Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Certified in Cybersecurity Certification Exam Outline
Certified in Cybersecurity Certification Exam Outline
Uploaded by
Benjamin Wolyan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views4 pagesCertified in Cybersecurity Certification Exam Outline
Certified in Cybersecurity Certification Exam Outline
Uploaded by
Benjamin WolyanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
About Certified in Cybersecurity
ISC2 developed the Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) credential for newcomers to
the field, to recognize the growing trend of people entering the cybersecurity
workforce without direct IT experience. Getting Certified in Cybersecurity
provides employers with the confidence that you have a solid grasp of the right
technical concepts, and a demonstrated aptitude to learn on the job. As an ISC2
certification, those who hold the CC are backed by the world’s largest network of
certified cybersecurity professionals helping them continue their professional
development and earn new achievements and qualifications throughout their
career.
The topics on the CC exam include:
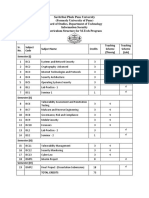
Security Principles
Incident Response, Business Continuity (BC) and Disaster Recovery (DR)
Concepts
Access Controls Concepts
Network Security
Security Operations
Certified in Cybersecurity Examination Information
Length of exam 2 hours
Number of items 100
Item format Multiple choice
Passing grade 700 out of 1000 points
Exam language availability English, Chinese, Japanese, German, Spanish
Testing center Pearson VUE Testing Center
Certified in Cybersecurity Examination Weights
Average
Domains
Weight
1. Security Principles 26%
2. Business Continuity (BC), Disaster Recovery (DR) & Incident Response
10%
Concepts
3. Access Controls Concepts 22%
4. Network Security 24%
5. Security Operations 18%
Average
Domains
Weight
Total 100%
Boost your chances of passing the exam with the CC eTextbook
Build your fundamental cybersecurity knowledge and prepare for the exam.
Get eTextbook
Domains
Domain 1: Security Principles
1.1 - Understand the security concepts of information assurance
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
Authentication (e.g., methods of authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA))
Non-repudiation
Privacy
1.2 - Understand the risk management process
Risk management (e.g., risk priorities, risk tolerance)
Risk identification, assessment and treatment
1.3 - Understand security controls
Technical controls
Administrative controls
Physical controls
1.4 - Understand ISC2 Code of Ethics
Professional code of conduct
1.5 - Understand governance processes
Policies
Procedures
Standards
Regulations and laws
Domain 2: Business Continuity (BC), Disaster Recovery (DR) & Incident Response Concepts
2.1 - Understand business continuity (BC)
Purpose
Importance
Components
2.2 - Understand disaster recovery (DR)
Purpose
Importance
Components
2.3 - Understand incident response
Purpose
Importance
Components
Domain 3: Access Controls Concepts
3.1 - Understand physical access controls
Physical security controls (e.g., badge systems, gate entry, environmental design)
Monitoring (e.g., security guards, closed-circuit television (CCTV), alarm systems,
logs)
Authorized versus unauthorized personnel
3.2 - Understand logical access controls
Principle of least privilege
Segregation of duties
Discretionary access control (DAC)
Mandatory access control (MAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Domain 4: Network Security
4.1 - Understand computer networking
Networks (e.g., Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) model, Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4),
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), WiFi)
Ports
Applications
4.2 - Understand network threats and attacks
Types of threats (e.g., distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), virus, worm, Trojan,
man-in-the-middle (MITM), side-channel)
Identification (e.g., intrusion detection system (IDS), host-based intrusion detection
system (HIDS), network intrusion detection system (NIDS))
Prevention (e.g., antivirus, scans, firewalls, intrusion prevention system (IPS))
4.3 - Understand network security infrastructure
On-premises (e.g., power, data center/closets, Heating, Ventilation, and Air
Conditioning (HVAC), environmental, fire suppression, redundancy, memorandum of
understanding (MOU)/memorandum of agreement (MOA))
Design (e.g., network segmentation (demilitarized zone (DMZ), virtual local area
network (VLAN), virtual private network (VPN), micro-segmentation), defense in
depth, Network Access Control (NAC) (segmentation for embedded systems, Internet
of Things (IoT))
Cloud (e.g., service-level agreement (SLA), managed service provider (MSP),
Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service
(PaaS), hybrid)
Domain 5: Security Operations
5.1 - Understand data security
Encryption (e.g., symmetric, asymmetric, hashing)
Data handling (e.g., destruction, retention, classification, labeling)
Logging and monitoring security events
5.2 - Understand system hardening
Configuration management (e.g., baselines, updates, patches)
5.3 - Understand best practice security policies
Data handling policy
Password policy
Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)
Bring your own device (BYOD) policy
Change management policy (e.g., documentation, approval, rollback)
Privacy policy
5.4 - Understand security awareness training
Purpose/concepts (e.g., social engineering, password protection)
Importance
https://www.isc2.org/certifications/cc/cc-certification-exam-outline
You might also like
- Cybersecurity by ISC2-UpdatedDocument13 pagesCybersecurity by ISC2-UpdatedYe Zeiya Shein57% (7)
- Certified in Cybersecurity Exam Outline Aug22Document8 pagesCertified in Cybersecurity Exam Outline Aug22R Nil100% (1)
- SEC401 Course OutlineDocument28 pagesSEC401 Course OutlinebbbbNo ratings yet
- COURSE 1 Basics of CybersecurityDocument7 pagesCOURSE 1 Basics of CybersecuritySohamNo ratings yet
- Certified in Cybersecurity Exam Outline Aug22 PDFDocument8 pagesCertified in Cybersecurity Exam Outline Aug22 PDFraspberries1No ratings yet
- CISSP ObjectivesDocument16 pagesCISSP ObjectivesRomeo SincereNo ratings yet
- CISSP Exam Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCISSP Exam Outline PDFsriNo ratings yet
- Certification: Exam OutlineDocument15 pagesCertification: Exam Outlinejustforfun2009No ratings yet
- CISSP Exam Outline April 2024 EnglishDocument15 pagesCISSP Exam Outline April 2024 EnglishBratu MadalinNo ratings yet
- Ec-Csa 1.0Document3 pagesEc-Csa 1.0Milbatta SannataNo ratings yet
- Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument39 pagesConversion Gate02 PDFBertin BidiasNo ratings yet
- CND BrochureDocument12 pagesCND Brochurevimawe3730No ratings yet
- Cissp CursDocument7 pagesCissp Cursf7vbzqcfztNo ratings yet
- CISSP Exam Outline-V1115Document16 pagesCISSP Exam Outline-V1115AsadMalikNo ratings yet
- Isrm PDFDocument4 pagesIsrm PDFarpan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Cissp: The 8 Domains of CISSPDocument52 pagesCissp: The 8 Domains of CISSPLacky KrishnanNo ratings yet
- CISSP ISSAP Exam Outline v0120Document11 pagesCISSP ISSAP Exam Outline v0120FedericoNo ratings yet
- ISSAP Exam Outline November 2020 EnglishDocument11 pagesISSAP Exam Outline November 2020 EnglishAnoopNo ratings yet
- Pune University IS Tech. SyllabusDocument9 pagesPune University IS Tech. SyllabusPav TechnicalsNo ratings yet
- System SecurityDocument4 pagesSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarNo ratings yet
- Course Plan Information SecurityDocument7 pagesCourse Plan Information SecurityMalik KashifNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity / Regulatory Overview: Tracy Monteith Director, Cybersecurity Black & Veatch Management ConsultingDocument23 pagesCybersecurity / Regulatory Overview: Tracy Monteith Director, Cybersecurity Black & Veatch Management ConsultingANDRU TUDOR BADIUNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Fundamentals Course OutlineDocument4 pagesCybersecurity Fundamentals Course Outlinem3lw1nNo ratings yet
- Comptia Security+ Sy0-601: Course ContentDocument8 pagesComptia Security+ Sy0-601: Course ContentShiva Chandrasekharan50% (2)
- CCST+Cybersecurity+Objecitve+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoDocument3 pagesCCST+Cybersecurity+Objecitve+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoQazi ZayadNo ratings yet
- SSCP Exam OutlineDocument11 pagesSSCP Exam Outlineironman100% (1)
- Introduction To Information SecurityDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Information SecurityjamesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Protection MechanismsDocument87 pagesLecture 8 - Protection MechanismsUmair AmjadNo ratings yet
- Information Security Management 2Document34 pagesInformation Security Management 2tuffahati meydina100% (1)
- SSCP Exam Outline Sept17Document13 pagesSSCP Exam Outline Sept17halakahiki82No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Protection and SecuirtDocument33 pagesLecture 3 Protection and SecuirtNadeem ShoukatNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Section QuizDocument5 pages1.2.4 Section QuizAshley AllenNo ratings yet
- Isc-V1 2024Document310 pagesIsc-V1 2024Roshan SNo ratings yet
- 2024 Becker CPA Information Systems & Controls (ISC) NotesDocument43 pages2024 Becker CPA Information Systems & Controls (ISC) NotescraigsappletreeNo ratings yet
- Ebook - 1.1 Comparing Security Roles and ControlsDocument21 pagesEbook - 1.1 Comparing Security Roles and ControlsprohitNo ratings yet
- Course Overview: This Course Provides In-Depth Coverage of The Eight Domains Required To Pass The CISSP ExamDocument30 pagesCourse Overview: This Course Provides In-Depth Coverage of The Eight Domains Required To Pass The CISSP ExamAbdul GhaffarNo ratings yet
- CISSP Exam Outline English April 2021 PDFDocument16 pagesCISSP Exam Outline English April 2021 PDFKevin MonkamNo ratings yet
- CCSPDocument14 pagesCCSPngtonhNo ratings yet
- Cisco Cybersecurity OD 0123Document3 pagesCisco Cybersecurity OD 0123itexamssimNo ratings yet
- CISSP Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesCISSP Cheat SheetMark Brown100% (1)
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Information Security Principles and Practices 2nd Edition PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Information Security Principles and Practices 2nd Edition PDF Ebookjorge.goldwyn787100% (37)
- CISM Chapter3-Info Sec Program DevelopmentDocument62 pagesCISM Chapter3-Info Sec Program DevelopmentLakshmiNo ratings yet
- Security AnalystDocument2 pagesSecurity AnalystHaemlet100% (1)
- CSSLP Exam Outline Sept2020Document14 pagesCSSLP Exam Outline Sept2020ziaur060382No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledHemal KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Cyber Security FundamentalsDocument6 pagesModule 1: Cyber Security FundamentalsAravind VbkNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Cyber Security Introduction and OverviewDocument23 pagesSection 1 - Cyber Security Introduction and OverviewfadhilNo ratings yet
- Is Scouse Outline VFDocument4 pagesIs Scouse Outline VFMuller MuleyNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security + Chapter 1Document13 pagesCompTIA Security + Chapter 1ALABINo ratings yet
- CCSP Exam OutlineDocument15 pagesCCSP Exam OutlineMaudyNo ratings yet
- PRES PUBLIC v2 QualysGuard - Vulnerability - ManagementDocument24 pagesPRES PUBLIC v2 QualysGuard - Vulnerability - ManagementProduction First FloorNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Security and Privacy Architecture: Technological University (Meiktila) Department of Information TechnologyDocument19 pagesChapter-9 Security and Privacy Architecture: Technological University (Meiktila) Department of Information Technologyfna4463No ratings yet
- CCSP Exam Outline English 20220511Document14 pagesCCSP Exam Outline English 20220511ironmanNo ratings yet
- CSSLP Exam OutlineDocument13 pagesCSSLP Exam OutlineLuis Felipe GaleanoNo ratings yet
- 2024 SSCP Detailed Content Outline With Weights Public Use OnlyDocument4 pages2024 SSCP Detailed Content Outline With Weights Public Use OnlyBlanchard KOUASSINo ratings yet
- Computersecurity OutlineDocument5 pagesComputersecurity Outlineshifara TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Ethical HackingDocument157 pagesEthical Hackingeduardo cerronNo ratings yet
- Noa Solutions SylabusDocument1 pageNoa Solutions SylabusArun MmohantyNo ratings yet
- Security SpecsDocument8 pagesSecurity SpecsTee BeeNo ratings yet
- Data CentersDocument30 pagesData Centersapi-364049439No ratings yet
- Qiu 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1684 012020Document9 pagesQiu 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1684 012020amandasilvaamandaNo ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery and BCP Service LevelDocument1 pageIt Disaster Recovery and BCP Service LevelHector Eduardo ErmacoraNo ratings yet
- ILL FAQsDocument8 pagesILL FAQsPrime RidesNo ratings yet
- AI - & - Robotics Automation - College-OrientationDocument18 pagesAI - & - Robotics Automation - College-OrientationArati BeheraNo ratings yet
- 1.5W 1-2 KM Range FM Transmitter by 2N2219 - Circuit ProjectDocument4 pages1.5W 1-2 KM Range FM Transmitter by 2N2219 - Circuit ProjectManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- IntroductionOpenSees PDFDocument27 pagesIntroductionOpenSees PDFali381No ratings yet
- 12-Bit ADCDocument24 pages12-Bit ADCSamvel YanNo ratings yet
- A JIT Translator For OberonDocument57 pagesA JIT Translator For OberonergodicNo ratings yet
- PS9830BDocument3 pagesPS9830BJuan Carlos Srafan100% (1)
- Principles of Operating SystemsDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Operating SystemsMelanie BuñalesNo ratings yet
- ARM11 Microarchitecture White PaperDocument9 pagesARM11 Microarchitecture White PaperDeepa DevarajNo ratings yet
- AAOD DeveloperGuide PDFDocument658 pagesAAOD DeveloperGuide PDFVictor Hugo SantosNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following QuestionsDocument1 pageAnswer The Following QuestionsGopi SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Digital Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorDocument70 pagesOperation Manual: Digital Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorJonathan MeloNo ratings yet
- ATA IT JD - Senior QA Engineer (Software Development in Test)Document2 pagesATA IT JD - Senior QA Engineer (Software Development in Test)The Generation's CodeNo ratings yet
- Alteon D Line 5820 5424 Tech SpecDocument2 pagesAlteon D Line 5820 5424 Tech SpecYo ChepoNo ratings yet
- SRS (Courier Tracking System) 1.1Document21 pagesSRS (Courier Tracking System) 1.1rana asimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Processing UnitsDocument68 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Processing UnitsAhan Tejaswi100% (1)
- Network Release DP 12.06a FTTC: NSO Training: Kenneth GreenDocument34 pagesNetwork Release DP 12.06a FTTC: NSO Training: Kenneth GreenAhsan Naeem100% (1)
- Mslearn dp100 10Document2 pagesMslearn dp100 10Emily RapaniNo ratings yet
- Jeler Grigore TraducereDocument10 pagesJeler Grigore TraducereGrigore JelerNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Mode 6Document26 pagesEngine Performance Mode 6BRADLEY FLORESNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: E3-E4 CM Rev Date:11-03-11Document108 pagesChapter-1: E3-E4 CM Rev Date:11-03-11Anuska SahaNo ratings yet
- Eplan American EgyDocument30 pagesEplan American EgySam JohnNo ratings yet
- Dr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS HyderabadDocument31 pagesDr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS Hyderabadsaket kumarNo ratings yet
- MTBF RUGGEDCOM April 2021Document5 pagesMTBF RUGGEDCOM April 2021Manuel Angulo - COINSINo ratings yet
- B19EI030 INTERNSHIP ReportDocument11 pagesB19EI030 INTERNSHIP ReportTejaswini ThogaruNo ratings yet
- MC33201, MC33202, MC33204, NCV33202, NCV33204 Low Voltage, Rail To Rail Operational AmplifiersDocument16 pagesMC33201, MC33202, MC33204, NCV33202, NCV33204 Low Voltage, Rail To Rail Operational AmplifiersAndres OrtizNo ratings yet
- Cisco Firepower 1120 ASA Image and FXOSDocument4 pagesCisco Firepower 1120 ASA Image and FXOSvetinh0607No ratings yet