Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasound Physics Notes
Ultrasound Physics Notes
Uploaded by
k789qfmsmgOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasound Physics Notes
Ultrasound Physics Notes
Uploaded by
k789qfmsmgCopyright:
Available Formats
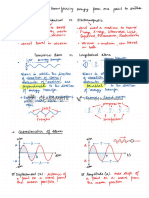
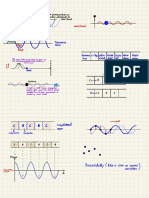
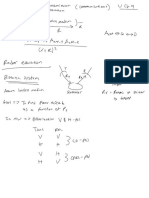
CH11 : DISPLAY MODES
formats, ormodesofdisplay
,
for viewing a
ultrason
A Aramcostosbeed
-
or is deflected upward e
on a
echos tall spikes
-
strong :
&
reflector depth
·
X-axis represents is measured
by the
time-of-flight
to
·
y-axis measures a
② B-MODE/BRIGHTNESS
·
appears as line of dots
we vary ing brightness
soundpuseisemittedby visible don moves ar aconstant
· reflection
speed across disaster
returns
~
-
weak reflection = dark
·s Desrecordepth measured
by time-of-linea
ents amp
③ M-MODE/MOTION
·appearsasgroup ofhorizontal wavylineeons move at constant speed from right to left
Minutmeg
·
various squiggly lines represent chang
saa
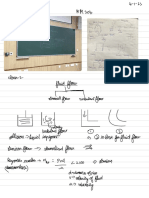
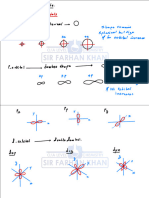
CH12 : ULTRASOUND TRANSDUCERS
* ARDMS 2D TYRS
& MECHANICAL TXR
↓
-
active element : single , circular/disc-shaped
Steering : mechanical
-
, physically moved by a motor
focus
Always ed, conventional ormechanica external
·
:
~
intern curved lens)
· imageshape : fasector-shaped,imagecomes
to a pot as
② ARRAY TXR
·outainmup active elementssetronics = channel
3 TYPES
1. LINEAR PHASED ARRAY
active
element : 100-300 elements , rectangular nar row
Steering :
electronically by phasing
directoraaped sing e focusing
PHASED ARRAY TECHNOLOGY : Can Steer 3 focus the beam
adjustable cocus/multifocus , produced electronically
Now electrical steeringneed for production of a focused beam
PHASED ARRAY TVR
All active elements excited by
are electrical signals to create a single ultrasound beam
·
T
BEAMSTEERING Chnique
·
various Living/spike patterns an used during excitation of the elements to steer 3 focus the beam
·electricaghaired atsignydifferenttimes,oneafteranother producing ,
a slope patter , steering the beam in a particular direc i s
beam former is component responsible for diff spike patterns
·en ↳ done
ned by
according
# elements
changing
to
dur in
depth of returning
used to receive
signal
reflected signal
receivedusing new innercrystals Gomary
echos arising early (superficial) are
increased in are used
a
aperture for echos returning from array
possible at dt as
allows beamto be as narrowas
a
· PHASED
rememberingshape eewens
ARRAY best focus at All depths #
w
common a
VECTORARRAY/VIRTUALSECT
rectangular , arranged in aa
inner crystals(smallrings-aquiredatafrom
shallow
·
dt is
·
outer crystals (large rings) - acquire data
less
from deeper depths
·Perignoneal d linear
sea
op
.
phased
array
sector
is
a re
↳ deep focus , long local depth , divergence
· umitaynamic
receive cocusing is area
-
ELECTRONIC focusing
AERADepns dropour & particular depth
acoustic cootprint : area of contact bown fr 3 Skin
mechanical linear phased array bannular phased array all have small footprint & sector
image
·
,
* FOR SPID if a doesn't mention "phasing" then assume it is switched/sequential tr
eX : linear array : linear "sequential" array
1 I NEAR SEQUENTIAL ARRAY
·rectangular
, arranged i ,
·Maccusing
DISC SHAPE CRYSTAL TUR 3 SLICE THICKNESS RESOLUTION
disshapeactive elementsproducethinnestslices Cous Bestelevationalresolutionssales
bottom or
image from scanline created by defective crystal
.
3 CONVEX , CURVED Or CURVILINEAR
CURVED SEQUENTIAL ARRAY / SWITCH ARRAY
active element 120-250
· :
crystals , rectangular , arranged side by side in a curved line
largeprinta directed straight
-
few ele ments fired simultaneously in a sequence
~
image shape : blunted Sector
-
focus : fixed ,
internal/external cocusing
·
damaged PIT : creates drop out from top to bottom of
image from scanline created by defective crystal
CH 13 : REAL-TIME IMAGING
↳ a series of single images/frames displayed in an extremely rapid fashion to appear as real-time scanning
time
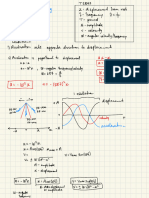
TEMPORAL RESOLUTION
- resolution pertaining to
·ablityutylate
moving structures at particular instant is
in i n
FRAME RATE
FRisLimitedbyspeedofsoundinthe mediuto scan
-
·
Unit : H2
· images/frames perseconda ?
lines , which medium will produce a Caster FR ? bone or soft tissue
th of imaging (2)# of pulses per frame
A : BONE be bone has faster sound speed t h an soft tissue
DEPTH OF IMAGING
Shallow deep
·wenation
·
long go-return time
longer T-frame
lowF r temporal resolution
·
INVERSELY related to FR
↑ depth = ↓ FR
·
double depth = FR decrease by 12
FR-#of pulses per image
↳ determined by 3 factors :
· multip
an ina mucous, annul ine
poor temporal res .
A
3 ·↑ LATA
d temporale s
E
SECTOR SIZE
narrow wide
morescan lines/
pulses per a n
a
·
few scan lines/pulses per frame
·
Short T-frame
↑F temp. res GF temp res.
SPATIAL RESOLUTION
refers to rall detail of an image
·
determinedby linedensity patial,a
·
·
approx . 100 -
200 scan lines per frame
·
low line density
widely
spardis e rame me
· s
Sewer
·
-
· Fr-
em es superimpsvial
P 00r
- s -
res.
nowToIMPROVE TEMPRESS
HOW TO DEGRADE TEMPORAL RES ?
1. deep image depth
·singleusi
.
2 multi-focus cannular array)
ue sectadensit
h improveimagequalit
a
me
IMAGE QUALITY US . TEMPRES
↑ image quality = ↓ temp res
res is INVERSEL related to
·
spatial .
temp . res
.
You might also like
- C Language Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesC Language Viva QuestionsRaghu Ram Nandyal75% (166)
- Your Thesis Title: Your Name Your Student IDDocument21 pagesYour Thesis Title: Your Name Your Student IDAndre MartinsNo ratings yet
- Bars and Beams Cheat SheetDocument1 pageBars and Beams Cheat SheetGhenal RiveraNo ratings yet
- Reflection:: ReflectedDocument4 pagesReflection:: ReflectedArpita SahuNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics 1Document32 pagesWave Optics 1vvjvp98w57No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 22 May 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 22 May 2024subhabuddy0No ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument11 pagesCircular MotionmveervivekNo ratings yet
- Waves ODocument6 pagesWaves OEye CareNo ratings yet
- Formulario Por Revisar PDFDocument1 pageFormulario Por Revisar PDFDanilo Malaver FonsecaNo ratings yet
- 620610305วรนิษฐา อุตส่าห์ 2Document3 pages620610305วรนิษฐา อุตส่าห์ 2voranitta utsahaNo ratings yet
- Olocity: FluidDocument75 pagesOlocity: FluidERRNo ratings yet
- String-Sound Waves Experimental DevicesDocument6 pagesString-Sound Waves Experimental DevicesGAURAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Biện pháp lắp dựng GL3.3Document20 pagesBiện pháp lắp dựng GL3.3Trâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 01, 2023Document21 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 01, 2023Amit SoniNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instrument 2022Document20 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instrument 2022Arush GautamNo ratings yet
- Final NotesDocument9 pagesFinal Notesgapalmeri05No ratings yet
- 0322物理笔记- Wave Basics,Doppler EffectDocument10 pages0322物理笔记- Wave Basics,Doppler Effectcoscos2001No ratings yet
- Application On Newton's Second Law V3Document2 pagesApplication On Newton's Second Law V38rc9ryj62zNo ratings yet
- GS IV Ethics, Integrity AptitudeDocument88 pagesGS IV Ethics, Integrity Aptitudenerdsonloose0906No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Part BDocument21 pagesAtomic Structure Part Bxxbackup67No ratings yet
- Beam Deflection - Theory PDFDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection - Theory PDFHaikal HakimNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Velocity & AccelerationDocument1 pageIGCSE Velocity & AccelerationhosannaNo ratings yet
- ME712 Notes Lecture 3Document4 pagesME712 Notes Lecture 3Benjamin OlowuNo ratings yet
- LEGEND ModelDocument1 pageLEGEND ModelHimanhsuNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Color Mode Artifacts Bioeffects Physics1 - 4perDocument15 pagesUltrasound Color Mode Artifacts Bioeffects Physics1 - 4perstoicea_katalinNo ratings yet
- Travers: WallDocument6 pagesTravers: WallZoha FaisalNo ratings yet
- CH 14 - IRDocument5 pagesCH 14 - IRElle QuizonNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument3 pagesForces and Motionjasonepic333No ratings yet
- Superposition of WavesDocument27 pagesSuperposition of WavesRayyan HashmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15, Principle of Physics, Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 15, Principle of Physics, Lecture NotesBushraNo ratings yet
- Physics Y1 ReviewDocument5 pagesPhysics Y1 ReviewRakeem McFarlaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Activity AnswersDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Activity Answers1sonirudNo ratings yet
- Paprint PoDocument18 pagesPaprint PoJOHN PHILIP LESTER PARAYONo ratings yet
- Technique For The Scanning of UltrasoundDocument1 pageTechnique For The Scanning of UltrasoundMichelle nananaNo ratings yet
- Terms Transpo SurveyingDocument15 pagesTerms Transpo SurveyingClint Jhan RualesNo ratings yet
- Human Bio Muscle PhysiologyDocument1 pageHuman Bio Muscle Physiology2mtsf5z7mdNo ratings yet
- Instrument NavigationDocument4 pagesInstrument Navigation9t42sn2pz5No ratings yet
- CPAC 7 SHM - Suraj MavadiaDocument3 pagesCPAC 7 SHM - Suraj MavadiaShastha VishnuhanNo ratings yet
- as101 笔记 - 1-3Document3 pagesas101 笔记 - 1-3nmedeuNo ratings yet
- Quantum: NumberDocument23 pagesQuantum: NumberKarigar DecorsNo ratings yet
- Applications.: RegeneratlveDocument1 pageApplications.: RegeneratlveCCI AVGNo ratings yet
- Summary Kinematic of Linear MotionDocument2 pagesSummary Kinematic of Linear Motionchong yokelaiNo ratings yet
- Ledged, Braced, Battened & Framed DoorsDocument8 pagesLedged, Braced, Battened & Framed DoorsUmesh Chakravarti100% (1)
- Week 4Document8 pagesWeek 4Mama PigNo ratings yet
- UpthrustDocument5 pagesUpthrustMOID AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion 2023Document12 pagesUniform Circular Motion 2023Mariam ImranNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and Magnetism 2024Document7 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetism 2024pingjin010No ratings yet
- T, of The Time Being e - inDocument13 pagesT, of The Time Being e - inBhargav J TalukdarNo ratings yet
- A Often: ThereDocument3 pagesA Often: ThereMatthew ListroNo ratings yet
- Stationary WavesDocument5 pagesStationary WavesRayyan HashmiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2DDocument14 pagesKinematics 2DRizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument6 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwanaastha.sawlaniNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes 1Document73 pagesHaloalkanes 1MahiNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Draft) (1)Document1 pageUntitled (Draft) (1)breadytam87No ratings yet
- Music NoteDocument2 pagesMusic Noteseung won OhNo ratings yet
- So High The Price (Choir Copy)Document4 pagesSo High The Price (Choir Copy)Christan Jomar CincoNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub - Buenos Dias Espiritu Santo Benny HinnpdfDocument1 pageIdoc - Pub - Buenos Dias Espiritu Santo Benny HinnpdfJuneidy Ogando tejedaNo ratings yet
- Firm !: of ofDocument15 pagesFirm !: of ofShivam DixitNo ratings yet
- Ranging: DogfightDocument7 pagesRanging: DogfightMatthew ListroNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of Forces O 2023Document5 pagesTurning Effect of Forces O 2023johnsmacks7No ratings yet
- CE361 - HydrologyDocument20 pagesCE361 - HydrologyAman KhilaniNo ratings yet
- Excel Skills For Business: Intermediate II: Week 3: Automating LookupsDocument12 pagesExcel Skills For Business: Intermediate II: Week 3: Automating LookupsYassine BOU-IRIGNo ratings yet
- A Voice Controlled Home Automation SystemDocument13 pagesA Voice Controlled Home Automation SystemBhushan BharatiNo ratings yet
- VRG1794741 PDFDocument4 pagesVRG1794741 PDFnanodocl5099No ratings yet
- PQT Model ExamDocument2 pagesPQT Model ExamBalachandar BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Sap Case StudyDocument13 pagesSap Case Studyabhishek_sudharshanNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering Department of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument7 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering Department of Computer Science & EngineeringDipak RajbharNo ratings yet
- Cyber AssessmentDocument27 pagesCyber AssessmentOusmane PENE100% (2)
- CSE-311 Spring 2020 Final ExamDocument3 pagesCSE-311 Spring 2020 Final ExamRisad AhmedNo ratings yet
- 6 RTU Specifications III A 2216Document10 pages6 RTU Specifications III A 2216rasim_m1146No ratings yet
- PythonDocument2 pagesPythonKr VedantNo ratings yet
- The User Should Be On The Home Page: Actual ResultDocument4 pagesThe User Should Be On The Home Page: Actual ResultsergejNo ratings yet
- HP 15c Collector's Edition Owner's Handbook (2023)Document308 pagesHP 15c Collector's Edition Owner's Handbook (2023)chuckuNo ratings yet
- Kionix CJ9-TJ9-TJ2 Windows Drivers 1.28.3 ReadmeDocument1 pageKionix CJ9-TJ9-TJ2 Windows Drivers 1.28.3 ReadmeEduardo Jahnke RojasNo ratings yet
- Excel Perhitungan Pengukuran Poligon TerDocument2 pagesExcel Perhitungan Pengukuran Poligon TerReza JonkNo ratings yet
- Designing and Building of A Catamaran and Its Stability AnalysisDocument5 pagesDesigning and Building of A Catamaran and Its Stability Analysisghulam mohi ud dinNo ratings yet
- Abloy: EL480, EL482 AND PE480 Scandinavian Range Solenoid Locks With Handle ControlDocument4 pagesAbloy: EL480, EL482 AND PE480 Scandinavian Range Solenoid Locks With Handle ControlUlfatNo ratings yet
- HCI - QB Unit4Document15 pagesHCI - QB Unit4Shruthi SNo ratings yet
- User Guide enDocument71 pagesUser Guide enAzeem HussainNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf Privilegeescalationtechniques ExcerptDocument23 pagesBookshelf Privilegeescalationtechniques ExcerptAssasin WolfNo ratings yet
- AVA Electric Actuator CatalogDocument11 pagesAVA Electric Actuator Catalogcapry_cornio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Application of Computer in TextileDocument20 pagesApplication of Computer in TextileFahmid Al RefatNo ratings yet
- HP EliteBoock 650 G9Document68 pagesHP EliteBoock 650 G9oecl1984No ratings yet
- NS BERO 2001 Chapter 6Document11 pagesNS BERO 2001 Chapter 6Pablo RosasNo ratings yet
- WQD7010 Network & Security: Dr. Saaidal Razalli Bin AzzuhriDocument40 pagesWQD7010 Network & Security: Dr. Saaidal Razalli Bin AzzuhriAbu Aisyah Yat SaaidalNo ratings yet
- HP Pavilion 15 Price in Pakistan, Specs & Reviews - TechJuice 2Document1 pageHP Pavilion 15 Price in Pakistan, Specs & Reviews - TechJuice 2Rohaankh69No ratings yet
- Group 9 Divij - Hari - Mini - Saket - ShikhaDocument9 pagesGroup 9 Divij - Hari - Mini - Saket - Shikhasaket ranaNo ratings yet
- Clarion: A Global Brand That Puts Your Future First: Catalogue For Car Audio, Multimedia and NavigationDocument4 pagesClarion: A Global Brand That Puts Your Future First: Catalogue For Car Audio, Multimedia and Navigationin kNo ratings yet
- Mini Marketing Plan The Steam DeckDocument19 pagesMini Marketing Plan The Steam Deckapi-678580280No ratings yet