Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NEW Reproductive Systems Nu2
NEW Reproductive Systems Nu2
Uploaded by
Aaysha Niyas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views21 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views21 pagesNEW Reproductive Systems Nu2
NEW Reproductive Systems Nu2
Uploaded by
Aaysha NiyasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 21
Reproductive Systems
Male & Female
Dr. Adel M. Hajjay
Male & Female
Include:
Reproductive organs called gonads that produce
gametes and hormones
Ducts that transport gametes
Accessory glands and organs that secrete fluids
Male & Female
Production of hormones that permit the
secondary sex characteristics, such as breast
development in women and beard growth in
men
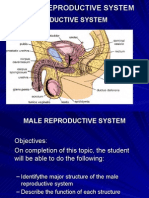
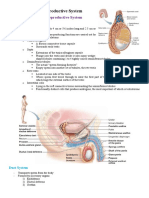
Male
Functions
To produce, maintain and transport sperm and
semen
To produce and secrete male sex hormones
Male
Consists of:
A pair of testes
excretory ducts
epididymis
vas deferens
ejaculatory ducts
Seminal vesicles
Prostate
Urethra
Penis
Male
Testes (Gonads)
Produce sperm
(Spermatogenesis)
Sperm production
begins at puberty and
continues throughout
the life of a male
Male
Testes Produce
testosterone
Hair patterns and voice
changes
Development of the male
accessory organs
(prostate, seminal vesicles
etc.)
Stimulates the muscle
development and strength
of the male
Male
Duct System
Epididymis
Sperm mature in
epididymis
Vas Deferens
Transports mature
sperm to the
urethra
Ejaculatory ducts
empty into the
urethra
Male
Seminal vesicles
Attached to vas
deferens
provides energy
to sperm
Male
Prostate Gland
Makes fluid
Present below the neck of bladder
Contains prostatic urethra and
Ejaculatory duct
Opens its duct into prostatic urethra
Male
Urethra
Tube that carries
urine from the
bladder to outside
of the body
Also carries semen
out of the body
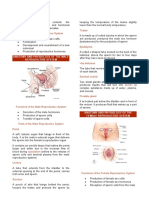
Female
Functions
Produces the female egg cells
Transports the eggs to the site of fertilization
The fertilization of an egg by a sperm, occurs in
the fallopian tubes
Female
Functions
After fertilization, provides a place for a baby to
develop
If fertilization does not take place, then
menstruation occurs
Produces female sex hormones
Female
Consists of:
Vagina
Uterus
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Female
Vagina
Canal that joins
the uterus to
the outside of
the body
Also is known
as the birth
canal
Female
Uterus
Hollow, pear-shaped
organ that is the home
to a developing fetus
Divided into two parts:
the cervix, the lower
part that opens into the
vagina
Main body of the uterus,
called the corpus.
The corpus can easily
expand to hold a
developing baby.
Female
Ovaries
Oval-shaped glands that
are located on either side
of the uterus
Produce eggs and
hormones.
Female
Fallopian Tubes
Narrow tubes that are
attached to the upper part
of the uterus
Fertilization of an egg by a
sperm, normally occurs in
the fallopian tubes
The fertilized egg then
moves to the uterus, where
it implants into the lining of
the uterine wall
You might also like
- African Penis Exercises & EnlargementDocument21 pagesAfrican Penis Exercises & Enlargementmindbodystorm_28327362% (13)
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (2)
- Seminal FluidDocument3 pagesSeminal Fluidsarguss1467% (3)
- Task 4Document20 pagesTask 4maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Reproductive Systemhoney faith labradorNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- 4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument26 pages4 Animal Reproduction and DevelopmentEGUIA, MARY SHENIETH M.No ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- 07 05 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages07 05 Reproductive SystemOkoye ClappinNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Reproductive SystemffingNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- 1.the Reproductive SystemDocument47 pages1.the Reproductive SystemAkai ShuichiNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument28 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemXyrhuz SedilloNo ratings yet
- Health 8 - Q1 W6Document5 pagesHealth 8 - Q1 W6Lanibelle TanteoNo ratings yet
- BIO 282 Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesBIO 282 Male Reproductive SystemLira Pagara100% (1)
- Reproductive System ModuleDocument17 pagesReproductive System ModulePATRICIA KAYE RIONo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Fantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Document4 pagesFantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Jushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Table of FunctionsDocument1 pageReproductive System Table of Functionseborangez5No ratings yet
- Q3 Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesQ3 Science ReviewerAldrin Abestano Jr.No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- Testis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BDocument8 pagesTestis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BSania BanoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Male and FemaleDocument27 pagesReproductive System - Male and FemaleJerome CameroNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionsimphiwemakhonjwaNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemJrp AneworNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Male Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesAnatomy of Male Reproductive SystemMariane GomezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Notes - 2014-15 DraftDocument62 pagesReproductive System Notes - 2014-15 DraftMiguel MenendezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems in HumansDocument3 pagesReproductive Systems in Humansvishalajagmohan3No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Old FormatDocument4 pagesReproductive System Old FormatRobie SanaoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMDocument10 pagesReviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems (Infographic)Document3 pagesReproductive Systems (Infographic)sofiareinhart0831No ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Reproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoDocument31 pagesReproduction System: By: Maharini, S.PD Anik Rahmawati, S.PD SMP Negeri 1 PonorogoYu HasNo ratings yet
- The Human Body 1 1Document14 pagesThe Human Body 1 1Dell2No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive Systemnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageReproductive Systemgeraldine gemillanNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument3 pagesScience ReviewAinieNo ratings yet
- Developmental Aspect of Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Aspect of Reproductive SystemFrancis ArceoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument8 pagesReproductive System NotesGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument48 pagesReproductive System97fcqmnnmnNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoDocument46 pagesThe Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoteacherashleyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Reproductive Organs and Their Function: Male/Femal e FunctionDocument4 pagesReproductive Organs and Their Function: Male/Femal e FunctionHanna KimNo ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument20 pagesThe Reproductive SystemeamlezahNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesMale Reproductive Systemאילן גרינולדNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document56 pagesReproductive System 1zekesergmanuedenina08No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- LTO in ScienceDocument1 pageLTO in ScienceNorman M.No ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale & Female Reproductive SystemCandly SHi100% (1)
- 12a. Final Notes On Male ReproductionDocument8 pages12a. Final Notes On Male ReproductionNishant ShahNo ratings yet
- Development of Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesDevelopment of Reproductive SystemGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THDocument7 pagesSpermatogenesis Practical File For Clas 12THSiddhartha SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16. The Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 16. The Reproductive SystemScianna Christel LastimosaNo ratings yet
- InseminationDocument3 pagesInseminationHemanta JenaNo ratings yet
- Male GenitalsDocument29 pagesMale Genitalssunielgowda100% (1)
- Final Seminal Fluid AnalysisDocument53 pagesFinal Seminal Fluid AnalysisMajdiBilbisi100% (1)
- Scrotum: Imp: Right Testicular TorsionDocument2 pagesScrotum: Imp: Right Testicular TorsionQuest Medinova Lab ManagerNo ratings yet
- Semen 3BDocument45 pagesSemen 3BLian Marie ViñasNo ratings yet
- Vet Andrology and AI Dr. Pradeep Kumar PDFDocument146 pagesVet Andrology and AI Dr. Pradeep Kumar PDFDinesh PathakNo ratings yet
- 431 417 1 PBDocument6 pages431 417 1 PBHanif KrisnajatiNo ratings yet
- SenSlip Instruction Page 1Document1 pageSenSlip Instruction Page 1bigbigbig90003270No ratings yet
- 10 1111@and 13509Document22 pages10 1111@and 13509Theylor RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Assessing Male Genitalia and InguinalDocument51 pagesAssessing Male Genitalia and InguinalJellaiza QuiozonNo ratings yet
- 17 Rizni FitrianaDocument10 pages17 Rizni FitrianaDidinNo ratings yet
- Avergae Bosnian Size For Penis - Google SearchDocument1 pageAvergae Bosnian Size For Penis - Google Searchproplayz2012No ratings yet
- Pengaruh Isobutil Metilxantina (IMX) Dan Waktu Pemisahan Terhadap Kualitas Dan Efektifitas Pemisahan Spermatozoa Dengan Metode Kolom Albumin TelurDocument6 pagesPengaruh Isobutil Metilxantina (IMX) Dan Waktu Pemisahan Terhadap Kualitas Dan Efektifitas Pemisahan Spermatozoa Dengan Metode Kolom Albumin Telurparkc6922No ratings yet
- CircumcisionDocument2 pagesCircumcisionAlvin L. RozierNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Male Reproductive Systemprasun_v100% (2)
- BallooningDocument4 pagesBallooningangginaharahapNo ratings yet
- Comparative Effect of Exposure Gel and Spray Fragrances For Sperm Motility and Spermatogenesis in The White Rat (Rattus Norvegicus)Document12 pagesComparative Effect of Exposure Gel and Spray Fragrances For Sperm Motility and Spermatogenesis in The White Rat (Rattus Norvegicus)xcavaholmesNo ratings yet
- Penis Size - Does It Matter ?Document4 pagesPenis Size - Does It Matter ?Dr. Muhammad TayubNo ratings yet
- Chapter 009Document8 pagesChapter 009api-281340024No ratings yet
- Be My Temptation (COMPLETED) - Shaleh - Wattpad - WattpadDocument256 pagesBe My Temptation (COMPLETED) - Shaleh - Wattpad - WattpadWeef hoofNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213576613000808 MainDocument2 pages1 s2.0 S2213576613000808 MainUmi AndikaNo ratings yet
- Sex Book Urdu PDFDocument124 pagesSex Book Urdu PDFKhalid Almas75% (8)
- O'Hara & O'Hara - The Effect of Male Circumcision On The Sexual Enjoyment of The Female Partner PDFDocument6 pagesO'Hara & O'Hara - The Effect of Male Circumcision On The Sexual Enjoyment of The Female Partner PDFOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesMale Reproductive SystemTracy zorcaNo ratings yet