Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matter & Materials
Matter & Materials
Uploaded by
nqobileswelindawo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesMatter & Materials
Matter & Materials
Uploaded by
nqobileswelindawoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Gr 10
Goals
Distinguish between pure substances & mixtures,
elements & compounds, conductors & insulators,
magnetic & non-magnetic materials
Describe properties of metals, metalloids & non-metals
Classify elements in these terms – based on
experimental observations of physical & chemical
properties
Why are materials important?
Write down three reasons why materials matter.
Spacesuits for astronauts
Homes that are better equipped for extreme temperatures
Transport options
Sport equipment
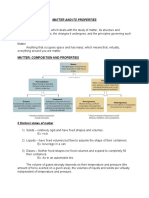
Classifying Matter
Substances classified by properties in order to
understand how matter behaves
Pure Substances
Made of one type of substance eg. Sugar
Every crystal of sugar made from same type of particle
Also known as a single substance eg. Single element or
single compound
Classified into two main groups: elements and
compounds
Elements
Simplest type of pure substance – cannot be broken down
by chemical reactions into simpler form
About 90 naturally occurring elements and about a dozen
produced artificially
Normally unstable and short-lived
Elements found on Periodic Table
Eg. Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) etc
Compounds
Pure substance made from two or more elements
bonded in a fixed ratio by chemical reaction
Chemical composition is fixed (constant ratio)
Can be broken down into simpler substances by
chemical reaction
Eg. Water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2)
Mixtures
Impure substances consisting of two or more different
substances physically blended together in any proportions
Eg. Sand and stone used when building
Can be physically separated by sieving it
Mixed physically and not chemically bonded
They keep their physical properties
Mixtures
Can be HOMOGENEOUS – uniform (all constituents
are in same phase)
Eg. Sugar in water
Can also be HETEROGENEOUS – non-uniform
(constituents are different phases)
Eg. Oil and water mixture
Microscopic view of substances
Smallest particle in element is an atom
All substances made of atoms
Atoms bond with each other to form different substances
Purity of substances
Melting point can be used to determine purity of substances
Melting point – constant temperature at which solid changes
to its liquid form
Pure substances each have a characteristic melting point,
which coincides with its freezing point
Temperature remains constant while pure substance change
phase
Purity of Substances
Impure substances melt at a range of temperatures eg.
paraffin wax melt through a range of temp from 34°C
to 60°C
Melting point differs from freezing point
Boiling points
Temperature at which pure substances boils
Condensation point is the temperature at which
vapor(gas) condenses to become a liquid
Pure substance our boiling point and condensation
point is the same
Solution consisting of a mixture will boil at two
different temperatures
You might also like
- Chemistry Reviewer PDFDocument10 pagesChemistry Reviewer PDFJom-Jom Fong Ronquillo75% (8)
- Chem 112 Final Exam NotesDocument32 pagesChem 112 Final Exam NotesZeba N. Siddiqui100% (2)
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 1 PowerPointDocument46 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 1 PowerPointLaurie Gardner100% (8)
- Reviewer in ChemistryDocument8 pagesReviewer in ChemistryChristineManrique89% (9)
- TCWY PROFILE General PDFDocument36 pagesTCWY PROFILE General PDFhendntdNo ratings yet
- OCEN 201 Introduction To Ocean & Coastal EngineeringDocument28 pagesOCEN 201 Introduction To Ocean & Coastal EngineeringbalumaxNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument48 pagesMatterReneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Matter-Properties and Changes: Section 3.4 Types of Matter Elements & CompoundsDocument58 pagesChapter 3: Matter-Properties and Changes: Section 3.4 Types of Matter Elements & CompoundseherrerahghsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument9 pagesChemistry ReviewerKeishaAaliyahNo ratings yet
- 1 Matter 2019Document67 pages1 Matter 2019Jonson NoahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 MatterDocument39 pagesLesson 5 MatterJoly Mae Montejo ErmejeNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 12Document77 pagesChem Unit 12Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IntroductionDocument15 pagesChemistry IntroductionScience 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- AtomsMatterMolecules - FINALDocument41 pagesAtomsMatterMolecules - FINALvedang1No ratings yet
- Chapt 2Document30 pagesChapt 2gaglionNo ratings yet
- Qca 1bDocument48 pagesQca 1bAlfredo Salamanca :No ratings yet
- What Is MatterDocument2 pagesWhat Is MatterEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument34 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesAshar NaveedNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review Science 7 Q1Document4 pagesPointers To Review Science 7 Q1jacobjosuejrs11No ratings yet
- 3 Classification of MatterDocument33 pages3 Classification of MatterGlen Mangali0% (1)
- Matter and EnergyDocument23 pagesMatter and Energylaica andalNo ratings yet
- S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument5 pagesS4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry羅絲雷朵No ratings yet
- Matter and EnergyDocument16 pagesMatter and EnergyKenneth José MedinaNo ratings yet
- Week #1Document32 pagesWeek #1EwartNo ratings yet
- What Is Pure Substance?: Pure Substances Are Substances That Are Made Up of Only One Kind ofDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pure Substance?: Pure Substances Are Substances That Are Made Up of Only One Kind ofNi Made FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument79 pagesTopic 2 Atoms, Elements and CompoundsNorazian Binti TaatNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument14 pagesIs Matter Around Us Purepunksnotdead_t7100% (1)
- Chapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurements: OutlineDocument70 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurements: Outlinelawchung93No ratings yet
- Materi Dan PerubahannyaDocument11 pagesMateri Dan PerubahannyaAniz DmurryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry (2020)Document38 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry (2020)Robert Angelo TulaganNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes-Half YearliesDocument6 pagesChemistry Notes-Half YearliesSharon WuNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Chemistry NotesDocument20 pagesPreliminary Chemistry NotesChristine Li40% (5)
- Prelim ChemDocument6 pagesPrelim ChemMim MimNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesAndrei Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chem Week 1 StudentsDocument33 pagesChem Week 1 Studentsmark porralNo ratings yet
- Identify The Difference Between Elements, Compounds and Mixtures in Terms of Particle TheoryDocument17 pagesIdentify The Difference Between Elements, Compounds and Mixtures in Terms of Particle TheoryBenjamin PangNo ratings yet
- Matter Mixtures and The AtomDocument24 pagesMatter Mixtures and The Atomapi-236069914No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Study Guide PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry Test Study Guide PDFapi-182328307No ratings yet
- Matter and ChangeDocument17 pagesMatter and ChangeMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterDocument40 pagesLesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterAngel MaeNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument24 pagesClassification of MatterJuloura PastorNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Document41 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Abcd Reyes100% (1)
- 1.1 Properties and Uses of MaterialsDocument34 pages1.1 Properties and Uses of Materialskoolbanning0078No ratings yet
- 2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleDocument5 pages2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleRegz GasparNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit Study SheetDocument7 pagesChemistry Unit Study SheetNivethine MahendranNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and MixturesDocument9 pagesElements, Compounds and MixturesOmkar DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Changes in MatterDocument55 pagesProperties of Matter and Changes in MatterPrinces April ArrezaNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument15 pagesProperties of MatterAngel AlarconNo ratings yet
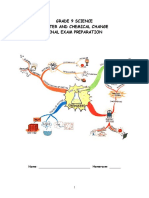
- Grade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationBekki VanderlendeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Polaris LectureDocument80 pagesChemistry Polaris LectureDonn SabalNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances and MixturesDocument6 pagesPure Substances and MixturesAIDYN TVNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2. Learning TimeDocument5 pagesLesson 1.2. Learning TimeCruella MajoNo ratings yet
- Pure Substance and MixtureDocument26 pagesPure Substance and MixtureELLEN MAE MONTERUBIONo ratings yet
- The Scientific Method: Science EnergyDocument4 pagesThe Scientific Method: Science EnergyJan Lian Enriquez NoolNo ratings yet
- Matter and ChangeDocument50 pagesMatter and ChangeShj OunNo ratings yet
- 3.01 Introduction To ChemistryDocument1 page3.01 Introduction To ChemistryDINH VIET LUONGNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem q1 w1 2Document7 pagesGen Chem q1 w1 2ARIEL ANGELIONo ratings yet
- Form 1 Science Chapter 4Document33 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 4Windy WayneNo ratings yet
- BiochemisDocument38 pagesBiochemismaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- What You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryFrom EverandWhat You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Activation EnergyDocument3 pagesEnzymes Activation EnergyDanielle WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Seawater Quality Assessment and Identification of Pollution Sources Along the Central Coastal Area of Gabes Gulf (SE Tunisia)_ Evidence of Industrial Impact and Implications for Marine Environment ProtectionDocument8 pagesSeawater Quality Assessment and Identification of Pollution Sources Along the Central Coastal Area of Gabes Gulf (SE Tunisia)_ Evidence of Industrial Impact and Implications for Marine Environment ProtectionChrister John UyNo ratings yet
- Novo SPTDocument24 pagesNovo SPTmoomeejeeNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Report1414SAMRUDHI CHOUDHARINo ratings yet
- Problem Class 2Document3 pagesProblem Class 2fadum099No ratings yet
- Environmental Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Fluid Mechanics PDFarulsidd74No ratings yet
- Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiDocument23 pagesProgress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiWalid BadrNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 MarkschemeDocument5 pagesTopic 3 MarkschemeGajendraNo ratings yet
- ch16 CompressDocument2 pagesch16 CompressOlsa NdoshaNo ratings yet
- Basic Well Logging Analysis - 8 (Neutron Log)Document22 pagesBasic Well Logging Analysis - 8 (Neutron Log)César Correa GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Future Proofing Cities Toolkit by Craig Applegath 2012-03-01sm PDFDocument20 pagesFuture Proofing Cities Toolkit by Craig Applegath 2012-03-01sm PDFJorge Fernández BaluarteNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Maturation 688 PDFDocument9 pagesOil and Gas Maturation 688 PDFAdel ALkhaligyNo ratings yet
- Radiant Tube BurnersDocument18 pagesRadiant Tube BurnersRajeshNo ratings yet
- Ecological Succession ObservationDocument3 pagesEcological Succession ObservationJessica Prias MoscardonNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry Strong and Weak ElectrolytesChris McLeanNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 5: Conservation of Mechanical Energy (Activities)Document17 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 5: Conservation of Mechanical Energy (Activities)Leo Jude Lopez0% (1)
- Fuel SystemDocument8 pagesFuel SystemManoj UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein The Theory of Relativity: February 2018Document3 pagesAlbert Einstein The Theory of Relativity: February 2018Ed VNo ratings yet
- 2018 (Even) : Time: 3 Hrs. Sem. I/II Eme & em Full Marks: 80 Pass Marks: 26Document9 pages2018 (Even) : Time: 3 Hrs. Sem. I/II Eme & em Full Marks: 80 Pass Marks: 26Md AdnanNo ratings yet
- 28th Feb Chem - 16th GRP Physical PropertiesDocument3 pages28th Feb Chem - 16th GRP Physical PropertiesPabitra PradhanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change 101 - IR PerspectiveDocument60 pagesClimate Change 101 - IR PerspectiveAri Wijanarko AdipratomoNo ratings yet
- JOSE LUIS LARA Design and Operational Experience of The Cerro Lindo Filtered Tailings Deposit PASTE 2011Document14 pagesJOSE LUIS LARA Design and Operational Experience of The Cerro Lindo Filtered Tailings Deposit PASTE 2011John PaulNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles in Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesBasic Principles in Fluid MechanicsChesterMercadoNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Hybrid Power Systems Using Homer: Mini Project ReportDocument18 pagesOptimization of Hybrid Power Systems Using Homer: Mini Project ReportMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- SPARK STAR-24 Impedance Fault 33 KVDocument3 pagesSPARK STAR-24 Impedance Fault 33 KVRam Dhani YadavNo ratings yet
- Mountain Waves-1Document18 pagesMountain Waves-1FixNo ratings yet
- TRANCA ES - Earth Day Celebration 2021Document3 pagesTRANCA ES - Earth Day Celebration 2021Sarah Jane EnriquezNo ratings yet