Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Environmental Impact On Ecology
Environmental Impact On Ecology
Uploaded by
Arush Arka GhoshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental Impact On Ecology
Environmental Impact On Ecology
Uploaded by
Arush Arka GhoshCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental impact on ecology
Environmental impact refers to the effect of human activities on the environment, including
ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources. Ecology, on the other hand, is the scientific
study of the relationships between organisms and their environment. Therefore, environmental
impact on ecology refers to how human actions and factors such as pollution, habitat
destruction, climate change, and resource exploitation can disrupt ecological systems and have
detrimental effects on the balance and functioning of ecosystems.
Habitat Destruction: Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and land conversion
for agriculture, result in the destruction and fragmentation of natural habitats. This disrupts
ecological processes, displaces native species, and reduces biodiversity.
Pollution: Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, transportation, and waste disposal has
severe consequences for ecology. Air pollution, water pollution, and soil contamination can
harm plants, animals, and microorganisms, leading to ecosystem imbalances and ecosystem
collapse in extreme cases.
Climate Change: The increase in greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, primarily
through the burning of fossil fuels, is causing global climate change. Rising temperatures,
altered precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events have profound
impacts on ecosystems and species. Shifts in habitats, changes in migration patterns, and
disrupted ecological interactions are some of the ecological consequences of climate change.
Invasive Species: Human activities, such as international trade and travel, have facilitated the
introduction of non-native species to new ecosystems. These invasive species can outcompete
native species for resources, disrupt food chains, and alter ecosystem dynamics, leading to the
decline or extinction of native species.
Overexploitation of Resources: Unsustainable extraction of natural resources, including
overfishing, deforestation, and excessive water consumption, can deplete ecosystems and
disrupt ecological balance. This can result in the loss of biodiversity, collapse of fisheries, soil
degradation, and water scarcity, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Loss of Biodiversity: Human activities contribute to the ongoing loss of biodiversity globally.
Habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and invasive species all contribute to the decline
of species populations and the extinction of species. Reduced biodiversity affects the stability
and resilience of ecosystems, as well as the provision of ecosystem services essential for
human well-being.
You might also like
- Natural Ecosystem: How Human Activities AffectDocument19 pagesNatural Ecosystem: How Human Activities AffectyhuijiexylieNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources Earth Science Presentation in Brown Green Organic StyleDocument19 pagesNatural Resources Earth Science Presentation in Brown Green Organic StyleyhuijiexylieNo ratings yet
- 1899 Malolos ConstitutionDocument2 pages1899 Malolos ConstitutionredonamitchlenardNo ratings yet
- Evs 3RD SemDocument24 pagesEvs 3RD SemAparna TithiNo ratings yet
- Our Environment Is Deteriorating For The Last Two Centuries and Almost Every Part of The PlanetDocument3 pagesOur Environment Is Deteriorating For The Last Two Centuries and Almost Every Part of The PlanetHeriniaina RandriamanantenaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Need For BiodiversityDocument12 pagesBiodiversity: The Need For BiodiversityAnonymous IM8HpC100% (1)
- English ProjectDocument6 pagesEnglish ProjectdivaNo ratings yet
- GoegraphyDocument9 pagesGoegraphyNDATIMANA JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- Natural Capital DegradationDocument2 pagesNatural Capital DegradationJ and J VlogNo ratings yet
- Folio BiologiDocument5 pagesFolio BiologiPrincipessa FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Ecology and The Environment - WordsDocument3 pagesEcology and The Environment - WordsTjaša VolovšekNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentwelsoncagasjrNo ratings yet
- human activities and their effects on the environmentDocument5 pageshuman activities and their effects on the environmentMeldrade NyuykongiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Science) PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 (Science) PDFmariam sharifNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Climate Change On Biodiversity and EcosystemsDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Climate Change On Biodiversity and Ecosystems6A DS //No ratings yet
- Human Activities That Affect The EcosystemDocument10 pagesHuman Activities That Affect The EcosystemJoyce Anne ManzanilloNo ratings yet
- Threats in The EnvironmentDocument1 pageThreats in The EnvironmentJudith LlemitNo ratings yet
- Core Energy: The Cry of the Earth: Climate Change and the Loss of BiodiversityFrom EverandCore Energy: The Cry of the Earth: Climate Change and the Loss of BiodiversityNo ratings yet
- Science ExtinctionDocument3 pagesScience ExtinctionRAIZZA MAE BARZANo ratings yet
- Causes and Impact of Environmental Degradation: Name: Dhruvika Kokate Roll No: 286 STD: Fybcom Div: 2Document8 pagesCauses and Impact of Environmental Degradation: Name: Dhruvika Kokate Roll No: 286 STD: Fybcom Div: 2Dhruvika KokateNo ratings yet
- Abiha Rehman Roll No.17855 Submitted To Shangoul Sajjad Subject: Essential of BiologyDocument5 pagesAbiha Rehman Roll No.17855 Submitted To Shangoul Sajjad Subject: Essential of BiologyUme LailaNo ratings yet
- Indian Ethos & Business Ethics UNIT VIDocument89 pagesIndian Ethos & Business Ethics UNIT VISujeet TambeNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Impacts On Global EcosystemsDocument1 pageClimate Change and Its Impacts On Global EcosystemsJhennNo ratings yet
- Threats To BiodiversityDocument7 pagesThreats To BiodiversityHarsh Vardhan Singh100% (1)
- EcosystemsDocument2 pagesEcosystemsKeira BishopNo ratings yet
- Assingment EG XMLDocument6 pagesAssingment EG XMLSaeid Hasan EmonNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document12 pagesDocument 1DevanshNo ratings yet
- Environment and Its IssuesDocument13 pagesEnvironment and Its IssuesAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Environmental IssuesDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Issuesmuskanwahab457No ratings yet
- Environmentat Issues Due To Human ActivityDocument2 pagesEnvironmentat Issues Due To Human ActivityAdnan AliNo ratings yet
- Impact of Human Activities On EcosystemDocument30 pagesImpact of Human Activities On Ecosystemchaithrashree kp100% (1)
- Morante, Monica C. Environmental Science BSN 1-3Document2 pagesMorante, Monica C. Environmental Science BSN 1-3Micky MoranteNo ratings yet
- đề cương TA2Document11 pagesđề cương TA2hangocle102No ratings yet
- Wall Magazine (Environment)Document5 pagesWall Magazine (Environment)saadmanrehman13No ratings yet
- Untitled Document-19Document2 pagesUntitled Document-19sonetra1616No ratings yet
- XyzDocument6 pagesXyzविज्ञान को समीप से जाने Anil Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Climate Change On BiodiversityDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Climate Change On BiodiversityKent MistolaNo ratings yet
- Threats in BiodiversityDocument8 pagesThreats in Biodiversityjorel6579No ratings yet
- The Impact of Humans On Planet Earth A Comprehensive AnalysisDocument3 pagesThe Impact of Humans On Planet Earth A Comprehensive Analysisabin4201No ratings yet
- Man and EnvironmentDocument18 pagesMan and EnvironmentSukhman Chawla100% (2)
- Essay 7Document2 pagesEssay 7Malik MuzamilNo ratings yet
- 4 Degradation L.Document24 pages4 Degradation L.monasteriomatthew7No ratings yet
- Sustainable Urban PlanningDocument3 pagesSustainable Urban PlanningSumit KaulNo ratings yet
- Conservation and BiodiversityDocument3 pagesConservation and BiodiversitySumit KaulNo ratings yet
- Our Planet Is Currently Facing A Crisis Due To A Combination of Human Activities That Are Causing Significant Damage To The EnvironmentDocument1 pageOur Planet Is Currently Facing A Crisis Due To A Combination of Human Activities That Are Causing Significant Damage To The EnvironmentAzbi NurediniNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Is One of The Most Pressing Challenges of Our TimeDocument2 pagesClimate Change Is One of The Most Pressing Challenges of Our TimePercy MokNo ratings yet
- Causes of Environmental DegradationDocument9 pagesCauses of Environmental DegradationAkanksha MhatreNo ratings yet
- The EnvironmentDocument1 pageThe EnvironmentNi EllaNo ratings yet
- JasonDocument5 pagesJasonLove Bella Mae AstilloNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractwigley44455444No ratings yet
- Assingment EGfnl XMLDocument7 pagesAssingment EGfnl XMLSaeid Hasan EmonNo ratings yet
- UCC 104bsclmr196920Document2 pagesUCC 104bsclmr196920Cheruiyot VictorNo ratings yet
- Environmental ProblemsDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Problemsliagiba_abbyNo ratings yet
- Threats To BiodiversityDocument10 pagesThreats To BiodiversityAnshika RanaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity IsDocument1 pageBiodiversity IsShen AureNo ratings yet
- Esco TarogDocument16 pagesEsco TarogMuhammad AbdulNo ratings yet
- Many Think That The Humankind Is in The Midst of An Environmental CrisisDocument4 pagesMany Think That The Humankind Is in The Midst of An Environmental CrisisAkash EkNo ratings yet
- The Devastating Effects of Deforestation - An Analysis of The Environmental, Social, and Economic ConsequencesDocument4 pagesThe Devastating Effects of Deforestation - An Analysis of The Environmental, Social, and Economic ConsequencesMarcos W. YapNo ratings yet
- Environmental Degradation and Conservation: Gursharn Singh, Beant SinghDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Degradation and Conservation: Gursharn Singh, Beant SinghFaraj eNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity LossDocument5 pagesBiodiversity LossBernard Flores BellezaNo ratings yet
- Rispana RiverDocument11 pagesRispana Riverbansalsatvik42No ratings yet
- كفر الشيخ ch8Document12 pagesكفر الشيخ ch8Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- A Review Study On Sustainable DevelopmentDocument4 pagesA Review Study On Sustainable DevelopmentPrakash KatdareNo ratings yet
- Amina 4Document33 pagesAmina 4-수suNo ratings yet
- Singh, Y.K 2006 - Environmental Science - Cap 1Document11 pagesSingh, Y.K 2006 - Environmental Science - Cap 1Maria Isabel Pérez HernándezNo ratings yet
- Sample PPT David Research ProposalDocument12 pagesSample PPT David Research Proposaldayas1979100% (1)
- Meaning of Environmental DegradationDocument5 pagesMeaning of Environmental DegradationTanuNo ratings yet
- Urban Management and Governance in Agege PDFDocument142 pagesUrban Management and Governance in Agege PDFShaguolo O. JosephNo ratings yet
- Amhara National Regional State Food Security: Research Assessment ReportDocument64 pagesAmhara National Regional State Food Security: Research Assessment ReportHaileyesus TayeNo ratings yet
- Care For The EnvironmentDocument18 pagesCare For The EnvironmentAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Resources & DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources & Developmentdhdahanuwala100% (1)
- Overpopulation in NigeriaDocument2 pagesOverpopulation in NigeriaEbo DennisNo ratings yet
- ECONDocument4 pagesECONAnna ReyesNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Rainwater Harvesting For Agriculture in The Carribean SubregionDocument74 pagesFeasibility Study of Rainwater Harvesting For Agriculture in The Carribean SubregionShiitakeNo ratings yet
- Geography EUEE 2003ANSWERDocument9 pagesGeography EUEE 2003ANSWERhabtamu yilmaNo ratings yet
- Elahera Sri Lanka - Eco Siphon Hydro SmaDocument28 pagesElahera Sri Lanka - Eco Siphon Hydro SmaJeff BarnardNo ratings yet
- NECR086 Edition 1Document189 pagesNECR086 Edition 1Jorge CuadrosNo ratings yet
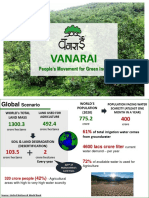
- Vanarai PresentationDocument42 pagesVanarai PresentationDnyaneshwar KhaireNo ratings yet
- Torrentira CourseModuleinReadingsinPhilippineHistory Researchgate PDFDocument119 pagesTorrentira CourseModuleinReadingsinPhilippineHistory Researchgate PDFElijah jarod BalanzaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Urban Expansion On Land Use and Land Cover Change in Rwanda, Bugesera DistrictDocument10 pagesImpact of Urban Expansion On Land Use and Land Cover Change in Rwanda, Bugesera DistrictInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Tut 21 - Team114 - MuhammadAadilSookia - CDS - FinalDocument35 pagesTut 21 - Team114 - MuhammadAadilSookia - CDS - FinalMary BrownNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 10-Pages-419-441Document23 pagesMAPEH 10-Pages-419-441peepee poopooNo ratings yet
- Crop Production TechnologiesDocument288 pagesCrop Production TechnologiesEMLNo ratings yet
- Brymer Ch3 14e PDFDocument8 pagesBrymer Ch3 14e PDFDr-Bashar Mohammad Al NajdawiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Project EndDocument20 pagesMarketing Project EndMohamed SheriffNo ratings yet
- Bamboo For Land RestorationDocument38 pagesBamboo For Land RestorationRij Gurung100% (1)
- Causes of Worldwide Land DegradationDocument4 pagesCauses of Worldwide Land DegradationKim KatNo ratings yet
- Economic Development and EnvironmentDocument25 pagesEconomic Development and EnvironmentNiloy KrittikaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument24 pagesProjectYemesirach MengistuNo ratings yet