Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsPcos311 - T2-T4
Pcos311 - T2-T4
Uploaded by
gelary sousaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- VendorsDocument774 pagesVendorslalit18970No ratings yet
- 5chapter 1 - Hair TrichologyDocument7 pages5chapter 1 - Hair TrichologyGupta Shekhar Sulabh80% (5)
- Cantu Presentation - General Brand Overview (Event Staff) NHADocument36 pagesCantu Presentation - General Brand Overview (Event Staff) NHAglamineNo ratings yet
- French FashionDocument15 pagesFrench FashionGarima Thakur100% (1)
- Valeria Dunyanin Amigurumisi ENGDocument14 pagesValeria Dunyanin Amigurumisi ENGözlem çelik100% (7)
- Cosmetic and Toiletry Formulation, 2nd Ed-Vol 8Document395 pagesCosmetic and Toiletry Formulation, 2nd Ed-Vol 8fahmi100% (1)
- Adjectives For Describing Appearance 1Document3 pagesAdjectives For Describing Appearance 1Helio KawakamiNo ratings yet
- 8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)Document14 pages8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)haytham aliNo ratings yet
- 6 Hair Cosmetics Spring 2023 2024 LC Mix Asynchronous+SynchronousDocument30 pages6 Hair Cosmetics Spring 2023 2024 LC Mix Asynchronous+Synchronousessa sunnaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Cosmetic Preparation of HairDocument8 pagesA Review On Cosmetic Preparation of HairEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Hair Structure Growth CycleDocument13 pagesHair Structure Growth Cyclesahubadalkumar89No ratings yet
- Hair Science (PG 14-20)Document9 pagesHair Science (PG 14-20)Izat ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Day 2Document32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Day 2Lake JazzNo ratings yet
- Herbal Hair Care - VPCDocument27 pagesHerbal Hair Care - VPCSatyam DarjiNo ratings yet
- 3C Experiment 7Document6 pages3C Experiment 7Mayck Jhoenell LomboyNo ratings yet
- Nishant Singh (The Forensic Analysis of Hair) FinalDocument23 pagesNishant Singh (The Forensic Analysis of Hair) FinalShikhar NigamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3-4Document13 pagesAnatomy 3-4Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- HAIRDocument66 pagesHAIRjohalyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of HairDocument2 pagesAnatomy of HairAkash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Colorimetry CourseDocument68 pagesColorimetry CourseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Hair and FibersDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 4 Hair and FibersRaymar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- CosmoDocument163 pagesCosmoTadtad FunfunNo ratings yet
- g9 4th Beauty CareDocument132 pagesg9 4th Beauty CarePrimrose MazoNo ratings yet
- Conditioner, Hair Dyes, Hair RemoversDocument3 pagesConditioner, Hair Dyes, Hair RemoversJan Aerielle AzulNo ratings yet
- PermingDocument11 pagesPermingJosh FontanillaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Part 4Document32 pagesUNIT II - Part 4mabreza.bolongaitaNo ratings yet
- HairDocument4 pagesHairRena Carissa100% (1)
- Cosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsDocument8 pagesCosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsmasorNo ratings yet
- Regrow Hair Protocol Ebook by David McKennaDocument29 pagesRegrow Hair Protocol Ebook by David McKennaXavier Gomes0% (2)
- Premature Graying of Hair and HomoeopathyDocument4 pagesPremature Graying of Hair and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom0% (1)
- Hair ProductsDocument3 pagesHair ProductsJan Aerielle AzulNo ratings yet
- ColorimetricDocument6 pagesColorimetric4gen_5No ratings yet
- Hair ShaftDocument10 pagesHair Shaftdevashish chouhanNo ratings yet
- The Forensic Analysis of HairDocument21 pagesThe Forensic Analysis of HairTJPlayzNo ratings yet
- Chp8hairanalysis 3Document11 pagesChp8hairanalysis 3Jess BinNo ratings yet
- Ebook HairLossEssentialsDocument158 pagesEbook HairLossEssentialsabhiNo ratings yet
- Croda Hair Necessities Hair Basics FINALDocument5 pagesCroda Hair Necessities Hair Basics FINALبدرالدين بن خليفةNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument71 pagesHair Careking100% (18)
- Hair Anatomy and Physiology 1Document15 pagesHair Anatomy and Physiology 1Dawn SanchezNo ratings yet
- Beauty Culture-HairDocument7 pagesBeauty Culture-HairAkshay Nitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Article 0011 44 50Document7 pagesArticle 0011 44 50apj abdulNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Hairbiology: Growth and PigmentationDocument10 pagesHairbiology: Growth and PigmentationAlexandra DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Hair and Hair Care ProductsDocument28 pagesHair and Hair Care ProductsDRx Sonali TareiNo ratings yet
- The Experimental Study Effects of Coconut Milk and Egg White As A Pack To Enhance The Hair Health Among Adult Male and Female VolunteersDocument4 pagesThe Experimental Study Effects of Coconut Milk and Egg White As A Pack To Enhance The Hair Health Among Adult Male and Female VolunteersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 9 Hair CleanseDocument11 pages9 Hair CleanseSeetha Chimakurthi0% (1)
- Unit 2, Lec No 16, Hair Dye ChemistryDocument56 pagesUnit 2, Lec No 16, Hair Dye ChemistryParameswari ArunNo ratings yet
- 1AD3 Group 5 - Human NatureDocument21 pages1AD3 Group 5 - Human NatureHANNAH CHELSEA ROLDANNo ratings yet
- Harrison Sinclairhairstylingl-2003-Journal of Cosmetic DermatologyDocument7 pagesHarrison Sinclairhairstylingl-2003-Journal of Cosmetic Dermatologyلمياء لعلاج وفرد الشعرNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Part 1 - PROPERTIES OF HAIR & SCALPDocument43 pagesUNIT II - Part 1 - PROPERTIES OF HAIR & SCALPmabreza.bolongaitaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Scalp and Hair Treatment SLKDocument24 pagesBenefits of Scalp and Hair Treatment SLKRica VillaNo ratings yet
- Hair StructureDocument21 pagesHair StructureCedrick GamatanNo ratings yet
- HairDocument12 pagesHairBere Praveen SaiNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument23 pagesHair Careapi-3736205100% (2)
- Cos - Chapter 11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpDocument9 pagesCos - Chapter 11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpRhoda Mica J. Limon100% (1)
- Hair and Fiber AnalysisDocument37 pagesHair and Fiber AnalysisKaleem KhanNo ratings yet
- Development of HairDocument28 pagesDevelopment of HairSAGAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Hair Diseases: AnatomyDocument36 pagesHair Diseases: AnatomyMasithaNo ratings yet
- Group7 Hair&scalp Care BrochureDocument2 pagesGroup7 Hair&scalp Care Brochurefirst70145No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Hairdressing (From Pointers)Document4 pagesReviewer in Hairdressing (From Pointers)peanut nutterNo ratings yet
- Hair Growth CycleDocument3 pagesHair Growth CycleReynan Cabatbat100% (1)
- THE Biology of Hair Care: Dermatologic Aspects of CosmeticsDocument8 pagesTHE Biology of Hair Care: Dermatologic Aspects of CosmeticsSiska B SiregarNo ratings yet
- The Science of Black Hair CompressDocument47 pagesThe Science of Black Hair CompressshivaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CLIL Cards SurpriseDocument2 pagesUnit 5 CLIL Cards SurpriseVanNo ratings yet
- Beauty Care Periodical Test Grade 7Document2 pagesBeauty Care Periodical Test Grade 7Jocelyn C. Dinampo86% (7)
- KOKI TOMLINSON Major-Model-ManagementDocument13 pagesKOKI TOMLINSON Major-Model-ManagementBlue hNo ratings yet
- SBFP FormsDocument15 pagesSBFP FormsCrystal CallanoNo ratings yet
- Product & Sales Aid Order Form: Brand Affiliate Brand AffiliateDocument2 pagesProduct & Sales Aid Order Form: Brand Affiliate Brand Affiliatekurnia ningsihNo ratings yet
- Afp Uniforms, Rank & InsigniaDocument12 pagesAfp Uniforms, Rank & InsigniaNCRRCDG ARESCOMNo ratings yet
- Types of Gym Vests To WearDocument2 pagesTypes of Gym Vests To WearClassic Polo eComNo ratings yet
- AMPM 2013 Catalog MexicoDocument88 pagesAMPM 2013 Catalog MexicoGabriel Siria LevarioNo ratings yet
- School Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoyDocument4 pagesSchool Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoySidNo ratings yet
- A Project On SunsilkDocument9 pagesA Project On SunsilkAakriti Sharma50% (2)
- Lily Gao Heffner ManagementDocument21 pagesLily Gao Heffner ManagementFrancis ChengNo ratings yet
- Pre-Wedding Outfit Ideas For GirlsDocument18 pagesPre-Wedding Outfit Ideas For GirlsVideo TailorNo ratings yet
- Human Hair Morphology - A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study On ADocument13 pagesHuman Hair Morphology - A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study On AGamer LoverNo ratings yet
- A Simple Model-Based Index of Abdominal AdiposityDocument2 pagesA Simple Model-Based Index of Abdominal AdiposityakaielfiusNo ratings yet
- 41 Kurta For Men PDFDocument2 pages41 Kurta For Men PDFviktor100% (2)
- Depilatory Waxing Supplies and Tools WholesaleihfxsDocument10 pagesDepilatory Waxing Supplies and Tools Wholesaleihfxsehdsports5269No ratings yet
- Harshbarger AddDocument1 pageHarshbarger Addlittledaisey3No ratings yet
- Names (M) : Nutritional Status ReportDocument7 pagesNames (M) : Nutritional Status ReportGrace V Mae JaymeNo ratings yet
- ISO Care Labels ReportDocument8 pagesISO Care Labels Reportvishnushrinet100% (1)
- Answer Key: Outcomes AdvancedDocument2 pagesAnswer Key: Outcomes AdvancedSereg LeiteNo ratings yet
- Sexy Monokinis - Some ThoughtsDocument1 pageSexy Monokinis - Some ThoughtsMendezHughes30No ratings yet
- Class 3Document5 pagesClass 3Meliza Rueda AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Composition, Arabian Saudit, DRAFTDocument3 pagesComposition, Arabian Saudit, DRAFTMelanie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Akingbola Traction Alopecia - A Neglected Entity in 2017Document6 pagesAkingbola Traction Alopecia - A Neglected Entity in 2017Ernawati HidayatNo ratings yet
- Viking Dress PDFDocument2 pagesViking Dress PDFVic Rs100% (2)
Pcos311 - T2-T4
Pcos311 - T2-T4
Uploaded by
gelary sousa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesOriginal Title
PCOS311 - T2-T4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesPcos311 - T2-T4
Pcos311 - T2-T4
Uploaded by
gelary sousaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
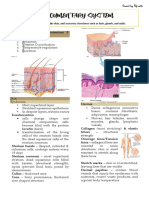
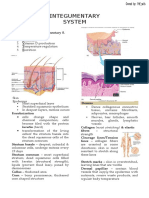
PCOS311 – T2 Hair Products (1) o Long, thick, pigmented hair
found on scalp, legs, arms,
HAIR PRODUCTS
and body
Hair
Shapes of Hair
- Composed primarily of 88% proteins
- Shape of hair shaft determines
or Keratin; a hard fibrous protein.
whether the hair will be straight or
Keratin is composed of polypeptide
curly
chains, which contributes to its
o Thick Round Shaft – straight
hardness
hair
- It is made up of 20 amino acids, to
o Thin Oval Shaft – wavy hair
which 11 of is endogenous and 9 is
o Thick Flat Shaft – curly hair
exogenous and must come from diet
o Very Thin Shaft – spiral coiled
o Proteins are sources of amino
hair
acids, and a healthy diet is
necessary for healthy hair Hair Anatomy
- Hair color results from two types of
hair pigments from melanin; Melanin 1. Shaft
is produced inside the hair follicles - Cuticle
and packed into granules found in o Outermost layer; single layer
fibers of transparent scale like cells
o Eumelanin – dominant overlapping like shingles on a
pigment in brown and black roof
hair o Primary defense against
o Pheomelanin – dominant damage
pigment in red hair - Cortex
o Blonde hair colors contain o Middle layer; fibrous protein
minimal melanin; Albinos lack core formed by elongated
the ability to produce melanin cells containing melanin
pigment
Normal Scalp Hair growth patterns o Accounts for 90% of hair
- Average of scalp hairs is 100,000 weight
- Average growth rate is 0.35mm/day o Protein structures in the
o Grows faster in summer than cortex contributes to hair
winter elasticity
- Average daily loss is 25-100 hairs/day o Chemical changes occur in the
- Fastest growth of hair is between 15- cortex
30 years old - Medulla
- Female hair grows faster than males o Innermost layer; referred to
as Pith/Core; composed of
Types of Hair round cells
o Very fine and naturally blonde
- Vellus or Lanugo hair
o Short, fine, downy, hair may not have medulla
while thick, coarse hair, as
unpigmented hair
well as beard hair always has
o Found in newborns/infants,
a medulla
and newly grown hairs
2. Root
- Terminal hair
- Hair Bulb
- Erector pili muscles 1. Powder Shampoos
2. Liquid shampoos/Lotion
Hair Life Cycle
3. Gel shampoos/Solid cream
3 Phases 4. Cream shampoos
5. Oil shampoos
- Active-Growth Phase; Anagen 6. Miscellaneous-Anti dandruff.
o 2-5 years before replacement Medicated shampoo
- Transition Phase; Catagen
o Lasts 1 or 2 weeks; hair follicle II. Based on Use
shrinks about 80% 1. Conditioning shampoos
- Resting Phase; Telogen 2. Antidandruff and Therapeutic
o After 5 or 6 weeks – dermal 3. Baby
papilla reconnects to base of 4. Balancing
hair follicle and blood stream 5. Clarifying
o Hair re-enters Anagen and
new hair begins to form Composition of Shampoo
PCOS311 – T2 Hair Products (2) 1. Water
2. Surfactants
Types and Preparation of Hair Care products 3. Foam Boosters
SHAMPOO 4. Stabilizers
5. Clarifying agents
- Etymology from Hindustani champo 6. Antidandruff agents
- Hair care product used to remove oils, 7. Conditioning agents
dirt, skin particles, dandruff, 8. Thickening agents
environmental pollutants, and other 9. Sequestering agents
contaminant particles gradually build
up in hair HAIR TONICS AND CONDITIONERS
Ideal Properties - Term “Hair Tonic” has been used for
hair preparations because it is used in
1. Smooth and Shiny therapeutics
2. Produce foam - Hair tonic is one kind of hair repairing
3. No irritation tonic and re-texturing hair;
4. Remove dirt completely - Two distinct types
5. Impart fragrance o Products dealing with specific
6. Readily removed problems (Greasy hair,
Functions dandruff)
o Products intended to
1. Completely remove dirt improve, restore, and
2. Protect Hair maintain condition of hair
3. Clean hair
4. Soothe scalp skin Medicated Products
5. Nourish hair - Purpose is to cure, reduce, and
6. Treat dandruff, lice, and/or other scalp restrain some abnormality in the scalp
problems function
Classification of Shampoo - In the past; often made of irritant,
keratolytic, and rubefacient
I. Based on Appearance compounds
- Recent trend is treatment should - Designed to be used similarly to hair
bring about return to normal state oil – prevents tangling of hair and
and promote balance keep it smooth
- Mainly delas with Dandruff; (3) Ordinary Conditioners
Seborrhea; Hair loss - Combines aspect of Pack and Leave in
conditioner
Conditioners
- Applied after shampoo use
- Viscous liquid applied to the hair and - Characterized into 3 types
usually used after washing hair with o Moisturizer
shampoo o Re-constructers
- Design to restore hair to natural state o Detanglers
o Repair damage by providing
Ordinary Hair Conditioner Types
shiny look to hair fibers
- Restores texture and appearance of A. Moisturizers
rough and harsh hair - Organic solvent concentrated with
o Renders hair shiny, easy to humectant; to retain hair moisture
comb, free from dryness - May not contain protein
B. Re-constructers
Purpose of Hair Conditioner
- Contains protein for hydrolyzation
1. Restore moisture; MAIN IMPORTANT - Human hair keratin protein has low
PURPOSE MW
2. Hair should be manageable after wash - Protein penetrates hair shaft and
3. Smoothen hair follicles; VITAL ROLE gives shiny hair
4. Maintain hair pH C. Detanglers
- Acidifiers and have low pH
Functions of Hair Conditioner
- Function is to close hair cuticle; which
1. Non-irritant causes tangles
2. Smoothen and Soften hair - Surfactant and polymers contribute to
3. Texture protection and shield mechanism
4. Protective Sheath
Conditioner Compositions
5. Tighten cuticle scales
6. Provide Bounce 1. Surfactants
2. Partially/Totally hydrolyzed proteins
Types of Conditioners
3. Oily materials
(1) Pack Conditioner 4. Glossers
- Thick and Heavy 5. Humectant
- High content of surfactant; binds hair 6. Thickeners
structure and glue hair surface scales 7. Bodying agent
together – forming thicker hair 8. Perfumes
surface layer
HAIR COLORANTS
- Applied to the hair for longer time
(2) Leave in Conditioners - Coloring hair is one of most important
- Thinner and have different surfactants acts of adornment among those made
- Lighter, less viscous mixture, thinner by men and women
layer on the hair - Reasons for getting hair colored have
been
o Change natural color
o Color which hair that appears - Other chemicals used act as
with age modifiers, stabilizing dye pigments or
o Change color of hair otherwise act to modify shade
temporarily on particular - Modifiers may bring out color tones
occasion like green or purple, which
complement dye pigment like
Ideal Characteristics of Hair Colorant resorcinol
1. Non-injurious to hair shaft, but colors - Antioxidants protect dye from
the hair without impairing natural oxidizing with air, most commonly
texture and gloss used is sodium sulfite
2. Possess no primary irritant action, - Alkali is added to change pH of dye
free from sensitizing properties formula, because dye works best in
3. Does not produce toxic effect when in highly alkaline composition.
contact with skin Ammonium hydroxide.
4. Color of dyed hair should be stable to Types of Hair Colorants
air, sunlight, friction, and sweat
5. Should not change color nor bleach Temporary Hair Color
out on application of toilet
- Available in various product forms:
preparations such as setting lotion,
Rinses, shampoos, gels, sprays, foams
hair waving preparation, soap, or
- Used to give brighter, vibrant shades
shampoo
or colors like orange or red that may
6. Colorants should be stable over time
be difficult to achieve with semi- and
in aqueous solutions and formulated
permanent hair color
products in form they are sold and
- While it holds lesser market than
used
semi- and permanent agents, they
7. Should not produce different
have value in that they can be easily
coloration on different parts of same
and quickly removed without
hair
bleaching or application of different
8. Should have affinity for hair keratin
coloring product
and capacity to penetrate the shaft
- Colorants does not penetrate Cortex
Hair Colorants Raw Materials or Medulla
o Which is why dye is easily
- Differ from manufacturer to
removed with shampoo
manufacturer;
- In general, should include: Semi-permanent Hair Color
o Modifiers
- Stronger and more permanent
o Antioxidants
coloration to hair than temporary
o Alkali
- Some colors are removed in 4-8
o Soaps
shampoo washing
o Ammonia - Dyes used are
o Wetting agents o Nitrophenylenediamine
o Fragrance o Nitroaminophenols
- Variety of chemicals used in small o Aminoanthraquinones
amounts impart special qualities to - Mixture is prepared before preparing
hair color shades
- Dye compounds usually amino - Should be studied on white wool or
compounds hair
- Contains no Ammonia Design
Data Collection
Permanent Hair Color
Evaluation
- All permanent hair color products and
Phase I: Pre-Clinical Testing
lighteners contain a developer (or
oxidizing agent) and an alkalizing - Pre-clinical dermal and ocular toxicity
agent as part of ammonia or ammonia and irritation test is required early in
substitute safety evaluation process
- Purpose is to - Dermal Sensitization tests on
o Raise cuticle of hair fiber so reconstructed human epidermis
tint can penetrate o Determines skin response
o Facilitate formation of tints - Ocular Irritation tests on corneal
within hair fiber models
o Bring lightening action of o Evaluates irritancy
peroxide - Occurs prior to clinical studies so
o When tint containing safety is assured, IRB review, when
alkalizing ingredient is mandated, should also occur after
combined with developer pre-clinical studies and before clinical
(Usually Hydrogen Peroxide), testing begins
peroxide becomes alkaline
Phase II: Clinical Study Data Collection and
and diffuses through hair
Evaluation
fiber, entering cortex where
melanin is located - Clinical data collection extends over
o Lightening occurs when months
alkaline peroxide breaks up - Planning and execution should begin
melanin and replaces it with as early as possible to meet desired
new color market release date
- Hair performance tests includes
PCOS311 – T2 Hair Products (3)
(A) Trichological (Hair Count) Analysis
Safety and Evaluation of Hair Care Products - Determines changes in hair growth
patterns, trained professional uses
- Hair care product performance and dermascope or videoscope to survey
safety ultimately determine product scalp and record changes in hair
success and longevity growth patterns
o Best market results – precisely (B) Traction Test
planned performance and - Or Gravimetric “Pull” Analysis;
safety evaluations required Sabouraud’s Sign; The Pull-Out Sign
- International regulatory agencies - Measure hair shedding patterns
require demonstration of product - Prior to shampooing, 20-60 strands of
safety hair are grasped at base and tugged
- Manufacturers and Distributors, firmly. More than 10% of strands
responsible for collecting ample info pulled indicates Active Hair Shedding
on product safety and efficacy (C) Hair Pluck Test
- Two Key phases for Comprehensive - Evaluates changes in hair growth cycle
Hair Care Product Performance and hair breakage over time using hair
testing; shafts plucked from scalp
o Pre-clinical Testing (D) Regimented Combing Technique
o Clinical Study
- Assess changes in hair fallout rates
- Panelists use specific combing
techniques to evaluate hair fallout
rates
(E) Tensile Test
- Measures any alterations in hair
strength and resilience
- Measured using Dia-Stron Mini Tensile
Tester (MTT)
- MTT uses 3-point bending and torsion
tests to measure force overtime
required to elongate and break a
strand of hair
You might also like
- VendorsDocument774 pagesVendorslalit18970No ratings yet
- 5chapter 1 - Hair TrichologyDocument7 pages5chapter 1 - Hair TrichologyGupta Shekhar Sulabh80% (5)
- Cantu Presentation - General Brand Overview (Event Staff) NHADocument36 pagesCantu Presentation - General Brand Overview (Event Staff) NHAglamineNo ratings yet
- French FashionDocument15 pagesFrench FashionGarima Thakur100% (1)
- Valeria Dunyanin Amigurumisi ENGDocument14 pagesValeria Dunyanin Amigurumisi ENGözlem çelik100% (7)
- Cosmetic and Toiletry Formulation, 2nd Ed-Vol 8Document395 pagesCosmetic and Toiletry Formulation, 2nd Ed-Vol 8fahmi100% (1)
- Adjectives For Describing Appearance 1Document3 pagesAdjectives For Describing Appearance 1Helio KawakamiNo ratings yet
- 8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)Document14 pages8 - Hair Disorders (Updated)haytham aliNo ratings yet
- 6 Hair Cosmetics Spring 2023 2024 LC Mix Asynchronous+SynchronousDocument30 pages6 Hair Cosmetics Spring 2023 2024 LC Mix Asynchronous+Synchronousessa sunnaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Cosmetic Preparation of HairDocument8 pagesA Review On Cosmetic Preparation of HairEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Hair Structure Growth CycleDocument13 pagesHair Structure Growth Cyclesahubadalkumar89No ratings yet
- Hair Science (PG 14-20)Document9 pagesHair Science (PG 14-20)Izat ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Day 2Document32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Day 2Lake JazzNo ratings yet
- Herbal Hair Care - VPCDocument27 pagesHerbal Hair Care - VPCSatyam DarjiNo ratings yet
- 3C Experiment 7Document6 pages3C Experiment 7Mayck Jhoenell LomboyNo ratings yet
- Nishant Singh (The Forensic Analysis of Hair) FinalDocument23 pagesNishant Singh (The Forensic Analysis of Hair) FinalShikhar NigamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3-4Document13 pagesAnatomy 3-4Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- HAIRDocument66 pagesHAIRjohalyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of HairDocument2 pagesAnatomy of HairAkash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Colorimetry CourseDocument68 pagesColorimetry CourseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Hair and FibersDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 4 Hair and FibersRaymar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- CosmoDocument163 pagesCosmoTadtad FunfunNo ratings yet
- g9 4th Beauty CareDocument132 pagesg9 4th Beauty CarePrimrose MazoNo ratings yet
- Conditioner, Hair Dyes, Hair RemoversDocument3 pagesConditioner, Hair Dyes, Hair RemoversJan Aerielle AzulNo ratings yet
- PermingDocument11 pagesPermingJosh FontanillaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Part 4Document32 pagesUNIT II - Part 4mabreza.bolongaitaNo ratings yet
- HairDocument4 pagesHairRena Carissa100% (1)
- Cosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsDocument8 pagesCosmetics Products Development Hair TreatmentsmasorNo ratings yet
- Regrow Hair Protocol Ebook by David McKennaDocument29 pagesRegrow Hair Protocol Ebook by David McKennaXavier Gomes0% (2)
- Premature Graying of Hair and HomoeopathyDocument4 pagesPremature Graying of Hair and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom0% (1)
- Hair ProductsDocument3 pagesHair ProductsJan Aerielle AzulNo ratings yet
- ColorimetricDocument6 pagesColorimetric4gen_5No ratings yet
- Hair ShaftDocument10 pagesHair Shaftdevashish chouhanNo ratings yet
- The Forensic Analysis of HairDocument21 pagesThe Forensic Analysis of HairTJPlayzNo ratings yet
- Chp8hairanalysis 3Document11 pagesChp8hairanalysis 3Jess BinNo ratings yet
- Ebook HairLossEssentialsDocument158 pagesEbook HairLossEssentialsabhiNo ratings yet
- Croda Hair Necessities Hair Basics FINALDocument5 pagesCroda Hair Necessities Hair Basics FINALبدرالدين بن خليفةNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument71 pagesHair Careking100% (18)
- Hair Anatomy and Physiology 1Document15 pagesHair Anatomy and Physiology 1Dawn SanchezNo ratings yet
- Beauty Culture-HairDocument7 pagesBeauty Culture-HairAkshay Nitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Article 0011 44 50Document7 pagesArticle 0011 44 50apj abdulNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Hairbiology: Growth and PigmentationDocument10 pagesHairbiology: Growth and PigmentationAlexandra DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Hair and Hair Care ProductsDocument28 pagesHair and Hair Care ProductsDRx Sonali TareiNo ratings yet
- The Experimental Study Effects of Coconut Milk and Egg White As A Pack To Enhance The Hair Health Among Adult Male and Female VolunteersDocument4 pagesThe Experimental Study Effects of Coconut Milk and Egg White As A Pack To Enhance The Hair Health Among Adult Male and Female VolunteersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 9 Hair CleanseDocument11 pages9 Hair CleanseSeetha Chimakurthi0% (1)
- Unit 2, Lec No 16, Hair Dye ChemistryDocument56 pagesUnit 2, Lec No 16, Hair Dye ChemistryParameswari ArunNo ratings yet
- 1AD3 Group 5 - Human NatureDocument21 pages1AD3 Group 5 - Human NatureHANNAH CHELSEA ROLDANNo ratings yet
- Harrison Sinclairhairstylingl-2003-Journal of Cosmetic DermatologyDocument7 pagesHarrison Sinclairhairstylingl-2003-Journal of Cosmetic Dermatologyلمياء لعلاج وفرد الشعرNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Part 1 - PROPERTIES OF HAIR & SCALPDocument43 pagesUNIT II - Part 1 - PROPERTIES OF HAIR & SCALPmabreza.bolongaitaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Scalp and Hair Treatment SLKDocument24 pagesBenefits of Scalp and Hair Treatment SLKRica VillaNo ratings yet
- Hair StructureDocument21 pagesHair StructureCedrick GamatanNo ratings yet
- HairDocument12 pagesHairBere Praveen SaiNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument23 pagesHair Careapi-3736205100% (2)
- Cos - Chapter 11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpDocument9 pagesCos - Chapter 11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpRhoda Mica J. Limon100% (1)
- Hair and Fiber AnalysisDocument37 pagesHair and Fiber AnalysisKaleem KhanNo ratings yet
- Development of HairDocument28 pagesDevelopment of HairSAGAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Hair Diseases: AnatomyDocument36 pagesHair Diseases: AnatomyMasithaNo ratings yet
- Group7 Hair&scalp Care BrochureDocument2 pagesGroup7 Hair&scalp Care Brochurefirst70145No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Hairdressing (From Pointers)Document4 pagesReviewer in Hairdressing (From Pointers)peanut nutterNo ratings yet
- Hair Growth CycleDocument3 pagesHair Growth CycleReynan Cabatbat100% (1)
- THE Biology of Hair Care: Dermatologic Aspects of CosmeticsDocument8 pagesTHE Biology of Hair Care: Dermatologic Aspects of CosmeticsSiska B SiregarNo ratings yet
- The Science of Black Hair CompressDocument47 pagesThe Science of Black Hair CompressshivaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CLIL Cards SurpriseDocument2 pagesUnit 5 CLIL Cards SurpriseVanNo ratings yet
- Beauty Care Periodical Test Grade 7Document2 pagesBeauty Care Periodical Test Grade 7Jocelyn C. Dinampo86% (7)
- KOKI TOMLINSON Major-Model-ManagementDocument13 pagesKOKI TOMLINSON Major-Model-ManagementBlue hNo ratings yet
- SBFP FormsDocument15 pagesSBFP FormsCrystal CallanoNo ratings yet
- Product & Sales Aid Order Form: Brand Affiliate Brand AffiliateDocument2 pagesProduct & Sales Aid Order Form: Brand Affiliate Brand Affiliatekurnia ningsihNo ratings yet
- Afp Uniforms, Rank & InsigniaDocument12 pagesAfp Uniforms, Rank & InsigniaNCRRCDG ARESCOMNo ratings yet
- Types of Gym Vests To WearDocument2 pagesTypes of Gym Vests To WearClassic Polo eComNo ratings yet
- AMPM 2013 Catalog MexicoDocument88 pagesAMPM 2013 Catalog MexicoGabriel Siria LevarioNo ratings yet
- School Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoyDocument4 pagesSchool Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoySidNo ratings yet
- A Project On SunsilkDocument9 pagesA Project On SunsilkAakriti Sharma50% (2)
- Lily Gao Heffner ManagementDocument21 pagesLily Gao Heffner ManagementFrancis ChengNo ratings yet
- Pre-Wedding Outfit Ideas For GirlsDocument18 pagesPre-Wedding Outfit Ideas For GirlsVideo TailorNo ratings yet
- Human Hair Morphology - A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study On ADocument13 pagesHuman Hair Morphology - A Scanning Electron Microscopy Study On AGamer LoverNo ratings yet
- A Simple Model-Based Index of Abdominal AdiposityDocument2 pagesA Simple Model-Based Index of Abdominal AdiposityakaielfiusNo ratings yet
- 41 Kurta For Men PDFDocument2 pages41 Kurta For Men PDFviktor100% (2)
- Depilatory Waxing Supplies and Tools WholesaleihfxsDocument10 pagesDepilatory Waxing Supplies and Tools Wholesaleihfxsehdsports5269No ratings yet
- Harshbarger AddDocument1 pageHarshbarger Addlittledaisey3No ratings yet
- Names (M) : Nutritional Status ReportDocument7 pagesNames (M) : Nutritional Status ReportGrace V Mae JaymeNo ratings yet
- ISO Care Labels ReportDocument8 pagesISO Care Labels Reportvishnushrinet100% (1)
- Answer Key: Outcomes AdvancedDocument2 pagesAnswer Key: Outcomes AdvancedSereg LeiteNo ratings yet
- Sexy Monokinis - Some ThoughtsDocument1 pageSexy Monokinis - Some ThoughtsMendezHughes30No ratings yet
- Class 3Document5 pagesClass 3Meliza Rueda AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Composition, Arabian Saudit, DRAFTDocument3 pagesComposition, Arabian Saudit, DRAFTMelanie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Akingbola Traction Alopecia - A Neglected Entity in 2017Document6 pagesAkingbola Traction Alopecia - A Neglected Entity in 2017Ernawati HidayatNo ratings yet
- Viking Dress PDFDocument2 pagesViking Dress PDFVic Rs100% (2)