Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsWorksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Worksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Uploaded by
Chelsea UysonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Population and SampleDocument6 pagesPopulation and SampleMaam ArenavlasNo ratings yet
- Parker Beck ch5Document23 pagesParker Beck ch5api-365463992No ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesSampling and Sampling TechniquesTeomar RomaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedDocument16 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedUsman DitucalanNo ratings yet
- Methods of SamplingDocument22 pagesMethods of SamplingAngel DeytaNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCollection of Data: Objectivesapple gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Gatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Document45 pagesGatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Caryl Mae BocadoNo ratings yet
- Sampling AutosavedDocument50 pagesSampling AutosavedJen FinanceNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument21 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityYdzel Jay Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument19 pagesSampling TechniquesMj DiolataNo ratings yet
- LU 2 Sampling Techniques and Data CollectionDocument29 pagesLU 2 Sampling Techniques and Data CollectionKristhel Jane Roxas NicdaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionManchilot TilahunNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M5 PDFDocument16 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M5 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- Week 4-6 Lessons: Collection of DataDocument8 pagesWeek 4-6 Lessons: Collection of Databernadeth salmoroNo ratings yet
- Statistics 9 Quarter 1 Week 5 6 Module IDocument10 pagesStatistics 9 Quarter 1 Week 5 6 Module IMaveriex Zon LingcoNo ratings yet
- WK 5 Statistics Probability Q3 Mod4 Random Sampling Parameter and StatisticDocument16 pagesWK 5 Statistics Probability Q3 Mod4 Random Sampling Parameter and StatisticRoxane RagaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods PDFDocument18 pagesSampling Methods PDFMary kris LariosaNo ratings yet
- Stat IIDocument10 pagesStat IIbarrichabarrichooNo ratings yet
- Q3 Mod 4Document8 pagesQ3 Mod 4nonkeannangela4No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log School Time: Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log School Time: Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayJerrylyn AnonteNo ratings yet
- Core08 M7Document6 pagesCore08 M7HanaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document38 pagesModule 4Alrac Anacta MalaitNo ratings yet
- Sampling Method Summary and ActivityDocument5 pagesSampling Method Summary and Activityjuvylynsumaylo8No ratings yet
- Statistics M4Document18 pagesStatistics M4Archimedes Arvie GarciaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingrmdn32529732No ratings yet
- Random SamplingDocument28 pagesRandom SamplingJelian MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Stat II CHAPTER 1 &2Document16 pagesStat II CHAPTER 1 &2Abdu YaYa AbeshaNo ratings yet
- Sampling ProceduresDocument53 pagesSampling Procedureschumenzoo100% (1)
- Sampling Designs/Techniques Why Sample?Document5 pagesSampling Designs/Techniques Why Sample?camilleescote562No ratings yet
- Sample - Is The Subset of The Entire PopulationDocument6 pagesSample - Is The Subset of The Entire PopulationRuby JaneNo ratings yet
- Data Management LESSON 1: Data Collection TIME FRAME: 2 Hours Code: Learning Outcome (S)Document25 pagesData Management LESSON 1: Data Collection TIME FRAME: 2 Hours Code: Learning Outcome (S)Bryan MerinaNo ratings yet
- Stat Q1W7Document36 pagesStat Q1W7nathan samuell dorigoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbDocument5 pagesLESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbMilanie lihaylihayNo ratings yet
- Definition of StatisticsDocument7 pagesDefinition of StatisticsLavinia Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- PR2 Population and SamplingDocument4 pagesPR2 Population and SamplingDandruma TaffNo ratings yet
- Bongabon Senior High SchoolDocument8 pagesBongabon Senior High SchoolMelody CairelNo ratings yet
- Collection of DataDocument8 pagesCollection of DataRosanna Jose CuevasNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics 4Document10 pagesBusiness Statistics 4solicitors firmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 2 PDFDmzjmb SaadNo ratings yet
- Sampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. IsmaelDocument17 pagesSampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. Ismaelalioden MarohomslicNo ratings yet
- Week 4 SPDocument6 pagesWeek 4 SPc1716811No ratings yet
- Sampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarDocument5 pagesSampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarAashis TamangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Module StatDocument9 pagesWeek 7 Module StatEy EmNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument7 pagesSampling Methodsapi-552158438No ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesSampling Techniquestantan GalamNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part 2Document25 pagesStatistics Part 2Nestor Gutiza Jr.No ratings yet
- STAT LeaP Wk5Document8 pagesSTAT LeaP Wk5PEACHES N' CREAMNo ratings yet
- Module 9-Sampling DesignDocument7 pagesModule 9-Sampling DesignJayashree ChakrapaniNo ratings yet
- J. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationDocument37 pagesJ. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationGautamNo ratings yet
- Sample Size and Sampling TechniqueDocument30 pagesSample Size and Sampling TechniqueSanchez A. RubenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inferential Statistics Objectives: ExampleDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Inferential Statistics Objectives: ExampleMarianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityDocument38 pagesSampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityPradeep M VineetaNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit 3Document42 pagesBRM Unit 3prem nathNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research Week 12 AssessmentDocument8 pagesMethods of Research Week 12 AssessmentJoeddy LagahitNo ratings yet
- Stat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK4Document10 pagesStat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK4Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- 5 Sampling Technique and Sample SizeDocument11 pages5 Sampling Technique and Sample Sizecluadine dinerosNo ratings yet
- Tehnik Sampel&penyiapan DataDocument5 pagesTehnik Sampel&penyiapan DataFerial FerniawanNo ratings yet
- Population, Sample and Sampling TechniquesDocument8 pagesPopulation, Sample and Sampling TechniquesMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Stat - Chpater ThreeDocument5 pagesStat - Chpater ThreeFeven FevitaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument8 pagesSamplingikatal20No ratings yet
- Unesco PDFDocument58 pagesUnesco PDFzakry80No ratings yet
- 227 - ch6 HW Soln PDFDocument21 pages227 - ch6 HW Soln PDFDavid CookNo ratings yet
- Maksić & Pavlović, 2011 - Tematska Analiza - Implicitne TeorijeDocument14 pagesMaksić & Pavlović, 2011 - Tematska Analiza - Implicitne TeorijeprigNo ratings yet
- SMETDocument3 pagesSMETYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- During These Days, To Practice and Record Her Valedictory Speech. Please Follow Our HealthDocument15 pagesDuring These Days, To Practice and Record Her Valedictory Speech. Please Follow Our HealthSunny PajoNo ratings yet
- 2004-2005 AchievementsDocument1 page2004-2005 AchievementsnsidneyNo ratings yet
- Economics of Education and Socioogy of EducationDocument54 pagesEconomics of Education and Socioogy of EducationSsentongo NazilNo ratings yet
- Katie Earhart ResumeDocument3 pagesKatie Earhart Resumeapi-279957784No ratings yet
- Messy Process of School Counselor LeadershipDocument3 pagesMessy Process of School Counselor LeadershipMus OubNo ratings yet
- SPANISH 3, Sem 2 (Avancemos) - Course Guide / Syllabus / Lesson Plans - by Marty J ReepDocument4 pagesSPANISH 3, Sem 2 (Avancemos) - Course Guide / Syllabus / Lesson Plans - by Marty J ReepMarty Reep100% (1)
- Resume Final - 2Document2 pagesResume Final - 2api-279988623No ratings yet
- James Brindley 1716-27 de Septiembre de 1772Document2 pagesJames Brindley 1716-27 de Septiembre de 1772Oscar ValleNo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 Academic CatalogueDocument225 pages2020-2021 Academic CatalogueError 404No ratings yet
- CrossBraining STEM/PBL Kits Delivered To Jackson Public SchoolsDocument2 pagesCrossBraining STEM/PBL Kits Delivered To Jackson Public SchoolsPR.comNo ratings yet
- LSAT Center Reading Comprehension IntroductionDocument28 pagesLSAT Center Reading Comprehension Introductionbharath_mv7100% (1)
- College SheetDocument80 pagesCollege SheetYashNo ratings yet
- Digital Studio: Course DescriptionDocument12 pagesDigital Studio: Course DescriptionCornNo ratings yet
- Using Youtube Video An It-Based Media To Improve Students' Speaking SkillDocument10 pagesUsing Youtube Video An It-Based Media To Improve Students' Speaking Skillbuat donlotNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Speaking and Listening (RRL - 1)Document11 pagesRelationship Between Speaking and Listening (RRL - 1)Gen PriestleyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - Week 4 Quarter 4 - Week 5: Challenge/s in Life & Cmmunity Life Skill/s Used Positive AttitudeDocument5 pagesQuarter 4 - Week 4 Quarter 4 - Week 5: Challenge/s in Life & Cmmunity Life Skill/s Used Positive AttitudeShiela AltoNo ratings yet
- Math in Real LifeDocument7 pagesMath in Real Lifeapi-342084091No ratings yet
- 0511 s11 Ms 41 Mark SchemeDocument13 pages0511 s11 Ms 41 Mark SchemevijthorNo ratings yet
- Level of English Reading ProficiencyDocument25 pagesLevel of English Reading Proficiencyjah gonzalesNo ratings yet
- How To Introduce Yourself To Your StudentsDocument12 pagesHow To Introduce Yourself To Your StudentsLaura TrifanNo ratings yet
- Cover and Back PDFDocument8 pagesCover and Back PDFMohammed KhanNo ratings yet
- GODocument5 pagesGOChandra KanthNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Joseph KaswaDocument69 pagesDissertation - Joseph KaswaJohn Fetiza ObispadoNo ratings yet
- tanu ahlawat cv-2Document2 pagestanu ahlawat cv-2Dharwi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Version 1 0Document83 pagesFinal Report Version 1 0valerio_rossi8298No ratings yet
Worksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Worksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Uploaded by
Chelsea Uyson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Worksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesWorksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Worksheet 4.2a Sampling and Sampling Techniques
Uploaded by
Chelsea UysonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Sampling and Sampling Techniques 2. Questionaire.
This method is referred to as the
indirect method of gathring beacause this makes use
SAMPLE is a part of the population that is subject to of written questions to be answered by the
research and used to represent the entire population as a respondent.
whole. 3. Observation. This method makes use of the different
human senses in gathering information.
SAMPLING TECHNIQUES ARE :
4. Registration or Census. This method requires the
1. RANDOM SAMPLING - each member of the enactment of law to take effect bacause it needs the
population has an equally likely chance of being participation of a large, if not the entire, population.
selected. 5. Experimentation. This method is usually conducted
Ex: Fish bowl procedure, Lottery in laboratories where specimens are subjected to
2. CONVENIENCE SAMPLING - it is a sample that is some aspects of control to find out cause and effect
chosen so that it is easy for the researcher. Least relationships.
expensive, least time consuming.
Ex: complete a survey using the students handled.
Data gathered may be classified as primary and
3. STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING - the
secondary.
population is divided into subgroups (Strata), so that
each population member is in only one subgroup. Primary Data- are information gathered directly
Ex: the company has 800 female employees and 200 from the source.
male employees. You want to ensure that the sample Secondary Data – are gathered from the
reflects the gender balance of the company, so you secondary sources, such as: books, journals,
sort the population into two strata based on gender. magazines, or thesis of other reserchers .
Then you use random sampling on each group,
selecting 80 women and 20 men, which gives you a In data gathering, information is usually taken from
representative sample of 100. a sample. The number of samples is determined by
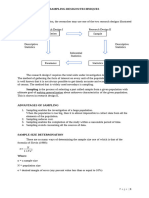
4. CLUSTER SAMPLING - it is a sample that involves using the Slovin’s Formula.
dividing the population into subgroups, but each
subgroup should have similar characteristics to the
whole sample. It is consists of items in a group such Slovin’s Formula
as a neighbourhood or a household. The group may
N
be chosen at random. n=
1+ Ne 2
5. SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING - is obtained using an Example: What is the sample size if the population is
ordered list of the population, thus selecting 3000 and the marginwhere,
of errornis=set
number
at : of samples
a. 5%
members systematically from the list. Every member N = number of population
b. 3%
of the population is listed with a number, but instead e = margin of error
of randomly generating numbers, individuals are Solution:
chosen at regular intervals.
a) The margin of error is 5% or 0.05. Thus,
n = __3000________
1 + (3000)(0.05)2
COLLECTION OF DATA n = 352.94
The first step in any statistical work after the formulation the sample size at 5% margin of error is 353.
of the problem is the collection of data. Data may be
gathered by the following methods: b) the margin of error is 3% or 0.03 . Hence,
n = ________3000____
1. Interview. This method is reffered to as the direct 1 + (3000)(0.03)2
method of gathering data because this requires a n = 810.81
face-to-face inquiry with the respondent. the sample size at 3% margin of error is 811.
number from 1 to 100. Then the numbers 1 to 100
Worksheets 4.2 are written on separate pieces of paper and shuffled.
Finally, the researcher picks 25 slips of paper and
A. Identify the most appropriate method(s) of collecting the numbers on the paper determine the 25
data to be used in each of the following research participants.
topic.
1. The effectiveness of Filipino as medium of
instruction in Mathematics. 4. A sociologist conducts an opinion survey in a major
2. The changes of behavior of drug dependents. city. Part of the research plan calls for describing
3. The physical and behavioral changes in a Guinea pig and comparing the opinions of four different ethnic
subjected to a new medicine for SARS. groups: African Americans, Asian Americans,
4. The number of private and public utility vehicles in European Americans, and Native Americans. For a
the country. total sample of 300, the researcher selects 75
5. The reaction of some celebrities to the participants from each of the four predetermined
announcement of the presidential bid of an actor. subgroups.
6. The recreational activities of third year students and 5. A researcher is interested in political attitudes of
its relative effects to their study habits. individuals within a particular state. The researcher
7. The values that are acquired by some teachers from uses the following procedure to obtain a sample: (a)
watching telenovelas. a random sample of counties is drawn, (b) within the
8. The learning style of students. counties selected, districts are randomly drawn, (c)
9. The characteristics, problems, and needs of the within each district, blocks are randomly sampled,
Filipino people. (d) within blocks selected, building are randomly
10. The average temperature in Baguio City from drawn, and (d) all residents within the buildings
December 1 to February 1. selected comprise the sample.
B. In each of the following examples, identify the
sampling method being used. 6. Instructors teaching research methods are interested
in knowing what study techniques their students are
1. A sample of 2,000 was sought to estimate the utilizing. Rather than assessing all students, the
average achievement in science of fifth graders in a researchers randomly select 10 students from each of
city’s public schools. The average fifth grade the sections to comprise their sample.
enrollment in the city’s elementary schools is 100
students. Thus, 20 schools were randomly selected
and within each of those schools all fifth graders 7. A researcher is interested in maximum-security
were tested. inmates. She groups maximum-security prisons by
state, randomly selects 10 states, and, from those 10,
selects three prisons. She includes all the inmates in
2. A researcher is interested in maximum-security those three prisons in her sample.
inmates. She groups inmates by the type of crime
committed, determines the percentage of the total in 8. To study the efficiency of a telephone company,
each crime category, and uses that percentage to Judy selects every 20th subscriber listed in the
determine the number of inmates randomly selected telephone directory for her sample.
from each group.
9. Annette wants to study the annual salaries of
professors in a certain university. She divides the
3. A researcher has a population of 100 third grade population according to their academic ranks and
children from a local school district from which a then selects a sample within these ranks.
sample of 25 children is to be selected. Each child’s
name is put on a list, and each child is assigned a
10. A researcher wants to know the relationships
between smoking and death rate by making a
nationwide survey on this matter. He selects the 13
regions of the country and picks 25 persons at
random from each region for interview.
C. Identify the type of data being described.
1) Scott is researching opinions on uniform in his school.
He asks a sample of pupils whether they believe the
uniform in the school should be changed.
2) Lauren is trying to find out about the percentage
employment rates for certain degrees. She does some
research on the internet on different employment and
university websites.
3) Kwame is interested in the number of goals that
different players score in the different football leagues.
He checks the Wikipedia pages of each player to try and
find out the values.
4) Alex wants to know about whether the school lunches
provide good value for money. She asks a sample of
pupils in the lunch hall how much they paid for their
meal.
5) Conor wants to find out about the history of Second
World War. One of the things he does is look up online
the number of people who died from each of the
countries who fought in the war.
6) Leanne is doing a geography project. As part of her
project she is looking at the population density of
different urban areas. She looks this up on a website.
7) Will is in maths class doing a practical lesson where
he measures the lengths of different objects in the
classroom.
8) Sam is carrying out a readability test in her English
lesson. As part of her test she counts the word length of
each word on a randomly selected page.
You might also like
- Population and SampleDocument6 pagesPopulation and SampleMaam ArenavlasNo ratings yet
- Parker Beck ch5Document23 pagesParker Beck ch5api-365463992No ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesSampling and Sampling TechniquesTeomar RomaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedDocument16 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 3 ModifiedUsman DitucalanNo ratings yet
- Methods of SamplingDocument22 pagesMethods of SamplingAngel DeytaNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesCollection of Data: Objectivesapple gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Gatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Document45 pagesGatheringofdata2 150513082553 Lva1 App6892Caryl Mae BocadoNo ratings yet
- Sampling AutosavedDocument50 pagesSampling AutosavedJen FinanceNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument21 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityYdzel Jay Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument19 pagesSampling TechniquesMj DiolataNo ratings yet
- LU 2 Sampling Techniques and Data CollectionDocument29 pagesLU 2 Sampling Techniques and Data CollectionKristhel Jane Roxas NicdaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Sampling and Sampling DistributionManchilot TilahunNo ratings yet
- Math11 SP Q3 M5 PDFDocument16 pagesMath11 SP Q3 M5 PDFJessa Banawan EdulanNo ratings yet
- Week 4-6 Lessons: Collection of DataDocument8 pagesWeek 4-6 Lessons: Collection of Databernadeth salmoroNo ratings yet
- Statistics 9 Quarter 1 Week 5 6 Module IDocument10 pagesStatistics 9 Quarter 1 Week 5 6 Module IMaveriex Zon LingcoNo ratings yet
- WK 5 Statistics Probability Q3 Mod4 Random Sampling Parameter and StatisticDocument16 pagesWK 5 Statistics Probability Q3 Mod4 Random Sampling Parameter and StatisticRoxane RagaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods PDFDocument18 pagesSampling Methods PDFMary kris LariosaNo ratings yet
- Stat IIDocument10 pagesStat IIbarrichabarrichooNo ratings yet
- Q3 Mod 4Document8 pagesQ3 Mod 4nonkeannangela4No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log School Time: Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log School Time: Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayJerrylyn AnonteNo ratings yet
- Core08 M7Document6 pagesCore08 M7HanaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document38 pagesModule 4Alrac Anacta MalaitNo ratings yet
- Sampling Method Summary and ActivityDocument5 pagesSampling Method Summary and Activityjuvylynsumaylo8No ratings yet
- Statistics M4Document18 pagesStatistics M4Archimedes Arvie GarciaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument7 pagesSamplingrmdn32529732No ratings yet
- Random SamplingDocument28 pagesRandom SamplingJelian MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Stat II CHAPTER 1 &2Document16 pagesStat II CHAPTER 1 &2Abdu YaYa AbeshaNo ratings yet
- Sampling ProceduresDocument53 pagesSampling Procedureschumenzoo100% (1)
- Sampling Designs/Techniques Why Sample?Document5 pagesSampling Designs/Techniques Why Sample?camilleescote562No ratings yet
- Sample - Is The Subset of The Entire PopulationDocument6 pagesSample - Is The Subset of The Entire PopulationRuby JaneNo ratings yet
- Data Management LESSON 1: Data Collection TIME FRAME: 2 Hours Code: Learning Outcome (S)Document25 pagesData Management LESSON 1: Data Collection TIME FRAME: 2 Hours Code: Learning Outcome (S)Bryan MerinaNo ratings yet
- Stat Q1W7Document36 pagesStat Q1W7nathan samuell dorigoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbDocument5 pagesLESSON 3 Elem Stat and ProbMilanie lihaylihayNo ratings yet
- Definition of StatisticsDocument7 pagesDefinition of StatisticsLavinia Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- PR2 Population and SamplingDocument4 pagesPR2 Population and SamplingDandruma TaffNo ratings yet
- Bongabon Senior High SchoolDocument8 pagesBongabon Senior High SchoolMelody CairelNo ratings yet
- Collection of DataDocument8 pagesCollection of DataRosanna Jose CuevasNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics 4Document10 pagesBusiness Statistics 4solicitors firmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 2 PDFDmzjmb SaadNo ratings yet
- Sampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. IsmaelDocument17 pagesSampling Procedure: Abdulrahman M. Ismaelalioden MarohomslicNo ratings yet
- Week 4 SPDocument6 pagesWeek 4 SPc1716811No ratings yet
- Sampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarDocument5 pagesSampling and Its Types Part - 2 - Ajay KumarAashis TamangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Module StatDocument9 pagesWeek 7 Module StatEy EmNo ratings yet
- Sampling MethodsDocument7 pagesSampling Methodsapi-552158438No ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesSampling Techniquestantan GalamNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part 2Document25 pagesStatistics Part 2Nestor Gutiza Jr.No ratings yet
- STAT LeaP Wk5Document8 pagesSTAT LeaP Wk5PEACHES N' CREAMNo ratings yet
- Module 9-Sampling DesignDocument7 pagesModule 9-Sampling DesignJayashree ChakrapaniNo ratings yet
- J. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationDocument37 pagesJ. K. Shah Classes Sampling Theory and Theory of EstimationGautamNo ratings yet
- Sample Size and Sampling TechniqueDocument30 pagesSample Size and Sampling TechniqueSanchez A. RubenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inferential Statistics Objectives: ExampleDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Inferential Statistics Objectives: ExampleMarianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityDocument38 pagesSampling: Dept. of Psychology Kurukshetra UniversityPradeep M VineetaNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit 3Document42 pagesBRM Unit 3prem nathNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research Week 12 AssessmentDocument8 pagesMethods of Research Week 12 AssessmentJoeddy LagahitNo ratings yet
- Stat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK4Document10 pagesStat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK4Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- 5 Sampling Technique and Sample SizeDocument11 pages5 Sampling Technique and Sample Sizecluadine dinerosNo ratings yet
- Tehnik Sampel&penyiapan DataDocument5 pagesTehnik Sampel&penyiapan DataFerial FerniawanNo ratings yet
- Population, Sample and Sampling TechniquesDocument8 pagesPopulation, Sample and Sampling TechniquesMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Stat - Chpater ThreeDocument5 pagesStat - Chpater ThreeFeven FevitaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument8 pagesSamplingikatal20No ratings yet
- Unesco PDFDocument58 pagesUnesco PDFzakry80No ratings yet
- 227 - ch6 HW Soln PDFDocument21 pages227 - ch6 HW Soln PDFDavid CookNo ratings yet
- Maksić & Pavlović, 2011 - Tematska Analiza - Implicitne TeorijeDocument14 pagesMaksić & Pavlović, 2011 - Tematska Analiza - Implicitne TeorijeprigNo ratings yet
- SMETDocument3 pagesSMETYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- During These Days, To Practice and Record Her Valedictory Speech. Please Follow Our HealthDocument15 pagesDuring These Days, To Practice and Record Her Valedictory Speech. Please Follow Our HealthSunny PajoNo ratings yet
- 2004-2005 AchievementsDocument1 page2004-2005 AchievementsnsidneyNo ratings yet
- Economics of Education and Socioogy of EducationDocument54 pagesEconomics of Education and Socioogy of EducationSsentongo NazilNo ratings yet
- Katie Earhart ResumeDocument3 pagesKatie Earhart Resumeapi-279957784No ratings yet
- Messy Process of School Counselor LeadershipDocument3 pagesMessy Process of School Counselor LeadershipMus OubNo ratings yet
- SPANISH 3, Sem 2 (Avancemos) - Course Guide / Syllabus / Lesson Plans - by Marty J ReepDocument4 pagesSPANISH 3, Sem 2 (Avancemos) - Course Guide / Syllabus / Lesson Plans - by Marty J ReepMarty Reep100% (1)
- Resume Final - 2Document2 pagesResume Final - 2api-279988623No ratings yet
- James Brindley 1716-27 de Septiembre de 1772Document2 pagesJames Brindley 1716-27 de Septiembre de 1772Oscar ValleNo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 Academic CatalogueDocument225 pages2020-2021 Academic CatalogueError 404No ratings yet
- CrossBraining STEM/PBL Kits Delivered To Jackson Public SchoolsDocument2 pagesCrossBraining STEM/PBL Kits Delivered To Jackson Public SchoolsPR.comNo ratings yet
- LSAT Center Reading Comprehension IntroductionDocument28 pagesLSAT Center Reading Comprehension Introductionbharath_mv7100% (1)
- College SheetDocument80 pagesCollege SheetYashNo ratings yet
- Digital Studio: Course DescriptionDocument12 pagesDigital Studio: Course DescriptionCornNo ratings yet
- Using Youtube Video An It-Based Media To Improve Students' Speaking SkillDocument10 pagesUsing Youtube Video An It-Based Media To Improve Students' Speaking Skillbuat donlotNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Speaking and Listening (RRL - 1)Document11 pagesRelationship Between Speaking and Listening (RRL - 1)Gen PriestleyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - Week 4 Quarter 4 - Week 5: Challenge/s in Life & Cmmunity Life Skill/s Used Positive AttitudeDocument5 pagesQuarter 4 - Week 4 Quarter 4 - Week 5: Challenge/s in Life & Cmmunity Life Skill/s Used Positive AttitudeShiela AltoNo ratings yet
- Math in Real LifeDocument7 pagesMath in Real Lifeapi-342084091No ratings yet
- 0511 s11 Ms 41 Mark SchemeDocument13 pages0511 s11 Ms 41 Mark SchemevijthorNo ratings yet
- Level of English Reading ProficiencyDocument25 pagesLevel of English Reading Proficiencyjah gonzalesNo ratings yet
- How To Introduce Yourself To Your StudentsDocument12 pagesHow To Introduce Yourself To Your StudentsLaura TrifanNo ratings yet
- Cover and Back PDFDocument8 pagesCover and Back PDFMohammed KhanNo ratings yet
- GODocument5 pagesGOChandra KanthNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Joseph KaswaDocument69 pagesDissertation - Joseph KaswaJohn Fetiza ObispadoNo ratings yet
- tanu ahlawat cv-2Document2 pagestanu ahlawat cv-2Dharwi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Version 1 0Document83 pagesFinal Report Version 1 0valerio_rossi8298No ratings yet