Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Output 9
Output 9
Uploaded by
bhartiygyanmanchngpCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- output_29Document1 pageoutput_29bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 12Document1 pageOutput 12bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 13Document1 pageOutput 13bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 19Document1 pageOutput 19bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 8Document1 pageOutput 8bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_27Document1 pageoutput_27bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 11Document1 pageOutput 11bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 14Document1 pageOutput 14bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 21Document1 pageOutput 21bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 20Document1 pageOutput 20bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 10Document1 pageOutput 10bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 17Document1 pageOutput 17bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 16Document1 pageOutput 16bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_28Document1 pageoutput_28bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 15Document1 pageOutput 15bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 18Document1 pageOutput 18bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 7Document1 pageOutput 7bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_26Document1 pageoutput_26bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 6Document1 pageOutput 6bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 24Document1 pageOutput 24bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 25Document1 pageOutput 25bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 23Document1 pageOutput 23bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 22Document1 pageOutput 22bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_30Document1 pageoutput_30bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument10 pagesUnit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document20 pagesTopic 1Ʋiŋêet ḠåuṯḁmNo ratings yet
- 4 5814692296314062904Document76 pages4 5814692296314062904Dagim KumilachewNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machines and SCDocument6 pagesSynchronous Machines and SCivancho04mNo ratings yet
- Em Ii PDFDocument76 pagesEm Ii PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motors and LoadsDocument24 pagesMotors and Loadsmanukjoy007No ratings yet
- 1-EM Section 1 Motor OperationDocument38 pages1-EM Section 1 Motor Operationmhafidz49No ratings yet
- Waveguide HandsomeDocument12 pagesWaveguide HandsomeJayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Citations VerificationDocument11 pagesInduction Motor: Citations VerificationChamika Dilshan WickramawardenaNo ratings yet
- Ece3414.7induction Machines IDocument18 pagesEce3414.7induction Machines IwillycanNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument21 pagesInduction Motoragbajelola idrisNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Three Phase Induction MotorDocument36 pagesUnit1 Three Phase Induction MotorPalak JioNo ratings yet
- IM Equivalent Circuit, Electrical FrequencyDocument17 pagesIM Equivalent Circuit, Electrical FrequencyHassan SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument28 pagesInduction MotorsKimsairng CheaNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument3 pagesAC MotorsalebalmoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFMegat Ahmad FaizNo ratings yet
- Module V Synchronous MotorsDocument21 pagesModule V Synchronous Motorsyanith kumarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Chapter # 01Document22 pagesInduction Motor: Chapter # 01smartengrzNo ratings yet
- Constructional Difference: Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesConstructional Difference: Synchronous Motormirza121No ratings yet
- Module 3b (Electrical Machines)Document43 pagesModule 3b (Electrical Machines)MohammedNo ratings yet
- Name: Abhijit Dilip Mahale PRN No.: 10303320181129310018Document30 pagesName: Abhijit Dilip Mahale PRN No.: 103033201811293100180004Prathamesh TayadeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Induction MachineDocument35 pagesMODULE 4 - Induction MachinedamoskidanielNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorsDocument28 pagesAc MotorsShilpa SweetyNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument14 pagesInduction Motorhamba0007No ratings yet
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument18 pagesConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
Output 9
Output 9
Uploaded by
bhartiygyanmanchngpOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Output 9
Output 9
Uploaded by
bhartiygyanmanchngpCopyright:
Available Formats
nine 9
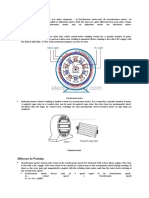
Three phase induction motors are one of the most widely used industrial machines.
This is mainly due to their simplicity, high reliability and robustness. Although
three phase induction motors have the same physical stator as a synchronous
machine, they do have different rotor constructions. In addition, three phase
induction motors are divided into two groups: squirrel-cage and wound rotor. The
magnitude of the flux in the quadrature axis in the stator diminishes, so that the
flux will be zero, but the speed is increased above the synchronous speed. The
rotor current comes from rotor voltage, so the resultant backward rotating for the
flux component provides the magnetomotive force (mmf) so the flux is positive in
the quadrature axis. So, the speed at which the magnetic field rotates can be
determined. If the motor is connected to rated frequency, the speed of the magnetic
field is called the synchronous speed (Ns).
The following table shows the relationship between number of poles and synchronous
speed when the frequency equals 50HZ.
Pole pairs
Number of poles
Synchronous speed
Table (3.1) relationship between number of poles and synchronous
The relationship between number of poles and synchronous speed is inversely
proportional.
3.2 Equivalent circuit of an induction motor.
The per phase equivalent circuit is very important for induction motors and can be
used to provide a great deal of understanding and prediction of performance of the
induction motor in a stable state. The induction motor needs to provide for
operation on the induction voltage and current in the rotor circuit from the stator
circuit (transformer action); this is because the voltage and current in the rotor
circuit of an induction motor is basically a transformer operation. So the
equivalent circuit of the induction motor is similar to the equivalent circuit of
the transformer. (In the transformer, primary like the stator in the induction
motor, secondary in the transformer like the rotor in the induction motor.
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- output_29Document1 pageoutput_29bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 12Document1 pageOutput 12bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 13Document1 pageOutput 13bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 19Document1 pageOutput 19bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 8Document1 pageOutput 8bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_27Document1 pageoutput_27bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 11Document1 pageOutput 11bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 14Document1 pageOutput 14bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 21Document1 pageOutput 21bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 20Document1 pageOutput 20bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 10Document1 pageOutput 10bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 17Document1 pageOutput 17bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 16Document1 pageOutput 16bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_28Document1 pageoutput_28bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 15Document1 pageOutput 15bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 18Document1 pageOutput 18bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 7Document1 pageOutput 7bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_26Document1 pageoutput_26bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 6Document1 pageOutput 6bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 24Document1 pageOutput 24bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 25Document1 pageOutput 25bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 23Document1 pageOutput 23bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Output 22Document1 pageOutput 22bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- output_30Document1 pageoutput_30bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2bhartiygyanmanchngpNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument10 pagesUnit - 3 Electrical Machines: 1. Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document20 pagesTopic 1Ʋiŋêet ḠåuṯḁmNo ratings yet
- 4 5814692296314062904Document76 pages4 5814692296314062904Dagim KumilachewNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machines and SCDocument6 pagesSynchronous Machines and SCivancho04mNo ratings yet
- Em Ii PDFDocument76 pagesEm Ii PDFRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motors and LoadsDocument24 pagesMotors and Loadsmanukjoy007No ratings yet
- 1-EM Section 1 Motor OperationDocument38 pages1-EM Section 1 Motor Operationmhafidz49No ratings yet
- Waveguide HandsomeDocument12 pagesWaveguide HandsomeJayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Citations VerificationDocument11 pagesInduction Motor: Citations VerificationChamika Dilshan WickramawardenaNo ratings yet
- Ece3414.7induction Machines IDocument18 pagesEce3414.7induction Machines IwillycanNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument21 pagesInduction Motoragbajelola idrisNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Three Phase Induction MotorDocument36 pagesUnit1 Three Phase Induction MotorPalak JioNo ratings yet
- IM Equivalent Circuit, Electrical FrequencyDocument17 pagesIM Equivalent Circuit, Electrical FrequencyHassan SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument28 pagesInduction MotorsKimsairng CheaNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument3 pagesAC MotorsalebalmoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word - 4 - Induction Machines PDFMegat Ahmad FaizNo ratings yet
- Module V Synchronous MotorsDocument21 pagesModule V Synchronous Motorsyanith kumarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Chapter # 01Document22 pagesInduction Motor: Chapter # 01smartengrzNo ratings yet
- Constructional Difference: Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesConstructional Difference: Synchronous Motormirza121No ratings yet
- Module 3b (Electrical Machines)Document43 pagesModule 3b (Electrical Machines)MohammedNo ratings yet
- Name: Abhijit Dilip Mahale PRN No.: 10303320181129310018Document30 pagesName: Abhijit Dilip Mahale PRN No.: 103033201811293100180004Prathamesh TayadeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Induction MachineDocument35 pagesMODULE 4 - Induction MachinedamoskidanielNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorsDocument28 pagesAc MotorsShilpa SweetyNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument14 pagesInduction Motorhamba0007No ratings yet
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument18 pagesConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet