Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BLOOD CELLS IN THE PERIPHERAL SMEAR Table
BLOOD CELLS IN THE PERIPHERAL SMEAR Table
Uploaded by
Aireen Jade BarcelonaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BLOOD CELLS IN THE PERIPHERAL SMEAR Table
BLOOD CELLS IN THE PERIPHERAL SMEAR Table
Uploaded by
Aireen Jade BarcelonaCopyright:
Available Formats
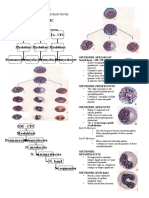
Formed Element Major Number present per Appearance in a standard Summary of function Comments
subtypes microliter and mean blood smear
5.2 million (4.4-6.0 million) Flattened biconcave disk; no Transport oxygen and some Lifespan of approximately
Erythrocytes (RBC) nucleus; pale red color carbon dioxide between 120 days
tissues and lungs
(WBC) 7000 (5000 -10,000) Obvious dark-staining nucleus All function in body defenses Exit capillaries and move
Into tissues; lifespan of
usually a few hours or
days
Granulocytes 4360 (1800 - 9950) Abundant granules in cytoplasm; Nonspecific (innate) Classified according to
nucleus normally lobed resistance to disease membrane-bound granules
in cytoplasm
Neutrophils 4150 (1800 - 7300) Nuclear lobes increase with age, Phagocytic: particularly Most common leukocyte;
pale lilac granules effective against bacteria lifespan of minutes to days
Release cytotoxic chemicals
from granules
Eosinophils 165 (0 - 700) Nucleus generally two-lobed; bright Phagocytic cells: particularly Lifespan of minutes to
red-orange granules effective with antigen- days
antibody complexes. Release
antihistamines. Increase in
Leukocytes allergies and parasitic
infections
Basophils 44 (0 - 150) Nucleus generally two-lobed but Promotes inflammation Least common leukocyte:
difficult to see due to presence of lifespan unknown
heavy dense, dark purple granules
Agranulocytes 2640 (1700-4950) Lack abundant granules in Body defenses Group consists of two
cytoplasm: have a simple-shaped major cell types from
nucleus that may be indented different lineages
Lymphocytes 2185 (1500 - 4000) Spherical cells with a single often Primarily specific (adaptive) Initial cells originate in
large nucleus occupying much of immunity: T cells directly bone marrow. but
the cell's volume; stains purple; attack other cells (cellular secondary production
seen in large (natural killer cells) immunity): B cells release occurs in lymphatic tissue;
and small (B and T cells) variants antibodies (humoral several distinct types:
immunity); natural killer cells memory cycle forms after
are similar to T cells but exposure to a pathogen
nonspecific and rapidly increases
response to subsequent
exposure; lifespan of many
years
Monocytes 455 (200 - 950) Largest leukocyte with an indented Very effective phagocytic Produced in red bone
or horseshoe-shaped nucleus cells engulfing pathogens or marrow; referred to as
worn out cells: also serve a8 macrophages after leaving
antigen-presenting cells circulation
(APCs) for other components
of the immune system
Platelets 350,000 (150,000 -500,000) Cellular fragments surrounded by a
plasma membrane and containing
Hemostasis plus release
growth factors for repair and
Formed from
megakaryocytes that
granules; purple stain healing of tissue remain in the red bone
marrow and shed platelets
into circulation
You might also like
- Immunology & Serology Review NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology & Serology Review Notesmaria email86% (7)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinalDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinaliamMye100% (1)
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14Document23 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14vyilmazNo ratings yet
- Activity 13 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument15 pagesActivity 13 The Cardiovascular SystemAdrianNo ratings yet
- 2 MICRO1 - Host vs. Microbes 2015BDocument5 pages2 MICRO1 - Host vs. Microbes 2015BCAMO SAMANTHA LOUISENo ratings yet
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14Document25 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14enam professorNo ratings yet
- BME365S 25 Immune Overview 2020 HODocument49 pagesBME365S 25 Immune Overview 2020 HOBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument7 pagesBloodRichard Castada Guanzon Jr.No ratings yet
- Micb 312Document5 pagesMicb 312Amanda AmiraultNo ratings yet
- Ana PhyDocument4 pagesAna PhyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Subject Name: Immunology Subject Code: MTI 401 Unit No: I Unit Name: Fundamentals of Immune SystemDocument23 pagesSubject Name: Immunology Subject Code: MTI 401 Unit No: I Unit Name: Fundamentals of Immune SystemShreya RautNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument4 pagesChembeloadrian20No ratings yet
- Blood ReviewerDocument6 pagesBlood ReviewerJeah Mae SantosNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Study GuideDocument16 pagesWeek 1 Study GuideKateNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.1 Immune System Introduction by DR Chaman Lal PTDocument54 pagesLecture No.1 Immune System Introduction by DR Chaman Lal PTChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- Pertaining To Extracellular Fluid Such As Plasma and Lymph. The Term Humoral Immunity Is Used To Denote Antibody Mediated Immune ResponsesDocument4 pagesPertaining To Extracellular Fluid Such As Plasma and Lymph. The Term Humoral Immunity Is Used To Denote Antibody Mediated Immune ResponsesZhon CabitacNo ratings yet
- 3B Blood PhysiologyDocument6 pages3B Blood PhysiologyRen AlvNo ratings yet
- Body DefensesDocument2 pagesBody DefensesKeihla NiebresNo ratings yet
- DR Sura Al Rawabdeh MD 31-10-2022Document56 pagesDR Sura Al Rawabdeh MD 31-10-2022Duha YousefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Leukocyte DevelopmentDocument16 pagesChapter 12 - Leukocyte DevelopmentAira Usi100% (1)
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33Document16 pagesChapter 33Shfici AdanNo ratings yet
- Page de GardeDocument10 pagesPage de Gardembm09blidaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Immune FunctionDocument13 pages4.1 Immune FunctionJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- L2 - Cells Under The Microscope - F23Document43 pagesL2 - Cells Under The Microscope - F23tjd243No ratings yet
- GranulocytesDocument1 pageGranulocytesHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- BIO202!19!23 Immune SystemDocument55 pagesBIO202!19!23 Immune SystemAbhilash Kumar MuthuramanNo ratings yet
- VETM 3004-LECTURE#2 Cells of The Immune System: Lecturer: Shirene M. Singh Date: Friday 6 September, 2019 Time: 8-9 AmDocument30 pagesVETM 3004-LECTURE#2 Cells of The Immune System: Lecturer: Shirene M. Singh Date: Friday 6 September, 2019 Time: 8-9 Ampainx7No ratings yet
- MICRO211 LecDocument3 pagesMICRO211 LecKathy HgNo ratings yet
- Microbial Morphology and TaxonomyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Morphology and TaxonomyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- Unidad 11Document6 pagesUnidad 11Daky ReaNo ratings yet
- Human Defence PDFDocument13 pagesHuman Defence PDFDarrell CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Inflammatory and Immune SystemDocument15 pagesConcept of Inflammatory and Immune SystemUchiha Dominic100% (1)
- LECTURE 1 HANDOUT Online ImmuneDocument28 pagesLECTURE 1 HANDOUT Online ImmuneFYMNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument21 pagesImmunitytayyaba farooqNo ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- BingoDocument11 pagesBingoOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- 11 Compressed Notes ImmunityDocument9 pages11 Compressed Notes ImmunityLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Document3 pagesKami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Achionta NandyNo ratings yet
- Immuno Notes LectureDocument30 pagesImmuno Notes LectureSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument5 pagesConnective Tissuesraphael100% (1)
- Immunology Chapter 1Document4 pagesImmunology Chapter 1Milad MovahediNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Dr. Anuar Sani FPSK UsimDocument35 pagesThe Immune System: Dr. Anuar Sani FPSK Usimcikgu_baruNo ratings yet
- Biology ModuleDocument8 pagesBiology Modulerian ririNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10. Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLecture 10. Lymphatic Systemyancereno19No ratings yet
- Microbiology Made Ludicrously Simpler1!!!Document59 pagesMicrobiology Made Ludicrously Simpler1!!!Laylee Clare100% (2)
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfDocument4 pagesAcute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY-NOTES-by-Red ImmuneDocument4 pagesHISTOLOGY-NOTES-by-Red ImmuneEdzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- Microparalab ReviewDocument4 pagesMicroparalab ReviewKeiNo ratings yet
- Pathology Exam 2Document5 pagesPathology Exam 2moneyy24No ratings yet
- Innate Immunity and Its Cells - GammaDocument9 pagesInnate Immunity and Its Cells - Gammachitrasharma1653No ratings yet
- IMMUNE SYSTEM Notes MidtermsDocument5 pagesIMMUNE SYSTEM Notes MidtermsAdiel Calsa100% (1)
- IMMUNE SYSTEM - MedSurgDocument5 pagesIMMUNE SYSTEM - MedSurgAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- W1 - Intro Biology - Chapter1Document25 pagesW1 - Intro Biology - Chapter1Ahmed AlbaderNo ratings yet
- Immune System DisordersDocument9 pagesImmune System DisordersFrancheskaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. The Cells That Surround UsDocument6 pagesExercise 3. The Cells That Surround Usjunso2771No ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Services - Laboratory: Biological Reference Interval Unit Result ParameterParchuri PraveenNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immunity - Immune ResponseDocument21 pagesAdaptive Immunity - Immune ResponseDrnarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Document21 pagesT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaNo ratings yet
- Choose Your Own Adventure!Document28 pagesChoose Your Own Adventure!Scott S100% (1)
- Vanjaarsveld MelodyM 1111992 PatientReportDocument2 pagesVanjaarsveld MelodyM 1111992 PatientReportmelodyvanjaasveldNo ratings yet
- Hbioana Le3Document3 pagesHbioana Le3bitangyarahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 CANVAS NOTES HematopoiesisDocument6 pagesModule 2 CANVAS NOTES HematopoiesisMohammad MasacalNo ratings yet
- Leukocytary Formula (The Leukogram)Document28 pagesLeukocytary Formula (The Leukogram)Sabina MarinoviciNo ratings yet
- 30a2131 Complete Blood Count Normal Pediatric Values PDFDocument1 page30a2131 Complete Blood Count Normal Pediatric Values PDFReziel Basilan Manalo100% (3)
- ABX Pentra DF 120: Flexible Hematology PlatformDocument29 pagesABX Pentra DF 120: Flexible Hematology PlatformYaser AlaniNo ratings yet
- CHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.Document2 pagesCHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.MAHESH GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- CBC ReportDocument1 pageCBC ReportKamal DeepNo ratings yet
- Hematopietic Stem Cell GM-CFC Ba - CFC Eo - CFC: LeukopoiesisDocument5 pagesHematopietic Stem Cell GM-CFC Ba - CFC Eo - CFC: LeukopoiesisJustine EscobalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoNo ratings yet
- MT1 HSCI LEC L7 HematopoiesisDocument10 pagesMT1 HSCI LEC L7 HematopoiesisSEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFENo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument7 pagesHEMATOPOIESISritaoktasariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 White Blood CellDocument11 pagesLab Report 3 White Blood CellAlyaa AthiraNo ratings yet
- Parham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaDocument10 pagesParham Ch. 1: An Overview of The Immune System: (Fig. 1.3) Pathogen An Organism That Causes Disease Eg: BacteriaAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- WWW Cram Com Flashcards Hematology Slides 872178Document8 pagesWWW Cram Com Flashcards Hematology Slides 872178Anonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- 2.peripheral Blood SmearDocument3 pages2.peripheral Blood SmearCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Zoheir Aissaoui Rals03 10016 1Document5 pagesZoheir Aissaoui Rals03 10016 1babelfirdaousNo ratings yet
- Complete blood count, CBC With Diff. and blood lm: B10845383 International Medical Center 20.5.2021 2:28 ًءﺎﺴﻣDocument6 pagesComplete blood count, CBC With Diff. and blood lm: B10845383 International Medical Center 20.5.2021 2:28 ًءﺎﺴﻣNizar AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Preparations HistologyDocument6 pagesBone Marrow Preparations Histology365 DaysNo ratings yet
- WBC SummaryDocument10 pagesWBC SummaryNeilJohnL.OrineoNo ratings yet
- Leukosit - Djaelani DKKDocument5 pagesLeukosit - Djaelani DKKcitraNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic SystemDocument47 pagesHematopoietic SystemAbbi Yanto ArtNo ratings yet
- XL22 - Basic HaematologyDocument18 pagesXL22 - Basic HaematologyAdi TrisnoNo ratings yet
- DG Reporting VFDocument2 pagesDG Reporting VFRamani DantuluriNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Lecture Adaptive NesterDocument56 pagesCh15 Lecture Adaptive NesterDonald FarquharsonNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immune Response To Extra Cellular Microbe (Presentation)Document21 pagesAdaptive Immune Response To Extra Cellular Microbe (Presentation)hisomaliland2009No ratings yet