Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exudates and Transudates
Exudates and Transudates
Uploaded by
Jils SureshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exudates and Transudates
Exudates and Transudates
Uploaded by
Jils SureshCopyright:
Available Formats
EXUDATES AND TRANSUDATES
Exudates are fluids, CELLS, or other cellular substances that are slowly discharged from BLOOD
VESSELS usually from inflamed tissues.
Transudates are fluids that pass through a membrane or squeeze through tissue or into the
EXTRACELLULAR SPACE of TISSUES. Transudates are thin and watery and contain few cells or
PROTEINS.
EXUDATE
Exudate is a fluid which is rich in proteins and other cellular components.
Blood vessels and organs release this fluid as a result of an inflammation.
Once it is oozed out, exudates get deposited in the surrounding tissue.
Due to an injury or inflammation, the walls of the blood vessels get damaged causing the increment in
permeability.
Alteration in blood vessel permeability causes the large molecules and different solid matter to pass
through the vessel walls.
This causes the leakage of fluids into the nearby tissues.
The oozing fluid or exudate is mainly composed of fibrin proteins, blood serum and white blood cells.
The oozed out exudate appear in a translucent cloudy appearance.
The protein content of exudates is high when compared to transudates.
The exudates could be of different types according to the location and constituents.
o The suppurative of purulent exudate is composed of plasma cells such as active and
dead neutrophils, necrotic cells, and fibrinogen. This exudate is commonly referred to as ‘pus’
that occurs due severe inflammatory conditions.
o Fibrinous exudate consists of proteins fibrinogen and fibrin in larger quantities. This
exudate is a common characteristic of rheumatic carditis. It is also present in severe cases of
injuries which include strep throat and pneumonia caused by bacteria.
TRANSUDATE
In the context of transudate, it is also a body fluid that is passed through a membrane.
The membrane mostly filters the cells and different proteins and yields a solution of watery liquid.
Mostly, transudates occur due to increment in hydrostatic and osmotic pressure that is built into the
veins and capillaries.
This imbalance in fluid forces results in high-pressure movement of fluids through the blood vessel
walls which get filtered.
Therefore, transudate is a filtrate of blood which accumulates in the surrounding tissues that are present
outside the blood vessels.
Transudates consist of a lower protein content.
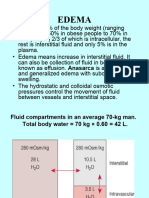
The occurrence of transudates causes edema.
Like exudates, inflammatory conditions do not lead to transudates.
Transudates contains a clear appearance.
This may be due to lower protein content.
Its specific gravity is low compared to exudates.
The nucleated cell count is also low. The most abundant cell types of this blood filtrate are
macrophages, mononuclear cells, lymphocytes, and mesothelial cells.
Transudates have a lower cholesterol content.
Different conditions lead to the formation of pathological transudates. The most common cause as
mentioned above is an increment in osmotic and hydrostatic pressure. This could lead to left ventricular
heart failure. Disease conditions like cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome and malnutrition are potential
causes of transudates.
You might also like
- Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery Table of ContentsDocument18 pagesYoumans and Winn Neurological Surgery Table of ContentsLuigi D'angelo0% (1)
- Callo, Dimple C. (Shutter Island)Document4 pagesCallo, Dimple C. (Shutter Island)Dimple Castañeto CalloNo ratings yet
- MK Hemodynamics PathologyDocument27 pagesMK Hemodynamics PathologyMoses Jr Kazevu100% (1)
- PathDocument5 pagesPathLenny MerdhaNo ratings yet
- Additional ReadingDocument11 pagesAdditional Readingsneha.roy.cse24No ratings yet
- Inflammation: Microorganisms Include The Broad Groups of Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Protozoa, and RickettsiaDocument4 pagesInflammation: Microorganisms Include The Broad Groups of Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Protozoa, and RickettsiaTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemCharise LigoresNo ratings yet
- MY GROUP Edema - Report2010Document5 pagesMY GROUP Edema - Report2010Nadhirah Mohamad NohNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument121 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammationbariq AlnawaisehNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePathogenesis of Pleural EffusionKlean Jee Teo-TrazoNo ratings yet
- Semester 3 Week 1: Funtion of SpleenDocument2 pagesSemester 3 Week 1: Funtion of SpleenRidzuanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Serous Fluid Cytology AmaDocument75 pages2022 Serous Fluid Cytology Amareuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Arteries and VeinsDocument143 pagesDisorders of Arteries and VeinsJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Eksudat:: Fisiologi Dan Cara Pengambilan SampelDocument13 pagesEksudat:: Fisiologi Dan Cara Pengambilan SampelJerry TjoanatanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 19 Anatomy and Physiology NotesZachary WatsonNo ratings yet
- Haemodynamic DisordersDocument28 pagesHaemodynamic DisordersOROKE JOHN EJENo ratings yet
- B6 Transport SystemsDocument2 pagesB6 Transport SystemsMisentaiNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockDocument127 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part Two PDFDocument26 pagesUnit 1 Part Two PDFKartik RajpootNo ratings yet
- Aubf FluidsDocument1 pageAubf FluidsMaryNo ratings yet
- Mechanism: Interstitium Swelling Interstitial Fluid HomeostasisDocument3 pagesMechanism: Interstitium Swelling Interstitial Fluid HomeostasisBryan MahendraNo ratings yet
- Edema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDDocument20 pagesEdema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDHassoun hassounNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System H. S. MayersonDocument14 pagesThe Lymphatic System H. S. MayersonGio Galanti100% (1)
- Morphology" ..: Liver Is Divided Histological Into Lobules. The Center of The Lobule IsDocument15 pagesMorphology" ..: Liver Is Divided Histological Into Lobules. The Center of The Lobule IsSawsan Z. JwaiedNo ratings yet
- Serous Fluids: 1 Dr. Mohamed Saad DaoudDocument19 pagesSerous Fluids: 1 Dr. Mohamed Saad DaoudPatrickNo ratings yet
- 1 Acute InflammationDocument6 pages1 Acute InflammationNauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- SG 4,5,6Document20 pagesSG 4,5,6Itadori YujiNo ratings yet
- Petechia PurpuraaDocument2 pagesPetechia PurpuraaAlifah SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- Defense Against Infectious Disease: Skin As A Barrier To InfectionDocument8 pagesDefense Against Infectious Disease: Skin As A Barrier To InfectionFranchesca Rosabel BudimanNo ratings yet
- EffusionsDocument26 pagesEffusionsfomishisilasNo ratings yet
- Pat Hop Harm OlogyDocument1 pagePat Hop Harm OlogyNoel BaluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 MedsurdgeDocument14 pagesChapter 13 MedsurdgeLaurence Angel H OrdonaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders-RevisedDocument118 pagesHemodynamic Disorders-Revisedspringding0% (1)
- Vascular Pathology - Lesson - 10Document81 pagesVascular Pathology - Lesson - 10Aya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in MammalsDocument8 pagesCirculatory System in MammalsObiora Ekene HilaryNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyDocument4 pagesPengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyAlmas PrawotoNo ratings yet
- Heamodynamic Disorders (Patho) - Dr. AnoodDocument62 pagesHeamodynamic Disorders (Patho) - Dr. AnoodfourtechmediadmeagentsNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyDocument4 pagesPengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyZakiyah ArrohmahNo ratings yet
- Underwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionDocument12 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionSANo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins and Spider Veins: BackgroundDocument6 pagesVaricose Veins and Spider Veins: BackgrounddockunNo ratings yet
- Fenestración y Transporte Endotelial: EndotelioDocument5 pagesFenestración y Transporte Endotelial: EndotelioYANDIRA JANET SOSA IBAÑEZNo ratings yet
- 44.physiology of The MicrocirculationDocument3 pages44.physiology of The MicrocirculationNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesBlood VesselsshinbiNo ratings yet
- (٦) المحاضرة السادسةDocument43 pages(٦) المحاضرة السادسةAbdulMalik AlHarbiNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and RepairDocument34 pagesInflammation and Repairanshum guptaNo ratings yet
- Hemo Dynamic DisDocument49 pagesHemo Dynamic Disjuna danadyaksaNo ratings yet
- Laxmi MamDocument7 pagesLaxmi MamkamalshrishNo ratings yet
- Underwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionDocument12 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionnyangaraNo ratings yet
- انواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبDocument3 pagesانواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبOmer AlsameiNo ratings yet
- Stasis - As Stasis Develops, Leukocytes (Principally Neutrophils) Begin To Accumulate AlongDocument2 pagesStasis - As Stasis Develops, Leukocytes (Principally Neutrophils) Begin To Accumulate AlongAli Ahmad KhameiniNo ratings yet
- Basic HemostasisDocument4 pagesBasic HemostasisMarvin SimbulanNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument15 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisviper121No ratings yet
- 1212 TransudateDocument3 pages1212 TransudateBoysz TheBestNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument1 pageAcute InflammationRainbow LinNo ratings yet
- L7: Vascular System, Capillaries and Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesL7: Vascular System, Capillaries and Lymphatic SystemJade CoetzeeNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: The Endothelium: Peter Takizawa Department of Cell BiologyDocument47 pagesBlood Vessels: The Endothelium: Peter Takizawa Department of Cell BiologySwarna RNo ratings yet
- Disease Process NarrativeDocument4 pagesDisease Process NarrativeFritz DecendarioNo ratings yet
- Bio Note 1Document11 pagesBio Note 1Aidah AmirNo ratings yet
- A Capillary Is A Small Blood VesselDocument10 pagesA Capillary Is A Small Blood VesselchibuikeNo ratings yet
- Microcirculation of Blood 101: The Next Generation of HealthcareFrom EverandMicrocirculation of Blood 101: The Next Generation of HealthcareNo ratings yet
- ThrombosisDocument2 pagesThrombosisJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Newborn ReflexesDocument12 pagesNewborn ReflexesJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Toddler Growth and DevelopmentDocument20 pagesToddler Growth and DevelopmentJils SureshNo ratings yet
- School AgeDocument10 pagesSchool AgeJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Pulmonary TBDocument3 pagesPathology of Pulmonary TBJils SureshNo ratings yet
- The Normal Toddler Growth and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesThe Normal Toddler Growth and DevelopmentJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument27 pagesBreast CancerJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Ratng ScaleDocument6 pagesRatng ScaleJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Seminar and SymposiumDocument13 pagesSeminar and SymposiumJils SureshNo ratings yet
- WeaningDocument4 pagesWeaningJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of PreschoolerDocument6 pagesGrowth and Development of PreschoolerJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Neurologic DisorderDocument77 pagesNeurologic DisorderJils SureshNo ratings yet
- GastroenteritisDocument14 pagesGastroenteritisJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow TransplantationDocument8 pagesBone Marrow TransplantationJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Typhoid in ChildrenDocument3 pagesTyphoid in ChildrenJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument28 pagesHirschsprung DiseaseJils SureshNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument15 pagesChemotherapyJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Radiation TherapyDocument13 pagesRadiation TherapyJils SureshNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument24 pagesOncologyJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The CervixDocument14 pagesCancer of The CervixJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument16 pagesGastric CancerJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal CancerDocument13 pagesLaryngeal CancerJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Oral CancerDocument11 pagesOral CancerJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Malarone JuniorDocument5 pagesMalarone Juniorhannah.g.pavNo ratings yet
- (Jurnal) Sonography in Male InfertilityDocument25 pages(Jurnal) Sonography in Male InfertilityIrni Dwi Aprianty IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Head N Neck Guidelines by Mbbs CafeteriaDocument11 pagesHead N Neck Guidelines by Mbbs CafeteriaFarah Khan100% (1)
- HEMA PracticalDocument14 pagesHEMA PracticalNanik AndianiNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care For Stroke Patients and Their Families: Barriers For ImplementationDocument8 pagesPalliative Care For Stroke Patients and Their Families: Barriers For ImplementationMaisury LadjidjiNo ratings yet
- Diamond-Blackfan Anemia Is A DisorderDocument22 pagesDiamond-Blackfan Anemia Is A DisorderDarem SoNo ratings yet
- Status Epilepticus: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDocument24 pagesStatus Epilepticus: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- Psychosis in The Older PatientDocument25 pagesPsychosis in The Older PatientKreshnik IdrizajNo ratings yet
- Necrosis BasophilsDocument6 pagesNecrosis BasophilsDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Beyond Thrombocytopaenia, Haemorrhage and Shock: The Expanded Dengue SyndromeDocument11 pagesBeyond Thrombocytopaenia, Haemorrhage and Shock: The Expanded Dengue SyndromePawan MishraNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and HygieneDocument32 pagesFood Safety and HygieneJulia El SamraNo ratings yet
- Class Action Lawsuit Against Lundy Manor Related To COVID-19 DeathsDocument19 pagesClass Action Lawsuit Against Lundy Manor Related To COVID-19 DeathsGrant LaFlecheNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Diseases Dr. TulaganDocument6 pagesCerebrovascular Diseases Dr. TulaganNdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Micro Notes 1Document49 pagesMicro Notes 1Apryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- The History of Tuberculosis: From The First Historical Records To The Isolation of Koch's BacillusDocument4 pagesThe History of Tuberculosis: From The First Historical Records To The Isolation of Koch's BacillusGrace Meigawati IwantoNo ratings yet
- Health and Disease Are Dynamic Complex-Adaptive States Implications For Practice and ResearchDocument14 pagesHealth and Disease Are Dynamic Complex-Adaptive States Implications For Practice and ResearchsanorenatNo ratings yet
- OMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusDocument51 pagesOMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusMaryam XANo ratings yet
- Assessing The Current State of Cognitive Frailty: Measurement PropertiesDocument9 pagesAssessing The Current State of Cognitive Frailty: Measurement PropertiesCarlos CarrilloNo ratings yet
- NCM 0114 Module 3 - Nursing Care Management of The Older Person With Chronic IllnessDocument84 pagesNCM 0114 Module 3 - Nursing Care Management of The Older Person With Chronic IllnessKristine Kim100% (1)
- New blanki eng ქირურგიის გამოცდაDocument12 pagesNew blanki eng ქირურგიის გამოცდაHarsh NimavatNo ratings yet
- Schizoaffective Disorder - Emedicine SourceDocument25 pagesSchizoaffective Disorder - Emedicine SourcenarseeNo ratings yet
- The Gravedigger's Guide To Cardiology Overview TOCDocument58 pagesThe Gravedigger's Guide To Cardiology Overview TOCsafasayedNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Life Care: Managing Common Symptoms: Ross H. Albert, MD, PHD, Hartford Hospital, Hartford, ConnecticutDocument6 pagesEnd-Of-Life Care: Managing Common Symptoms: Ross H. Albert, MD, PHD, Hartford Hospital, Hartford, ConnecticutDoc CheebirdNo ratings yet
- MCQ Nelson 20Document588 pagesMCQ Nelson 20della mouradNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDocument4 pagesDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Marine Drugs: Microbial Diseases of Bivalve Mollusks: Infections, Immunology and Antimicrobial DefenseDocument36 pagesMarine Drugs: Microbial Diseases of Bivalve Mollusks: Infections, Immunology and Antimicrobial DefenseJuanita Marcela Méndez MalagónNo ratings yet
- Pedia Review Final Growth and DevelopementDocument553 pagesPedia Review Final Growth and Developementervin_agena394No ratings yet
- European Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Document6 pagesEuropean Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Mihai stancaNo ratings yet