut with the
oxidation-reduction is utilized for the same restriction enzyme.
production of proton gradient required for Restriction enzymes are proteins
phosphorylation, thus, this process is also that cut DNA at specific
called oxidative phosphorylation. recognition sequences.
The TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle) starts Isolation of desired DNA fragment (C)
with the condensation of acetyl group with ● Following the enzymatic digestion,
oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and water to yield the desired DNA fragment
citric acid. The reaction is catalysed by the containing the gene of interest is
enzyme citrate synthase. Thus, option (3) is isolated from the mixture. This is
correct. often done using techniques such as
(Respiration, TCA cycle and ETS) gel electrophoresis, which separates
DNA fragments based on size,
149. (4) allowing the specific fragment to be
Sol. A flower is a modified shoot wherein identified and extracted.
the shoot apical meristem changes to floral Amplification of gene of interest using PCR
meristem. Internodes do not elongate and (Step D):
the axis gets condensed. The apex ● Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
produces different kinds of floral is a technique used to amplify
appendages laterally at the successive specific DNA sequences.
nodes instead of leaves. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the
Therefore, both A and R are true and R is host cell (Step A):
correct explanation of A. ● Once the gene of interest has been
(Morphology of plant, Flower) amplified and isolated, it is inserted
into the host cell. This is typically
150. (4) achieved by ligating (joining) the
Sol. The correct answer is option (4) gene of interest into a vector, such
because as a plasmid, that has been cut with
Cutting of DNA at specific location by the same restriction enzyme.
restriction enzyme (Step B): Hence, transferring the recombinant DNA
● In this step, the DNA containing the into the host, culturing the host cells in a
gene of interest and a vector (often
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
medium at large scale and extraction of the technique in India and is not a strategy of
desired product. RCH.
(Principles and process of
biotechnology, Steps involved in (Reproductive health, RCH and
recombinant DNA technology) Amniocentesis)
SECTION-A
153. (4)
151. (3)
Sol. A leopard and a lion in a
Sol. The correct answer is option (3) as
forest/grassland exemplify competition
first menstrual cycle that begins at puberty
where both the species are competing for
is called menarche.
the same resources.
Cyclic menstruation is an indicator of
A cuckoo laying egg in a crow’s nest is
normal reproductive phase and extends
brood parasitism where cuckoo is the
between menarche and menopause.
parasitic bird that lays its egg in the nest of
In primates, cyclical changes during
crow (host bird).
reproduction are called menstrual cycle.
Fungi and root of a higher plant in
(Human reproduction, Menstrual
mycorrhizae exemplify mutualism where
Cycle)
both the species are benefitted. The fungi
help the plant in the absorption of essential
152. (3)
nutrients from the soil while the plant in
Sol. The correct choice is option (3)
turn provides the fungi with energy yielding
because the 'Reproductive and Child
carbohydrates.
Health Care (RCH) programme' primarily
A cattle egret and a cattle in a field
focuses on educating individuals about
exemplify commensalism where one
various aspects related to reproduction
species benefits and the other remains
and providing resources and assistance to
unaffected.
promote a healthy reproductive society.
The egrets always forage close to where
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure cattle are grazing because the cattle, as
utilized to detect certain genetic disorders, they move, stir up and flush out insects
such as Down syndrome and hemophilia, from the vegetation that otherwise might
to assess the viability of the fetus. be difficult for the egrets to find and catch.
Amniocentesis is not a sex determination
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
(Organisms and environment, during normal breathing,
Population Interaction) without any extra effort.
● It represents the typical
154. (3) amount of air moved in and
Sol. Option (3) is the correct answer out of the lungs with each
because vital capacity is the maximum breath.
volume of air a person can breathe in after
forced expiration. This includes ERV, TV and IRV.
(Respiration in Human, Respiratory
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): volumes)
● Inspiratory reserve volume
is the additional volume of 155. (1)
air that can be inhaled Sol. The correct answer is option (1)
forcefully after a normal because except for hepatitis-B, genital
inhalation. herpes and HIV infection other STIs are
● It represents the maximum completely curable if detected early and
amount of air that can be treated properly.
inspired beyond the tidal Gonorrhoea is caused by the bacterium
volume. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and can be
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): effectively treated with antibiotics. Early
● Expiratory reserve volume detection and prompt treatment can lead
is the additional volume of to a complete cure of the infection. Other
air that can be exhaled diseases mentioned are viral diseases.
forcefully after a normal (Reproductive health, STDs)
exhalation.
● It represents the maximum 156. (4)
amount of air that can be Sol. The correct answer is option (4) as
expired beyond the tidal • Cholecystokinin (CCK) acts on
volume. both gall bladder and pancreas and
Tidal Volume (TV): stimulates the secretion of bile juice and
● Tidal volume is the volume pancreatic enzymes respectively.
of air inspired or expired
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
• GIP inhibits gastric secretion and inflammatory condition of the lung
motility. primarily caused by bacteria.
• Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF) is (Human health and disease, Diseases
released from the atrial wall of our heart. in humans and their causative
• Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) acts organism)
mainly on the kidney and stimulates
resorption of water and electrolytes by the
distal tubules.
(Human physiology, Hormones and 158. (4)
their role) Sol. The correct answer is option (4) as in
a standard ECG, P-wave represents the
157. (4) electrical excitation (or depolarisation) of
Sol. Option (4) is the correct answer the atria which leads to the contraction of
because: both the atria.
(i) Ringworm is caused by • QRS complex represents the
Trichophyton. Ringworm is a common depolarisation of ventricles which initiates
fungal infection of the skin, hair, or nails, the ventricular contraction.
caused by various species of fungi known as • T-wave represents the return of the
dermatophytes. ventricles from excited to normal state.
(ii) Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria
bancrofti. Wuchereria bancrofti is one of
the major causative agents of lymphatic
filariasis, a condition characterized by the
obstruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to
swelling and inflammation.
i(iii) Malaria is caused by Plasmodium
species. Malaria is a mosquito-borne
infectious disease caused by protozoan (Body fluids and circulation, ECG)
parasites of the genus Plasmodium.
(iv) Pneumonia is caused by 159. (4)
Haemophilus influenzae. Pneumonia is an Sol. The human immunodeficiency virus
(HIV) primarily targets and replicates
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
within T-helper cells (also known as CD4+ not classified as dense regular tissue.
T cells or TH cells). The progeny viruses Therefore Statement II is also incorrect.
released into blood attack other helper (Structural Organisation in Animals,
lymphocytes. Ligaments)
Therefore, the correct answer is: (4) TH
cells 162. (1)
( Human health and disease, HIV)
The endomembrane system includes
160. (4) various membrane-bound organelles
Sol. The correct answer is option (4) as involved in the synthesis, processing, and
low temperature preserves the enzyme in transport of proteins and lipids within the
a temporarily inactive state whereas high cell. These organelles include the
temperature destroys enzymatic activity endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi
because proteins are denatured by heat. complex, lysosomes, and vesicles.
Competitive inhibitor due to its close Mitochondria and chloroplasts, on the
structural similarity with the substrate, other hand, are not part of the
competes with the substrate for the endomembrane system as they are
substrate-binding site of the enzyme. semi-autonomous organelles involved in
(Biomolecules, Enzymes) energy production (mitochondria) and
photosynthesis (chloroplasts), respectively.
161. (1) Peroxisomes, although involved in various
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer metabolic processes, are also not
because Ligaments are fibrous bands of considered part of the endomembrane
tissue that connect bones to other bones, system.
providing stability and strength to joints.
Ligament is an example of dense regular Therefore, the organelles NOT considered
connective tissue so Statement I is as part of the endomembrane system are:
incorrect and Cartilage is not composed of
A. Mitochondria
dense regular tissue. Cartilage is a
C. Chloroplasts
specialized type of connective tissue that is
E. Peroxisomes
characterized by a firm, flexible matrix
(Cell, Endomembrane system)
containing collagen and elastic fibers. It is
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
thalassemia primarily involve symptoms
163. (3) related to anaemia, such as pale skin,
Sol. The correct answer is option (3) as a fatigue, and shortness of breath.
protein is imagined as a line, the left end (Principles of Inheritance and
represented by the first amino acid and the Variation, Chromosomal disorders in
right end is represented by the last amino humans)
acid. The first amino acid is also called
N-terminal amino acid. The last amino acid 165. (1)
is called the C-terminal amino acid. Sol. Increase in the concentration of the
The correct composition of adult human toxicant at successive trophic levels is
hemoglobin is two α-globin chains and two called biomagnification.
β-globin chains. Large amount of nutrients in water
(Biomolecules, Protein) promotes the growth of algal blooms. Algal
bloom increases fish mortality.
164. (4) Eutrophication refers to the natural ageing
Sol. Down’s syndrome is caused by an of a lake by nutrient enrichment of its
additional copy of chromosome number water.
21. Its symptoms include– (Environmental issues,
a. Broad palm with characteristic palm Eutrophication)
crease
b. Short statured with small round 166. (2)
head Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer
c. Furrowed tongue and partially open because protonephridia or flame cells are
mouth, etc. the excretory structures in
Turner's syndrome is a genetic condition platyhelminthes. Nephridia are the tubular
that occurs in females when one of the X excretory structures of earthworms
chromosomes is missing. Klinefelter's (Pheretima) and other annelids. Single
syndrome is a genetic condition in males celled organisms like Paramoecium have
that results from an extra X chromosome, contractile vacuoles for excretion. Urecose
leading to XXY chromosome configuration glands are present in cockroach.
instead of the typical XY configuration. The (Excretory products and their
physical features associated with elimination, Modes of excretion)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
● Statement II: The cavity of the
167. (2) cervix is indeed called the cervical
Sol. Electrostatic precipitator is most canal, and along with the vagina, it
widely used in thermal power plants. They forms the birth canal. This is part of
are commonly employed to remove the female reproductive system.
particulate matter (such as dust and ash) (Human reproduction, Reproductive
from the flue gas emitted by combustion organs of males and females)
processes in power plants. This helps to
reduce air pollution and comply with 169. (1)
environmental regulations. However, Sol. Option (1) is accurate because
electrostatic precipitators do not remove hemichordates exhibit bilateral symmetry.
ionizing radiation. Instead, they are Option (2) is incorrect since coelenterates
designed to remove solid particles from gas demonstrate radial symmetry.
streams using electrostatic forces. Option (3) is also incorrect as adult
It can remove over 99 percent particulate echinoderms typically display radial
matter present in the exhaust from a symmetry.
thermal power plant. Option (4) is likewise incorrect because
(Environmental issues, Electrostatic ctenophores are known for their radial
precipitator) symmetry.
168. (4)
Sol. Both Statement I and Statement II are
true.
Explanation:
● Statement I: Vas deferens does
indeed receive a duct from the ( Animal Kingdom, Types of
seminal vesicle and opens into the Symmetry)
urethra as the ejaculatory duct.
This is part of the male 170. (2)
reproductive system.
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer helps maintain the shape of the eye.
because gastric glands contain three main Composed primarily of dense connective
types of cells: tissue, the sclera provides protection for
(i) Mucus neck cells, responsible for the delicate internal structures of the eye.
secreting mucus. (Neural control and coordination,
(ii) Peptic or chief cells, which secrete the Eye)
proenzyme pepsinogen.
(iii) Parietal or oxyntic cells, which secrete 172. (2)
hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor Sol. The complex system of filamentous
for the absorption of vitamin B12. protein structures made up of
(Digestion and absorption, Alimentary microtubules, microfilaments, and
canal and digestive glands) intermediate filaments found within the
cytoplasm is known as the cytoskeleton. It
171. (4) plays various roles including providing
Sol. Option (4) is the correct answer mechanical support, enabling cellular
because movement, and maintaining cell shape.
(i) Fovea is the point of greatest visual ( Cell, Cytoskeleton)
acuity or resolution.
(ii) Iris is the visible coloured portion 173. (1)
of the eye that regulates diameter of pupil. Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer
(iii) Blind Spot: The blind spot, also because the undigested food (faeces)
known as the optic disc, is the point on the enters into caecum of the large intestine
retina where the optic nerve exits the eye through ileo-caecal valve, which prevents
and where photoreceptor cells (rods and the backflow of the faecal matter.
cones) are absent. This area lacks Option (2) is not the answer because a
photoreceptor cells because it's where the muscular sphincter i.e., the
optic nerve fibers converge to form the gastro-oesophageal sphincter regulates the
optic nerve, which carries visual opening of oesophagus into the stomach.
information from the retina to the brain. Option (3) is not the answer because
(iv) The sclera is the tough, fibrous, pyloric sphincter regulates the opening in
white outer layer of the eye. It forms the between stomach and duodenum.
structural framework of the eyeball and
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Option (4) is not the answer because the between the adjacent vertebrae in the
opening of common hepato-pancreatic vertebral column.
duct is guarded by sphincter of Oddi. Option (2) is incorrect because
(Digestion and absorption; cartilaginous joint is not present between
Alimentary canal and digestive flat skull bones.
glands) Option (3) is incorrect because fibrous
joint is absent in between the carpal and
174. (1) metacarpal of thumb.
Sol. (i) Vasectomy is indeed a surgical Option (4) is not the answer because
method of contraception involving the saddle joint is not present in between
cutting or blocking of the vas deferens to humerus and pectoral girdle.
prevent the passage of sperm. (Locomotion and Movement, Types
(ii) Coitus interruptus, also known as the of Joints)
withdrawal method, is indeed a natural
method of contraception where ejaculation 176. (4)
is intentionally interrupted before Sol. RNA, being less stable than DNA,
ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering undergoes mutations at a faster rate.
the vagina. Viruses with RNA genomes have shorter
(iii) The cervical cap is indeed a barrier life spans and mutate more rapidly as a
method of contraception, consisting of a result. This rapid mutation allows RNA
small, thimble-shaped device made of viruses to evolve quickly, leading to the
silicone that fits over the cervix to prevent emergence of new strains with altered
sperm from entering the uterus. characteristics, which can impact human
(iv) Saheli is indeed an oral method of health and necessitate continuous
contraception, specifically a non-steroidal monitoring and adaptation of control
pill designed to prevent pregnancy. strategies.
( Reproductive health, Birth (Molecular basis of inheritance, RNA)
control-Need and Methods)
177. (3)
175. (1) Sol. In prokaryotes, such as bacteria, the
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer genetic material consists of a single circular
because cartilaginous joint is present in chromosome located in the nucleoid
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
region. This DNA molecule, which carries Sol. The symbol representing mating
the organism's genetic information, is between relatives (consanguineous mating)
negatively charged due to the phosphate in human pedigree analysis is
groups in its backbone. Within the
nucleoid, the negatively charged DNA is
bound by various positively charged (Heredity and variation, Pedigree
proteins, though it lacks a true analysis)
membrane-bound nucleus.
In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA 179. (1)
is wrapped around the positively charged Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer
histone octamer to form a structure called because numbat, spotted cuscus and flying
nucleosome. The DNA wraps around the phalanger are Australian marsupials
histone octamer in approximately 1.65 exhibiting adaptive radiation. Adaptive
turns, forming a "bead on a string" radiation is a process in evolutionary
structure. This packaging not only biology where a single ancestral species
condenses the DNA to fit within the rapidly diversifies into a wide variety of
confines of the nucleus but also provides a forms, each adapted to a specific
mechanism for regulating gene expression environment or niche.
and accessing the genetic information Option (2) is incorrect because mole and
stored within the DNA. flying squirrel are placental mammals.
Option (3) is incorrect because lemur and
wolf are placental mammals. Placental
mammals are a diverse group of mammals
characterized by the presence of a
placenta, a specialized organ that allows for
the exchange of nutrients and waste
between the mother and the developing
offspring.
Option (4) is incorrect because bobcat is a
(Molecular basis of inheritance, DNA
placental mammal.
Packaging)
( Evolution, Adaptive radiation)
178. (1)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
180. (3) Morphine which is also derived from the
Sol. Option (3) is correct answer because a opium poppy plant is used is a sedative and
single stranded DNA or RNA tagged with painkiller.
a radioactive molecule is called a probe and (Human Health and Disease, Drugs
it helps in the detection of mutated gene. and their sources)
Option (1), (2) and (4) are not correct
because YAC, BAC, pBR322 are vectors. 182. (1)
YAC (Yeast Artificial Chromosome): YACs Sol. The correct answer is option (1)
are vectors derived from the DNA of yeast because using conventional methods of
cells, typically Saccharomyces cerevisiae. diagnosis like serum and urine analysis, etc,
BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome): do not help in early diagnosis. Recombinant
BACs are vectors derived from bacterial DNA technology, Polymerase Chain
plasmids, such as the F plasmid of Reaction [PCR] and Enzyme Linked
Escherichia coli. Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) are some
pBR322 is one of the earliest and most of the techniques that serve the purpose of
well-known plasmid vectors used in early diagnosis. PCR relies on the repeated
molecular biology. cycles of DNA denaturation, annealing of
(Biotechnology: Principles and primers, and extension by DNA
Processes, Types of vector) polymerase to exponentially replicate a
target DNA sequence. ELISA involves the
181. (4) binding of target proteins or antibodies to
Sol. The correct answer is option (4) as a solid surface (e.g., microplate wells)
• Heroin derived from opium poppy followed by the addition of
plant belongs to the category of opioids enzyme-conjugated detection reagents. The
and it is a depressant that slows down enzymatic reaction generates a measurable
body functions. signal, typically colorimetric or fluorescent,
• Marijuana derived from the which indicates the presence and quantity
Cannabis plant is known for its effect on of the target molecule.
the cardiovascular system of the body. (Biotechnology and Its Applications,
• Cocaine derived from the coca ELISA)
plant interferes with the transport of the
neurotransmitter dopamine. 183. (1)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer 185. (2)
because both Assertion and Reason are Sol. The accurate response is choice (2)
true. due to the fact that the Assertion is valid,
Implantation is embedding of the blastocyst given the existence of two distinct types of
into endometrium of uterus. Correct nephrons—cortical nephrons and
explanation of reason is juxtamedullary nephrons—distinguished by
Corpus luteum secretes a large amount of their locations within the cortex and
progesterone which is essential for medulla. However, the Reason is incorrect,
maintenance of endometrium of uterus. In as the loop of Henle in juxtamedullary
absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum nephrons is notably elongated and extends
degenerates hence the decrease in the deeply into the medulla. Hence, while the
level of progesterone hormone will cause Assertion is correct, the Reason is
disintegration of endometrium leading to inaccurate.
menstruation. (Excretory Products and Their
(Human Reproduction, Menstrual Elimination, distinct types of
Cycle) nephrons)
SECTION-B
184. (1) 186. (1)
Sol. In a lac operon, Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer
Gene a codes for enzyme transacetylase. because anal styles are present in male
Gene y codes for enzyme permease. cockroaches and absent in female
Gene i codes for repressor protein cockroaches.
Gene z codes for enzyme -galactosidase. Option (2), (3) and (4) are not the correct
answers because sclerites, anal cerci and
dark brown body colour are common
features of both male and female
cockroaches.
(Structural Organisation in Animals,
Difference between male and female
(Molecular Basis of Inheritance, Lac cockroaches)
Operon)
187. (1)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. Tetrad formation occurs during the proliferate unless called on to do so
zygotene stage. depending on the requirement of the
During anaphase, the centromeres divide, organism.
leading to the separation of chromatids. In animal cells, during the S-phase, DNA
The terminalization of chiasmata occurs replication begins in the nucleus, and the
during diakinesis. centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm.
During telophase, the nucleolus, Golgi (Cell cycle and division, S-phase)
complex, and endoplasmic reticulum are
reassembled. 190. (3)
Crossing over occurs between non-sister Sol. Option (3) is the correct answer
chromatids of homologous chromosomes. because decreasing the productivity of
(Cell cycle and division, Prophase 1) inbred population is not an advantage of
inbreeding.
188. (1) Options (1) and (2) are not the answers
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer because they are the advantages of
because statements B, C and D are true inbreeding.
statements. ADH facilitates water Option (4) is an incorrect statement.
reabsorption from DCT of nephron to (Strategies for Enhancement in Food
prevent diuresis, which causes increase in Production, advantage of inbreeding)
blood pressure. ANF which is secreted by
the heart is a vasodilator. 191. (4)
Options (2), (3) and (4) are not correct Sol. Logistic growth occurs when there is
because statements A and E are false. limited resource availability condition.
Excessive loss of body fluid from the body Exponential growth occurs when there is
switches on the osmoreceptors. unlimited resource availability condition.
(Excretory Products and Their Expanding age pyramid reflects growing
Elimination, Role of hormones in population where the percent individuals of
excretion) pre-reproductive age is largest followed by
reproductive and post-reproductive age
189. (3) groups.
Sol. Cells in the G0 stage remain Stable age pyramid shows stable population
metabolically active but no longer where the percent individuals of
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
pre-reproductive and reproductive age Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer
group are same. because statements B and C are only
(Organisms and Populations, Pyramid correct statements while A and D are
of age) incorrect statements.
Muscle bundles are held together by
192. (2) collagenous connective tissue layer called
Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer fascia. Muscle bundles are called fascicles.
because thyroid hormones play an The portion of the myofibril between two
important role in the regulation of basal successive ‘Z’ lines is considered as
metabolic rate, maintenance of water and functional unit of contraction called
electrolyte balance and support the sarcomere.
process of RBCs formation, whereas this (Locomotion and Movement, Muscle
hormone is not involved in regulating bundles)
normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle and
development of immune system. 195. (2)
Sol. Option (2) is the answer because,
193. (1) basophils secrete histamine, serotonin,
Sol. Option (1) is correct answer because heparin etc. and are involved in
presence of hairs, pinna and mammary inflammatory response.
glands are unique features of mammals. Option (1) is not the answer because,
Options (2), (3) and (4) are not correct basophils are granulocytes.
because, monocondylic skull is present in Option (3) is not the answer because,
reptiles and aves whereas mammals have neutrophils are the most abundant cells
dicondylic skull. Tympanic membrane is (60–65 %) of the total WBCs whereas
present in amphibians also, so it is not basophils are least (0.5–1%) abundant of all
considered as unique feature. WBCs.
Indirect development is not seen in Option (4) is not the answer because,
mammals. monocytes have a kidney-shaped nucleus.
(Animal Kingdom, Features of (Body Fluids and Circulation, Various
Mammals) Blood cells and their functions)
194. (1) 196. (2)
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
Sol. The sequence of coding strand is same 198. (2)
as RNA except thymine at the place of Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer
uracil. Template strand because,
3’-TAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCTAGCT ● Areolar connective tissue
AGC-5’ comprises fibroblasts (which generate and
Coding strand 5’-ATCGATCGATCG discharge fibers), macrophages, and mast
ATCGATCGATCGATCG-3’ cells.
Transcription mRNA 5’
AUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCG ● The interior lining of bronchioles
AUCG 3’ consists of ciliated epithelium.
(Molecular Basis of Inheritance, ● Blood is a specialized type of
Transcription) connective tissue.
● The tubular segments of the
197. (4) nephron are covered by cuboidal
Sol. Option (4) is the correct answer epithelium.
because limbic system along with (Structural Organisation in Animals,
hypothalamus regulate the sexual Connective Tissue)
behaviour, expression of excitement,
pleasure, rage, fear, etc. 199. (2)
Option (1), (2) and (3) are not correct Sol. Option (2) is the answer because,
because corpora quadrigemina is a part of In cockroach, excretion is brought about
the midbrain and consists of four round by Malpighian tubules, fat body,
swellings. Corpus callosum is a tract of nephrocytes and urecose glands.
nerve fibres that connects right and left Urecose glands are present in male
cerebral hemispheres. Thalamus is a major cockroach of some species. They
coordinating centre in the forebrain for synthesise uric acid. Nephrocytes are large,
sensory and motor signalling. Midbrain, colourless, ovoid, binucleate cells attached
pons and medulla oblongata together form to the dorsal diaphragm in the body cavity.
the brain stem. Fat body accumulates, produces and stores
(Neural Control and Coordination, uric acid.
Parts of Brain) Phallic gland is the structure of male
reproductive system of cockroach and it
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
secretes the outer layer of spermatophore. three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm,
Collaterial gland is the structure of female and mesoderm and coelomate.
reproductive system of cockroach and it (Animal Kingdom, Features of
secretes the hard egg-case or ootheca Chordates)
around fertilised eggs.
(Structural Organisation in Animals,
cockroach)
200. (1)
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer
because statements B and C only are
correct. Option (2), (3) and (4) are not
correct. The chordate characters are
presence of closed circulatory system and
presence of pharyngeal gill slits. Chordates
typically exhibit paired pharyngeal gill slits,
which are openings in the pharynx (throat
region) that connect the pharynx to the
outside environment. In many chordates,
these gill slits are involved in respiration,
allowing water to flow through them,
enabling gas exchange (oxygen uptake and
carbon dioxide release). While in some
chordates, such as fish, gill slits are retained
throughout life, in others, they may be
present only during embryonic
development before transforming into
other structures. Nerve cord is dorsal,
hollow and single. Heart is ventral.
Chordates are triploblastic organisms,
meaning their bodies are composed of
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
*Install the MemoNeet Mobile App to scan your OMR sheet
*To get the detailed Test Paper Analysis and solution by Top Subject
Matter Experts, Scan this QR and subscribe to the MemoNeet-Official
YouTube channel.
(Analysis will only be available after the test is done).
MemoNeet-NCERT Line By Line-Brahmastra Test Series
You might also like
- E400 User GuideDocument24 pagesE400 User Guideleonardo.maximiliano.salasNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 21 Paper Key (02-05-2023)Document8 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 21 Paper Key (02-05-2023)vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Test 8 Solution Superfinal 8 FebDocument15 pagesTest 8 Solution Superfinal 8 Febabhi SinghNo ratings yet
- NEET Key - 05Document15 pagesNEET Key - 05oraclepucollegecptNo ratings yet
- GT-1 KeyDocument14 pagesGT-1 KeyThamizharuvi. ANo ratings yet
- Mock Test-10 (200mcqs) SolDocument9 pagesMock Test-10 (200mcqs) SolMohammed FaizanNo ratings yet
- 20190705142956134KEYS JUNE 2019 Mathematical SciencesDocument3 pages20190705142956134KEYS JUNE 2019 Mathematical Sciencesms2sl4No ratings yet
- AnsKEYS JUNE 2019 Mathematical SciencesDocument3 pagesAnsKEYS JUNE 2019 Mathematical SciencesSaumya MishraNo ratings yet
- Nurture Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDocument8 pagesNurture Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeRebanta BeraNo ratings yet
- CSIR DEC 2015 Maths Ans KeyDocument3 pagesCSIR DEC 2015 Maths Ans KeySunanda VinodNo ratings yet
- Final Common Neet Grand Test-04 Key Paper Ex - DT-22-04-2024Document8 pagesFinal Common Neet Grand Test-04 Key Paper Ex - DT-22-04-2024lavendar31selenNo ratings yet
- Booklet Code: A - (Bilingual and English) : Joint Csir-Ugc-Jrf/Net June, 2018 Answer Key Subject: Mathematical SciencesDocument3 pagesBooklet Code: A - (Bilingual and English) : Joint Csir-Ugc-Jrf/Net June, 2018 Answer Key Subject: Mathematical SciencesSourav BijlwanNo ratings yet
- Milestone Test 06 ROI Phase 2 Class 11th NEET 31 12 2023 SolutionDocument5 pagesMilestone Test 06 ROI Phase 2 Class 11th NEET 31 12 2023 Solutionmraarush2700xNo ratings yet
- SR Neet Co Ut-1 Key DT 06-06-2022Document16 pagesSR Neet Co Ut-1 Key DT 06-06-2022Vikranth TNo ratings yet
- MathkeyRep Dec2018 PDFDocument3 pagesMathkeyRep Dec2018 PDFSudha SagarNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys of Joint Csir-Ugc Test For Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and Eligibility For Lectureship (Net) Held On 16-12-2018Document3 pagesAnswer Keys of Joint Csir-Ugc Test For Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and Eligibility For Lectureship (Net) Held On 16-12-2018lakshita goyalNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning Programme: Test Syllabus: Half Syllabus (11 Class Syllabus)Document4 pagesDistance Learning Programme: Test Syllabus: Half Syllabus (11 Class Syllabus)Kamlesh NishadNo ratings yet
- Sec: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Neet Model Date: 30-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Grand Test-4 Max. Marks: 720MDocument9 pagesSec: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Neet Model Date: 30-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Grand Test-4 Max. Marks: 720MAyan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Question No. Key Question No. Key Question No. Key: Change Indicated in BoldDocument3 pagesQuestion No. Key Question No. Key Question No. Key: Change Indicated in BoldBhupi.SamNo ratings yet
- File 9Document5 pagesFile 9ShrutheeNo ratings yet
- Solution Report 27Document8 pagesSolution Report 27dudecool713713No ratings yet
- MOCK TEST-2 (200MCQS) Answers and SolDocument8 pagesMOCK TEST-2 (200MCQS) Answers and SolAshok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Leader & Achiever CourseDocument7 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Leader & Achiever CoursealeemhakNo ratings yet
- Leader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDocument4 pagesLeader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeSurendra BaniyaNo ratings yet
- NEET GT-2 KeyDocument8 pagesNEET GT-2 Keyabcxyz7799No ratings yet
- Test Series Paper - 11 (Answer Key) : Chemistry Physics Zoology BotanyDocument8 pagesTest Series Paper - 11 (Answer Key) : Chemistry Physics Zoology Botanykashish joshiNo ratings yet
- Allen Aiims Test Answers 3-03-2019Document7 pagesAllen Aiims Test Answers 3-03-2019Subhan NasirNo ratings yet
- Actual CLAT 2015: Answer KeyDocument6 pagesActual CLAT 2015: Answer KeyManasvi KuchuruNo ratings yet
- Set A Key: Change in Key Indicated in Bold Benefit of Marks To Those Who AttemptedDocument3 pagesSet A Key: Change in Key Indicated in Bold Benefit of Marks To Those Who AttemptedDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- NEET GT-13 KeyDocument20 pagesNEET GT-13 Keyabcxyz7799No ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: Key Sheet MathematicsDocument1 pageSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: Key Sheet MathematicsVaishakNo ratings yet
- Booklet Code: A - (Bilingual and English)Document3 pagesBooklet Code: A - (Bilingual and English)SrikantjNo ratings yet
- CTET Paper - 1 Unofficial Answer Key (Series - L) Child Development & Pedagogy Mathematics Environmental Studies English Lang-1 Hindi Lang-2Document1 pageCTET Paper - 1 Unofficial Answer Key (Series - L) Child Development & Pedagogy Mathematics Environmental Studies English Lang-1 Hindi Lang-2eshwariNo ratings yet
- AITS-07 Dropper NEET Evening 09-04-2023 SolutionsDocument15 pagesAITS-07 Dropper NEET Evening 09-04-2023 Solutionshemagowda2132005No ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India.: Neet Weekend Test - 12 KeyDocument6 pagesSri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India.: Neet Weekend Test - 12 KeyMohd AdilNo ratings yet
- Answer Key 17-04-2024 Major Test-01Document5 pagesAnswer Key 17-04-2024 Major Test-01DivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Leader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDocument8 pagesLeader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDjNo ratings yet
- Important Zoology SolutionDocument8 pagesImportant Zoology SolutionBISWADIP SASMALNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-02 Arjuna NEET (2025) 09.06.2024 SolutionsDocument15 pagesPractice Test-02 Arjuna NEET (2025) 09.06.2024 Solutionskenyen.jarekNo ratings yet
- TRT SGT TM Pre KeyDocument4 pagesTRT SGT TM Pre KeysekkharNo ratings yet
- Pre - Medical: Test Type: MINOR Test Pattern: NEET (UG)Document6 pagesPre - Medical: Test Type: MINOR Test Pattern: NEET (UG)nabarunNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya: IIT Academy.,IndiaDocument2 pagesSri Chaitanya: IIT Academy.,IndiaPAINT DIAMOND GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Allen Rank Booster Test 02 SolDocument8 pagesAllen Rank Booster Test 02 Solscifi techNo ratings yet
- XI NEET NR FT-02 DT. 03-07-2023 - Key&SolDocument14 pagesXI NEET NR FT-02 DT. 03-07-2023 - Key&Solazmath pkNo ratings yet
- Sub: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Date: 12-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Neet Pt-03 Max. Marks: 720Document10 pagesSub: SR Bipc (Chaina & Elite) Date: 12-01-2019 Time: 3 Hrs Neet Pt-03 Max. Marks: 720Shivalgiri GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 24.03.19 - SR Aiims S 60 & Neet MPL - Neet PT-3 - Key & SolutionsDocument4 pages24.03.19 - SR Aiims S 60 & Neet MPL - Neet PT-3 - Key & SolutionssiddhantaNo ratings yet
- Solutions - AIATS Medical-2019 (XII Passed) - Test-4 - (Code-E & F) - (20-01-2019) - 0 PDFDocument30 pagesSolutions - AIATS Medical-2019 (XII Passed) - Test-4 - (Code-E & F) - (20-01-2019) - 0 PDFTanishq Verma100% (1)
- NEET GT-5 SolutionsDocument12 pagesNEET GT-5 Solutionsabcxyz7799No ratings yet
- Solutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XII Passed) Test-4 - (Code-E & F) - (12-01-2020)Document32 pagesSolutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XII Passed) Test-4 - (Code-E & F) - (12-01-2020)rajNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series (NEET-2023)Document12 pagesAll India Test Series (NEET-2023)Jatin MoolchandaniNo ratings yet
- Leader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDocument7 pagesLeader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning Programmekhushal_bhavsar26No ratings yet
- Final Answer Keys of Joint Csir-Ugc Test For Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and Eligibility For Lectureship (Net) Held On 16-12-2018Document3 pagesFinal Answer Keys of Joint Csir-Ugc Test For Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and Eligibility For Lectureship (Net) Held On 16-12-2018nagalaxmi manchalaNo ratings yet
- TS TET Paper 2 Maths Sceince EM - HMDocument4 pagesTS TET Paper 2 Maths Sceince EM - HMnishatNo ratings yet
- December Answer NETDocument3 pagesDecember Answer NETSonuNo ratings yet
- Answers: T Est - 2Document7 pagesAnswers: T Est - 2Ayushi MittalNo ratings yet
- Full Syllabus: Test Paper No-02 by Dr. Rishabh Choubey SirDocument13 pagesFull Syllabus: Test Paper No-02 by Dr. Rishabh Choubey Sirdigvijay singhNo ratings yet
- NCERT Based Test Series 2024 Test - 1 Solution - (NCERT Based) - 3Document19 pagesNCERT Based Test Series 2024 Test - 1 Solution - (NCERT Based) - 3Arsaniya KumariNo ratings yet
- Solutions - AIATS Medical-2016 Test-08 - (Code-A & B)Document19 pagesSolutions - AIATS Medical-2016 Test-08 - (Code-A & B)gnkstarNo ratings yet
- Some Proof Which I Verified With Facts About Neet Paper Leake and Some QuestionsDocument2 pagesSome Proof Which I Verified With Facts About Neet Paper Leake and Some QuestionsshivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Neet Questions 2025 Leaks (Download Fast)Document1 pageNeet Questions 2025 Leaks (Download Fast)shivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Concept - 1 Co-Ordinate of A Point Space, Division RuleDocument12 pagesConcept - 1 Co-Ordinate of A Point Space, Division RuleshivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Appointment Letter Hb164781Document2 pagesAppointment Letter Hb164781shivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsshivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Edu GeniusDocument2 pagesEdu GeniusshivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Regd NoDocument1 pageRegd NoshivaysinghrajputofficialNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam: College of Architecture, Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 pagesQualifying Exam: College of Architecture, Engineering and TechnologyLance CastilloNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure and Heat of Vaporization (Solved)Document5 pagesVapor Pressure and Heat of Vaporization (Solved)Arhaan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- HW4 1Document4 pagesHW4 1smkeshkamatNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument22 pagesPressure Measurement21UME003 TUSHAR DEBNo ratings yet
- Physics ExamDocument19 pagesPhysics ExamAji Nikka AngelesNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws - TEST 1Document8 pagesNewton's Laws - TEST 1ThabeloNo ratings yet
- Cable Mv2009Document53 pagesCable Mv2009Yulian Dea ZollaNo ratings yet
- BS 7591-1-1992 - (2020-12-09 - 03-49-15 PM)Document16 pagesBS 7591-1-1992 - (2020-12-09 - 03-49-15 PM)benderman1No ratings yet
- Takamisawa Sy 24w K PCB Mount Relay 24vdc 1 Co SPDT Sy 24w K Data SheetDocument5 pagesTakamisawa Sy 24w K PCB Mount Relay 24vdc 1 Co SPDT Sy 24w K Data Sheetremon thereminNo ratings yet
- GCSE Current and Charge AnswersDocument2 pagesGCSE Current and Charge AnswersLakhan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2007bDocument1 pageFinal Exam 2007bchetanNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know: System of MeasurementDocument9 pagesWhat I Need To Know: System of Measurementzest ishuriNo ratings yet
- Calibration Certificate For UTMDocument2 pagesCalibration Certificate For UTMraja qammar100% (1)
- Exp1 SheetDocument6 pagesExp1 SheetMajdy gamingNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Manual PDFDocument12 pagesMetrology Lab Manual PDFBollu Satyanarayana0% (1)
- Print Section 1 Yamatake SFC For DSTJ TransmittersDocument4 pagesPrint Section 1 Yamatake SFC For DSTJ TransmittersaloordominicNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws and Specific Heat Capacity PracticeDocument3 pagesGas Laws and Specific Heat Capacity PracticeEsther ParNo ratings yet
- Mahr Federal XR1 Surface Roughness Bench TypleDocument28 pagesMahr Federal XR1 Surface Roughness Bench TypleBhavesh Santosh MhaskarNo ratings yet
- Rotational DynamicsDocument78 pagesRotational DynamicsAryA JackNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics by Akansha Karnwal - WatermarkDocument1 pageThermodynamics by Akansha Karnwal - Watermarktechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- BAM-S10-07 CO2 in Beer in Bulk - Zahm Nagel - Feb99aDocument10 pagesBAM-S10-07 CO2 in Beer in Bulk - Zahm Nagel - Feb99aRiyanNo ratings yet
- Per Phase Cable Schedule (Voltage Drop) - Excel FileDocument8 pagesPer Phase Cable Schedule (Voltage Drop) - Excel FileAhmed AboelgoodNo ratings yet
- 01 NWML STA GuidanceDocument10 pages01 NWML STA GuidanceBima SaktiNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Practical ManualDocument24 pages11th Physics Practical ManualAmol MahajanNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0Document21 pagesUtkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0T VpNo ratings yet
- Method of Lighting CalculationsDocument3 pagesMethod of Lighting CalculationsSpencer Josh RegedorNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 2)Document7 pagesModule 10 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 2)Jhess GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument7 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignjanakNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument25 pagesPhysics PracticalYukti SharmaNo ratings yet