Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2024-02-21 at 10.19.44 PM
Screenshot 2024-02-21 at 10.19.44 PM
Uploaded by
Lorna Primus-Joseph0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Screenshot 2024-02-21 at 10.19.44 PM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views14 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-21 at 10.19.44 PM
Screenshot 2024-02-21 at 10.19.44 PM
Uploaded by
Lorna Primus-JosephCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 14
14 Easy Ways to Lower
Blood Sugar Levels
Naturally
● High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is associated
with diabetes and prediabetes. Prediabetes is when your blood
sugar is high, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
● Your body usually manages your blood sugar levels by
producing insulin, a hormone that allows your cells to use the
circulating sugar in your blood. As such, insulin is the most
important regulator of blood sugar levels (1
● However, multiple factors can impair blood sugar management
and lead to hyperglycemia.
● Internal causes for high blood sugar include when your liver
produces too much glucose, your body makes too little insulin,
or your body can’t effectively use insulin. The latter is known as
insulin resistance
● External factors include dietary choices, certain medications, a
sedentary lifestyle, and stress The Centers for Disease Control
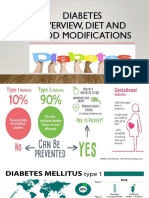
and Prevention (CDC) reports that 13% of U.S. adults live with
diabetes and that another 34.5% have prediabetes. This
means that close to 50% of all U.S. adults have diabetes or
prediabetes
●
● Blood sugar management is especially important for people
with diabetes, as chronically high blood sugar levels can lead
to limb and life threatening complications
■1. Exercise regularly
● Regular exercise can help you reach and maintain a moderate
weight and increase insulin sensitivity Increased insulin
sensitivity means your cells can more effectively use the
available sugar in your bloodstream.
● Exercise also helps your muscles use blood sugar for energy
and muscle contraction. If you have problems with blood sugar
management, consider routinely checking your levels before
and after exercising. This will help you learn how you respond
to different activities and keep your blood sugar levels from
getting too high or lowWhat’s more, researchers recommend
doing so-called “exercise snacks” to lower blood sugar and
prevent the damage that sitting all day can doExercise snacks
simply mean that you break up your sitting time every 30
minutes for just a few minutes throughout the day. Some of the
recommended exercises include light walking or simple
resistance exercises like squats or leg raises.
● Other useful forms of exercise include weightlifting, brisk
walking, running, biking, dancing, hiking, swimming, and more.
In fact, any activity that regularly gets you up and moving —
regardless of the intensity — beats a sedentary lifestyle.
● Plus, know that if you have trouble dedicating longer periods to
exercise throughout the week, you can still gain many benefits
by doing shorter sessions. For example, try aiming for
10-minute exercise sessions 3 times a day for 5 days, with the
goal of 150 minutes per week.
● SUMMARY
Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and helps your muscles use blood
sugar for movement. This can lead to reduced blood sugar levels.
2. Manage your carb intake
● Your carb intake strongly influences your blood sugar levels Your
body breaks carbs down into sugars, mainly glucose. Then, insulin
helps your body use and store it for energy.
● When you eat too many carbs or have insulin-function problems, this
process fails, and blood glucose levels can rise.
● That’s why the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends
that people with diabetes manage their carb intake by counting carbs
and being aware of how many they need.
● Some studies find that this can help you plan your meals
appropriately, further improving blood sugar management. Many
studies also show that eating a low carb diet helps reduce blood
sugar levels and prevent blood sugar spikes. It’s important to note
that low carb diets and no carb diets are not the same.
● You can still eat some carbs when monitoring your blood sugar.
However, prioritizing whole grains over processed ones and refined
carbs provides greater nutritional value while helping decrease your
blood sugar levels.
● SUMMARY
● Your body breaks down the carbs you eat into glucose, which then
raises your blood sugar levels. As such, reducing your carb intake
can aid blood sugar regulation.
3. Eat more fiber
● Fiber slows carb digestion and sugar absorption, thereby promoting a
more gradual rise in blood sugar levelsThere are two types of fiber —
insoluble and soluble.
● While both are important, soluble fiber has explicitly been shown to
improve blood sugar management, while insoluble fiber hasn’t been
shown to have this effect. A high fiber diet can improve your body’s
ability to regulate blood sugar and minimize blood sugar lows. This
could help you better manage type 1 diabetes. Foods that are high in
fiber include:
● vegetables
● fruits
● legumes
● whole grains
● The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women
and 35 grams for men. That’s about 14 grams for every 1,000
calories.
● SUMMARY
● Eating plenty of fiber can aid blood sugar management. Soluble
dietary fiber appears to be more effective than insoluble fiber for this
purpose.
4. Drink water and stay hydrated
● Drinking enough water could help you keep your blood sugar levels
within healthy ranges.
● In addition to preventing dehydration, it helps your kidneys flush out
any excess sugar through urine.
● One review of observational studies showed that those who drank
more water had a lower risk of developing high blood sugar levels.
Drinking water regularly may rehydrate the blood, lower blood sugar
levels, and reduce diabetes risk.Keep in mind that water and other
zero-calorie drinks are best. Avoid sugar-sweetened options, as
these can raise blood glucose, drive weight gain, and increase
diabetes risk.
● SUMMARY
● Staying hydrated can reduce blood sugar levels and diabetes risk.
Choose water and zero-calorie drinks and avoid sugar-sweetened
beverages.
5. Implement portion control
● Portion control can help you regulate your calorie intake and maintain
a moderate weight Consequently, weight management promotes
healthy blood sugar levels and has been shown to reduce the risk of
developing type 2 diabetes Monitoring your serving sizes also helps
prevent blood sugar spikes.
● Here are some helpful tips for managing portion sizes:
● measure and weigh your portions
● use smaller plates
● avoid all-you-can-eat restaurants
● read food labels and check the serving sizes
● keep a food journal
● eat slowly
● SUMMARY
● Focusing on your portion sizes can help you manage your blood
sugar levels.
6. Choose foods with a low
glycemic index
● The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly carbs break down
during digestion and how rapidly your body absorbs them. This
affects how quickly your blood sugar levels rise. The GI divides foods
into low, medium, and high GI and ranks them on a scale of 0–100.
Low GI foods have a ranking of 55 or less.
● Both the amount and type of carbs you eat determine how a food
affects your blood sugar levels. Specifically, eating low GI foods has
been shown to reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes
● Some examples of foods with a low to moderate GI include:
● bulgur
● barley
● unsweetened Greek yogurt
● oats
● beans
● lentils
● legumes
● whole wheat pasta
● non-starchy vegetables
● Furthermore, adding protein or healthy fats helps minimize blood
sugar spikes after a meal.
● SUMMARY
● Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI) and monitor your overall
carb intake.
●7. Try to manage your stress
levels
● Stress can affect your blood sugar levels .
● When stressed, your body secretes hormones called glucagon and
cortisol, which cause blood sugar levels to riseOne study including a
group of students showed that exercise, relaxation, and meditation
significantly reduced stress and lowered blood sugar levels Exercises
and relaxation methods like yoga and mindfulness-based stress
reduction may also help correct insulin secretion problems among
people with chronic diabetes.
● SUMMARY
● Managing your stress levels through exercise or relaxation methods
like yoga may help you regulate blood sugar levels.
8. Monitor your blood sugar
levels
● Monitoring blood glucose levels can help you better manage them.
You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which
is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your
doctor.
● Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust
your meals or medications. It also helps you learn how your body
reacts to certain foodsTry measuring your levels regularly every day
and keeping track of the numbers in a log. Also, it may be more
helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs — for example, before and
after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal.
● This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a
meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite
meals altogether. Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side
for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful.
● SUMMARY
● Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you
to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage
your blood sugar levels.
9. Get enough quality sleep
● Getting enough sleep feels excellent and is necessary for good
health. In fact, poor sleeping habits and a lack of rest can affect blood
sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing
type 2 diabetes. They can also increase appetite and promote weight
gainAdditionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of the hormone
cortisol, which, as explained, plays an essential role in blood sugar
management. Adequate sleep is about both quantity and quality. The
National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults get at least 7–8
hours of high quality sleep per nightTo improve the quality of your
sleep, try to:
● follow a sleep schedule
● avoid caffeine and alcohol late in the day
● get regular exercise
● cut down on screen time before bed
● keep your bedroom cool
● limit your naps
● create a bedtime routine
● use soothing and calming scents such as lavender
● avoid working in your bedroom
● take a warm bath or shower before bed
● try meditation or guided imagery
● SUMMARY
● Good sleep helps maintain your blood sugar levels and promotes a
healthy weight. On the other hand, poor sleep can disrupt critical
metabolic hormones.
10. Eat foods rich in chromium
and magnesium
● High blood sugar levels and diabetes have been linked to
micronutrient deficiencies. Some examples include deficiencies in the
minerals chromium and magnesium Chromium is involved in carb
and fat metabolism. It may potentiate the action of insulin, thus aiding
blood sugar regulation Chromium-rich foods include:
● meats
● whole grain products
● fruit
● vegetables
● nuts
● However, the mechanisms behind this proposed connection are not
entirely known, and studies report mixed findings. As such, more
research is neededMagnesium has also been shown to benefit blood
sugar levels. In fact, diets rich in magnesium are associated with a
significantly reduced risk of diabetes In contrast, low magnesium
levels may lead to insulin resistance and decreased glucose
tolerance in people with diabetes.That said, if you already eat plenty
of magnesium-rich foods and have adequate blood magnesium
levels, you likely won’t benefit from taking magnesium supplements.
● Magnesium-rich foods include:
● dark leafy greens
● squash and pumpkin seeds
● tuna
● whole grains
● dark chocolate
● bananas
● avocados
● beans
● SUMMARY
● Eating foods rich in chromium and magnesium can help prevent
deficiencies and reduce the risk of blood sugar problems.
11. Consider adding specific
foods to your diet
● Multiple foods and plants are known to have medicinal properties.
● However, the overall quality of evidence on these ingredients is low
due to insufficient human studies or small sample sizes. Therefore,
no conclusive recommendations can be made regarding their use.
● Some of the foods touted to have anti-diabetes effects includeApple
cider vinegar. According to older research, this ingredient may reduce
blood sugar levels by delaying the emptying of your stomach after a
meal Cinnamon. This spice may improve blood sugar levels by
enhancing insulin sensitivity and slowing the breakdown of carbs in
your digestive tract. This moderates the rise in blood sugar after a
meal
● Nevertheless, more research is needed.
● Berberine. Research suggests that this compound lowers blood
sugar by stimulating enzymes’ breakdown of glucose, promoting your
tissue’s use of sugar and increasing insulin production. Fenugreek
seeds. These seeds may support blood sugar management due to
their high fiber content, which delays stomach emptying and
subsequently prevents your blood sugar levels from spiking
● It’s essential to talk with your doctor before adding any of these foods
to your diet if you’re already taking blood-sugar-lowering medications,
as some herbal supplements may negatively interact with
them.Finally, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not
regulate supplements in the same way that it regulates prescription
medications. As such, it’s important to purchase supplements that
have been tested by an independent lab for purity and ingredient
content.
● SUMMARY
● Some foods are believed to have blood-sugar-lowering effects.
However, research is still inconclusive, and they may negatively
interact with your diabetes medication.
12. Maintain a moderate weight
● Maintaining a moderate weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels
and reduces your risk of developing diabetes .
● Research shows that even a 5% reduction in body weight can
improve your blood sugar regulation and reduce the need for
diabetes medication. For example, if a person weighs 200 pounds
(91 kg) and loses just 10–14 pounds (4.5–6 kg), they may see
significant improvements in their blood sugar levels.
● What’s more, losing more than 5% of your initial weight may benefit
your glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) readings. These are used as
indicators of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
● SUMMARY
● Maintaining a moderate weight will support blood sugar management
and decrease your risk of developing diabetes.
13. Eat healthy snacks more
frequently
● Spreading your meals and snacks throughout the day may help you
avoid both high and low blood sugar levels. Snacking between meals
may also reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes. In fact, several studies
suggest that having smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day
could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
● In addition, eating smaller meals and healthy snacks throughout the
day may lower glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) readings, indicating
improvements in blood sugar levels over the previous 3 months.
Check out this article on snack ideas if you have diabetes if you’re
unsure about what to eat between meals.
● SUMMARY
● Snacking between meals could keep your blood sugar levels from
spiking or plummeting throughout the day.
14. Eat probiotic-rich foods
● Probiotics are friendly bacteria that offer numerous health benefits,
including improved blood sugar regulation. Research shows that
probiotic intake may lower fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin
(HbA1c), and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes.
● Interestingly, studies have found that improvements in blood sugar
levels are more significant in people who consume multiple species
of probiotics and for at least 8 weeks. Probiotic-rich foods include
fermented foods, such as:
● yogurt, as long as the label states that it contains live active cultures
● kefir
● tempeh
● sauerkraut
● kimchi
● SUMMARY
● A probiotic-rich diet may help you manage your blood sugar levels.
The bottom line
● There are multiple ways to naturally manage your blood sugar levels.
● Many of them include making lifestyle changes, like managing your
weight, stress levels, and sleep quality, exercising, and staying
hydrated. That said, some of the biggest improvements have to do
with your dietary choices.
● Be sure to talk with your healthcare professional before making
lifestyle changes or trying new supplements— especially if you have
problems with blood sugar management or are taking medications.
You might also like
- Quick Cleanse 15 Day DetoxDocument44 pagesQuick Cleanse 15 Day DetoxAnonymous YtbUfrXYNo ratings yet
- No Sugar No Starch DietDocument8 pagesNo Sugar No Starch DietBarbara100% (1)
- Nikki Sharp 5 Day Detox 3rd EditionDocument37 pagesNikki Sharp 5 Day Detox 3rd EditionMadlynNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Serious Athletes - Dan BenardotDocument346 pagesNutrition For Serious Athletes - Dan BenardotHercules Le100% (3)
- GUIDE ON HOW TO LOWER BLOOD SUGAR: Learn all it takes to lower blood sugar naturally and enjoy a healthy lifestyleFrom EverandGUIDE ON HOW TO LOWER BLOOD SUGAR: Learn all it takes to lower blood sugar naturally and enjoy a healthy lifestyleNo ratings yet
- How Can You Lower Your Blood Sugar LevelsDocument5 pagesHow Can You Lower Your Blood Sugar LevelspjeanNo ratings yet
- Your Cheat Sheet To The Glycemic Index Diet Boost Energy And Lose Weight With The GI DietFrom EverandYour Cheat Sheet To The Glycemic Index Diet Boost Energy And Lose Weight With The GI DietRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- What Is DiabetesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Diabetesmkthakur6410No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: A Guide To Carbohydrate Containing Foods For People With DiabetesDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: A Guide To Carbohydrate Containing Foods For People With DiabetesRahmanita S IINo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Subsistence Formula: Full Guide to Control Your Blood SugarFrom EverandBlood Sugar Subsistence Formula: Full Guide to Control Your Blood SugarNo ratings yet
- What Is Diabetes ? Types of Diabetes Symptoms of Diabetes Interesting FactsDocument12 pagesWhat Is Diabetes ? Types of Diabetes Symptoms of Diabetes Interesting FactshuehueNo ratings yet
- 5 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallyDocument14 pages5 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallySunil HjNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesType 2 Diabetes MellitusCadiz Etrama Di RaizelNo ratings yet
- 5 Best Millets For Diabetes That Lowers Blood SugarDocument6 pages5 Best Millets For Diabetes That Lowers Blood Sugarshawana rajpootNo ratings yet
- The Low Carb No Sugar Solution: How to Carb Detox with 38 Keto and Paleo Diet Friendly RecipesFrom EverandThe Low Carb No Sugar Solution: How to Carb Detox with 38 Keto and Paleo Diet Friendly RecipesNo ratings yet
- What To Know About Insulin and Weight GainDocument4 pagesWhat To Know About Insulin and Weight GainWidya Dwi Saputri100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Case Study PresentationDocument19 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Case Study PresentationJilyan KanaweyNo ratings yet
- Pre DiabetesDocument4 pagesPre DiabetessweetloliepopNo ratings yet
- SERBAN ANCUTA NICOLETA - ProjectDocument7 pagesSERBAN ANCUTA NICOLETA - ProjectSoare Ancuta-NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Can Diabetes Be ReversedDocument8 pagesCan Diabetes Be Reversedvinay pathakNo ratings yet
- How Does Eating Affect Your Blood SugarDocument3 pagesHow Does Eating Affect Your Blood SugarRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet - Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesPatient Information Leaflet - Diabetes MellitusCatalina NegranzaNo ratings yet
- Steroid Induced DiabetesDocument6 pagesSteroid Induced DiabetesMelindaRachmadiantyNo ratings yet
- Guide To Care: For PatientsDocument2 pagesGuide To Care: For PatientsAli AlmukhtarNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionBhatia JyotikaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument12 pagesFinalNaveen TNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Diabetes With Indian Diet PlanDocument31 pagesHow To Manage Diabetes With Indian Diet PlanMohammed Siddiqui100% (1)
- Diabetes: EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesDiabetes: EndocrinologyZhanyar Omer Mustafa F210050No ratings yet
- Your Food Choices & DiabetesDocument2 pagesYour Food Choices & DiabetesDeknis StyawnNo ratings yet
- Tips To Get Rid of DiabetesDocument16 pagesTips To Get Rid of DiabetesPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Quiz SummaryDocument16 pagesDiabetes Quiz Summarycaleb.fireproofNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and ExerciseDocument12 pagesDiabetes and ExercisePranav SNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 9 - DiabetesDocument26 pagesPertemuan 9 - Diabetesnada nabillaNo ratings yet
- CMC Vellore Diabetes Info SheetDocument14 pagesCMC Vellore Diabetes Info SheetShwetal ShindeNo ratings yet
- Diabetic DietDocument10 pagesDiabetic DietTonee Marie Gabriel100% (1)
- Sample Diabetic DietDocument4 pagesSample Diabetic DietNavya VadlamuriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Regularly: 15 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallyDocument14 pagesExercise Regularly: 15 Easy Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Levels NaturallyDavid and OneVoiceCrewNo ratings yet
- M M M MDocument8 pagesM M M MAudrey MaeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Reversal PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Reversal PlanMohammed ShazebNo ratings yet
- DIABETESDocument10 pagesDIABETESMackoy LoganNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesDiabetes MellitusVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Natural Remedies For Type 2 DiabetesDocument10 pagesNatural Remedies For Type 2 DiabetesHimangshu NathNo ratings yet
- Fasting Blood SugarDocument5 pagesFasting Blood SugarKhamron BridgewaterNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Diabetes-: What Is Diabetes ? Types of Diabetes Symptoms of Diabetes Interesting FactsDocument12 pagesIntroduction - Diabetes-: What Is Diabetes ? Types of Diabetes Symptoms of Diabetes Interesting FactsC RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Diet: A Complete Step By Step Guide for BeginnersFrom EverandDiabetic Diet: A Complete Step By Step Guide for BeginnersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Diabetes Treatments:: Learn More About Drugs That Lower Blood Sugar LevelsDocument10 pagesDiabetes Treatments:: Learn More About Drugs That Lower Blood Sugar Levelslovepreet12345No ratings yet
- Diet For Diabetes Step by Step Guide - 636b5747Document69 pagesDiet For Diabetes Step by Step Guide - 636b5747vrunda shahNo ratings yet
- The Diabetic Chef's Guide: Navigating Diabetes with Delicious Recipes and a Step-by-Step Meal Plan for NewFrom EverandThe Diabetic Chef's Guide: Navigating Diabetes with Delicious Recipes and a Step-by-Step Meal Plan for NewNo ratings yet
- Staying Healthy With Diabetes SeriesDocument3 pagesStaying Healthy With Diabetes SeriesSehaRizaNo ratings yet
- Annexure-7 Call Script Self-Management of DiabetesDocument3 pagesAnnexure-7 Call Script Self-Management of DiabetesrmnjrddyNo ratings yet
- 05-Dawn PhenomenonDocument7 pages05-Dawn Phenomenonraginivermaa20No ratings yet
- Dermatology Surgeries PhoenixDocument3 pagesDermatology Surgeries Phoenixleocpelletier1No ratings yet
- Understanding Type 2 Diabetes: Fewer Highs, Fewer Lows, Better HealthFrom EverandUnderstanding Type 2 Diabetes: Fewer Highs, Fewer Lows, Better HealthNo ratings yet
- Random Blood SugarDocument19 pagesRandom Blood SugarSounak NandyNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Intermittent Fasting For BeginnersDocument16 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Intermittent Fasting For Beginnersscott pearce100% (1)
- Glycemic Index Diet: A Proven Diet Plan For Weight Loss and Healthy Eating With No Calorie CountingFrom EverandGlycemic Index Diet: A Proven Diet Plan For Weight Loss and Healthy Eating With No Calorie CountingNo ratings yet
- Nme Assignment - Yoga and WelnessDocument13 pagesNme Assignment - Yoga and WelnessParkavi KGNo ratings yet
- Section B - Group 6Document94 pagesSection B - Group 6CHRISTIAN ASHLEY PASCUANo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument137 pagesUntitled DocumentVibhuti GoelNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets in Type 2 Diabetes ManagementDocument3 pagesVegetarian and Vegan Diets in Type 2 Diabetes Managementapi-259343531No ratings yet
- Unicity PresentationDocument64 pagesUnicity PresentationJustin WhiteNo ratings yet
- The World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsDocument39 pagesThe World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsKyle J. NortonNo ratings yet
- Processes For Waste Utilization From Fruit and VegetableDocument29 pagesProcesses For Waste Utilization From Fruit and VegetablemrunmayeeNo ratings yet
- What Does My Hospital Diet MeanDocument6 pagesWhat Does My Hospital Diet Meanapi-455513786No ratings yet
- Cocoa Agronomy Quality Nutritional and Health Aspects PDFDocument41 pagesCocoa Agronomy Quality Nutritional and Health Aspects PDFLuz Angela Galindo LevaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For The Ostomy Patient PDFDocument32 pagesNutrition For The Ostomy Patient PDFapi-336553865No ratings yet
- Nutritional Guidelines Menu Checklist: For Residential and Nursing HomesDocument54 pagesNutritional Guidelines Menu Checklist: For Residential and Nursing HomesJeffrey PeekoNo ratings yet
- 10 Ways To Reduce Blood Sugar NaturallyDocument4 pages10 Ways To Reduce Blood Sugar NaturallyAnkur PatelNo ratings yet
- Dietary FiberDocument4 pagesDietary Fibermaria dulceNo ratings yet
- Five Day Diet AnalysisDocument4 pagesFive Day Diet AnalysisphyreflyNo ratings yet
- Dietary Intravention On Cardiac PatientsDocument45 pagesDietary Intravention On Cardiac Patients9415697349No ratings yet
- Soyabean Milk Project Class 12Document7 pagesSoyabean Milk Project Class 12RishabJaiswal100% (4)
- Comparative Study of Soy Paneer Prepared From Soymilk Blends of Soymilk and Skimmed Milk 2157 7110.1000301Document5 pagesComparative Study of Soy Paneer Prepared From Soymilk Blends of Soymilk and Skimmed Milk 2157 7110.1000301Dr. Pankaj WankhadeNo ratings yet
- 10 Best Superfoods For Weight LossDocument10 pages10 Best Superfoods For Weight LossabihaNo ratings yet
- Dietary Fibre: Crude Fibre NSP Dietary Fibre NDF ADF ADLDocument15 pagesDietary Fibre: Crude Fibre NSP Dietary Fibre NDF ADF ADLIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris SMA XDocument16 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris SMA XHANIF GGNo ratings yet
- Classification & Components of VegetablesDocument43 pagesClassification & Components of VegetablesQui RainNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryDocument4 pagesAyurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryAnonymous vfzbbCKaENo ratings yet
- BajraDocument4 pagesBajrahitain kumar BerwaNo ratings yet
- Student Copy LIVESTOCK AND POULTRY MANAGEMENT - IIDocument162 pagesStudent Copy LIVESTOCK AND POULTRY MANAGEMENT - IIBhàvyà Shréé ÆgríNo ratings yet
- Accepted ManuscriptDocument34 pagesAccepted ManuscriptOmmi Samuel G SNo ratings yet
- The 30 Healthiest Fruits On EarthDocument27 pagesThe 30 Healthiest Fruits On EarthCharm_27No ratings yet
- Uses of Multigrain Flour in Food Products - A ReviewDocument3 pagesUses of Multigrain Flour in Food Products - A ReviewNeha VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Rajinder BhallaDocument4 pagesRajinder BhallaNajeeb DogarNo ratings yet
- Squash Papaya ChipsDocument74 pagesSquash Papaya Chipsjanine barilla100% (2)
- Dietaryfibre - PPT (Faiza Khalid)Document51 pagesDietaryfibre - PPT (Faiza Khalid)shy girlNo ratings yet