Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
Uploaded by
tadele.teka1717Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (KPI) ISSUE1.00Document98 pagesLTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (KPI) ISSUE1.00Dhananjay Shrivastav50% (2)
- LTE KPI OptimizationDocument17 pagesLTE KPI OptimizationMuhammd Sohail Khan0% (2)
- Service Drop Optimization GuideDocument53 pagesService Drop Optimization GuideNik100% (1)
- CISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Check Digit,Parity Bit & AtomicityFrom EverandCISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Check Digit,Parity Bit & AtomicityRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Scoping NIDDDocument44 pagesScoping NIDDMihaela PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Devices PreparationDocument70 pagesDevices Preparationaditya naik100% (1)
- 4G KPI and Trouble ShootingDocument58 pages4G KPI and Trouble ShootingRamanuj Singh100% (3)
- LTE DropDocument3 pagesLTE Dropmoses100% (1)
- Handover ProceduresDocument6 pagesHandover ProceduresshikhaNo ratings yet
- Huawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Document104 pagesHuawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Muhammad Usman100% (1)
- LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Document100 pagesLTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Mesfin TibebeNo ratings yet
- Guide To TD LTE Handover Problem AnalysisDocument58 pagesGuide To TD LTE Handover Problem AnalysiskakaNo ratings yet
- Intra Lte MobiltyDocument5 pagesIntra Lte MobiltyechakhaouiNo ratings yet
- LTE KPI Optimization: Huawei ConfidentialDocument17 pagesLTE KPI Optimization: Huawei Confidentialfastlink100% (1)
- Major Lte KpisDocument82 pagesMajor Lte KpisKarem AshrafNo ratings yet
- LTE HandoversDocument33 pagesLTE HandoversAnshul Gupta100% (1)
- Guide To TD-LTE Handover Problem AnalysisDocument58 pagesGuide To TD-LTE Handover Problem Analysisfahadmalik89No ratings yet
- Netmanias.2012.07.05 EMM Procedure 6. Handover Without TAU (Part 2)Document18 pagesNetmanias.2012.07.05 EMM Procedure 6. Handover Without TAU (Part 2)박지홍No ratings yet
- LTE Handovers: Satish Kumar SDocument27 pagesLTE Handovers: Satish Kumar Ssandhya24No ratings yet
- Inter-EnodeB Handover Over The X2 InterfaceDocument1 pageInter-EnodeB Handover Over The X2 InterfaceAnjit RajkarnikarNo ratings yet
- LTE X2 Handover Call Flow ProcedureDocument8 pagesLTE X2 Handover Call Flow Proceduresophie10694No ratings yet
- Huawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Drive Test)Document109 pagesHuawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Drive Test)Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- ZTE FDD LTE Radio Network Optimization Guideline V1 4-1-108Document1 pageZTE FDD LTE Radio Network Optimization Guideline V1 4-1-108Sameer IbraimoNo ratings yet
- LTE eRAN17.1 Intra-RAT Handover FeatureDocument70 pagesLTE eRAN17.1 Intra-RAT Handover Featuretadele.teka1717No ratings yet
- Radio Resource Management: 1. Intra LTE Mobility: A. ECM Connected ModeDocument3 pagesRadio Resource Management: 1. Intra LTE Mobility: A. ECM Connected ModeahlemNo ratings yet
- Lte s1 HandoverDocument5 pagesLte s1 HandoverTheduyet PhamNo ratings yet
- Training - LTE Call FlowDocument21 pagesTraining - LTE Call FlowFarah Souri100% (2)
- Inter-EnodeB Handover Over The S1 Interface (I)Document1 pageInter-EnodeB Handover Over The S1 Interface (I)Anjit RajkarnikarNo ratings yet
- ReportCGI in Measurement Report and ANRDocument3 pagesReportCGI in Measurement Report and ANRسفيان بن يوسف100% (1)
- Qualcomm Research Performance of Dual Searcher Mobiles in Hotspot ScenariosDocument11 pagesQualcomm Research Performance of Dual Searcher Mobiles in Hotspot ScenarioseliaezekielNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover PPT Rakesh RAJDocument28 pagesLTE Handover PPT Rakesh RAJteam DinnerNo ratings yet
- 02 150723164805 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument23 pages02 150723164805 Lva1 App6891 PDFbmmarko5483No ratings yet
- Guide To Optimizing LTE Service DropsDocument52 pagesGuide To Optimizing LTE Service Dropsfidelkaey100% (1)
- Huawei Optimizing Service Drop RateDocument52 pagesHuawei Optimizing Service Drop RateMustafa WattooNo ratings yet
- Lte Kpis: Optimizacion de Redes MovilesDocument30 pagesLte Kpis: Optimizacion de Redes MovilesGiancarlo PolancoNo ratings yet
- Sign Magnitude:: Computer ArithmeticsDocument9 pagesSign Magnitude:: Computer Arithmeticsjahid hasanNo ratings yet
- LTE Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesLTE Interview QuestionsramuorNo ratings yet
- PDCCHDocument11 pagesPDCCHgolden_hunter_1980No ratings yet
- Analyzing X2 Handover in LTE/LTE-A: Konstantinos Alexandris, Navid Nikaein, Raymond Knopp, and Christian BonnetDocument7 pagesAnalyzing X2 Handover in LTE/LTE-A: Konstantinos Alexandris, Navid Nikaein, Raymond Knopp, and Christian BonnetIndrajit RoyNo ratings yet
- Using Boolean Statements To Provide Custom Alarms in The Flow ComputerDocument2 pagesUsing Boolean Statements To Provide Custom Alarms in The Flow Computersyed jeelani ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mobility 3G With Huawei Team My PresentationDocument47 pagesMobility 3G With Huawei Team My PresentationessaiesmeriamNo ratings yet
- X2ho LteDocument7 pagesX2ho LtePrasoon PuthuvattilNo ratings yet
- 02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEDocument69 pages02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEprakashbaranwal100% (1)
- PDCCH Cce PDFDocument9 pagesPDCCH Cce PDFAbhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- All About Automatic Neighbor RelationDocument4 pagesAll About Automatic Neighbor RelationDebayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- EEE211 - ETE211 - Lecture 5Document33 pagesEEE211 - ETE211 - Lecture 5BBNo ratings yet
- Data Communications & Networking Lecture-20Document20 pagesData Communications & Networking Lecture-20mahamd saiedNo ratings yet
- Lte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCDocument9 pagesLte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCseeinamNo ratings yet
- Lte x2 Handover Sequence DiagramDocument6 pagesLte x2 Handover Sequence DiagramsoueeeNo ratings yet
- 7 - Data Link LayerDocument31 pages7 - Data Link Layeranshikac.it.21No ratings yet
- 5 The PCRF Triggers The Establishment of The Dedicated BearerDocument24 pages5 The PCRF Triggers The Establishment of The Dedicated BearerPihu KashyapNo ratings yet
- 04 Chapter-4Document43 pages04 Chapter-4pratham.sagittarusNo ratings yet
- Target Enodeb s1 Handover FlowDocument3 pagesTarget Enodeb s1 Handover FlowLeuLeuNo ratings yet
- Lte x2 Handover Source Enodeb FlowDocument3 pagesLte x2 Handover Source Enodeb Flowsunan handiriNo ratings yet
- Handover Events in LTE - V - UpdateDocument8 pagesHandover Events in LTE - V - UpdateFebritoNo ratings yet
- New Handove Call Flow-Updated PDFDocument3 pagesNew Handove Call Flow-Updated PDFArun BaidyaNo ratings yet
- MRO Feature ParameterDocument22 pagesMRO Feature ParameterFerry PlbNo ratings yet
- Low Battery Communication ReportDocument2 pagesLow Battery Communication ReportMayam AyoNo ratings yet
- Handover Events in LTEDocument10 pagesHandover Events in LTEBryanNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Attach SignalingDocument44 pagesAttach Signalingbrr.rezvaniNo ratings yet
- 901-00-0081D LI ConfigDocument162 pages901-00-0081D LI ConfigSri VagiralaNo ratings yet
- Nova-227 - OD - TDD - eNB - Data - Sheet (SRv1.5 - 31-Jan-2019)Document3 pagesNova-227 - OD - TDD - eNB - Data - Sheet (SRv1.5 - 31-Jan-2019)yigit ozcanNo ratings yet
- 02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEDocument69 pages02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEprakashbaranwal100% (1)
- OAM Ping 2G Part: Document Valid For All Baseband TypesDocument4 pagesOAM Ping 2G Part: Document Valid For All Baseband TypesSofiane KhelfaouiNo ratings yet
- LTE Mobility Concept & Case StudyDocument45 pagesLTE Mobility Concept & Case Studyvicky_211287No ratings yet
- Mobile Network Architecture FundamentalsDocument47 pagesMobile Network Architecture FundamentalsIoniță Sorin Cristian100% (1)
- Nokia Network in A Box White PaperDocument14 pagesNokia Network in A Box White PaperSunny Girija Sapru100% (1)
- Design and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFDocument51 pagesDesign and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFsafyh2005No ratings yet
- LTE OverviewDocument98 pagesLTE Overviewmohamed fadlNo ratings yet
- 4G LTE Attacks PaperDocument15 pages4G LTE Attacks PaperObserver123No ratings yet
- LGF-Flexi NG-2016-w17Document24 pagesLGF-Flexi NG-2016-w17jpbarcelosNo ratings yet
- Reference System Description: Packet Core System Paco 2.1, System DocumentationDocument13 pagesReference System Description: Packet Core System Paco 2.1, System DocumentationDwi Kris AndroidNo ratings yet
- Lte Kpi PDFDocument11 pagesLte Kpi PDFNguyen Thanh VuNo ratings yet
- Asee13 LteDocument10 pagesAsee13 LtePete AirNo ratings yet
- 4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFDocument17 pages4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFAutomotriz BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Initial Attachement For VoLTE UserDocument11 pagesInitial Attachement For VoLTE UserVusal SuleymanovNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Specification ListDocument491 pages3GPP Specification Listanh00100% (1)
- LTE and EPC Roaming Guidelines IR 88-V10 0Document68 pagesLTE and EPC Roaming Guidelines IR 88-V10 0David Yepez JijonNo ratings yet
- Importance of Telecom OSS and BSSDocument24 pagesImportance of Telecom OSS and BSSDolly Roliyan50% (2)
- Lte 1800-Mop-Inst & Comms-Vf v1.1Document40 pagesLte 1800-Mop-Inst & Comms-Vf v1.1ArghyaPodderNo ratings yet
- LTE4193 Feature AssessmentDocument55 pagesLTE4193 Feature AssessmentAdil MuradNo ratings yet
- Lte Product-Sdr Bbu&RruDocument22 pagesLte Product-Sdr Bbu&RruDer Größte Weisheit100% (1)
- LTE Radio Interface Section 1Document82 pagesLTE Radio Interface Section 1Nikan AminiNo ratings yet
- Volte Optimization - v2Document29 pagesVolte Optimization - v2roy tanjungNo ratings yet
- Handover LTE To WifiDocument17 pagesHandover LTE To WifiAhmedNo ratings yet
- TEMS Discovery 21.0.2 Release NoteDocument22 pagesTEMS Discovery 21.0.2 Release NoteDanilo Benitez100% (1)
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
Uploaded by
tadele.teka1717Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
LTE eRAN17.1 Handover KPI Introduction
Uploaded by
tadele.teka1717Copyright:
Available Formats
LTE eRAN17.
1 KPI Introduction
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-1
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
This KPI can be used to evaluate the intra/inter-frequency Handover out success rate in a
cell or a cluster. The intra-frequency handover (HO) includes both inter-eNodeB and intra-
eNodeB.
The intra/inter-frequency handover (HO) includes both inter-eNodeB and intra-eNodeB
scenarios.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
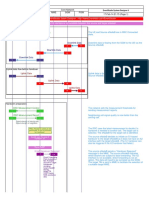
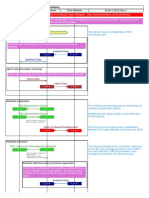
As shown at point A, during an intra-eNodeB handover the corresponding counter is incremented
by 1 each time the eNodeB decides to perform an intra-eNodeB blind handover or decides to
perform an intra-eNodeB handover after receiving a measurement report from the UE.The counters
are measured as follows:
If the source cell and the target cell work on the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.IntraFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and the target cell work on different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.InterFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
During a handover where the source cell and target cell are controlled by the same eNodeB, as
shown in point B, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each time the eNodeB sends an
RRC Connection Reconfiguration message to the UE. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell work at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.IntraFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell work at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.InterFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
As shown in point C , the corresponding counter is incremented each time the eNodeB receives an
RRC Connection Reconfiguration Complete message from the UE and the subsequent operations are
successful. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell are at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.IntraFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell are at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntraeNB.InterFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
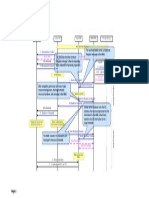
As shown at point A, during an X2-based handover the corresponding counter is incremented by 1
each time the source eNodeB decides to perform an X2-based blind handover or the source eNodeB
decides to perform an X2-based handover after the source cell receives a measurement report from
the UE. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and the target cell work on the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and the target cell work on different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
During such a handover where the source cell and target cell are controlled by different eNodeBs, as
shown in point B in the figure above, the corresponding counter is incremented each time the
source eNodeB sends an RRC Connection Reconfiguration message to the UE after receiving a
HANDOVER REQUEST ACKNOWLEDGE from the target eNodeB or receiving a HANDOVER
COMMAND message from the MME. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell work at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell work at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
As shown in point C , the corresponding counter is incremented each time the source eNodeB
receives a UE CONTEXT RELEASE message from the target eNodeB or a UE CONTEXT RELEASE
COMMAND message from the MME. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell are at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell are at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
As shown at point A, during an S1-based handover the corresponding counter is incremented by 1
each time the source eNodeB decides to perform an S1-based blind handover or the source eNodeB
decides to perform an S1-based handover after the source cell receives a measurement report from
the UE. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and the target cell work on the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and the target cell work on different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.PrepAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
During such a handover where the source cell and target cell are controlled by different eNodeBs, as
shown in point B in the figure above, the corresponding counter is incremented each time the
source eNodeB sends an RRC Connection Reconfiguration message to the UE after receiving a
HANDOVER REQUEST ACKNOWLEDGE from the target eNodeB or receiving a HANDOVER
COMMAND message from the MME. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell work at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell work at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.ExecAttOut counter is incremented by 1.
As shown in point C , the corresponding counter is incremented each time the source eNodeB
receives a UE CONTEXT RELEASE message from the target eNodeB or a UE CONTEXT RELEASE
COMMAND message from the MME. The counters are measured as follows:
If the source cell and target cell are at the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.IntraFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
If the source cell and target cell are at different frequencies, the
L.HHO.IntereNB.InterFreq.ExecSuccOut counter is incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
This KPI can be used to evaluate the handover in success rate in a cell or a cluster.
The HO includes both inter-eNodeB and intra-eNodeB scenarios.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
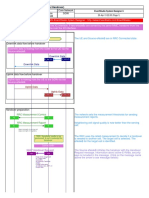
Number of Intra-eNB incoming handover attempts
During a handover where the source cell and target cell are controlled by the same
eNodeB, as shown in point B, the counter is incremented by 1 in the target cell
each time the eNodeB sends an RRC Connection Reconfiguration message to the
UE.
Number of successful intra-eNB incoming handovers
As shown in point C , the counter is incremented by 1 in the target cell each time
the eNodeB receives an RRC Connection Reconfiguration Complete message from
the UE and the subsequent operations are successful
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction
Related Counters (Inter eNB) X2 Handover
Number of Inter-eNB incoming handover attempts
The source cell and target cell of a handover are controlled by different
eNodeBs. As shown in point B, the counter is incremented by 1 in the
target cell each time the target eNodeB sends a HANDOVER REQUEST
ACKNOWLEDGE message to the source eNodeB over the X2 interface or to
the MME over the S1 interface.
Number of successful Inter-eNB incoming handovers
As shown in point C , the counter is incremented by 1 in the target cell
each time the target eNodeB sends a UE CONTEXT RELEASE to the source
eNodeB over the X2 interface after receiving a PATH SWITCH ACK message
from the MME or the target eNodeB sends a HANDOVER NOTIFY message
to the MME over the S1 interface.
Related Counters (Inter eNB) S1 Handover
Number of Inter-eNB incoming handover attempts
The source cell and target cell of a handover are controlled by different
eNodeBs. As shown in point B, the counter is incremented by 1 in the
target cell each time the target eNodeB sends a HANDOVER REQUEST
ACKNOWLEDGE message to the source eNodeB over the X2 interface or to
the MME over the S1 interface.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-13
L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.MME
Number of intra-duplex-mode outgoing handover preparation failures because of faults on
the MME side
L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.NoReply
Number of intra-duplex-mode outgoing handover preparation failures because of no
responses from the target cell
L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.PrepFailure
Number of intra-duplex-mode outgoing handover preparation failures because of the
handover preparation failure messages sent from the target cell
L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.HOCancel
Number of failed intra-duplex-mode outgoing handover preparations because of the
handover cancellation messages sent from the source cell
L.IntraFreqHO.NoNRT / L.InterFreqHO.NoNRT
Number of intra-frequency handover initiation failures because the adjacent cell is not on
the NRT of the source cell
L.HHO.Prep.FailIn.AdmitFail
Number of intra-duplex-mode incoming handover preparation failures because of admission
failure
L.HHO.PrepAttIn.disc.FlowCtrl
Number of times the HANDOVER REQUEST message is discarded over the S1 or X2
interface because of flow control (without returning a preparation failure message)
L.HHO.Prep.FailIn.FlowCtrl
Number of times that the target eNodeB sends a handover preparation failure message for
an intra-duple-mode handover over the S1 or X2 interface to the source eNodeB because of
flow control
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-14
As shown at point B in Figure 1 during the preparation phase of an S1-based handover or
as shown at point B in Figure 2 during the preparation phase of an X2-based handover,
the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each time the source cell receives a UE
CONTEXT RELEASE COMMAND message from the MME.
No matter whether the source and target cells work on the same frequency or
different frequencies, the L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.MME counter is incremented by 1.
If the source and target cells work on the same frequency, the
L.HHO.IntraFreq.Prep.FailOut.MME counter is incremented by 1. If the source
and target cells work in different duplex modes, the
L.HHO.InterFddTdd.Prep.FailOut.MME counter is incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-15
As shown at point B in Figure 3 at the end of the preparation phase of an S1-based
handover or as shown at point B in Figure 4 at the end of the preparation phase of an X2-
based handover, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each time the source cell
does not receive any messages from the target eNodeB, such as the HANDOVER REQUEST
ACKNOWLEDEG and HANDOVER PREPARATION FAILURE messages sent from the target
eNodeB during the X2-based handover and the HANDOVER COMMAND and HANDOVER
PREPARATION FAILURE messages sent from the MME during the S1-based handover.
No matter whether the source and target cells work on the same frequency or
different frequencies, the L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.NoReply counter is incremented
by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-16
As shown at point B in Figure 5, during the handover preparation phase of an S1-based
handover, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each time the source cell
receives a HANDOVER PREPARATION FAILURE message from the MME.
As shown at point B in Figure 6, during the handover preparation phase of an X2-based
handover, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each time the source cell
receives a HANDOVER PREPARATION FAILURE message from the target cell.
No matter whether the source and target cells work on the same frequency or
different frequencies, the L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.PrepFailure counter is
incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-17
As show at point B in Figure 7 during an S1-based handover or as shown at point B in
Figure 8 during an X2-based handover, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1
each time the source cell cancels the handover and sends a HANDOVER CANCEL message
before the preparation phase ends. However, if the handover preparation phase ends and
the handover for the UE is not finished for other abnormal reasons, the corresponding
counter is not incremented when the source cell sends a HANDOVER CANCEL message to
the target cell.
No matter whether the source and target cells work on the same frequency or
different frequencies, the L.HHO.Prep.FailOut.HOCancel counter is incremented
by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-18
As shown at point A in the figure, the corresponding counter is incremented by 1 each
time the source cell receives a Measurement Report message from the UE and decides to
perform a handover, but the handover initiation fails because the neighboring relationship
with the target cell that has the best signal quality in the first measurement report is not
configured on the source cell.The counters are calculated as follows:
If the eNodeB receives a measurement report on intra-frequency neighboring cells,
the L.IntraFreqHO.NoNRT counter is incremented by 1.
If the eNodeB receives a measurement report on inter-frequency neighboring cells,
the L.InterFreqHO.NoNRT counter is incremented by 1.
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
LTE eRAN17.1 KPI Introduction P-19
Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission
You might also like
- LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (KPI) ISSUE1.00Document98 pagesLTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (KPI) ISSUE1.00Dhananjay Shrivastav50% (2)
- LTE KPI OptimizationDocument17 pagesLTE KPI OptimizationMuhammd Sohail Khan0% (2)
- Service Drop Optimization GuideDocument53 pagesService Drop Optimization GuideNik100% (1)
- CISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Check Digit,Parity Bit & AtomicityFrom EverandCISA EXAM-Testing Concept-Check Digit,Parity Bit & AtomicityRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Scoping NIDDDocument44 pagesScoping NIDDMihaela PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Devices PreparationDocument70 pagesDevices Preparationaditya naik100% (1)
- 4G KPI and Trouble ShootingDocument58 pages4G KPI and Trouble ShootingRamanuj Singh100% (3)
- LTE DropDocument3 pagesLTE Dropmoses100% (1)
- Handover ProceduresDocument6 pagesHandover ProceduresshikhaNo ratings yet
- Huawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Document104 pagesHuawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Muhammad Usman100% (1)
- LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Document100 pagesLTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Traffic KPIs)Mesfin TibebeNo ratings yet
- Guide To TD LTE Handover Problem AnalysisDocument58 pagesGuide To TD LTE Handover Problem AnalysiskakaNo ratings yet
- Intra Lte MobiltyDocument5 pagesIntra Lte MobiltyechakhaouiNo ratings yet
- LTE KPI Optimization: Huawei ConfidentialDocument17 pagesLTE KPI Optimization: Huawei Confidentialfastlink100% (1)
- Major Lte KpisDocument82 pagesMajor Lte KpisKarem AshrafNo ratings yet
- LTE HandoversDocument33 pagesLTE HandoversAnshul Gupta100% (1)
- Guide To TD-LTE Handover Problem AnalysisDocument58 pagesGuide To TD-LTE Handover Problem Analysisfahadmalik89No ratings yet
- Netmanias.2012.07.05 EMM Procedure 6. Handover Without TAU (Part 2)Document18 pagesNetmanias.2012.07.05 EMM Procedure 6. Handover Without TAU (Part 2)박지홍No ratings yet
- LTE Handovers: Satish Kumar SDocument27 pagesLTE Handovers: Satish Kumar Ssandhya24No ratings yet
- Inter-EnodeB Handover Over The X2 InterfaceDocument1 pageInter-EnodeB Handover Over The X2 InterfaceAnjit RajkarnikarNo ratings yet
- LTE X2 Handover Call Flow ProcedureDocument8 pagesLTE X2 Handover Call Flow Proceduresophie10694No ratings yet
- Huawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Drive Test)Document109 pagesHuawei LTE Handover Fault Diagnosis (Drive Test)Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- ZTE FDD LTE Radio Network Optimization Guideline V1 4-1-108Document1 pageZTE FDD LTE Radio Network Optimization Guideline V1 4-1-108Sameer IbraimoNo ratings yet
- LTE eRAN17.1 Intra-RAT Handover FeatureDocument70 pagesLTE eRAN17.1 Intra-RAT Handover Featuretadele.teka1717No ratings yet
- Radio Resource Management: 1. Intra LTE Mobility: A. ECM Connected ModeDocument3 pagesRadio Resource Management: 1. Intra LTE Mobility: A. ECM Connected ModeahlemNo ratings yet
- Lte s1 HandoverDocument5 pagesLte s1 HandoverTheduyet PhamNo ratings yet
- Training - LTE Call FlowDocument21 pagesTraining - LTE Call FlowFarah Souri100% (2)
- Inter-EnodeB Handover Over The S1 Interface (I)Document1 pageInter-EnodeB Handover Over The S1 Interface (I)Anjit RajkarnikarNo ratings yet
- ReportCGI in Measurement Report and ANRDocument3 pagesReportCGI in Measurement Report and ANRسفيان بن يوسف100% (1)
- Qualcomm Research Performance of Dual Searcher Mobiles in Hotspot ScenariosDocument11 pagesQualcomm Research Performance of Dual Searcher Mobiles in Hotspot ScenarioseliaezekielNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover PPT Rakesh RAJDocument28 pagesLTE Handover PPT Rakesh RAJteam DinnerNo ratings yet
- 02 150723164805 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument23 pages02 150723164805 Lva1 App6891 PDFbmmarko5483No ratings yet
- Guide To Optimizing LTE Service DropsDocument52 pagesGuide To Optimizing LTE Service Dropsfidelkaey100% (1)
- Huawei Optimizing Service Drop RateDocument52 pagesHuawei Optimizing Service Drop RateMustafa WattooNo ratings yet
- Lte Kpis: Optimizacion de Redes MovilesDocument30 pagesLte Kpis: Optimizacion de Redes MovilesGiancarlo PolancoNo ratings yet
- Sign Magnitude:: Computer ArithmeticsDocument9 pagesSign Magnitude:: Computer Arithmeticsjahid hasanNo ratings yet
- LTE Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesLTE Interview QuestionsramuorNo ratings yet
- PDCCHDocument11 pagesPDCCHgolden_hunter_1980No ratings yet
- Analyzing X2 Handover in LTE/LTE-A: Konstantinos Alexandris, Navid Nikaein, Raymond Knopp, and Christian BonnetDocument7 pagesAnalyzing X2 Handover in LTE/LTE-A: Konstantinos Alexandris, Navid Nikaein, Raymond Knopp, and Christian BonnetIndrajit RoyNo ratings yet
- Using Boolean Statements To Provide Custom Alarms in The Flow ComputerDocument2 pagesUsing Boolean Statements To Provide Custom Alarms in The Flow Computersyed jeelani ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mobility 3G With Huawei Team My PresentationDocument47 pagesMobility 3G With Huawei Team My PresentationessaiesmeriamNo ratings yet
- X2ho LteDocument7 pagesX2ho LtePrasoon PuthuvattilNo ratings yet
- 02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEDocument69 pages02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEprakashbaranwal100% (1)
- PDCCH Cce PDFDocument9 pagesPDCCH Cce PDFAbhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- All About Automatic Neighbor RelationDocument4 pagesAll About Automatic Neighbor RelationDebayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- EEE211 - ETE211 - Lecture 5Document33 pagesEEE211 - ETE211 - Lecture 5BBNo ratings yet
- Data Communications & Networking Lecture-20Document20 pagesData Communications & Networking Lecture-20mahamd saiedNo ratings yet
- Lte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCDocument9 pagesLte Mobility: Connected Mode. The Network Controls Transition of UE Between The Idle and RRCseeinamNo ratings yet
- Lte x2 Handover Sequence DiagramDocument6 pagesLte x2 Handover Sequence DiagramsoueeeNo ratings yet
- 7 - Data Link LayerDocument31 pages7 - Data Link Layeranshikac.it.21No ratings yet
- 5 The PCRF Triggers The Establishment of The Dedicated BearerDocument24 pages5 The PCRF Triggers The Establishment of The Dedicated BearerPihu KashyapNo ratings yet
- 04 Chapter-4Document43 pages04 Chapter-4pratham.sagittarusNo ratings yet
- Target Enodeb s1 Handover FlowDocument3 pagesTarget Enodeb s1 Handover FlowLeuLeuNo ratings yet
- Lte x2 Handover Source Enodeb FlowDocument3 pagesLte x2 Handover Source Enodeb Flowsunan handiriNo ratings yet
- Handover Events in LTE - V - UpdateDocument8 pagesHandover Events in LTE - V - UpdateFebritoNo ratings yet
- New Handove Call Flow-Updated PDFDocument3 pagesNew Handove Call Flow-Updated PDFArun BaidyaNo ratings yet
- MRO Feature ParameterDocument22 pagesMRO Feature ParameterFerry PlbNo ratings yet
- Low Battery Communication ReportDocument2 pagesLow Battery Communication ReportMayam AyoNo ratings yet
- Handover Events in LTEDocument10 pagesHandover Events in LTEBryanNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Attach SignalingDocument44 pagesAttach Signalingbrr.rezvaniNo ratings yet
- 901-00-0081D LI ConfigDocument162 pages901-00-0081D LI ConfigSri VagiralaNo ratings yet
- Nova-227 - OD - TDD - eNB - Data - Sheet (SRv1.5 - 31-Jan-2019)Document3 pagesNova-227 - OD - TDD - eNB - Data - Sheet (SRv1.5 - 31-Jan-2019)yigit ozcanNo ratings yet
- 02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEDocument69 pages02 Huawei Counters and KPI - VoLTEprakashbaranwal100% (1)
- OAM Ping 2G Part: Document Valid For All Baseband TypesDocument4 pagesOAM Ping 2G Part: Document Valid For All Baseband TypesSofiane KhelfaouiNo ratings yet
- LTE Mobility Concept & Case StudyDocument45 pagesLTE Mobility Concept & Case Studyvicky_211287No ratings yet
- Mobile Network Architecture FundamentalsDocument47 pagesMobile Network Architecture FundamentalsIoniță Sorin Cristian100% (1)
- Nokia Network in A Box White PaperDocument14 pagesNokia Network in A Box White PaperSunny Girija Sapru100% (1)
- Design and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFDocument51 pagesDesign and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFsafyh2005No ratings yet
- LTE OverviewDocument98 pagesLTE Overviewmohamed fadlNo ratings yet
- 4G LTE Attacks PaperDocument15 pages4G LTE Attacks PaperObserver123No ratings yet
- LGF-Flexi NG-2016-w17Document24 pagesLGF-Flexi NG-2016-w17jpbarcelosNo ratings yet
- Reference System Description: Packet Core System Paco 2.1, System DocumentationDocument13 pagesReference System Description: Packet Core System Paco 2.1, System DocumentationDwi Kris AndroidNo ratings yet
- Lte Kpi PDFDocument11 pagesLte Kpi PDFNguyen Thanh VuNo ratings yet
- Asee13 LteDocument10 pagesAsee13 LtePete AirNo ratings yet
- 4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFDocument17 pages4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFAutomotriz BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Initial Attachement For VoLTE UserDocument11 pagesInitial Attachement For VoLTE UserVusal SuleymanovNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Specification ListDocument491 pages3GPP Specification Listanh00100% (1)
- LTE and EPC Roaming Guidelines IR 88-V10 0Document68 pagesLTE and EPC Roaming Guidelines IR 88-V10 0David Yepez JijonNo ratings yet
- Importance of Telecom OSS and BSSDocument24 pagesImportance of Telecom OSS and BSSDolly Roliyan50% (2)
- Lte 1800-Mop-Inst & Comms-Vf v1.1Document40 pagesLte 1800-Mop-Inst & Comms-Vf v1.1ArghyaPodderNo ratings yet
- LTE4193 Feature AssessmentDocument55 pagesLTE4193 Feature AssessmentAdil MuradNo ratings yet
- Lte Product-Sdr Bbu&RruDocument22 pagesLte Product-Sdr Bbu&RruDer Größte Weisheit100% (1)
- LTE Radio Interface Section 1Document82 pagesLTE Radio Interface Section 1Nikan AminiNo ratings yet
- Volte Optimization - v2Document29 pagesVolte Optimization - v2roy tanjungNo ratings yet
- Handover LTE To WifiDocument17 pagesHandover LTE To WifiAhmedNo ratings yet
- TEMS Discovery 21.0.2 Release NoteDocument22 pagesTEMS Discovery 21.0.2 Release NoteDanilo Benitez100% (1)