Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptations of The Heart To Is Functions
Adaptations of The Heart To Is Functions
Uploaded by
euginemwakhaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adaptations of The Heart To Is Functions
Adaptations of The Heart To Is Functions
Uploaded by
euginemwakhaCopyright:
Available Formats
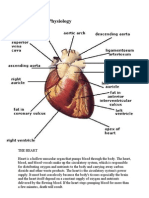
Adaptations of the heart to is functions.
1. It has cardiac muscles which are myogenic, (does not need nervous stimulation to contract and relax ) for
pumping of blood.
2. It connected to vagus and sympathetic nerves; which controls the rate of heart beat depending on the
body’s physiological requirements.
3. It has tricuspid and bicuspid valves between articles and ventricles which prevents back flow of blood
into the right and left ventricles respectively.
4. The heart is connected to the coronary artery; which supplies food and oxygen to the cardiac muscles for
the pumping action.
5. The coronary vein in removes metabolic wastes from the heart.
6. The heart is divided into two by atrio-ventricular septum; which prevents mixing of oxygenated blood and
deoxygenated blood.
7. The heart is enclosed by the pericardial membrane that secretes pericardial fluid which prevents
friction in the walls during pumping.
8. The outer pericardium layer surrounded by a layer of fat; to act as shock absorbers thus protecting it from
mechanical damage.
9. It has sino atrial node (S.A.N) which initiates the contraction and relaxation of the cardiac muscles and act
as a pace maker by regulating the rate of beating and excitation of the heart.
10. The walls of the left ventricle are thicker than those of the right ventricles, to generate more pressure to
pump blood over longer distance to the rest of the body.
11. The tricuspid and bicuspid valves are held by tendrons; which prevents the valves from turning inside
out during ventricular contractions.
12. The heart is joined by blood vessels aorta distributes blood to all body tissues except the lungs.
13. Pulmonary artery which leaves the heart/left ventricle carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
14. Pulmonary vein entering the heart /left atrium convey oxygenated blood form the lungs to the heart.
15. Vena cava entering the right atrium brings in de-oxygenated blood from body tissues.
16. Semi lunar valve at the base of the aorta and pulmonary artery; prevents back flow of blood to the
ventricles once it has been pumped out.
17. The cardiac muscles of the heart never get fatigued hence the rhythmic contractions goes on throughout
life.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology SLEDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology SLEMoti Pagador100% (4)
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 8 Transport in AnimalsDocument24 pages8 Transport in AnimalsMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- Double CirculationDocument2 pagesDouble CirculationUmar AfzalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Systemmitsuki_sylphNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System IIDocument13 pagesCirculatory System IIsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument58 pagesCardiovascular SystemSinem TunalıNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFDocument11 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory System PDFAnonymous e6LINHNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- الجهاز الدوريDocument16 pagesالجهاز الدوريHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCH 6 - The Circulatory SystemPuguh HadiNo ratings yet
- Heart ValvesDocument3 pagesHeart ValveschloeesperanoNo ratings yet
- Unit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesUnit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemKath RubioNo ratings yet
- The Heart, Part 1 - Under Pressure: Crash Course A&P # 25Document5 pagesThe Heart, Part 1 - Under Pressure: Crash Course A&P # 25Jordan TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - HeartDocument5 pagesChapter 13 - Heartbussniesm05No ratings yet
- Assignment On Anatomy and Physiology of Heart: Submitted By: Submitted To: Jayita Gayen Madam S. PoddarDocument10 pagesAssignment On Anatomy and Physiology of Heart: Submitted By: Submitted To: Jayita Gayen Madam S. PoddarJayita Gayen DuttaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assessment 12 (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesAnatomy Assessment 12 (AutoRecovered)Jellisa Fuentes AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assessment 12 (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesAnatomy Assessment 12 (AutoRecovered)Jellisa Fuentes AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 (Cardiac & Respiratory Therapy Equipment) FinalDocument37 pagesUnit - 1 (Cardiac & Respiratory Therapy Equipment) FinalanniepersiasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in AnimalsDocument42 pagesCirculatory System in AnimalsAlaina SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter VIII CardiovascularDocument7 pagesChapter VIII CardiovascularTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Document7 pagesVocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Agustín Bravo Arreyes100% (2)
- Salcedo ANPH111 The Cardiovascular System23Document46 pagesSalcedo ANPH111 The Cardiovascular System23ajline.esto23No ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemAnkit PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Cnat AllDocument7 pagesCnat AllZaid Bin salmanNo ratings yet
- The Heart StructureDocument48 pagesThe Heart StructureBoliticNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Control CentreDocument8 pagesCardiac Control CentregeorgeloxdaleNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Document5 pagesCirculatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Jumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Cardiovascular-SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 11. Cardiovascular-SystemScianna Christel LastimosaNo ratings yet
- CARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedDocument117 pagesCARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedBayan TahaNo ratings yet
- Function of The HeartDocument27 pagesFunction of The HeartAb Ab100% (1)
- Anatomy Central Nervous System - AapDocument6 pagesAnatomy Central Nervous System - AapLinsha BerylNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 The Cardiovascular System: Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesUnit 6 The Cardiovascular System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument19 pagesTransport in Animalsmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Heart and BrainDocument29 pagesHeart and BrainDIPANJAN MAJUMDAR100% (6)
- Anaphysio of The HeartDocument6 pagesAnaphysio of The HeartChamCham AquinoNo ratings yet
- Prevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMIDocument4 pagesPrevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMIdwi krismaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesCardiovascular SystemArun Kumar DhupamNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemChekaina Rain BaldomarNo ratings yet
- Structure of Heart To SendDocument12 pagesStructure of Heart To SendlaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument9 pagesThe Cardiovascular System The HeartMarjorie AbelgasNo ratings yet
- CH-9 - Transport in AnimalsDocument45 pagesCH-9 - Transport in Animalsjihen chouchenNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysiologyDocument102 pagesCardiac PhysiologyPeter Larsen100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentSiti Sumari HarahapNo ratings yet
- Acfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Document60 pagesAcfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Bala GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Transport in Mammals NotesDocument80 pagesTransport in Mammals NotesangelinechikonoNo ratings yet
- Heart: Layers of The Heart WallDocument3 pagesHeart: Layers of The Heart WallAdaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The HeartxXjhmXxNo ratings yet
- Tuason - Activity 1-CardioDocument4 pagesTuason - Activity 1-CardioTheriz Angelique TuasonNo ratings yet
- Loreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanDocument4 pagesLoreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Cycles of Heart Contraction Drive Double Circulate in MammalsDocument5 pagesCoordinated Cycles of Heart Contraction Drive Double Circulate in MammalsMayar HasanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860No ratings yet
- BMICCT 102 Cardio Vascular System SUJOY TONTUBAYDocument11 pagesBMICCT 102 Cardio Vascular System SUJOY TONTUBAYSujoy TontubayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The HeartHerman DjawaNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet