Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsBlockchain
Blockchain
Uploaded by
aankurkhannaabstract for blockchain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Technology: Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyDocument1 pageTechnology: Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyIvan TadićNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Unit-1Document18 pagesBlock Chain Unit-1pilli maheshchandraNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Unit-1Document17 pagesBlock Chain Unit-1paramata priya madhuriNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument63 pagesBlock ChainPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology ExplainedDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology ExplaineddusabeyezusangwafabriceNo ratings yet
- LMS 13Document11 pagesLMS 13prabakar1No ratings yet
- The Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioDocument3 pagesThe Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioSᴇʀᴇɴᴅɪᴘɪᴛʏNo ratings yet
- NodejsDocument1 pageNodejsvaibhavwani008No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument1 pageBlockchainbintang Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument60 pagesBlock Chainromeesh jainNo ratings yet
- (Kit061) Blockchain QuestionbankDocument36 pages(Kit061) Blockchain Questionbankranjeet2213005-dNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Blockchain NotesDocument19 pagesUNIT I Blockchain Notesmanoj tilakchandNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologykkpatilb21No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document52 pagesUnit 2shreya kharolaNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument35 pagesBlock ChainSai VamshiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology - SlidesDocument22 pagesBlockchain Technology - SlidesAnagh Paul - CSTNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Management 2Document13 pagesContemporary Issues in Management 2joseph mbuguaNo ratings yet
- Block Chain IntroDocument15 pagesBlock Chain IntroveronicaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 DissertationDocument110 pagesCHAPTER 1 Dissertationsimpykalla29No ratings yet
- Report On BlockchainDocument5 pagesReport On BlockchainShubham NawaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BlockchainDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BlockchainmiranahumasaNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument11 pagesBlock ChainPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Computer SecurityDocument9 pagesComputer Securityjdfksa dhsgjksghNo ratings yet
- Crypto and BlockchainDocument2 pagesCrypto and BlockchainchannahalladhaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part - 1Document12 pagesUnit-1 - Part - 1shaikharmanazmi30No ratings yet
- Blockchain Unit-2Document86 pagesBlockchain Unit-2Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document92 pagesUnit 1rocky2003rajkumarNo ratings yet
- What Is BlockchainDocument2 pagesWhat Is BlockchainVIPLAV SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Module1Document10 pagesBlockchain Module1Pawan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain 3Document28 pagesBlockchain 3Neel PatelNo ratings yet
- Abid AssignmenDocument6 pagesAbid Assignmenabidniazi3443No ratings yet
- What Is BlockchainDocument2 pagesWhat Is Blockchainsantunsantoso013No ratings yet
- Sam 5Document5 pagesSam 5saurabhumbarkar2002No ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology (Distributed Ledger Technology)Document4 pagesBlockchain Technology (Distributed Ledger Technology)Vivek KavtaNo ratings yet
- Abhi 5Document5 pagesAbhi 5saurabhumbarkar2002No ratings yet
- Practical File FormatDocument6 pagesPractical File Formatip5 GaminGNo ratings yet
- Basics of CryptocurrenciesDocument12 pagesBasics of CryptocurrenciesAmulya SNo ratings yet
- Lecture Text 4 - Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesLecture Text 4 - Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyJuan BrattiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesBlockchain Technology Literature Reviewrafghanyar1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument3 pagesBlockchainTusharNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Blockchain PDFDocument12 pagesFundamentals of The Blockchain PDFApoorv Gupta LaviNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology PPT ProjectDocument22 pagesBlockchain Technology PPT ProjectHACKERS HOVELNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock ChainNurul Rofifah MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Is A DecentralizedDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology Is A DecentralizedNakanakanaknakNo ratings yet
- Banking and Insurance II Unit NewDocument31 pagesBanking and Insurance II Unit NewKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of BlockchainDocument2 pagesAdvantages of BlockchainNisha MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Notes With QuestionsDocument9 pagesBlockchain Notes With QuestionsAniket SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument8 pagesBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMNo ratings yet
- BCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayDocument21 pagesBCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayKoti RondiNo ratings yet
- 51251FTV Lecture 5Document28 pages51251FTV Lecture 5Noman NaeemNo ratings yet
- Tasya Novaliana Utomo - SumaryBlockcain and Its Impact On Finance and AccountingDocument2 pagesTasya Novaliana Utomo - SumaryBlockcain and Its Impact On Finance and AccountingTasyaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PPT Group DDocument18 pagesBlockchain PPT Group DPrachi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesRecent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationAkshay SachuNo ratings yet
- 11 Exam PracticeDocument1 page11 Exam PracticeQian APNo ratings yet
- AL802 (A) Blockchain PracticalDocument29 pagesAL802 (A) Blockchain PracticalPreet TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)Document2 pagesBlockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)RahulMondol100% (1)
- Enterprise Systems and Blockchain TechnologyDocument10 pagesEnterprise Systems and Blockchain Technologywm364740No ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument1 pageMachine LearningaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- To Declare CursorDocument8 pagesTo Declare CursoraankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- The Buying and Selling of Products and Services by Businesses and Consumers Through An Electronic MediumDocument11 pagesThe Buying and Selling of Products and Services by Businesses and Consumers Through An Electronic MediumaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- Afsal .PK M.Ed 2010-2011 Pondicherry University School of EducationDocument25 pagesAfsal .PK M.Ed 2010-2011 Pondicherry University School of EducationaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Database Management Systems: 4.1: B-TreesDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Database Management Systems: 4.1: B-TreesaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
Blockchain
Blockchain
Uploaded by
aankurkhanna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageabstract for blockchain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentabstract for blockchain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageBlockchain
Blockchain
Uploaded by
aankurkhannaabstract for blockchain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Blockchain
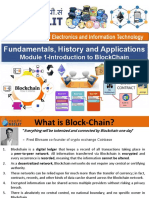
Abstract
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that records
transactions across multiple computers. It ensures data integrity and security through
cryptographic techniques, making it a cornerstone for secure and transparent digital
transactions.
Introduction
Blockchain, initially conceptualized for Bitcoin by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi
Nakamoto, has evolved beyond cryptocurrencies. Its applications now span various
industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
Key Components
1. Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority,
blockchain is managed by a network of nodes.
2. Immutability: Once recorded, data in a blockchain cannot be altered, ensuring the
integrity of transactions.
3. Consensus Mechanisms: Protocols like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake
(PoS) ensure agreement on the ledger's state across all nodes.
Applications
1. Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain
for secure and transparent transactions.
2. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain ensures transparency and traceability in
supply chains, reducing fraud and inefficiencies.
3. Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly
written into code, automating and securing transactions.
Challenges
Despite its potential, blockchain faces challenges such as scalability, energy consumption
(particularly in PoW systems), regulatory issues, and the need for interoperability between
different blockchain platforms.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology holds transformative potential across various sectors by ensuring
transparency, security, and efficiency. Continued advancements and regulatory clarity will be
crucial for its broader adoption and integration.
You might also like
- Technology: Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyDocument1 pageTechnology: Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyIvan TadićNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Unit-1Document18 pagesBlock Chain Unit-1pilli maheshchandraNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Unit-1Document17 pagesBlock Chain Unit-1paramata priya madhuriNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument63 pagesBlock ChainPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology ExplainedDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology ExplaineddusabeyezusangwafabriceNo ratings yet
- LMS 13Document11 pagesLMS 13prabakar1No ratings yet
- The Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioDocument3 pagesThe Role of Blockchain in The Current It Industry ScenarioSᴇʀᴇɴᴅɪᴘɪᴛʏNo ratings yet
- NodejsDocument1 pageNodejsvaibhavwani008No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument1 pageBlockchainbintang Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument60 pagesBlock Chainromeesh jainNo ratings yet
- (Kit061) Blockchain QuestionbankDocument36 pages(Kit061) Blockchain Questionbankranjeet2213005-dNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Blockchain NotesDocument19 pagesUNIT I Blockchain Notesmanoj tilakchandNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologykkpatilb21No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document52 pagesUnit 2shreya kharolaNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument35 pagesBlock ChainSai VamshiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology - SlidesDocument22 pagesBlockchain Technology - SlidesAnagh Paul - CSTNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Management 2Document13 pagesContemporary Issues in Management 2joseph mbuguaNo ratings yet
- Block Chain IntroDocument15 pagesBlock Chain IntroveronicaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 DissertationDocument110 pagesCHAPTER 1 Dissertationsimpykalla29No ratings yet
- Report On BlockchainDocument5 pagesReport On BlockchainShubham NawaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BlockchainDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BlockchainmiranahumasaNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument11 pagesBlock ChainPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Computer SecurityDocument9 pagesComputer Securityjdfksa dhsgjksghNo ratings yet
- Crypto and BlockchainDocument2 pagesCrypto and BlockchainchannahalladhaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part - 1Document12 pagesUnit-1 - Part - 1shaikharmanazmi30No ratings yet
- Blockchain Unit-2Document86 pagesBlockchain Unit-2Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document92 pagesUnit 1rocky2003rajkumarNo ratings yet
- What Is BlockchainDocument2 pagesWhat Is BlockchainVIPLAV SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Module1Document10 pagesBlockchain Module1Pawan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain 3Document28 pagesBlockchain 3Neel PatelNo ratings yet
- Abid AssignmenDocument6 pagesAbid Assignmenabidniazi3443No ratings yet
- What Is BlockchainDocument2 pagesWhat Is Blockchainsantunsantoso013No ratings yet
- Sam 5Document5 pagesSam 5saurabhumbarkar2002No ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology (Distributed Ledger Technology)Document4 pagesBlockchain Technology (Distributed Ledger Technology)Vivek KavtaNo ratings yet
- Abhi 5Document5 pagesAbhi 5saurabhumbarkar2002No ratings yet
- Practical File FormatDocument6 pagesPractical File Formatip5 GaminGNo ratings yet
- Basics of CryptocurrenciesDocument12 pagesBasics of CryptocurrenciesAmulya SNo ratings yet
- Lecture Text 4 - Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesLecture Text 4 - Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyJuan BrattiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesBlockchain Technology Literature Reviewrafghanyar1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument3 pagesBlockchainTusharNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Blockchain PDFDocument12 pagesFundamentals of The Blockchain PDFApoorv Gupta LaviNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology PPT ProjectDocument22 pagesBlockchain Technology PPT ProjectHACKERS HOVELNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument9 pagesBlock ChainNurul Rofifah MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Is A DecentralizedDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology Is A DecentralizedNakanakanaknakNo ratings yet
- Banking and Insurance II Unit NewDocument31 pagesBanking and Insurance II Unit NewKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of BlockchainDocument2 pagesAdvantages of BlockchainNisha MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Notes With QuestionsDocument9 pagesBlockchain Notes With QuestionsAniket SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument8 pagesBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMNo ratings yet
- BCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayDocument21 pagesBCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayKoti RondiNo ratings yet
- 51251FTV Lecture 5Document28 pages51251FTV Lecture 5Noman NaeemNo ratings yet
- Tasya Novaliana Utomo - SumaryBlockcain and Its Impact On Finance and AccountingDocument2 pagesTasya Novaliana Utomo - SumaryBlockcain and Its Impact On Finance and AccountingTasyaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain PPT Group DDocument18 pagesBlockchain PPT Group DPrachi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesRecent Advances of Blockchain and Its ApplicationAkshay SachuNo ratings yet
- 11 Exam PracticeDocument1 page11 Exam PracticeQian APNo ratings yet
- AL802 (A) Blockchain PracticalDocument29 pagesAL802 (A) Blockchain PracticalPreet TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)Document2 pagesBlockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)RahulMondol100% (1)
- Enterprise Systems and Blockchain TechnologyDocument10 pagesEnterprise Systems and Blockchain Technologywm364740No ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument1 pageMachine LearningaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- To Declare CursorDocument8 pagesTo Declare CursoraankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- The Buying and Selling of Products and Services by Businesses and Consumers Through An Electronic MediumDocument11 pagesThe Buying and Selling of Products and Services by Businesses and Consumers Through An Electronic MediumaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- Afsal .PK M.Ed 2010-2011 Pondicherry University School of EducationDocument25 pagesAfsal .PK M.Ed 2010-2011 Pondicherry University School of EducationaankurkhannaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Database Management Systems: 4.1: B-TreesDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Database Management Systems: 4.1: B-TreesaankurkhannaNo ratings yet