Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 2 - Alkanes
Section 2 - Alkanes
Uploaded by
salma19.asCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 2 - Alkanes
Section 2 - Alkanes
Uploaded by
salma19.asCopyright:
Available Formats
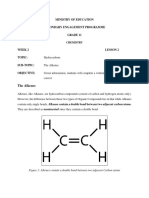
Q: What is the basic structural
Q: What is the difference between saturated characteristic of alkanes?
hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon? Section 2: Alkanes (Contains single bonds between carbon
atoms)
H H H H
H C C H C C H C C H
H H
H H
CnH2n+2 CnH2n CnH2n-2
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 16 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
: Hydrocarbons that contain single covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
Examples of the most commonly used alkanes: natural gas (methane - ethane - propane -
butane)
60-90% 0-20%
Note: Benzene flame = (natural gas + propane)
In it, the carbon atoms are connected by one
continuous line
Q1: What is the molecular formula of saturated hydrocarbon (alkane) containing 13 carbon atoms?
-------------------------------------
-
Q2: What is the basic structural characteristic of alkanes?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of carbon atom Prefix
1 Meth
2 Eth
3 Prop
4 but
5 Pent
6 Hex
7 Hept
8 Oct
9 Non
10 Dec
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 17 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Alkane
Molecular
Prefix suffix
Structural formula Condensed formula
Met ane
formula
)CnH2n+2(
methane H
H C H
C H4 CH4
H
(smallest alkane)
H H
ethane C2H6 H C C H 𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻3
The prefix underlined by a line represents the number of carbon atoms
H H
C3H8
propane
H H H H
C4H10 H C C C C H 𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3
butane H H H H
H H H H H
C5H12 H C C C C C H 𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3
pentane H H H H H
C6H14
hexane
H H H H H H H 𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3
C7H16 H C C C C C C C H
heptane H
𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻2 𝐶𝐻3
H H H H H H
C8H18
octane
H H H H H H H H H
C9H20 H C C C C C C C C C H 𝐶𝐻3 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻2 − 𝐶𝐻3
nonane H H H H H H H H H
H H H H H H H H H H
C10H22
H C C C C C C C C C C H
decane
H H H H H H H H H H
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 18 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Example1: Methane: CH4, the smallest hydrocarbon: H
H C H
A - Fuel is used in homes and science laboratories H
B - It results from many vital processes
Example2: Ethane C2H6: consists of two carbon atoms bound together by a single covalent
H H
bond, and six hydrogen atoms.
H C C H
H H
Example3: Propane gas C3H8: consists of 3 carbon atoms bound together by a single covalent
H H H
bond, and 8 hydrogen atoms.
H C C C H
Some uses: H H H
► Propane (Liquefied propane or LP): fuel for cooking and heating.
► Butane: fuel in small lighter, in some torches, and manufacture of synthetic
rubber.
Notes:
1 - The methane, ethane, propane and butane compounds were named before the knowledge of
the construction of alkanes, so the first syllables of their names are not derived from a
numerical prefix.
2 - The pentane is a pentagon
3 - Octane like Octopus or the eight probes.
:
1 - Which of the following compounds is alkane?
A - C2H2 B -C5H10 C - C7H12 D - C14H30
2 - The compound C8H18is called:
A - octene B - octyne C - octane D – propane
3 - which of the following is organic compounds:
A - CO2 B - CO C - SiC D - CH4
4 - Which of the following is not organic compounds:
A - Na2CO3 B - C2H5OH C - CH3NH2 D - CH4
5 - Which of the following is not a carbon characteristic:
A - It has 4 valence electrons B - it combines with similar or other elements
C - It creates 4 mono covalent bonds C - cannot form chains or rings
9 - Compounds that contain only elements C and H are:
A - hydrocarbons B - hydrocarbon derivatives C - alcohols D - carboxylic acids
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 19 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
35 -The general formula for alkanes is:
A - CnH2n B - CnH2n+2 C - CnH2n-2 D - CnHn
36 - Which of the following belongs to alkanes:
A - C30H61 B - C30H60 B - C30H58 D - C30H62
39 -The general formula for alkenes is:
A - CnH2n B - CnH2n+2 C - CnH2n-2 D - CnHn
40 - Which of the following alkenes:
A - C30H62 B - C30H60 C - C30H58 D - C30H62
41 -The general formula for alkenes is:
A - CnH2n B - CnH2n+2 C - CnH2n-2 D - CnHn
42 - Which of the following of the alkynes:
A - C30H62 B - C30H60 C - C30H58 D - C30H62
43 - Which of the following is the smallest alkane?
A - C2H6 B - C4H10 C - CH4 D - C5H12
44 - Which of the following is the smallest alkene?
A - C2H4 B - C4H8 C - CH2 D - C3H6
45 - Which of the following is the smallest alkyne?
A - C2H4 B - C4H6 C - C2H2 – د D -C2H6
46 -Which of the following is the saturated hydrocarbon?
A - C2H4 B - C4H8 C - C2H2 D - C2H6
47 -Which of the following is unsaturated hydrocarbons?
A - C6H14 B - C4H8 C - C3H8 D - 2H6
48 - Which of the following is not considered a cycloalkane?
A - C6H12 B - C4H8 C - C3H6 D - C2H6
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 20 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
General formula: CnH2n +2.
Note: The branched and straight alkanes have the same molecular formula.
Discuss and compare:
Butane Isobutane
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3 CH CH3
Although the structural formula for both is C4H10, they differ in chemical and physical properties
* Used in safe refrigerants.
It is used in lighters and torches * A driving substance in similar products as shaving
gel.
Note: Both butane and isobutane are used as raw materials in many chemical processes.
The parent chain (main): is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms (continuous).
Q: specifyCH
the parent chain by
3
CH2 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH3
CH2 CH2 CH2
CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH3 CH3 CH3
CH2
CH3
CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH3
C2H5 C2H5 CH2 CH2
CH3 CH3
CH3
CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH3
CH CH2 CH2
C2H5 C3H7
C2H5 CH2 CH2
CH3
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 21 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Substituent groups (alkyl group): are all side branches of the parent chain.
:It is the alternative group that replaces the hydrogen atom in the straight (non-branching) chain.
-H
Alkane Alkyl
Note: The “substitutent group of the parent chain” has the same “name of the straight-chain parent alkanes
that have the same number of carbon atoms” with the substitution of the suffix “ane” with the suffix “yl”
Alkane alkyl
H
C H4 methane H C
m methyl H -C H3
C2H6 ethane -CH2-CH3 e ethyl -C2H5
C3H8 propane -CH2-CH2-CH3 p propyl -C3H7
C4H10 butane -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 b butyl -C4H9
Nomenclature of the substituent group (the alkyl group):
number of carbon atoms + the suffix "yl" instead of the suffix "ane" in the alkanes.
CH3
CH2
CH3 CH2
C C C C C C C C C C
H2C CH2
CH3 CH2
CH2
CH3
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 22 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Nomenclature of branched chain alkanes: The chemists used the following methodological
rules approved by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to
name organic compounds.
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
Step 1: Number carbon atoms in the longest continuous chain and name the alkanes.
Step 2: Number each carbon atom in the parent chain, starting numbering from the terminal carbon atom closest
to the substituent group.
“This step allows all substituent group sites to be given the smallest possible numbers”
Step 3: Name each substituent alkyl group and put the group name before the parent string name.
Step 4: If the same alkyl group is repeated more than once as a branched chain from the parent chain, use a
prefix (Di-tri-Tetra ... and so on) before the name of the parent chain to indicate the number of
occurrences, then use the carbon atom number to which each group is related To locate it.
Step 5: When different alkyl groups are linked on similar sites of the parent chain, alphabetical order of the
English language is used (the prefixes Di, Tri, .... not considered)
Step 6: Use dashes to separate numbers from words, commas to separate numbers, and leave no space between
the name of the substitutent (alkyl) and the name of the parent chain.
Q: Use IUPAC rules to name the structural formula for the following compounds:
CH3 (CH2)4 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH CH3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH3
CH3
CH3 CH CH CH3 CH3 - CH 2 - CH 2 - CH - CH - CH 3
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3
CH 3 CH 3
CH3 CH3
CH 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH CH 3
CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH3
CH 3
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 23 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
CH3
CH3 CH CH2 CH CH CH3
CH3 CH2 C CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH3
CH2 CH3 CH2 C CH3
CH3 - CH - CH - CH - CH-CH 3
CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3
CH 3 CH 3
CH 2
CH 3 CH CH 2 CH CH2 CH 3
CH 3 CH 2 CH CH 2 CH 2 CH CH 3
CH 2 CH3
CH 2
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
CH 2 CH 2
CH 3 CH CH 2 CH 2 CH2 CH CH3 CH 3 CH CH 2 CH 2 CH2 CH CH3
C3H7 CH3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3 C CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3 - CH 2 - CH - CH - CH 2
CH3 CH3 CH2 - CH 2 - CH 2 - CH 3
CH3
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 24 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
CH3
CH3 CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH CH3
C2H5
CH3 CH3
H 5C 2 C C 2H 5
CH3 C CH2 CH CH3
C2H5 CH3
Additional exercises
CH3CH2CH2CHCH3CH3 CH(CH3)3
CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 C(CH3)4
(CH3)3CCH2CH3 CH2 CH2
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH3 CH2
CH CH3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH
CH2 CH2
CH3
CH3
CH2 C2H5 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
CH CH3 CH2 CH3
CH2 C2H5
CH2 CH2 CH2 CH
CH3
CH3 CH3
CH3 CH2 C CH2 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH CH3
CH2 CH3
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 25 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH CH CH2 CH CH CH3 CH3 CH2 C CH2 CH3
CH2 CH3
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH CH CH2 CH2 C CH2 CH3
CH3 CH CH CH2 CH2 CH CH3
CH2
CH2
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3
CH3 CH CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH CH CH3 CH3 CH CH CH2 CH2 C CH2 CH3
CH2 CH3 CH2
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 CH3
CH2 CH2
CH2 CH2
CH3
Q: Draw structural formulas for the following alkanes:
3.3 - Dimethyl - 2, 5 - Dimethyl Nonane 2, 4 - dimethyl pentane
2 - methyl propane 4- Ethyl-3-methyl heptane
4 - methyl octane 3, 3, 4 - trimethyl-4-methyl hexane
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 26 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
2,3 - dimethyl - 5 - propyl decane 2, 2 - dimethyl-4-propyl octane
Isobutane 3, 4, 5 - Triethyl Octane
H
Q1: The correct name for the adjacent shape is:
H H C H H H
A - 2,2 - dimethyl butane B - 1,1,1 - trimethyl propane
H C C C C H
C- 2-Ethyl-2-Methyl Propane D-3,3-Dimethyl Butane (A) H H C H H H
Q2 - Determine if the naming of the alkanes is correct in each of the following, and if not, write the correct name
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2
CH3 CH 3
(Nonane) (1 - methylpropane)
) .................................................... ( ) .................................................... (
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH CH2 CH CH3
CH3
CH2 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH3
(4 - ethyl-2 - methylhexane) (4 - methylhexane)
) ........................................ ............ ( ) .................................................... (
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 27 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
an organic compound containing a hydrocarbon ring.
Note: The rings in the cyclic alkanes consist of 3, 4, 5 or 6 carbon atoms or more.
Cyclic alkane: Cyclic hydrocarbons contain only single bonds between carbon atoms.
removing 2 hydrogen atoms from two carbon atoms
Alkane -2H
Cyclic alkane
Explain: Because one valence electron from each of the two carbon atoms in the cycloalkane forms a carbon-
carbon bond instead of a carbon-hydrogen bond.
Example: Hexane has the molecular formula C6H14, and cyclohexane has the molecular
formula C6H12
H H H H H H H H H H H H
HC C C C C CH H C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H H H H H
The structural formula
of cyclohexane in several ways:
CH2 CH2
CH2
H2C CH2 CH2 CH2
H2C CH2 CH2
CH2
CH2
C CH2
C C H2C CH2
C C H2C CH2
C CH2
liear formula Skeletal formula Condensed structural formula
Only the bonds between carbon atoms are shown,
and the angles explain the locations of
carbon atoms, and the hydrogen atoms are
supposed to occupy the remaining
positions in the bond unless there are
alternatives.
Cyclohexane is extracted from petroleum and is used in:
1 - Paint Solvents 2 - Polishing Materials 3 - Extract the essential oils used in perfumery
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 28 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Naming alternate cyclic alkanes: There is no need to search for the longest carbon or
chain, because the cyclic chain is endless, so the parent chain is the cycle.
1 - the parent hydrocarbon = cyclo + number of cyclo carbon atoms
2 - Add the names of the alkyl groups.
3 - number of the parent carbon atoms closest to the branch, giving the smallest numbers possible
4- If there is one branch, there is no need for numbering.
5 - Place the number of branching.
6 - Set dashes and commas
Don't forget the notes:
1 - There is no need to find the longest chain.
2 - The numbering is carried out from the carbon atom associated with the substituted group.
3 - When there is more than one substituted group, the carbon atoms are numbered around the
ring, provided that the substituted groups get the smallest possible set of numbers.
4 - If there are two different groups at the same distance from the numbering, then we resort to
the English alphabet.
5 - If there is one substituted group connected to the ring, there is no need for numbering.
Q: Use the IUPAC rules to name the following formulas:
CH2 CH2
H2C CH2
H2C CH2
H2C CH2
Cyclopropane
CH2 CH2 CH2
H2C CH2 H2C CH2
H2C CH2 H2C CH2
CH2 CH2 CH2
H3C
CH 3
CH3
Methyl cyclohexane
4 1 CH3 CH3
3 2 CH3 4 1
CH3
1,2 dimethyl cyclobutane 3 2
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 29 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
CH3 CH3
CH2 CH2
CH3 CH3
CH3
CH3 CH3
CH3
CH2
CH3
CH3
H3C CH2 CH2
CH2
CH2 CH3
H3 CH CH3
3
C CH3
CH2
CH3
H3C CH2 CH2 H3C CH3
CH3 CH3
H2C CH3 CH3
H3C
H2C CH2 CH2 CH2
CH3 CH3
CH3
CH3
CH3 CH3
CH2CH3
CH3
CH3 CH2 CH
3 CH3CH2
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 30 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
Q - Draw the condensed formula for:
A) 1,1 - Dimethyl cyclopropane B) 2,2,4,4 – tetramethylpentane
2-ethyl-3- methyl pentane 1-methyl-3-propyl cyclopentane
1-ethyl-3-propyl cyclopentane 1,2,2,4-tetramethyl cyclohexane
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 31 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
properties of alkanes:
A - Physical properties:
►Alkanes of C1 → C4 : Gases (example : natural constituents of natural gas) as they have low
molecular mass and weak London dispersion forces between their molecules.
►Alkanes of C5 → C10 : liqiuds (example : Kerosene and gasoline) as they have higher molecular
mass and an increasing in London dispersion forces between their molecules.
►Alkanes of C11 → C---- : solids (example : Paraffin wax)
Explain: Alkanes of high carbon atoms are more united and have a higher boiling point.
Due to an increase in the molecular mass, which leads to an increase in London dispersion
force and an increase in attraction force.
Explain: Alkanes are Non-polar molecules: Because the bond is carbon - carbon is non-polar
Explain: Alkanes are good solvents for other non-polar materials: because alkanes are non-polar, and like
dissolves like.
Explain: there is significant difference between boiling point of water and methane, use the
information in the following table.
+δ
H +δ
In water: There are strong hydrogen bonds between O -δ H O -δ
water molecules, which increase the boiling point of water
H H
+δ +δ
In methane: the particles are non-polar, there is weak London dispersion forces among
methane molecules, so there is low boiling point H H H
H C C C H
H H H
H H H
H C C C H
H H H
Explain: The boiling point of decane is higher than that of the pentane.
Because of the higher the molecular mass, the greater London dispersion forces between
the molecules, and thus the greater the boiling point.
Explain: Alkanes or hydrocarbons (such as lubricating oil) not mixed in water.
Because like dissolves like, so the attraction forces between the non-polar alkane molecules
with each other are stronger than the attraction forces between the non-polar alkanes and
the polar water.
Note: Alkanes and hydrocarbons (non-polar) are dissolved in non-polar solvents such as
toluene and benzene (both non-polar).
A - Chemical properties:
Chemical reaction principle: Most chemical reactions occur when a reactant with a full electrical
charge such as an ion or a partial charge such as a polar molecule is attracted to another
substance with an opposite charge.
Explain: Weak chemical activity of alkanes.
1 - Because its molecules are non-polar, so their attraction to ions or polar molecules is very weak
2- The C-C and C-H bonds are relatively strong.
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 32 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 33 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 34 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
chemistry Grade 12 Advance third semester 35 Prepared by Mr. Ibrahim elNagar
You might also like
- Drainage Design Report For Perbadanan PutrajayaDocument21 pagesDrainage Design Report For Perbadanan PutrajayaLokman Hakim100% (1)
- Chemsheets GCSE 1285 QC Organic A ANSDocument1 pageChemsheets GCSE 1285 QC Organic A ANSchinkey lolNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Alkanes HQDocument28 pagesAlkanes HQHaslimi Bin HassanNo ratings yet
- Organic: ChemistryDocument16 pagesOrganic: ChemistryroythomascNo ratings yet
- CH 2 (Crude Oil Characterisation) 2018 BDocument63 pagesCH 2 (Crude Oil Characterisation) 2018 Bnafisa afariNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry SlidesDocument53 pagesOrganic Chemistry SlidesmbaguleekaristiNo ratings yet
- Organic NomenclatureDocument12 pagesOrganic Nomenclatureitbwng100% (1)
- Bonding & Molecular StructureDocument3 pagesBonding & Molecular Structureapi-320784618No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesOrganic ChemistryAnonymous 1c0HNRTC9GNo ratings yet
- 13.CHM 123 - Hydrocarbons & Alkanes (Lecture 13) 2Document19 pages13.CHM 123 - Hydrocarbons & Alkanes (Lecture 13) 2JoshNo ratings yet
- Reviw RemiDocument4 pagesReviw RemiBuena QuintinNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundDocument15 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundChee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Csec1Document103 pagesOrganic Chemistry Csec1dela2No ratings yet
- Goc and Isomerism Notes - PMDDocument32 pagesGoc and Isomerism Notes - PMDMahesh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - General Organic ChemistryDocument42 pagesPadhle 11th - General Organic Chemistryveeru kumarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AlkenesDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry AlkeneskhssciencedepartmentNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry WorksheetDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry WorksheetOrane CassanovaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument17 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesChristopher gotemNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For AlevelDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry For AlevelNahida HossainNo ratings yet
- Genchem NomenclaturesDocument90 pagesGenchem NomenclaturesMitch Jasdale Mentar QuimotNo ratings yet
- Part XI - CHEMISTRY OF CARBON COMPOUNDS (Part 1)Document67 pagesPart XI - CHEMISTRY OF CARBON COMPOUNDS (Part 1)yana LAUNo ratings yet
- Yr12CHEM - M7 Organic Chemistry - Filled - in - NewDocument210 pagesYr12CHEM - M7 Organic Chemistry - Filled - in - Newryan.li20180211No ratings yet
- 4.1 Organic ChemistryDocument55 pages4.1 Organic ChemistryYusuf NaeemNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry AlkanesDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry AlkaneskhssciencedepartmentNo ratings yet
- Organic NomenclatureDocument9 pagesOrganic NomenclatureCarlos ChNo ratings yet
- AlkaneDocument2 pagesAlkaneMukisa Esther graceNo ratings yet
- OCI Lecture2-3Document9 pagesOCI Lecture2-3Baga DagaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Section 2Document14 pagesHydrocarbons: Section 2Karam AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - AlkanesDocument7 pagesTopic 2 - AlkanesRichard WalkerNo ratings yet
- Fuel, Turbo ChargingDocument25 pagesFuel, Turbo Chargingحسن محمود حسن محمد 3760No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon & It S Compounds - F825d4ae 704e 4c3b b378 1fa70c60f74eDocument78 pagesChapter 4 Carbon & It S Compounds - F825d4ae 704e 4c3b b378 1fa70c60f74eSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Week 2 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Week 2 Lesson 2RealGenius (Carl)No ratings yet
- WTF Bharat Panchal FinalDocument135 pagesWTF Bharat Panchal FinalDhruv KarheNo ratings yet
- Basic of Organic Chemistry by Bharat PanchalDocument24 pagesBasic of Organic Chemistry by Bharat Panchalrashimaths06100% (1)
- Mind Map Organic - PDT 2021Document11 pagesMind Map Organic - PDT 2021ROS EZRA HANNY A/P ROSLI MoeNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Carbon and Its Compound ArshDocument17 pagesCH-4 Carbon and Its Compound ArshArsh GaurNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Organic ChemistryDocument32 pagesFundamentals of Organic ChemistryBJDarkMusicRain ArmyNo ratings yet
- Revision 2Document26 pagesRevision 2tettehebenezer901No ratings yet
- Classification of Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification of Organic CompoundsGrace L. AmorNo ratings yet
- 2 AlkaneDocument22 pages2 AlkaneNatashamazukiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1&2Document142 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1&2Kennedy ChitayiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - 1.3 Alkanes, Enes, Ynes, AromaticsDocument44 pages1.1 - 1.3 Alkanes, Enes, Ynes, AromaticsTiwanka MadugalleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PT 2Document37 pagesChemistry Notes PT 2Leng RyanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument3 pagesHydrocarbon NotesMark AnidNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsDocument24 pagesHydrocarbons and Functional GroupsMaricel MagnoNo ratings yet
- 03 Hydrocarbon ChemistryDocument18 pages03 Hydrocarbon Chemistryfaraj100% (1)
- C Aims Dts@AlkanesDocument13 pagesC Aims Dts@AlkanesAditya RamNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument29 pagesHydrocarbongoswamiaddNo ratings yet
- Cell04 ChemistryDocument10 pagesCell04 ChemistryAnisam AbhiNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Document12 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 4nicole lagumbayNo ratings yet
- Orgarnic Chemistry Functional Group TestDocument9 pagesOrgarnic Chemistry Functional Group TestShourya veer singhNo ratings yet
- 12 Nomenclature Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument11 pages12 Nomenclature Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaNo ratings yet
- 13 General Organic Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument22 pages13 General Organic Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaNo ratings yet
- Iupac NamingDocument11 pagesIupac Namingjyoti.rani3092No ratings yet
- HeiAssignment 2 Key PDFDocument2 pagesHeiAssignment 2 Key PDF分開倉庫喔噢罰款No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsvivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Organic ChemistrySelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1 - Chem - f3 - v1 1Document77 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1 - Chem - f3 - v1 1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature NOTESDocument25 pagesNomenclature NOTESalex caitlinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - OrganicDocument50 pagesChemistry - Organicsgw67No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Health and Wellbeing: Academic Year 2021/2022 - Term 1Document11 pagesGrade 11 Health and Wellbeing: Academic Year 2021/2022 - Term 1salma19.asNo ratings yet
- Diseases and disorders ملخصDocument4 pagesDiseases and disorders ملخصsalma19.asNo ratings yet
- AcidsandbasesstudentDocument7 pagesAcidsandbasesstudentsalma19.asNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical Bondingsalma19.asNo ratings yet
- Online Class Notes & Study MaterialDocument4 pagesOnline Class Notes & Study MaterialsudhaNo ratings yet
- DK Lok v33 Series Inline Check ValveDocument4 pagesDK Lok v33 Series Inline Check Valvecenter steel110No ratings yet
- Modular Air Cooled Chillers PDFDocument22 pagesModular Air Cooled Chillers PDFBehnamNo ratings yet
- Fujifilm Water Pump JW-3 Brochure EN 2022Document2 pagesFujifilm Water Pump JW-3 Brochure EN 2022singh018No ratings yet
- Philips hd9110Document8 pagesPhilips hd9110smallmitaNo ratings yet
- P. Inorganic Chemistry Lab ManualDocument45 pagesP. Inorganic Chemistry Lab ManualDean PharmacyNo ratings yet
- CPVC Technical Manual: Jeevan Bhar Ki SurakshaDocument20 pagesCPVC Technical Manual: Jeevan Bhar Ki SurakshaManas Kumar SamalNo ratings yet
- Water Diversion WebquestDocument5 pagesWater Diversion Webquestapi-236051971No ratings yet
- Water Supply Legend 5 Sanitary and StormDocument1 pageWater Supply Legend 5 Sanitary and Stormheba barryNo ratings yet
- Required Docs EMILDocument27 pagesRequired Docs EMILChimchar AlbaNo ratings yet
- Full ReportDocument24 pagesFull Reportbravo deltafoxNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation Practices Using A Single Pot ProcessorDocument9 pagesCleaning Validation Practices Using A Single Pot Processorjljimenez1969No ratings yet
- Pressure Relief, Flares, Flame Arrestors PDFDocument15 pagesPressure Relief, Flares, Flame Arrestors PDFRenanNo ratings yet
- Zinc SilicatesDocument4 pagesZinc SilicatesAnuar SalehNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasDanica ChuaNo ratings yet
- Session 2c Armenia Voskanyan Business Plan Final 10APR14Document38 pagesSession 2c Armenia Voskanyan Business Plan Final 10APR14biniamNo ratings yet
- Fournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFDocument10 pagesFournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFAnonymous FdickkSXcNo ratings yet
- 978 0321814050 Essentials of OceanographyDocument61 pages978 0321814050 Essentials of Oceanographyaudrey.walston606100% (58)
- Dust Deposition (DD) and Air Pollution Tolerance Index (APTI) Analysis of Common Plant Species A Comparative Study of Seven Plant Species in Industrial and Residential AreasDocument18 pagesDust Deposition (DD) and Air Pollution Tolerance Index (APTI) Analysis of Common Plant Species A Comparative Study of Seven Plant Species in Industrial and Residential AreasInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Are Human Activities A Substantial Cause of Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesAre Human Activities A Substantial Cause of Climate ChangeKai Chun Ng0% (1)
- Cryogenic CoolingDocument16 pagesCryogenic CoolingGissmoNo ratings yet
- Exam Weekly Exam9Document7 pagesExam Weekly Exam9Astra BeckettNo ratings yet
- CCI+GR70+Ink+Degradent Stain+Remover+MSDS PDFDocument2 pagesCCI+GR70+Ink+Degradent Stain+Remover+MSDS PDFobed100% (1)
- 2020 Multi V VRF CatalogDocument149 pages2020 Multi V VRF CatalogTechnical OfficeNo ratings yet
- Alejandro - Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)Document45 pagesAlejandro - Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)Dondee Sibulo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Frater Albertus - Alchemical Laboratory Bulletins PDFDocument18 pagesFrater Albertus - Alchemical Laboratory Bulletins PDFtravellerfellowNo ratings yet
- Eolo Star 24 4E NON CE - 1040470Document32 pagesEolo Star 24 4E NON CE - 1040470tmisulicaNo ratings yet
- Storm Water CalculationDocument7 pagesStorm Water CalculationTrang NgoNo ratings yet
- Student Research: Utilizing Kinetic Energy Source Through Electromagnetism and Its Relevance To The Natural WorldDocument12 pagesStudent Research: Utilizing Kinetic Energy Source Through Electromagnetism and Its Relevance To The Natural WorldNorvin LeynesNo ratings yet