Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem Xi Chap 5 Worksheet 1
Chem Xi Chap 5 Worksheet 1
Uploaded by
ayesha nazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem Xi Chap 5 Worksheet 1
Chem Xi Chap 5 Worksheet 1
Uploaded by
ayesha nazCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY -XI CHAPTER -5 WORKSHEET-1
KINETIC MOLECULAR INTERPRETATION OF LIQUIDS
(i) Liquid molecules are close together having small spaces.
(ii) Liquid molecules are in constant motion but their movement is restricted with Brownian motion.
(iii) There are weak attractive forces.
(iv) No appreciable increase in their volumes by heating.
Simple properties of Liquids
Diffusion: Liquid diffuses but slower than gases due to small molecular gapes.
Compression: Negligibly compress on applying pressure due to small space.
Expansion and contraction:
Liquids expand on heating due to increase in kinetic energy while compress on cooling due to decrease in K.E.
Molecular motion: Liquid molecules move randomly but slowly due to small gapes.
Kinetic energy: Kinetic energy can be increased by increasing temperature.
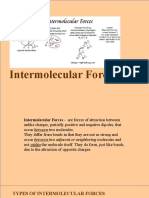
INTER-MOLECULAR FORCES IN LIQUIDS (Van der Waal forces)
(1) Dipole-Dipole Interaction
“The electrostatic force of attraction between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of
other polar molecule are called dipole-dipole interaction”.
The strength of these forces depends upon difference of electro negativities (almost 1% of normal covalent bond)
Hydrogen Bonding
“The force of attraction between partially positive charged hydrogen atom of one molecule and lone pair of
electron of highly electronegative (N, O, F) atom of another molecule is called Hydrogen bonding”.
Strongest among all intermolecular forces about 5 to 10% of the strength of covalent bond.
Application of Hydrogen bonding:
(i)H2O is a liquid while H2S is a gas, due to hydrogen bonding in water while H2S has dipole dipole forces.
(ii) Macro bimolecular such as protein, Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has hydrogen bonds particular sequence.
(iii) Cleaning action of soap and detergent is based on hydrogen bond formation between the polar part of detergent
and soap with water molecules. hydrophilic bonds with water and hydrophobic end with oils and fats.
(iv) Paints are viscous due to adhesive (hydrogen bonds).
(v) The rigidity and tensile of fabrics (silk, polyester, Nylon) is developed by hydrogen bonding.
Concept of hydrogen bonding to explain the properties of water
Water possesses some unique properties due to the presence of hydrogen bonding among its molecules.
High specific heat:
Specific heat is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of any substance by
1°C.High specific heat of water has marked effect on the weather. It plays important role in moderating the
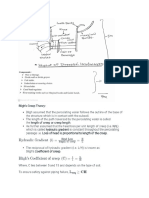
temperature of earth’s surface. water forms 4 HB with 4 surrounding 4 water molecules
High boiling point of water
Water molecule can form maximum four hydrogen bonds in three dimensional spaces hence extra energy is
required for breaking hydrogen bonds that is why water boils at high temperature (100°C) HF has less no
hydrogen bonds than H2O, so B.P of H2O of is greater than HF. HF forms 2 HB so it has BP of 20
High density of water: Due to the presence of hydrogen bonds water molecules are strongly attracted
and occupy less volume So it has high density.
High viscosity of water: Hydrogen bond is the strongest attractive force among other intermolecular
attractions. So this led to its high viscosity.
High surface tension of water: High surface tension of water molecules is due to the strong cohesive
forces. These cohesive forces are hydrogen bonds.
Anomalous behavior of water: Water has highest density at 40C below 4oC it forms four permanent
hydrogen bonds in regular hexagonal pattern so it expands and it density decreases its volume expands up to
10%. The low density of ice can be seen when ice float on water.
London Dispersion Forces
“The attractive force which develop between an instantaneous dipole and an induce dipole is known as
London dispersion force”.
Factors:
(i) Size of atom or molecule: Large size atom or molecule possess greater number of electrons therefore
more distortion of electrons is possible which increases the strength of London forces.
Atoms in the molecules :The greater the number of atoms in a non polar molecule the more
is the number of electrons hence the stronger the electronic distortion which results in
enhancing the strength of London forces.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF LIQUIDS
Evaporation: “Escaping the molecules of liquid from surface is called evaporation”
It is a surface phenomenon where change of state only takes place at the surface of liquids.
Volatile liquids evaporates quickly b/c they have weak van der waal forces such as, ethanol, acetone gasoline
etc
Non volatile liquids evaporates slowly b/c they have strong van der waal forces e.g mobile oil , mercury etc
Evaporation is an endothermic process or cooling process. When it starts, the high energy molecules leave
the liquid surface. Therefore the average kinetic energy of remaining molecules decreases. As
a consequence the temperature of the liquid falls.
SIR SALMAN AZHAR Page 1
CHEMISTRY -XI CHAPTER -5 WORKSHEET-1
The rate of evaporation is affected by following three factors.
Surface AreaGreater the surface area, greater the evaporation, b/c more molecules are getting energy to
escape.
Intermolecular Forces: Stronger the intermolecular forces, slower the process of evaporation.
Non polar liquids have London forces so they evaporates quickly, while those liquids which have hydrogen
bonding evaporates slowly e.g water.
TemperatureEvaporation takes place at all the temperature but increase in temperature increases
evaporation.
Vapor pressure:
“The pressure exerted by the vapors when they are in equilibrium with liquid phase at that
temperature is called as vapours pressure”.
Vapours pressure is independent upon the amount of liquid and surface area.
Factors:
Increase in temperature, increases vapour pressure.
Those liquids which have strong intermolecular forces e.g water has low vapor pressure while non polar liquids
have London forces so they have vapor pressure.
Boiling point: “Boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of liquid becomes equal to
its atmosphere pressure”
Boiling point is directly proportional to atmospheric pressure. So at high altitudes decrease in pressure
decreases boiling point so water boils below 100 0C hence cooking take longer time.
In pressure cooker, vapours do not escape so external pressure in the cooker increases so water boils at high
temperature so cooking time is reduced.
For example glycerin boils at 290°C at 760 torr but it decomposes at this temperature.
If it is heated under reduced pressure (50 torr), it boils at 210°C without decomposition.
Viscosity: “Viscosity is the measure of internal resistance of a liquid to flow”.
Viscosity of a liquid is affected by following three factors.
i) Intermolecular forces: Stronger the intermolecular forces, greater the viscosity, e.g viscosity of
non polar liquids is less like gasoline, benzene while polar liquids have viscosities e.g glycerol , water
(ii) Temperature:Increase in temperature increases kinetic energy of molecules so intermolecular
forces become weak hence viscosity decreases. O°C 20°C 50°C
Acetone 0.395 0.322 0.246
Water 1.789 1.005 0.55
Ethyl alcohol 1.78 1.19 0.701
Glycerin 12100 1499 —
(iii) Molecular Size: Greater the molecular size, greater the intermolecular forces.
Units of Viscosity: The unit of viscosity is Poise and centi poise. The S.I unit of viscosity is N.s.m-2
Surface Tension: “Surface tension is the force acting at right angle on the unit length of surface of
liquid”. Or “The amount of energy that cause to increase the unit area of liquid”.
The unit of surface tension is dyne/cm or erg/cm2.
Falling drop of liquid is spherical due to surface tension, because it tends to acquire smallest surface area and
smallest surface area is for spherical in shape.
Attractive forces between the molecules of same type are known as cohesive forces whereas the attractive
forces between the molecules of different type are known as adhesive forces.
Surface tensions of some common liquids at 20°C
Ethanol 22.03 Benzene 28.88 Acetone 23.7
Water 72.583 Chloroform 27.1 Mercury 471.6
Factors: Intermolecular force:
The stronger the intermolecular forces the higher the surface For example surface tension of water is stronger
than many other liquids, due to the presence of stronger intermolecular forces (Hydrogen bonds). Mercury has
much higher surface tension than water because its atoms are held together by strong metallic bond.
Temperature: High temperature weakens the cohesive forces among the molecules which results in
decreasing the surface tension.
ENERGETIC OF PHASE CHANGE
Molar heat of fusion: It is the amount heat required to convert one mole of a solid completely into liquid at its
melting point.
Molar heat of vaporization: The amount of heat required to convert one mole of a liquid into its vapours at
boiling point is referred as molar heat of vaporization.
Molar heat of sublimation: The amount of heat absorbs when one mole of a solid is directly convert into
vapors without going through a liquid state is known as molar heat of Sublimation.
LIQUID CRYSTALS:A liquid crystal is a state of matter between liquid and solid. It was first discovered by
Fredrich Reintzer (1888),E.g. Cholesterol -Benzoate has two melting points at 145.5°C it first melted into a
cloudy liquid and then at 178.5°C it melted.
Properties:
They have ability to flow like liquid but the molecular arrangement is similar to crystalline solids.
Liquid crystal has optical properties as found in crystalline solid but exhibit anisotropy.
SIR SALMAN AZHAR Page 2
CHEMISTRY -XI CHAPTER -5 WORKSHEET-1
Uses of liquid crystals:
Liquid crystals are commonly used to prepare liquid crystal displays (LCDs) like wrist watches, mobile phones,
tablet computers, screens of computers.
Liquid crystals are used as temperature sensors in thermometers and other devices to measure the body
temperatures.
Liquid crystals are used in many fields of science and engineering to detect faulty connections in
microelectronic circuit boards.
In the medical science liquid crystals help to detect blockage of veins, arteries and tumors.
Liquid crystals are used in the chromatographic techniques as solvents for the separation of many components.
Some of liquid crystals are also used in the hydraulic machines due to their high viscosities.
MCQs
1. Which of the following properties increases with increases of temperature?
a) Vapor pressure b) Surface tension c) Viscosity d) all of them
2. The fall of the liquid in a capillary tube indicates that the liquid is a
a) Wet liquid b) Dry liquid c) Viscous liquid d) Less viscous liquid
3. The vapor pressure of liquid is independent on
a) Temperature b) Pressure c) Intermolecular forces d) Amount of liquid
4. Which of the following reduces the surface tension?
a) Catalyst b) Wetting agent c) Inhibitors d) Initiator
5. Capillary action is due to
a) Cohesion b) Adhesion c) Both cohesion and adhesion d) None of these
6. The unit in which surface tension is measured is
a) Dyne cm b) dyne cm–1 c) dyne–1 cm d) dyne–1 cm–1
7. The reciprocal of viscosity is called
a) Surface tension b) frictional resistance c) Fluidity d) none of these
8. The dimensions in which coefficient of viscosity is expressed are
a) Mass × length×time–1 b) Mass × length–1 × time–1 c) Mass × length–1 × time d) mass–1×length–1× time–1
9. with the increasing molecular mass of a liquid, the viscosity
a) Increases b) decreases c) No effect d) none of these
10. The rate of evaporation of a liquid depends upon
a) Surface area b) temperature c) Nature of liquid d) all of these
11. The highest temperature at which vapor pressure of a liquid can be measured is
a) boiling point of the liquid c) Inversion temperature
b) Freezing point of the liquid d) Critical temperature
12. Small droplets are spherical in shape. It is due to
a) High viscosity c) Their tendency to acquire maximum surface area
b) Their tendency to acquire minimum surface area d) less viscosity
13. Insects can walk on the surface of water due to
a) Viscosity b) surface tension c) Refractivity d) optical activity
14. While determining viscosity of a liquid with the help of a viscometer, the liquid was pipit out with
great difficulty. The liquid may be
a) Water b) acetone c) Ether d) glycerine
15. The vapor pressure of non-polar liquids are
a) Fairly high as compared to polar liquids c) The same as that of polar
b) Fairly low as compared to polar d) None of these
16. 16. Correct order of boiling points of the given liquid is
a) H2O>HF>HCl>NH3 b) H2O>HF>NH3>HCl c) HF>H2O>HCl>NH3 d) HF>H2O>NH3>HCl
17. Ice is less dense than water at:
a) 0 oC b) -4oC c) 4 oC d) 2 oC
18. Boiling point of propanone is greater than propane. This is because
a) Propanone has hydrogen bonding c) Propanone has ion dipole forces
b) Propanone has dipole forces d) Propanone has debye forces
19. Which of the following is incorrect about evaporation?
a) It is a continuous process c) It causes cooling
b) It is a surface phenomena d) It is exothermic
20. With the increase of carbon atoms in class of organic compounds, which property decreases?
a) Viscosity b) Density c) Melting point d) Vapour pressure
21. Which liquid has minimum vapour pressure?
a) Iso pentane b) Chloroform c) Diethyl ether d) Caron tetrachloride
SIR SALMAN AZHAR Page 3
CHEMISTRY -XI CHAPTER -5 WORKSHEET-1
22. A sample of 5.0g of which substance is held together by dipole dipole forces
a) H2 b) HBr c) NH3 d) CaH2
23. A substance which possess characteristically low vapor pressure can be expected to have
a) Weak intermolecular forces b) Smaller ∆Hv c) High boiling point d) All of the above
24. Vapor pressure of water at 100oC is:
a) 55 mm Hg b) 760 mm Hg c) 355 mm Hg d) 1489 mm Hg
25. Which one of the following does not show hydrogen bonding
a) H2O b) C2H5OH c) Phenol d) di ethylether
26. They hydrogen bonding is absent is:
a) Ice b) CHCl3 & CH3COCH3 c) Steam d) DNA
27. In crystal lattice of ice, each O-atom of water molecule is attached to:
a) Four H-atoms b) Two H-atoms c) One H-atom d) Three H-atoms
28. for the wetting liquids:
a) Force of adhesion exceeds the force of cohesion c) Force of adhesion becomes equal to force of cohesion
b) Force of cohesion exceeds the force of adhesion d) All statements are incorrect
29. How does the movement of liquid molecules compare to that of gases?
a) Liquid molecules are not in constant motion.
b) Liquid molecules move faster than gas molecules.
c) Liquid molecules move more slowly and are restricted in their motion compared to gases.
d) Liquid molecules move in a perfectly orderly fashion.
30. What type of forces exists among liquid molecules in the kinetic molecular interpretation of liquids?
a) Strong covalent bonds. c) Weak attractive intermolecular forces.
b) No forces; liquid molecules are completely independent. d) Strong repulsive forces.
31. Which type of intermolecular force is the weakest and exists in all molecules?
a) Hydrogen bonding b) Dipole-dipole forces c) London dispersion forces d) Ion-dipole forces
32. Which intermolecular force is involved when an ionic compound is dissolved in a polar solvent?
a) London dispersion forces b) Dipole-dipole forces c) Hydrogen bonding d) Ion-dipole forces
33. What role do hydrogen bonds play in DNA?
a) Holding the nitrogenous bases together c) maintaining the double helix structure
b) stabilizing the sugar-phosphate backbone d) enabling the formation of peptide bonds
34. How do soap and detergents clean surfaces effectively?
a) By breaking chemical bonds in dirt c) By forming hydrogen bonds with water and dirt
b) Through ionic interactions with dirt particles d) By physically scrubbing the surface
35. What provides rigidity and tensile strength to fabrics like silk, polyester, and nylon?
a) Covalent bonds within the fibers c) Hydrogen bonds between polymer chains
b) Ionic interactions with water d) Van der Waals forces between fibers
36. How does water's high specific heat affect its ability to moderate temperature?
a) It causes rapid temperature changes in response to heat.
b) It prevents any absorption of heat energy.
c) It allows water to absorb and release heat without significant temperature changes.
d) It makes water resistant to temperature fluctuations.
37. Why do coastal areas typically experience milder and more stable temperatures compared to desert
areas?
a) Coastal areas receive less sunlight. c) Water has a higher specific heat, moderating temperature changes.
b) Coastal areas have more trees. d) Desert areas have more advanced climate control systems.
38. Weak intermolecular forces
a) Formation of covalent bonds c) High surface tension
b) Formation of a hexagonal lattice structure d) None of these
39. Why do larger atoms or molecules tend to have stronger London dispersion forces?
a) Because they have more protons d) Because they possess a greater number of
b) Because they are more electronegative electrons, allowing for more significant electron
c) Because they have a higher melting point fluctuations
40. Who is credited with the discovery of liquid crystals?
a) Friedrich Reinitzer b) Albert Einstein c) Isaac Newton d) Marie Curie
41. What is the unique property of cholesteryl benzoate was observed by Friedrich Reinitzer?
a) It has a single melting point. c) It remains solid at all temperatures.
b) It has two distinct melting points. d) It remains in a gaseous state.
42. In what field of technology are liquid crystals commonly used?
a) Aerospace engineering b) Agriculture c) Medicine d) Display technology
43. What term describes the property of liquid crystals where their optical properties depend on the
direction of measurement?
a) Isotropy b) Anisotropy c) Transparency d) Opacity
44. Liquid crystals are used as temperature sensors in:
a) Digital cameras b) Thermometers c) Refrigerators d) Automobile engines
45. How are liquid crystals employed in medical science?
a) To enhance the taste of medicines c) To detect blockages in veins, arteries, and tumors
b) To create colorful dyes for medical imaging d) To replace conventional surgical tools
46. Why are some liquid crystals used in hydraulic machines?
a) They taste good b) They are colorful c) They have high viscosities d) They are easy to find in nature
SIR SALMAN AZHAR Page 4
You might also like
- General Chemistry 2 1Document94 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 1Alice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- LiquidDocument7 pagesLiquidmiraniwaqar16No ratings yet
- PropertiesDocument41 pagesPropertiesMarielle LabradoresNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Document53 pagesProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Liquid and SolidDocument43 pagesLiquid and Solidhammad javedNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Aubrey GuilaranNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces PDFDocument15 pagesProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces PDFpie100% (1)
- Properties of LiquidDocument28 pagesProperties of LiquidYeh I'mBreadNo ratings yet
- 11.S Liquids and Intermolecular Forces (Summary)Document6 pages11.S Liquids and Intermolecular Forces (Summary)ethanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryliennev02No ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument44 pagesPhysical ChemistryEnabewhkom OhpmNo ratings yet
- Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument7 pagesTypes of Intermolecular ForcesRhenczell Angela VelascoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Water and Intermolecular ForcesDocument34 pagesProperties of Water and Intermolecular Forcesjoshua gollosoNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 Q3 Module1B Properties-Of-Liquids v4Document12 pagesGenChem2 Q3 Module1B Properties-Of-Liquids v4Ana Leah BacusNo ratings yet
- Properties of LiquidsDocument31 pagesProperties of LiquidsVelvety 01No ratings yet
- What Holds Molecules Together?Document40 pagesWhat Holds Molecules Together?Vanya QuistoNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.Document11 pagesGenchem 2 Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.JessicaNo ratings yet
- 6.2 LiquidDocument19 pages6.2 LiquidAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocument62 pagesLesson 2 Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGen Chem 2 ReviewerJake Aldred CabelaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 2aDocument9 pagesGen Chem Module 2aCharles David NavidadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ActivitiesDocument4 pagesChemistry ActivitiesKristel GarciaNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230308 012401 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20230308 012401 0000Bbq c JihyoNo ratings yet
- Liquid & Solid: Erinne Dwi Amadea/01034190002 Febiana Salim Pranata/01034190008 Timothy Marvel/01034190031Document33 pagesLiquid & Solid: Erinne Dwi Amadea/01034190002 Febiana Salim Pranata/01034190008 Timothy Marvel/01034190031Erinne Dwi AmadeaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesIntermolecular ForcesMharlo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 'Reviewer'Document9 pagesChemistry 'Reviewer'Amar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- 1 CHEM Intermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids PDFDocument34 pages1 CHEM Intermolecular Forces in Liquids and Solids PDFXyress Archer GosinganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 2Document23 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 2PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocument20 pagesProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesTiburcio JayzelNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument13 pagesUntitled PresentationKristalyn CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Sections 11.1 - 11.3Document82 pagesChapter 11 Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Sections 11.1 - 11.3Michael MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- ACTs Notes State of MatterDocument5 pagesACTs Notes State of MatterAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces,, And: LiquidsDocument72 pagesIntermolecular Forces,, And: LiquidsGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesChem ReviewerTERESA MATEONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Cristian CorralesNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 Grp3 Gutierrez, Crisha Andrea MDocument4 pagesExperiment No 7 Grp3 Gutierrez, Crisha Andrea MCrisha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Self-Check 1.1Document12 pagesSelf-Check 1.1Justine AmarantoNo ratings yet
- Molecules That Are Usually Found Commonly in Living OrganismsDocument25 pagesMolecules That Are Usually Found Commonly in Living OrganismsKhawlah FakeerkhanNo ratings yet
- Liquid StateDocument16 pagesLiquid Statesaurenstha0No ratings yet
- Liquids and Water Properties: Material Science & Chemistry Week Seven LectureDocument21 pagesLiquids and Water Properties: Material Science & Chemistry Week Seven LectureIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 2 ModelDocument72 pagesCHEMISTRY 2 ModelJuvzNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2jcjimz259No ratings yet
- Chemistry Water NotesDocument15 pagesChemistry Water NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For SSC ExamsDocument58 pagesChemistry For SSC ExamsKunwar Sameer SolankiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document10 pagesModule 1Aira Bauzon ValerioNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 05: Physical States of Matter (Topic Wise Questions)Document18 pagesChapter # 05: Physical States of Matter (Topic Wise Questions)husain aliNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument17 pagesStates of MatterThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Chem LHT 2 UnfinfihedDocument7 pagesChem LHT 2 Unfinfihederika sabelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document27 pagesChemistry 2Atria Mariz Ricamonte OrbistaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 M1cDocument5 pagesGen Chem 2 M1cJohndee Mozart Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL PROPER Abe Assignment-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL PROPER Abe Assignment-WPS OfficeCarpenter BreadNo ratings yet
- Colloid, Emulsion, Mixture Worksheet0Document82 pagesColloid, Emulsion, Mixture Worksheet0sayedrezha1No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument42 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling and EvaporationDocument19 pagesMelting Boiling and EvaporationAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 CHEM HandoutsDocument4 pagesLesson 4 CHEM Handoutscarl.keiron03No ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids-Lesson3Document25 pagesProperties of Liquids-Lesson3Jazzy OcuamanNo ratings yet
- Notes CompilationDocument2 pagesNotes CompilationAkwaka ClintonNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pagesIntermolecular Forcesnot meanieNo ratings yet
- Basher Science: Chemistry: Getting a Big ReactionFrom EverandBasher Science: Chemistry: Getting a Big ReactionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- GE-511 Adjustable Differential Pressure SwitchesDocument3 pagesGE-511 Adjustable Differential Pressure Switchessales1068No ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Annexd1 - Infrastructure Works Grand BoisDocument25 pagesAnnexd1 - Infrastructure Works Grand BoisAl Jameel100% (1)
- Ex. 11Document18 pagesEx. 11Zaher Zaher100% (1)
- P11.2 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Pressure and DepthDocument5 pagesP11.2 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Pressure and DepthHarryNo ratings yet
- Composite Shell Lining For Tunnels and Mined StationsDocument7 pagesComposite Shell Lining For Tunnels and Mined StationsDEBASIS BARMANNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cover Specifications For Reinforcement in Different CodesDocument7 pagesConcrete Cover Specifications For Reinforcement in Different Codesvenkateswara rao PothinaNo ratings yet
- Rautitan Sales BrochureDocument18 pagesRautitan Sales BrochureGeorge PetziNo ratings yet
- 17bedw 12sanakhanam 190502164239Document13 pages17bedw 12sanakhanam 190502164239Rowena Odhen UranzaNo ratings yet
- Ecotourism in Borawan Island of Quezon Province Inputs To Tourism DevelopmentDocument8 pagesEcotourism in Borawan Island of Quezon Province Inputs To Tourism DevelopmentjasjaisjajsNo ratings yet
- Ta 274 273Document9 pagesTa 274 273adamNo ratings yet
- Role of Micro Irrigation in Changing Agricultural Scenario of IndiaDocument8 pagesRole of Micro Irrigation in Changing Agricultural Scenario of IndiafarhanNo ratings yet
- Moran, Robert E. (2001) A Proposed Mine in Tambogrande Peru, An Alternative Look (Oxfam America)Document30 pagesMoran, Robert E. (2001) A Proposed Mine in Tambogrande Peru, An Alternative Look (Oxfam America)cqnvalNo ratings yet
- Mock Cat 2Document88 pagesMock Cat 2Arshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- GCS C ManualDocument54 pagesGCS C Manualwei zhouNo ratings yet
- Causes of Failure of Weirs On Permeable Soils and Their RemediesDocument18 pagesCauses of Failure of Weirs On Permeable Soils and Their RemediesMr. Y. RajeshNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument13 pagesJurnal InternasionaldhitawdyNo ratings yet
- Stamicarbon Y2kDocument11 pagesStamicarbon Y2kvariable26100% (1)
- Geography Internal AssessmentDocument14 pagesGeography Internal AssessmentJuleika S. SierraNo ratings yet
- Thesis 4d Final NEUSTDocument31 pagesThesis 4d Final NEUSTEldwin Jay L MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chryso Cure Acrylic TdsDocument2 pagesChryso Cure Acrylic TdsModesty GumbieNo ratings yet
- Swatmodel 190304053321 PDFDocument54 pagesSwatmodel 190304053321 PDFAshraf E'daibatNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach in Utilization of Flower Waste From Chickballapur Market Towards Development of Value Added ProductsDocument5 pagesA Novel Approach in Utilization of Flower Waste From Chickballapur Market Towards Development of Value Added ProductsSonalSinghNo ratings yet
- Grundfos A Wide Range of Quality Pumps 60 HZDocument24 pagesGrundfos A Wide Range of Quality Pumps 60 HZAdan Serrano CaroNo ratings yet
- RELITE CNS - Weakly Acidic ResinDocument2 pagesRELITE CNS - Weakly Acidic ResinMohamed TallyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Population Growth On Environmental Degradation: Case of IndiaDocument6 pagesImpact of Population Growth On Environmental Degradation: Case of IndiaiisteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Chapter 23: Chelsey Juarez, Robin Ramey, David T. Flaherty and Belinda S. AkpaDocument23 pagesChapter 23 Chapter 23: Chelsey Juarez, Robin Ramey, David T. Flaherty and Belinda S. AkpabelenNo ratings yet
- US7111950-Method For Forming A Metallic Mirror Surface On A Receiving SurfaceDocument11 pagesUS7111950-Method For Forming A Metallic Mirror Surface On A Receiving SurfacethiruvilanNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch3 2Document8 pages10 Science Imp Ch3 2raviNo ratings yet
- Internship Project Darshan PDocument68 pagesInternship Project Darshan PManoj SVNo ratings yet