Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PathophysiologyofPepticUlcer2829
PathophysiologyofPepticUlcer2829
Uploaded by
destroyerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PathophysiologyofPepticUlcer2829
PathophysiologyofPepticUlcer2829
Uploaded by
destroyerCopyright:
Available Formats
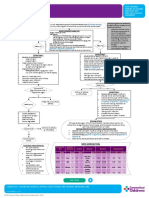
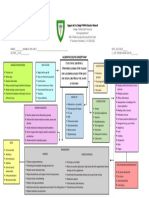
PEPTIC ULCER
PREDISPOSING MAIN IDEA
CONTRIBUTING MAIN IDEA
PRECIPITATING
FACTORS FACTORS FACTORS
Age: 61 years old History of chronic gastritis with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for Weight loss, Bloating and Fullness, Stomach
Gender: Female
Family history of gastric cancer (mother) and duodenal
osteoarthritis. Ache, Nausea, Vomiting
Recent increase in NSAID intake due to knee pain.
ulcers (brother). History of smoking for 30 years.
MAIN IDEA
CHIEF
COMPLAINT
2-month history of burning pain in the epigastric
abdomen and chest, which radiates toward her
back
LABORATORY/DIAGNOSIS
TEST
LIVER UPPER ENDOSCOPY ABDOMINAL
CBC (ESOPHAGOGASTROD FECAL OCCULT
FUNCTION ULTRASOUND COLONOSCOPY
UODENOSCOPY OR BLOOD TEST
TESTS EGD) OR CT SCAN
Hemoglobin (Hb): Decreased Alanine Aminotransferase
(indicating anemia due to (ALT) and Aspartate finding may include:
Aminotransferase (AST): May
Findings may include: Positive result (indicating Pancreatic inflammation or
chronic blood loss). Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach Inflammation, polyps, or
Hematocrit (Hct): Decreased be elevated (suggestive of the presence of blood in changes consistent with
lining, possibly with erosions or ulcers.
pancreatitis. tumors in the colon or
(consistent with anemia). liver inflammation or injury). Peptic Ulcers: Ulcerations in the the stool, suggestive of
Mean Corpuscular Volume Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): stomach or duodenum. Liver abnormalities such as rectum, depending on the
Esophagitis: Inflammation of the gastrointestinal bleeding). fatty liver disease or liver
(MCV): May be normal or May be elevated (indicative of
esophagus, often due to
extent of examination.
decreased. biliary obstruction or liver metastases.
gastroesophageal reflux disease
White Blood Cell Count (WBC): involvement). (GERD). Abdominal masses or
May be normal or elevated Bilirubin: Elevated levels may Possible presence of Helicobacter lymphadenopathy suggestive
(indicating inflammation or suggest liver dysfunction or pylori infection. of malignancy.
infection). obstruction.
DISEASE
PROCESS
Acquisition of H pylori
Chronic H pylori infection in stomach
cagA+ tox+ cagA-tox -
Intense gastritis (Increase IL-8, nreutophil
infiltration), epithelial damage
Peptic Ulcer
CLINICAL
MANIFESTATIONS
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Epigastric pain Proton Pump Inhibitors (Omeprazole) Nausea and vomiting Antiemetics (Ondansetron)
help control nausea and vomiting by Bloating and fullness
Hyoscyamine Gastrointestinal (Pantoprazole)
suppress gastric acid production, Alleviate abdominal discomfort and
promoting ulcer healing and symptom blocking neurotransmitter receptors or bloating by reducing smooth bleeding inhibit gastric acid secretion,
relief. inhibiting gastric motility and sensitivity. promoting hemostasis and
muscle spasms in the
preventing rebleeding from ulcer
gastrointestinal tract.
sites.
Acute Pain related to gastric Nausea and Vomiting related to gastric Impaired Comfort related to abdominal Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume related to actual or
mucosal irritation and ulceration as irritation, inflammation, or bleeding distention, bloating, and early satiety as potential gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to
evidenced by patient reports of secondary to peptic ulcer disease, as evidenced by patient reports of peptic ulcer disease, as evidenced by patient
evidenced by patient reports of nausea reports of hematemesis (vomiting blood), melena
burning or gnawing sensation in the discomfort and fullness in the upper (black, tarry stools), or hematochezia (bright red
and episodes of vomiting.
upper abdomen. abdomen. blood in stools).
1. Assess patient’s vital sign. 1. Assess patient’s vital sign. 1. Assess the patient’s vital sign.,
1. Monitor vital signs and oxygen
2. Assess the severity and 2. Assess the frequency, severity, 2. Assess the patient's abdominal
discomfort, bloating, and fullness, saturation.
characteristics of pain, including and duration of nausea and
location, intensity, and including any associated factors or 2. Administer oxygen, blood
vomiting episodes.
exacerbating factors. 3. Administer antiemetic exacerbating triggers. transfusions, and medications
3. Administer prescribed pain relief medications, such as
3. Encourage the patient to maintain a as prescribed.
low-fat, low-fiber diet to reduce 3. Insert an IV catheter for fluid
medications, such as antacids, ondansetron or metoclopramide, bloating and discomfort.
H2 receptor antagonists, or as prescribed to alleviate nausea resuscitation.
4. Administer prescribed medications,
proton pump inhibitors, as and prevent vomiting. such as prokinetic agents or 4. Prepare the client for
scheduled. 4. Encourage the patient to antispasmodics, to improve endoscopy or surgery, if
4. Encourage relaxation consume small, frequent meals gastrointestinal motility and reduce necessary.
techniques, positioning for and avoid triggers that may bloating. 5. Educate the client on dietary
comfort, and distraction methods exacerbate nausea, such as 5. Encourage the patient to avoid
modifications and medication
to help alleviate pain. strong odors or spicy foods. carbonated beverages and gas-
producing foods that may management post-discharge.
5. Educate the patient on the 5. Offer oral hygiene measures,
importance of adhering to exacerbate bloating.
such as mouth rinses or chewing
medication regimens to control 6. Provide education on relaxation
gum, to help alleviate the
techniques and stress management
pain and promote ulcer healing. sensation of nausea. strategies to help alleviate
6. Monitor the patient's response to 6. Monitor fluid intake and output, abdominal discomfort.
pain management interventions as persistent vomiting can lead
and adjust as needed based on to dehydration and electrolyte
effectiveness and side effects. imbalances.
References
https://nursinganswers.net/case-studies/study-of-a-patient-with-shortness-of-breath-nursing-essay.php
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002934396002732
LEGEND
DISEASE CHIEF COMPLAINT
PHARMARCOLOGICAL
LAB TEST TEST RESULT DISEASE PROCESS CLINICAL MANIFESTATION NURSING DIAGNOSIS NURSING MANAGEMENT
MANAGEMENT
You might also like
- Peptic Ulcer Disease (Pud) Concept Map PUDDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer Disease (Pud) Concept Map PUDIris Mambuay0% (1)
- German Word List - Learn - FamilySearchDocument30 pagesGerman Word List - Learn - FamilySearchperrigalgoNo ratings yet
- Philip Merlan, From Platonism To NeoplatonismDocument267 pagesPhilip Merlan, From Platonism To NeoplatonismAnonymous fgaljTd100% (1)
- Drug Study RPDocument2 pagesDrug Study RPJustine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyJoshua Dumanjug SyNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida - GDMDocument1 pageOral Revalida - GDMMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- REBAMIPIDEDocument2 pagesREBAMIPIDEMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- Nilai Raport Kelas ASTSDocument17 pagesNilai Raport Kelas ASTSAYANANo ratings yet
- Icu DrugstudyDocument3 pagesIcu DrugstudyMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Patient's DataDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Patient's DataKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of First Seizure and Newly Diagnosed.4Document31 pagesEvaluation of First Seizure and Newly Diagnosed.4CARMEN NATALIA CORTÉS ROMERONo ratings yet
- Inpatient Asthma: Clinical PathwayDocument9 pagesInpatient Asthma: Clinical PathwaydedeNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument2 pagesDiverticulitisyapyapvinx50% (2)
- 4pain ManagementDocument1 page4pain ManagementrajeshNo ratings yet
- Texas Health Steps Periodicity ScheduleDocument2 pagesTexas Health Steps Periodicity ScheduleLujain Al OmariNo ratings yet
- DR - Dr. Fardah Akil, SP - PD (K) Geh Paracetamol 500mg/6jam/oral (Selama 3x24jam) Dr. Faisal Muchtar, SP - An-KICDocument2 pagesDR - Dr. Fardah Akil, SP - PD (K) Geh Paracetamol 500mg/6jam/oral (Selama 3x24jam) Dr. Faisal Muchtar, SP - An-KICfatimah syamNo ratings yet
- DNP Project PosterDocument1 pageDNP Project Posterapi-555348585No ratings yet
- Notas Primer Quimestre 2p 3 Bgu D - Ueee ArregladoDocument7 pagesNotas Primer Quimestre 2p 3 Bgu D - Ueee ArregladoCeciliamp3 MoreiraNo ratings yet
- NFT 1Document2 pagesNFT 1cliffwinskyNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Points For Diabetes PDFDocument4 pagesAcupressure Points For Diabetes PDFRanganathanNo ratings yet
- Men's Health - May 2017 UK PDFDocument148 pagesMen's Health - May 2017 UK PDFAakash BanthiaNo ratings yet
- ADA Adult Pain Guideline 2023 ToothacheDocument2 pagesADA Adult Pain Guideline 2023 ToothacheElaf AlBoloshiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyGWYNETH MAEHRAM DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument2 pagesAnalgesicsJe EcleoNo ratings yet
- Earth - UDAYA Yoga & FitnessDocument1 pageEarth - UDAYA Yoga & FitnesslinsimsNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesErythromycin Drug StudyJude LabajoNo ratings yet
- Certa 2Document1 pageCerta 2Sajeda A. HadiNo ratings yet
- Tabulation Report BDS FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION MARCH - 2021Document1 pageTabulation Report BDS FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION MARCH - 2021Nilesh MandowarNo ratings yet
- The Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalDocument26 pagesThe Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalsoeNo ratings yet
- Expert Advice For Today's Ob/Gyn: ObstetricsDocument66 pagesExpert Advice For Today's Ob/Gyn: Obstetricsjavierv44No ratings yet
- LAPORAN PENJARINGAN 2018 - EmailDocument6 pagesLAPORAN PENJARINGAN 2018 - EmailMoch RikiNo ratings yet
- Instituciòn Educativa Josè Asunciòn Silva CICLO: 5-1 Periodo: 1Document66 pagesInstituciòn Educativa Josè Asunciòn Silva CICLO: 5-1 Periodo: 1ANDREAS LOPEZ GOMEZNo ratings yet
- My PG Notes® - Disorders With Café-Au-Lait SpotsDocument1 pageMy PG Notes® - Disorders With Café-Au-Lait SpotsSubhajitPaulNo ratings yet
- Total 8 C Formato ActualizadoDocument12 pagesTotal 8 C Formato Actualizadotoala AdonisNo ratings yet
- Omeprazol Brand - Generi C Name Action Contraindica Tion Indication S Adverse Reaction Prioritized Nursing Consideration SDocument5 pagesOmeprazol Brand - Generi C Name Action Contraindica Tion Indication S Adverse Reaction Prioritized Nursing Consideration SJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFDocument9 pagesAbdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFFIA SlotNo ratings yet
- Welcome!: Pre-Admission FormsDocument8 pagesWelcome!: Pre-Admission FormsFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Master Rotation Anm 2 ND YearDocument2 pagesMaster Rotation Anm 2 ND YearJyoti Prem UttamNo ratings yet
- CRP 1st SemDocument10 pagesCRP 1st SemMy hidden memoriesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RosillosaDocument4 pagesDrug Study RosillosaJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Menu 7498Document2 pagesMenu 7498Antony StarkNo ratings yet
- Cush-HTT 025 036 17OCT 14Document7 pagesCush-HTT 025 036 17OCT 14radu nicolaeNo ratings yet
- Jadwal PelajaranDocument1 pageJadwal PelajaranshahnazNo ratings yet
- 2020-Banner-Rootcause-All of You-ProdoDocument1 page2020-Banner-Rootcause-All of You-Prodoapi-615872422No ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug Study RevisionDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug Study RevisionJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Treatments 2024 Letter 3 24v1Document2 pagesRespiratory Treatments 2024 Letter 3 24v1Duc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis Concept MapDocument1 pageUlcerative Colitis Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Registro Personal de Calificaciones Nro: Unidad Educativa "Pacto Andino"Document56 pagesRegistro Personal de Calificaciones Nro: Unidad Educativa "Pacto Andino"MARTIN SALTOSNo ratings yet
- Lap. Promkes September Amondo 2017Document28 pagesLap. Promkes September Amondo 2017Hendrik SuparwanNo ratings yet
- TN Pharmacology in Tables PDFDocument54 pagesTN Pharmacology in Tables PDFCean ObinaNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Kelas 45 Menit PDFDocument18 pagesJadwal Kelas 45 Menit PDFZaki FuadiNo ratings yet
- Case Study MajriDocument63 pagesCase Study Majridiana malekNo ratings yet
- Attendance JHS Als 2023-2024Document3 pagesAttendance JHS Als 2023-2024LORLITO MALABORBORNo ratings yet
- Menu 188Document2 pagesMenu 188Antony StarkNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH MASTER Tips+for+dealing+with+Covid-19+at+home V5Document1 pageENGLISH MASTER Tips+for+dealing+with+Covid-19+at+home V5Pankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Hyperdoc Handbook SlidesManiaDocument14 pagesHyperdoc Handbook SlidesManiaMarah AbdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KetorolacDocument4 pagesDrug Study KetorolacFermary NicolèNo ratings yet
- Dacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsDocument2 pagesDacanay Jungco Omeprazole DsTRISHA JUNGCONo ratings yet
- Total 8 D Formato ActualizadoDocument12 pagesTotal 8 D Formato Actualizadotoala AdonisNo ratings yet
- Ilovepathology - Com (1) UrinDocument2 pagesIlovepathology - Com (1) UrinNori VeilaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitleddestroyerNo ratings yet
- How Pandemic Has Changed Education.Document1 pageHow Pandemic Has Changed Education.destroyerNo ratings yet
- CEU The University of The First ChoiceDocument1 pageCEU The University of The First ChoicedestroyerNo ratings yet
- M5CIA2 Dela Pena BSN1L 1Document2 pagesM5CIA2 Dela Pena BSN1L 1destroyerNo ratings yet
- Group 1 InfographicsDocument1 pageGroup 1 InfographicsdestroyerNo ratings yet
- Aldanese vs. SalutilloDocument2 pagesAldanese vs. SalutilloArthur Kenneth lavapizNo ratings yet
- 2 Ubales Vs PeopleDocument21 pages2 Ubales Vs PeopleRozaiineNo ratings yet
- My HR ProjectDocument29 pagesMy HR ProjectAshish ChaudhaRyNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Costs and Government Grants ProblemsDocument1 pageBorrowing Costs and Government Grants Problemstough mamaNo ratings yet
- Rizal Sunny SpainDocument34 pagesRizal Sunny SpainPao NachorNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSiop Lesson Planapi-306937002No ratings yet
- Sectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryDocument4 pagesSectional Title Ownership Podcast SummaryannNo ratings yet
- Using Deep Learning To Recognize Therapeutic Effects of Music Based On EmotionsDocument13 pagesUsing Deep Learning To Recognize Therapeutic Effects of Music Based On EmotionsJan LAWNo ratings yet
- The Patriot PDFDocument17 pagesThe Patriot PDFHansikaNo ratings yet
- Homeschooling PDFDocument8 pagesHomeschooling PDFapi-396621343100% (1)
- Tax MatrixDocument1 pageTax MatrixJulo R. TaleonNo ratings yet
- Management Theories 1Document39 pagesManagement Theories 1Prajapati SanjayNo ratings yet
- Book - 2005 - Dov Schwartz - Astral Magic in Medieval Jewish Thought PDFDocument258 pagesBook - 2005 - Dov Schwartz - Astral Magic in Medieval Jewish Thought PDFAung Hein AyeNo ratings yet
- Fsec CR 1537 05Document613 pagesFsec CR 1537 05Amber StrongNo ratings yet
- Scott Wolcott - CVDocument3 pagesScott Wolcott - CVapi-413609470No ratings yet
- Difference Equations 3 PDFDocument24 pagesDifference Equations 3 PDFBiswaranjan NayakNo ratings yet
- 19th Performance Studies International Conference Program, 2013, Stanford UniversityDocument27 pages19th Performance Studies International Conference Program, 2013, Stanford UniversityAndra YountNo ratings yet
- PrudentialDocument2 pagesPrudentialJiang HengyiNo ratings yet
- Zero BDocument11 pagesZero Bvy143cyNo ratings yet
- The Fontan Circulation Contin EducDocument5 pagesThe Fontan Circulation Contin EducAishu BNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFDocument716 pagesSchaeffler Technical Pocket Guide PDFStoica ValentinNo ratings yet
- 8 Fibrinolytic DrugsDocument41 pages8 Fibrinolytic DrugsIman SaksoukNo ratings yet
- Tao Te ChingDocument26 pagesTao Te ChingdrevenackNo ratings yet
- Implications of The TrinityDocument6 pagesImplications of The TrinityTh3Lov3OfG0dNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Attitudes, Self-Concept,: Values, and EthicsDocument27 pagesChapter 3 - Attitudes, Self-Concept,: Values, and EthicsTanuj KumarNo ratings yet
- Online Software Testing Training For BeginnersDocument30 pagesOnline Software Testing Training For BeginnersVibrantGroup MumbaiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Valuation Approach - TP-S4HANA, On-Premise REL-19.07.2021Document10 pagesMultiple Valuation Approach - TP-S4HANA, On-Premise REL-19.07.2021Parvati sbNo ratings yet
- (Anton Drake) Poker Isometrics and Poker Fitness PDFDocument209 pages(Anton Drake) Poker Isometrics and Poker Fitness PDFLeonardo Amaral100% (1)