Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Uploaded by
Alexandra RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealDocument13 pagesDry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealAhmad Riaz Khan100% (1)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Sizing SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesControl Valve Sizing SpreadsheetmakamahamisuNo ratings yet
- Accumulator BOP Volume Calculation - Jean-VergesDocument12 pagesAccumulator BOP Volume Calculation - Jean-VergesSudish Bhat100% (1)
- GPSA Control Valve SizingDocument10 pagesGPSA Control Valve Sizingbakhtyar21100% (1)
- Half and Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf and Full Wave Rectifierlucy lucy67% (3)
- Gec220 Questions Functions of Several VariablesDocument6 pagesGec220 Questions Functions of Several VariablesPrincess Oria-Arebun0% (1)
- Honeywell 01061GBDocument25 pagesHoneywell 01061GBKyriakos MichalakiNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Analysis1Document13 pagesControl Valve Analysis1Ekundayo JohnNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulator For An Electro-Hydraulic Wet Clutch: Emanuel Feru, Daniel Pătraşcu and Corneliu LazărDocument18 pagesDynamic Simulator For An Electro-Hydraulic Wet Clutch: Emanuel Feru, Daniel Pătraşcu and Corneliu LazărnboulegrouneNo ratings yet
- Control Valve: Mr. Mouto YDocument86 pagesControl Valve: Mr. Mouto YDuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Zawory LDM Z Napedami Siemens (Landis & Staefa) (KK) (EN)Document28 pagesZawory LDM Z Napedami Siemens (Landis & Staefa) (KK) (EN)ChiefNo ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument21 pagesControl Valve Sizingtiwarishailendra2198No ratings yet
- Control Valve PDFDocument26 pagesControl Valve PDFRoona Thankam VargheseNo ratings yet
- Primer Chapter5 PDFDocument26 pagesPrimer Chapter5 PDF1qazwsxNo ratings yet
- Control-Valve-Handbook-En-3661206 Pages 111-120Document10 pagesControl-Valve-Handbook-En-3661206 Pages 111-120trevNo ratings yet
- Wet Gas Metering With V-Cone Meters: RD TH THDocument14 pagesWet Gas Metering With V-Cone Meters: RD TH THMichelle GuerraNo ratings yet
- (控制阀) Chaos in a Hydraulic Control ValveDocument24 pages(控制阀) Chaos in a Hydraulic Control ValveEric CNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument33 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual instant download all chaptersymonsmelakNo ratings yet
- 1 PulseDocument21 pages1 Pulsefatma belkacemiNo ratings yet
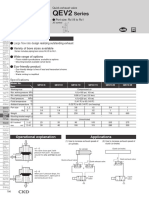
- QEV2 Series Specifications・How to Order・Dimensions (0.2MB)Document4 pagesQEV2 Series Specifications・How to Order・Dimensions (0.2MB)renanta_adiyasNo ratings yet
- Grove Regulator Engineering Handbook Sections 1-8Document212 pagesGrove Regulator Engineering Handbook Sections 1-8Alfredo CastravelliNo ratings yet
- Control Valve CalcDocument7 pagesControl Valve Calcartneves100% (1)
- Inphorm Online: Click Here To AccessDocument10 pagesInphorm Online: Click Here To AccessconimecNo ratings yet
- 05-2 Exercise Well Test Evaluation (Modified Isochronal - Simplified Analysis)Document2 pages05-2 Exercise Well Test Evaluation (Modified Isochronal - Simplified Analysis)David John MarcusNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Description Symbol Data Unit: CF 1 P V 2 2Document11 pagesSr. No Description Symbol Data Unit: CF 1 P V 2 2Dharmik PatelNo ratings yet
- 3 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesDocument19 pages3 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesShahzaib Anwar OffNo ratings yet
- Expt Guide - F2 - Pressure DropDocument7 pagesExpt Guide - F2 - Pressure DropBabyyFacedNo ratings yet
- Product-Data-Sheet-Catalog-12 - (Two Phase Control Valve Sizing Calculation Fisher)Document41 pagesProduct-Data-Sheet-Catalog-12 - (Two Phase Control Valve Sizing Calculation Fisher)reninbabaski100% (1)
- 2 Nozzle Pressure DistributionDocument5 pages2 Nozzle Pressure DistributionRuqiyya IsrafilovaNo ratings yet
- CHE 435 Project #1: Air Emission ControlDocument14 pagesCHE 435 Project #1: Air Emission Controlhafizul_aimranNo ratings yet
- Method Taken From Spirax Sarco Technical Guidance: Calculation No.: Sheet: Device Tag: DescriptionDocument9 pagesMethod Taken From Spirax Sarco Technical Guidance: Calculation No.: Sheet: Device Tag: Descriptionfahmi0% (1)
- Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manualmarthanhati5s100% (30)
- Process Dynamics and Control 4Th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4Th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkarinawarrenpkmgsxdfrc100% (11)
- 4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesDocument23 pages4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesSyedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulicsystemdesign 240304145623 6202be91Document76 pagesHydraulicsystemdesign 240304145623 6202be91masrydrarNo ratings yet
- Zexel VRZ Pump PDFDocument12 pagesZexel VRZ Pump PDFalvarikokexNo ratings yet
- Om012 - Waldnieler Fruit JuiceDocument4 pagesOm012 - Waldnieler Fruit JuiceshekharshindeNo ratings yet
- Valve SizingDocument1 pageValve SizingfitobNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Hydraulic Circuit and Operations (Option)Document10 pagesExplanation of Hydraulic Circuit and Operations (Option)dhanysiregarNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Capacity Testing: Standard Formatted For Publication in This Handbook by A. Bálint, 2005)Document4 pages6.6 Capacity Testing: Standard Formatted For Publication in This Handbook by A. Bálint, 2005)jigjigawNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Flow in Pipes, 2006, Critical Velocity, PresentacionDocument62 pagesMultiphase Flow in Pipes, 2006, Critical Velocity, PresentacionjoreliNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow Valve Sizing Made EasyDocument8 pagesLaminar Flow Valve Sizing Made Easy1940LaSalleNo ratings yet
- 405166720-BOP-Control-System-Calculation-Sheet-pdfDocument8 pages405166720-BOP-Control-System-Calculation-Sheet-pdfDon AskmeNo ratings yet
- BOP Control System Calculation Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesBOP Control System Calculation Sheet PDFAlecs Nedea100% (1)
- Centrifugal Compressor - Lab HandoutDocument5 pagesCentrifugal Compressor - Lab HandoutMohammad Usman Habib50% (2)
- Power Lines Pro ValidationDocument13 pagesPower Lines Pro ValidationRonish ChandraNo ratings yet
- Valve SizingDocument6 pagesValve Sizingsaad_arif_10No ratings yet
- KSB MIL Controls Limited Valve Specification SheetDocument2 pagesKSB MIL Controls Limited Valve Specification SheetPablo TorresNo ratings yet
- Acid PerfTechDocument5 pagesAcid PerfTechazareiforoushNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Modern Sensors HandbookFrom EverandModern Sensors HandbookPavel RipkaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- Normas LinkDocument2 pagesNormas LinkAlexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- FED STD H28-Handbook28supp1957pt1Document220 pagesFED STD H28-Handbook28supp1957pt1Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Jsa Jis B 7502 2016Document51 pagesJsa Jis B 7502 2016Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Iso 13000 1 2021Document10 pagesIso 13000 1 2021Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- DPM Class-NotesDocument38 pagesDPM Class-NotesZephaniah MuneneNo ratings yet
- Pem Mmps EngDocument39 pagesPem Mmps EngAdedamola AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Unit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFDocument8 pagesUnit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFManansala LindsayNo ratings yet
- List of The ExperimentsDocument10 pagesList of The ExperimentsSainadh Reddy Syamala AP21110010703No ratings yet
- API Table 54b PDF FreeDocument1 pageAPI Table 54b PDF FreeAsdi SInrangNo ratings yet
- Shadan Zolghani - Gizmos-DistancetimevelocityDocument8 pagesShadan Zolghani - Gizmos-Distancetimevelocityapi-531290004No ratings yet
- NPSHDocument17 pagesNPSHcrazynup100% (3)
- Brushless DC Motor Design PDFDocument3 pagesBrushless DC Motor Design PDFtejas9280No ratings yet
- Ipe Exit OtDocument5 pagesIpe Exit OtJotham MorciloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDocument5 pagesExperiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue enDocument106 pagesCatalogue enANGELICANo ratings yet
- Manual Portable Absolut Gravimeter 1Document59 pagesManual Portable Absolut Gravimeter 1Haidar BaqirNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term PhysicsDocument14 pages3rd Term Physicssaidu musaNo ratings yet
- Khaled GalalDocument1 pageKhaled Galalkhaled galalNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson EdexcelDocument24 pagesPhysics: Pearson EdexceltyNo ratings yet
- Fisika Zaka Nurfadilah 1903035003 TM2ADocument5 pagesFisika Zaka Nurfadilah 1903035003 TM2Azaka nurfadilahNo ratings yet
- Elsum 2023 Rofiul HudaDocument71 pagesElsum 2023 Rofiul HudaViq HenNo ratings yet
- CP213: Tutorial Notebook 5Document1 pageCP213: Tutorial Notebook 5Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)Document10 pagesModel Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)TANUJIT MONDALNo ratings yet
- Code MatlabDocument18 pagesCode Matlabvanlinh leNo ratings yet
- ABB Exd 2pole 45kw Load CurvaDocument1 pageABB Exd 2pole 45kw Load CurvaAgung AfrizalNo ratings yet
- 2 - 3 Force Mass AccelerationDocument15 pages2 - 3 Force Mass Accelerationanton082117No ratings yet
- RQA0009SXAQS: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETDocument13 pagesRQA0009SXAQS: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETRickyNSNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument20 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesGlenn Posadas50% (4)
- 514C DC Controller: Product ManualDocument44 pages514C DC Controller: Product ManualRIGID TYRESNo ratings yet
- Calibración de Instrumentación - UG2Document28 pagesCalibración de Instrumentación - UG2javier donayre0% (1)
- Development and Present Status of Solar Water HeaterDocument25 pagesDevelopment and Present Status of Solar Water HeaterRam Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- File 1506318592 PDFDocument60 pagesFile 1506318592 PDFnataraNo ratings yet
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Uploaded by
Alexandra RuizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Semi F32-0211 - 2011
Uploaded by
Alexandra RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
SEMI F32-0211
TEST METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF FLOW COEFFICIENT FOR
HIGH PURITY SHUTOFF VALVES
This Standard was technically approved by the global Gases Committee. This edition was approved for
publication by the global Audits & Reviews Subcommittee on December 21, 2010. Available at
www.semiviews.org and www.semi.org in February 2011; originally published in 1998; previously published
July 2009.
1 Purpose
1.1 This test method describes how to determine two criteria used in selecting valves of appropriate size for gases
and liquids.
1.2 Methods and equations are specified and/or referenced to assist in accurate calculation of pressure drops across
valves tested by this method.
2 Scope
2.1 This method establishes the testing criteria for determination of two coefficients specified in ANSI/ISA-S75.02:
Valve flow coefficient (Cv)
Critical pressure drop ratio factor (xT )
2.2 This method is to be used with ANSI/ISAS75.02. This method applies to manual and actuated valves for use in
both gas and liquid distribution systems used in semiconductor manufacturing facilities. It is a test method, where
existing test methods are referenced and limitations are imposed on test conditions. Specific equations for
calculating flow coefficients, choked flow parameters, and pressure drops are referenced to the appropriate ISA
section.
NOTICE: SEMI Standards and Safety Guidelines do not purport to address all safety issues associated with their
use. It is the responsibility of the users of the documents to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and
determine the applicability of regulatory or other limitations prior to use.
3 Limitations
3.1 This method will limit the use and interpretation of ANSI/ISA-S75.02 for use by manufacturers and users of
valves designed for the semiconductor industry.
3.2 This method is not intended to be used to determine flow coefficients for valves used in vacuum service.
4 Referenced Standards and Documents
4.1 ANSI Standards 1
ANSI/ISA-S75.01 — Flow Equations for Sizing Control Valves
ANSI/ISA-S75.02 — Control Valve Capacity Test Procedures
NOTICE: Unless otherwise indicated, all documents cited shall be the latest published versions.
5 Terminology
5.1 Abbreviations and Acronyms
5.1.1 ΔP — pressure drop across valve, kPa (psi)
5.1.2 Fk — ratio of specific heats factor, where:
1
American National Standards Institute, Headquarters: 1819 L Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. Telephone: 202.293.8020; Fax:
202.293.9287. New York Office: 11 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036, USA. Telephone: 212.642.4900; Fax: 212.398.0023;
http://www.ansi.org
--``,,,,`,,```,``,,``,,,,`,,`,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
1 SEMI F32-0211 © SEMI 1998, 2011
k
Fk
1.40 (1)
5.1.3 FL — liquid pressure recovery factor:
Qmax
m3
FL hr (2)
P1kPa 0.96 PvkPa
0.0865 Cv
Sf
Qmax gpm
F (3)
L
P1psia 0.96 Pv psia
1.00 Cv
Sf
5.1.4 gpm — gallons per minute
5.1.5 k — specific heat ratio
5.1.6 P1 — absolute pressure at upstream pressure tap, kPa (psi)
5.1.7 P2 — absolute pressure at downstream pressure tap, kPa (psi)
5.1.8 Pv — absolute vapor pressure of liquid at inlet temperature, kPa (psi)
5.1.9 psia — pounds per square inch absolute
5.1.10 psid — pounds per square inch differential
5.1.11 Q — volumetric flow rate
5.1.12 Qmax — maximum flow rate (choked flow conditions) at a given upstream condition
5.1.13 scfh — standard cubic feet per hour
5.1.14 Sf — specific gravity of a liquid relative to water
5.1.15 Sg — specific gravity of a gas relative to air
5.1.16 T — absolute temperature of test gas or liquid, °K (°R)
5.1.17 x — ratio of pressure drop to absolute inlet pressure, dimensionless, where:
P P
x kPa x psid
P1 P1
kPa psia
(4)
5.1.18 xT — ratio of pressure drop to absolute inlet pressure (P/P1) at choked flow condition, dimensionless
5.1.19 Y — expansion factor for compressible fluids, where:
x
Y 1
3 Fk xT
(Limits 1.0 ≥ Y ≥ 0.67) (5)
5.2 Definitions
5.2.1 flow coefficient Cv — a numeric constant used to characterize the flow capacity of a valve.
5.2.2 vapor pressure condensation point — pressure at which fluid phase changes from liquid to gas, for a given
upstream condition.
5.2.3 vena contracta — point in a duct where the diameter of the fluid stream is smaller than the diameter of the
duct.
--``,,,,`,,```,``,,``,,,,`,,`,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
SEMI F32-0211 © SEMI 1998, 2011 2
6 Test Fluids
6.1 Incompressible (Liquid) Fluid — Water is the standard liquid test fluid.
6.2 Compressible (Gaseous) Fluid — Nitrogen is the standard gaseous test fluid. When using nitrogen, care should
be taken to assure that the fluid does not approach the vapor pressure condensation point at the vena contracta.
7 Test Setup
7.1 Test Valve
7.1.1 The test valve can be any high purity valve, or a combination of valve with tube connections, fittings
connection, or expanders which are normally attached as part of the valve assembly as purchased. It is important to
note that the definition of the “test valve” is inclusive of all connections and fittings, as supplied by the manufacturer.
This specifically differs from the ISA procedure, whereby a method is provided to differentiate the pressure drop
contribution of the attached fittings. It is recognized that flow coefficients may vary slightly depending upon the end
connection used. Examples of typical test valves are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Test Valve with Various Connections
7.2 Test Section Requirements
7.2.1 Fixturing of the test valve shall be made in accordance with ANSI/ISA-S75.02, Table 1, where the test valve
is the complete valve assembly including connections, as described above. For reference, ANSI/ISA-S75.02 test
setup is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
Fixturing Requirements, Standard Test Section
7.2.2 Tube Connections — Connections to the test valve are to be the same as would normally be performed by the
end user as installed. Tube connections are to be full penetration welded by automatic orbital head, with purge gas.
7.2.3 Face Seal Connections — Face seal connectors supplied with the test valve may be either male or female. An
appropriate mating connector shall be welded into the inlet and outlet tubing using full penetration orbital head
welds, and connected to the valve with standard seals.
--``,,,,`,,```,``,,``,,,,`,,`,`,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`--- 3 SEMI F32-0211 © SEMI 1998, 2011
You might also like
- Dry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealDocument13 pagesDry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealAhmad Riaz Khan100% (1)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Sizing SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesControl Valve Sizing SpreadsheetmakamahamisuNo ratings yet
- Accumulator BOP Volume Calculation - Jean-VergesDocument12 pagesAccumulator BOP Volume Calculation - Jean-VergesSudish Bhat100% (1)
- GPSA Control Valve SizingDocument10 pagesGPSA Control Valve Sizingbakhtyar21100% (1)
- Half and Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf and Full Wave Rectifierlucy lucy67% (3)
- Gec220 Questions Functions of Several VariablesDocument6 pagesGec220 Questions Functions of Several VariablesPrincess Oria-Arebun0% (1)
- Honeywell 01061GBDocument25 pagesHoneywell 01061GBKyriakos MichalakiNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Analysis1Document13 pagesControl Valve Analysis1Ekundayo JohnNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulator For An Electro-Hydraulic Wet Clutch: Emanuel Feru, Daniel Pătraşcu and Corneliu LazărDocument18 pagesDynamic Simulator For An Electro-Hydraulic Wet Clutch: Emanuel Feru, Daniel Pătraşcu and Corneliu LazărnboulegrouneNo ratings yet
- Control Valve: Mr. Mouto YDocument86 pagesControl Valve: Mr. Mouto YDuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Zawory LDM Z Napedami Siemens (Landis & Staefa) (KK) (EN)Document28 pagesZawory LDM Z Napedami Siemens (Landis & Staefa) (KK) (EN)ChiefNo ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument21 pagesControl Valve Sizingtiwarishailendra2198No ratings yet
- Control Valve PDFDocument26 pagesControl Valve PDFRoona Thankam VargheseNo ratings yet
- Primer Chapter5 PDFDocument26 pagesPrimer Chapter5 PDF1qazwsxNo ratings yet
- Control-Valve-Handbook-En-3661206 Pages 111-120Document10 pagesControl-Valve-Handbook-En-3661206 Pages 111-120trevNo ratings yet
- Wet Gas Metering With V-Cone Meters: RD TH THDocument14 pagesWet Gas Metering With V-Cone Meters: RD TH THMichelle GuerraNo ratings yet
- (控制阀) Chaos in a Hydraulic Control ValveDocument24 pages(控制阀) Chaos in a Hydraulic Control ValveEric CNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument33 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual instant download all chaptersymonsmelakNo ratings yet
- 1 PulseDocument21 pages1 Pulsefatma belkacemiNo ratings yet
- QEV2 Series Specifications・How to Order・Dimensions (0.2MB)Document4 pagesQEV2 Series Specifications・How to Order・Dimensions (0.2MB)renanta_adiyasNo ratings yet
- Grove Regulator Engineering Handbook Sections 1-8Document212 pagesGrove Regulator Engineering Handbook Sections 1-8Alfredo CastravelliNo ratings yet
- Control Valve CalcDocument7 pagesControl Valve Calcartneves100% (1)
- Inphorm Online: Click Here To AccessDocument10 pagesInphorm Online: Click Here To AccessconimecNo ratings yet
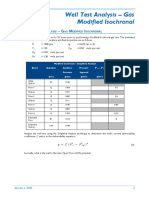
- 05-2 Exercise Well Test Evaluation (Modified Isochronal - Simplified Analysis)Document2 pages05-2 Exercise Well Test Evaluation (Modified Isochronal - Simplified Analysis)David John MarcusNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Description Symbol Data Unit: CF 1 P V 2 2Document11 pagesSr. No Description Symbol Data Unit: CF 1 P V 2 2Dharmik PatelNo ratings yet
- 3 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesDocument19 pages3 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesShahzaib Anwar OffNo ratings yet
- Expt Guide - F2 - Pressure DropDocument7 pagesExpt Guide - F2 - Pressure DropBabyyFacedNo ratings yet
- Product-Data-Sheet-Catalog-12 - (Two Phase Control Valve Sizing Calculation Fisher)Document41 pagesProduct-Data-Sheet-Catalog-12 - (Two Phase Control Valve Sizing Calculation Fisher)reninbabaski100% (1)
- 2 Nozzle Pressure DistributionDocument5 pages2 Nozzle Pressure DistributionRuqiyya IsrafilovaNo ratings yet
- CHE 435 Project #1: Air Emission ControlDocument14 pagesCHE 435 Project #1: Air Emission Controlhafizul_aimranNo ratings yet
- Method Taken From Spirax Sarco Technical Guidance: Calculation No.: Sheet: Device Tag: DescriptionDocument9 pagesMethod Taken From Spirax Sarco Technical Guidance: Calculation No.: Sheet: Device Tag: Descriptionfahmi0% (1)
- Process Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4th Edition Seborg Solutions Manualmarthanhati5s100% (30)
- Process Dynamics and Control 4Th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4Th Edition Seborg Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkarinawarrenpkmgsxdfrc100% (11)
- 4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesDocument23 pages4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesSyedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulicsystemdesign 240304145623 6202be91Document76 pagesHydraulicsystemdesign 240304145623 6202be91masrydrarNo ratings yet
- Zexel VRZ Pump PDFDocument12 pagesZexel VRZ Pump PDFalvarikokexNo ratings yet
- Om012 - Waldnieler Fruit JuiceDocument4 pagesOm012 - Waldnieler Fruit JuiceshekharshindeNo ratings yet
- Valve SizingDocument1 pageValve SizingfitobNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Hydraulic Circuit and Operations (Option)Document10 pagesExplanation of Hydraulic Circuit and Operations (Option)dhanysiregarNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Capacity Testing: Standard Formatted For Publication in This Handbook by A. Bálint, 2005)Document4 pages6.6 Capacity Testing: Standard Formatted For Publication in This Handbook by A. Bálint, 2005)jigjigawNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Flow in Pipes, 2006, Critical Velocity, PresentacionDocument62 pagesMultiphase Flow in Pipes, 2006, Critical Velocity, PresentacionjoreliNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow Valve Sizing Made EasyDocument8 pagesLaminar Flow Valve Sizing Made Easy1940LaSalleNo ratings yet
- 405166720-BOP-Control-System-Calculation-Sheet-pdfDocument8 pages405166720-BOP-Control-System-Calculation-Sheet-pdfDon AskmeNo ratings yet
- BOP Control System Calculation Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesBOP Control System Calculation Sheet PDFAlecs Nedea100% (1)
- Centrifugal Compressor - Lab HandoutDocument5 pagesCentrifugal Compressor - Lab HandoutMohammad Usman Habib50% (2)
- Power Lines Pro ValidationDocument13 pagesPower Lines Pro ValidationRonish ChandraNo ratings yet
- Valve SizingDocument6 pagesValve Sizingsaad_arif_10No ratings yet
- KSB MIL Controls Limited Valve Specification SheetDocument2 pagesKSB MIL Controls Limited Valve Specification SheetPablo TorresNo ratings yet
- Acid PerfTechDocument5 pagesAcid PerfTechazareiforoushNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Modern Sensors HandbookFrom EverandModern Sensors HandbookPavel RipkaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- Normas LinkDocument2 pagesNormas LinkAlexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- FED STD H28-Handbook28supp1957pt1Document220 pagesFED STD H28-Handbook28supp1957pt1Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Jsa Jis B 7502 2016Document51 pagesJsa Jis B 7502 2016Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Iso 13000 1 2021Document10 pagesIso 13000 1 2021Alexandra RuizNo ratings yet
- DPM Class-NotesDocument38 pagesDPM Class-NotesZephaniah MuneneNo ratings yet
- Pem Mmps EngDocument39 pagesPem Mmps EngAdedamola AdedayoNo ratings yet
- Unit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFDocument8 pagesUnit HW Momentum Collisions Ans Key PDFManansala LindsayNo ratings yet
- List of The ExperimentsDocument10 pagesList of The ExperimentsSainadh Reddy Syamala AP21110010703No ratings yet
- API Table 54b PDF FreeDocument1 pageAPI Table 54b PDF FreeAsdi SInrangNo ratings yet
- Shadan Zolghani - Gizmos-DistancetimevelocityDocument8 pagesShadan Zolghani - Gizmos-Distancetimevelocityapi-531290004No ratings yet
- NPSHDocument17 pagesNPSHcrazynup100% (3)
- Brushless DC Motor Design PDFDocument3 pagesBrushless DC Motor Design PDFtejas9280No ratings yet
- Ipe Exit OtDocument5 pagesIpe Exit OtJotham MorciloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDocument5 pagesExperiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue enDocument106 pagesCatalogue enANGELICANo ratings yet
- Manual Portable Absolut Gravimeter 1Document59 pagesManual Portable Absolut Gravimeter 1Haidar BaqirNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term PhysicsDocument14 pages3rd Term Physicssaidu musaNo ratings yet
- Khaled GalalDocument1 pageKhaled Galalkhaled galalNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson EdexcelDocument24 pagesPhysics: Pearson EdexceltyNo ratings yet
- Fisika Zaka Nurfadilah 1903035003 TM2ADocument5 pagesFisika Zaka Nurfadilah 1903035003 TM2Azaka nurfadilahNo ratings yet
- Elsum 2023 Rofiul HudaDocument71 pagesElsum 2023 Rofiul HudaViq HenNo ratings yet
- CP213: Tutorial Notebook 5Document1 pageCP213: Tutorial Notebook 5Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)Document10 pagesModel Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)TANUJIT MONDALNo ratings yet
- Code MatlabDocument18 pagesCode Matlabvanlinh leNo ratings yet
- ABB Exd 2pole 45kw Load CurvaDocument1 pageABB Exd 2pole 45kw Load CurvaAgung AfrizalNo ratings yet
- 2 - 3 Force Mass AccelerationDocument15 pages2 - 3 Force Mass Accelerationanton082117No ratings yet
- RQA0009SXAQS: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETDocument13 pagesRQA0009SXAQS: Silicon N-Channel MOS FETRickyNSNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument20 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesGlenn Posadas50% (4)
- 514C DC Controller: Product ManualDocument44 pages514C DC Controller: Product ManualRIGID TYRESNo ratings yet
- Calibración de Instrumentación - UG2Document28 pagesCalibración de Instrumentación - UG2javier donayre0% (1)
- Development and Present Status of Solar Water HeaterDocument25 pagesDevelopment and Present Status of Solar Water HeaterRam Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- File 1506318592 PDFDocument60 pagesFile 1506318592 PDFnataraNo ratings yet