Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Javobi 9ga
1 Javobi 9ga
Uploaded by
DAVRONBEK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
1 javobi 9ga
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pages1 Javobi 9ga
1 Javobi 9ga
Uploaded by
DAVRONBEKCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
The organizational structure of an enterprise is a systematic arrangement of roles,
responsibilities, and relationships that dictate how activities and processes are conducted
within the organization. An effective structure ensures clarity, efficient workflow, and
alignment with the organization's strategic goals. Understanding the hierarchical management
links—from lower to upper levels—is crucial for maximizing efficiency.
Organizational Structure
1. Upper Link (Top Management)
o Roles: CEO, CFO, COO, Board of Directors.
o Responsibilities: Strategic decision-making, setting overall goals, policy
formulation, and long-term planning.
o Functions:
Developing corporate strategy.
Establishing company policies.
Making major financial decisions.
Representing the company externally.
o Efficiency Factors:
Clear vision and strategic direction.
Effective leadership and governance.
Robust decision-making frameworks.
2. Middle Link (Middle Management)
o Roles: Department heads, Regional managers, Division managers.
o Responsibilities: Implementing strategies set by top management, managing
departmental operations, and ensuring coordination between departments.
o Functions:
Translating top-level strategies into operational plans.
Resource allocation and budget management.
Performance monitoring and reporting.
Facilitating communication between upper and lower management.
o Efficiency Factors:
Effective delegation and empowerment.
Strong coordination and communication skills.
Ability to manage and resolve conflicts.
3. Lower Link (Lower Management)
o Roles: Supervisors, Team leaders, Line managers.
o Responsibilities: Overseeing day-to-day operations, managing frontline
employees, and ensuring task completion.
o Functions:
Supervising work activities and providing guidance.
Addressing immediate operational issues.
Ensuring quality control and productivity.
Reporting performance and issues to middle management.
o Efficiency Factors:
Strong supervisory and motivational skills.
Quick decision-making and problem-solving.
Effective communication with frontline staff.
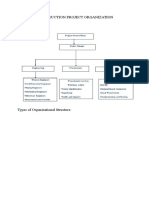
Types of Organizational Structures
1. Functional Structure
o Description: Groups employees based on specialized functions (e.g.,
marketing, finance, production).
o Efficiency: High due to specialization but may lead to silos and poor inter-
departmental communication.
2. Divisional Structure
o Description: Organizes the company into semi-autonomous divisions based
on products, services, or geographical locations.
o Efficiency: Focus on specific markets or products but can result in resource
duplication.
3. Matrix Structure
o Description: Combines functional and divisional structures, allowing
employees to report to both functional and project managers.
o Efficiency: Enhances flexibility and collaboration but can create complexity
and confusion in reporting relationships.
4. Flat Structure
o Description: Few hierarchical levels, with a broad span of control.
o Efficiency: Speeds up decision-making and communication but may
overburden managers.
5. Network Structure
o Description: Relies on a central core with external entities connected through
various contractual agreements.
o Efficiency: Provides flexibility and access to specialized resources but can be
challenging to manage and coordinate.
Enhancing Organizational Efficiency
1. Clear Communication Channels: Ensure open and transparent communication
across all levels.
2. Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outline duties and expectations for each
role to prevent overlap and confusion.
3. Employee Empowerment: Empower employees to make decisions and take initiative
within their roles.
4. Effective Training and Development: Invest in continuous learning and skill
development to keep the workforce competent and motivated.
5. Performance Management: Implement systems to monitor, evaluate, and reward
performance consistently.
6. Technological Integration: Leverage technology to streamline processes, enhance
data management, and improve overall productivity.
You might also like
- Supervision Concepts and Practices of Management 12th Edition Leonard Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesSupervision Concepts and Practices of Management 12th Edition Leonard Solutions Manualcynthiapierceeapdsbnwzk100% (15)
- Construction Project OrganizationDocument7 pagesConstruction Project OrganizationAnonymous cQHVRleTv100% (2)
- Info@ks-Legal - In: Rating/Loan Eligibility Across The IndustryDocument2 pagesInfo@ks-Legal - In: Rating/Loan Eligibility Across The IndustryChinmoy DeNo ratings yet
- Environmental AuditDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Auditbuson1100% (1)
- Principle of ManagementDocument3 pagesPrinciple of Managementanon_962013772100% (1)
- Urdaneta City University San Vicente West Urdaneta City, Pangasinan 2438 Graduate School and Advanced StudiesDocument10 pagesUrdaneta City University San Vicente West Urdaneta City, Pangasinan 2438 Graduate School and Advanced StudiesAlyssa Santos JavierNo ratings yet
- Essay Es27 NotesDocument10 pagesEssay Es27 NotesJake Lobrigas0% (1)
- Parts ModelDocument4 pagesParts Modelapi-238591889No ratings yet
- Year End Activity Is SAPDocument13 pagesYear End Activity Is SAP233598No ratings yet
- PM Module 3Document86 pagesPM Module 3yashantsh4No ratings yet
- Q 4Document3 pagesQ 4nchimunyaclement5No ratings yet
- Quality Management Unit 2Document22 pagesQuality Management Unit 2Vishesh RaiNo ratings yet
- Topic Three Organizing FunctionDocument10 pagesTopic Three Organizing Functionstill earvinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE MGDocument3 pagesCHAPTER ONE MGNikodimos yeshitilaNo ratings yet
- Organization StuctureDocument28 pagesOrganization StucturekamalniNo ratings yet
- Organizational Design Apuntes FinalDocument68 pagesOrganizational Design Apuntes FinalMarinaNo ratings yet
- Osd Notes 1Document37 pagesOsd Notes 1yogendra choukikerNo ratings yet
- Management Principles & Practice: Tinku Ibmr-HDocument15 pagesManagement Principles & Practice: Tinku Ibmr-HtyrappNo ratings yet
- Analysing Project Organisation StructureDocument6 pagesAnalysing Project Organisation StructureEnock PhiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 OrganisingDocument11 pagesChapter - 5 OrganisingGauravSinghNo ratings yet
- Aom Topic4 BarcobuitizoncadeliñaDocument53 pagesAom Topic4 BarcobuitizoncadeliñaJohn Lloyd BarcoNo ratings yet
- Managerial RolesDocument39 pagesManagerial RolesRedemption SalvationNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure & DesignDocument37 pagesOrganization Structure & Designmridsinghster64No ratings yet
- UJMC2033 Applied Organisational CommunicationDocument28 pagesUJMC2033 Applied Organisational CommunicationKeith 777No ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument29 pagesOrganizingTewodros GetahunNo ratings yet
- Introduction ManagmentDocument175 pagesIntroduction ManagmentbarkeNo ratings yet
- Organizational Levels or Levels of ManagementDocument7 pagesOrganizational Levels or Levels of ManagementammuajayNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Start-Ups 03600201: Lecturer-Applied Science, Diploma StudyDocument85 pagesEntrepreneurship and Start-Ups 03600201: Lecturer-Applied Science, Diploma StudySMIT CHRISTIANNo ratings yet
- ORGANIZATION HandoutsDocument2 pagesORGANIZATION HandoutsJoana AlduhesaNo ratings yet
- MGT101 Principles of ManagementDocument2 pagesMGT101 Principles of Managementthanhvynguyn11No ratings yet
- BSN4 NCM 119 FinalsDocument14 pagesBSN4 NCM 119 FinalsAlexie NicoleNo ratings yet
- 5 Main Types of Organisational StructureDocument7 pages5 Main Types of Organisational Structurerobin sonNo ratings yet
- Types of Organisation StructuresDocument15 pagesTypes of Organisation StructuresViral OkNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Internal Organisation EnvironmentDocument24 pagesSection 2 - Internal Organisation Environmentstevinfisher8No ratings yet
- ITM EndtermDocument10 pagesITM EndtermashleynowoddaisyNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument21 pagesOrganization Structuresimply_coool100% (3)
- Chapter 3 Project Management 1Document7 pagesChapter 3 Project Management 1escramosaaravellaNo ratings yet
- Construction Project OrganizationDocument2 pagesConstruction Project OrganizationRica Jewel VistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document55 pagesChapter 3assemtharwat1960No ratings yet
- OrganisingDocument29 pagesOrganisingAnsh RawatNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice 2Document5 pagesProfessional Practice 2Jonane AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management ProcessDocument10 pagesNursing Management ProcessGilbert BagsicNo ratings yet
- BUSA (Chapter 1)Document3 pagesBUSA (Chapter 1)JuStin KeIth RamosNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument37 pagesOrganizingMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Oam Topic 3Document20 pagesOam Topic 3mwagadijohnathan65No ratings yet
- CH-4 MGT IntDocument11 pagesCH-4 MGT IntwubeNo ratings yet
- PPM NotesDocument14 pagesPPM NotesNilabjo Kanti PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OrganisingDocument6 pagesChapter 5 OrganisingTiya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- A Concept of Organizational Structure..Document14 pagesA Concept of Organizational Structure..Tesfaye NokoNo ratings yet
- Iom Module 1Document52 pagesIom Module 1Niranjana VannadilNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument21 pagesOrganization Structurevinaycool12344150100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Management Today-DoneDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Management Today-Donebbypia johnNo ratings yet
- Management Science Midterm HandoutsDocument30 pagesManagement Science Midterm Handoutsyennytobesa123No ratings yet
- 1st Lecture ITMDocument54 pages1st Lecture ITMIqra FarrukhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Designing The Organizational StructureDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2 Designing The Organizational StructureJames Paul RaquelNo ratings yet
- Office Management Is Vital in Any Organization Because It Makes The Business and Employee Efficient andDocument3 pagesOffice Management Is Vital in Any Organization Because It Makes The Business and Employee Efficient andVenz De VegaNo ratings yet
- From Top DownDocument13 pagesFrom Top DownZainab AamirNo ratings yet
- Management Short NotesDocument20 pagesManagement Short NotesUpul GamageNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument43 pagesOrganizingshimahkarungi989No ratings yet
- HD Mgmt1001 NotesDocument71 pagesHD Mgmt1001 NotesRohit LouisNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Management CH1 SummaryDocument7 pagesContemporary Management CH1 SummaryNour AliNo ratings yet
- O&M Module PDF File-1Document177 pagesO&M Module PDF File-1Strewbary BarquioNo ratings yet
- Business Management Principles for Today's Leaders: A Practical Guide for ProfessionalsFrom EverandBusiness Management Principles for Today's Leaders: A Practical Guide for ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Common Efficiency Mistakes Companies Make And How To Avoid ThemFrom EverandCommon Efficiency Mistakes Companies Make And How To Avoid ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microeconomics Cha 4Document8 pagesMicroeconomics Cha 4haile GetachewuNo ratings yet
- PepsiDocument8 pagesPepsiAleem MalikNo ratings yet
- CAA CH 2 Questions Pt.1Document4 pagesCAA CH 2 Questions Pt.1JohnNo ratings yet
- ADL Leveraging AI To Transform Bank Sales 2023Document12 pagesADL Leveraging AI To Transform Bank Sales 2023Gaspar BlaserNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesFinancial AccountingMikeNo ratings yet
- Business To Business Marketing 4th Edition Brennan Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesBusiness To Business Marketing 4th Edition Brennan Solutions ManualAnthonyJacksonekdpb100% (17)
- Pengaruh Content Marketing TikTok Terhadap Customer EngagementDocument6 pagesPengaruh Content Marketing TikTok Terhadap Customer EngagementSonya PatreciaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Lesson 1Document59 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Lesson 1Lorraine Sambile Arroyo67% (3)
- Problem 1 Dream Co. and Theater CoDocument4 pagesProblem 1 Dream Co. and Theater CoskyNo ratings yet
- First Four Chapters of How To Value InvestDocument23 pagesFirst Four Chapters of How To Value InvestJason RiveraNo ratings yet
- Glossary: © Canadian Securities Institute (2015)Document32 pagesGlossary: © Canadian Securities Institute (2015)john tinkaNo ratings yet
- BM Short Notes (PBP)Document99 pagesBM Short Notes (PBP)Asim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Ba100 ReviewerDocument15 pagesBa100 ReviewerSay SayNo ratings yet
- The Digital Marketing To Influence Customer SatisfDocument15 pagesThe Digital Marketing To Influence Customer SatisfIH RamayNo ratings yet
- 08 Konys IncDocument44 pages08 Konys IncAshish Kumar0% (1)
- Revision Problem For Final Exam INS3032 2017Document2 pagesRevision Problem For Final Exam INS3032 2017magical_life96100% (1)
- Assignment 1 WorksheetDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Worksheetgolemwitch01No ratings yet
- Business IndustrialDocument2 pagesBusiness Industrialakshay.gupta993207No ratings yet
- Notes Link Notes Link: Risk Assessment Link Risk Response LinkDocument4 pagesNotes Link Notes Link: Risk Assessment Link Risk Response Linkmentor_muhaxheriNo ratings yet
- Auditing Presentation 1Document1 pageAuditing Presentation 1Yuqiao LinNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset - Capitalization and Depreciation Guidelines - FinalDocument16 pagesFixed Asset - Capitalization and Depreciation Guidelines - FinalEunice WongNo ratings yet
- Summary EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesSummary EntrepreneurshipMelodie BrionesNo ratings yet
- Chap 008Document43 pagesChap 008Areeba Mushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digital - Marketing - Plan - For - Bosch - in - Grai TASK 1Document4 pagesDigital - Marketing - Plan - For - Bosch - in - Grai TASK 1Sserunkuma MosesNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AssertionsDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement AssertionsJus EneroNo ratings yet
- Demantra Benefit AnalyzerDocument20 pagesDemantra Benefit Analyzeranishokm2992No ratings yet