Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chegbn
Chegbn
Uploaded by
sasae4980Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chegbn
Chegbn
Uploaded by
sasae4980Copyright:
Available Formats
Question:
✍ None
You can view the question in original Chegg URL page.
Expert answer: 0 0
✍ None
Step: 1
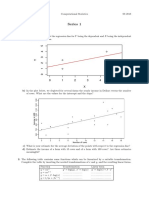
To create X- and R-charts, you can follow these steps:
**X-bar Chart (X-chart):**
1. Calculate the average (X-bar) for each subgroup.
2. Calculate the overall average (Grand Mean) of all the subgroup averages.
3. Plot the subgroup averages on the X-bar chart.
**Range Chart (R-chart):**
1. Calculate the range (R) for each subgroup.
2. Calculate the average range (R-bar) of all the subgroup ranges.
3. Plot the subgroup ranges on the R-chart.
Step: 2
Based on the provided data:
1. **X-bar Chart:**
Explanation
The X-bar chart displays subgroup averages, and the R-chart shows subgroup ranges for 20 samples of engine component diameters.
Calculate subgroup averages, overall average (X-bar), subgroup ranges, and average range (R-bar). Plot points on respective charts and
assess if they fall within control limits to determine process stability.
- Calculate X-bar for each subgroup.
- Calculate the Grand Mean.
- Plot the subgroup averages on the X-bar chart.
2. **R-chart:**
- Calculate R for each subgroup.
- Calculate R-bar (average range).
- Plot the subgroup ranges on the R-chart.
These control charts help assess whether the process is in control or exhibits special cause variation. Control limits are typically set at
±3 times the standard deviation. If points fall within these limits, the process is considered in control; otherwise, it may indicate a
special cause variation.
Please provide the calculated values if you need further assistance.
Final Answer
The data comprises 20 samples of engine component diameters, each with subgroups of size 5. Constructing X-bar and R-charts
involves calculating subgroup averages, overall average (X-bar), subgroup ranges, and average range (R-bar). Plotting these values helps
assess process stability. Control limits, typically set at ±3 times the standard deviation, determine if points are within acceptable
bounds. The X-bar chart monitors subgroup averages, while the R-chart evaluates subgroup ranges. If points fall within control limits,
the process is considered stable; otherwise, it suggests special cause variation, warranting further investigation into potential issues in
the manufacturing process.
None
You might also like
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Summarizing Academic TextsDocument25 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Summarizing Academic TextsCharles Lacuna100% (9)
- Deploying Enterprise SIP Trunks With CUBE, CUCM and MediaSense SBC PDFDocument96 pagesDeploying Enterprise SIP Trunks With CUBE, CUCM and MediaSense SBC PDFZeeshan DawoodaniNo ratings yet
- CheggghDocument2 pagesCheggghsasae4980No ratings yet
- WB SpcxbarandrintroDocument4 pagesWB SpcxbarandrintromitiwanaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Quality Control Charts For VariablesDocument15 pagesStatistical Quality Control Charts For VariablesChetal BharaiNo ratings yet
- Unit2-Regression NGPDocument81 pagesUnit2-Regression NGPanimehv5500No ratings yet
- Xbar and R Chart Formula and ConstantsDocument13 pagesXbar and R Chart Formula and ConstantsklausgreatevilNo ratings yet
- Pearson's Correlation CoefficientDocument7 pagesPearson's Correlation Coefficientyasas_bandaraNo ratings yet
- Economics 536 Transformations and The Specification of Econometric ModelsDocument13 pagesEconomics 536 Transformations and The Specification of Econometric ModelsMaria RoaNo ratings yet
- MEC462B-IQC-Control Charts For VariablesDocument21 pagesMEC462B-IQC-Control Charts For VariablesANH NGUYỄN ĐỨCNo ratings yet
- The Classical Jacobi Algorithm: Bill Venables 2021-04-17Document9 pagesThe Classical Jacobi Algorithm: Bill Venables 2021-04-17Lucas SantosNo ratings yet
- R Handbook - Regression For Count DataDocument13 pagesR Handbook - Regression For Count Dataclyn.beeNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Linear Regreation CHP14Document21 pagesTopic 7 Linear Regreation CHP14Natasha Mgt JoharNo ratings yet
- 1 Simplex MethodDocument17 pages1 Simplex MethodPATRICIA COLINANo ratings yet
- 1-7 Least-Square RegressionDocument23 pages1-7 Least-Square RegressionRawash Omar100% (1)
- 10 Cor1Document18 pages10 Cor1tanmay.bhatnagar03No ratings yet
- Statistical Quality Control: Dr. Eng. Mohamed ElwakilDocument60 pagesStatistical Quality Control: Dr. Eng. Mohamed ElwakilOmar Abdelsameia GalAllahNo ratings yet
- ML Assignment No. 1: 1.1 TitleDocument8 pagesML Assignment No. 1: 1.1 TitleKirti PhegadeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear Regression: BIOST 515 January 15, 2004Document32 pagesMultiple Linear Regression: BIOST 515 January 15, 2004HazemIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Notes 3 - Linear RegressionDocument6 pagesNotes 3 - Linear Regressionkjogu giyvgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - Linear RegressionDocument12 pagesLecture 05 - Linear RegressionRamona CirstianNo ratings yet
- Statistical ComputingDocument36 pagesStatistical ComputingMuhd KamisNo ratings yet
- Pearson's Correlation CoefficientDocument7 pagesPearson's Correlation CoefficientEsmaelDawudNo ratings yet
- ARMv7 ReferenceDocument7 pagesARMv7 ReferenceAngela BarberNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlsDocument7 pagesQuality ControlsHamada AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Group 5Document96 pagesChapter 6 - Group 5Hà TrangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Complex Sample Survey DataDocument24 pagesAnalysis of Complex Sample Survey DataCamilo Gutiérrez PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Lec # 05Document24 pagesLec # 05Zeeshan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Lab 6 - Factorial DesignsDocument23 pagesSolutions - Lab 6 - Factorial DesignsAbery AuNo ratings yet
- Lect#6 - Relational AlgebraDocument33 pagesLect#6 - Relational AlgebraElyzza RoynieNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics II-SLRDocument23 pagesApplied Statistics II-SLRMagnifico FangaWoro100% (1)
- STAT501 Online - HW3R - Spring2024Document5 pagesSTAT501 Online - HW3R - Spring2024Harsh Vardhan DubeyNo ratings yet
- PR 4-6Document9 pagesPR 4-6mech bhabhaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Power Point 2Document35 pages3.2 Power Point 2krothrocNo ratings yet
- LR AssumptionsDocument9 pagesLR AssumptionsJyo BrahmaraNo ratings yet
- Review: Preparing Journal-Format GraphsDocument5 pagesReview: Preparing Journal-Format GraphsWendy CohenNo ratings yet
- Chat Openai Com Share 42b24a73 839b 4128 Ade9 7d8eed9e9533Document21 pagesChat Openai Com Share 42b24a73 839b 4128 Ade9 7d8eed9e9533NadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Control Charts For VariablesDocument25 pagesControl Charts For VariablesJassfer AlinaNo ratings yet
- Question 1 (Linear Regression)Document4 pagesQuestion 1 (Linear Regression)Salton GerardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Control Charts For VariablesDocument38 pagesChapter 5. Control Charts For VariablesJigar Patel's100% (2)
- CCS-PL-3003Document6 pagesCCS-PL-3003David RIPNo ratings yet
- Variables Control ChartDocument22 pagesVariables Control Chartbobby510No ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument43 pagesRegression AnalysisPRIYADARSHI GOURAV100% (1)
- 7 OLS AssumptionsDocument37 pages7 OLS AssumptionsSaitejNo ratings yet
- Table Used in Control ChartDocument10 pagesTable Used in Control ChartRonillo PormonNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Geostatistics: Mg. Sc. Marco A. CotrinaDocument51 pagesMultivariate Geostatistics: Mg. Sc. Marco A. CotrinaEdgarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - MultipleLinearRegression - Afterclass1bDocument34 pagesModule 3 - MultipleLinearRegression - Afterclass1bVanessa WongNo ratings yet
- Line GraphsDocument10 pagesLine GraphsthaerNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDocument18 pagesX-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareAldrige LuisNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R ChartsDocument26 pagesX-Bar and R ChartsscjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajNo ratings yet
- MultivariateRGGobi PDFDocument60 pagesMultivariateRGGobi PDFDiogo BarriosNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareDocument26 pagesX-Bar and R Charts: NCSS Statistical SoftwareukavathekarNo ratings yet
- Control Charts: Production and Operations ManagementDocument37 pagesControl Charts: Production and Operations ManagementNeelima AjayanNo ratings yet
- Control Charts: Walter ShewartDocument7 pagesControl Charts: Walter ShewartAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument23 pagesStatistical Quality ControlFreddy GarcíaNo ratings yet
- A 45301Document6 pagesA 45301heyguys77No ratings yet
- Tai Lieu Bo Tro IELTSDocument352 pagesTai Lieu Bo Tro IELTSNguyễn Khánh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Linear RegressionDocument41 pagesChapter 3. Linear RegressionNguyễn Quang TrườngNo ratings yet
- ch.3 Part 2Document4 pagesch.3 Part 2Mohamed ZizoNo ratings yet
- Series 1Document2 pagesSeries 1Sangwoo KimNo ratings yet
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument32 pagesStatistical Quality ControlParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Smith Et Al., 2018 (Analytical Chemistry)Document7 pagesSmith Et Al., 2018 (Analytical Chemistry)Leticia SakaiNo ratings yet
- Bhutiani2016 Article AssessmentOfGangaRiverEcosyste PDFDocument7 pagesBhutiani2016 Article AssessmentOfGangaRiverEcosyste PDFDipakNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For The Installation and Recovery of Temporary RoadwaysDocument15 pagesMethod Statement For The Installation and Recovery of Temporary Roadwaysandreipopa84No ratings yet
- ESOP Whitepaper PDFDocument11 pagesESOP Whitepaper PDFnkashimpuriaNo ratings yet
- Lms - Question Bank Unit 3Document6 pagesLms - Question Bank Unit 3JAYAPRAKASH SNo ratings yet
- StockDocument60 pagesStockPhan Tú AnhNo ratings yet
- 1 Script200302090903033030Document9 pages1 Script200302090903033030gever29816No ratings yet
- Overstrength Factor Calculation Procedure - ACI 318-08 (R) - Overstrength Factor - R - Part-2Document5 pagesOverstrength Factor Calculation Procedure - ACI 318-08 (R) - Overstrength Factor - R - Part-2Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower LessonsDocument26 pagesCooling Tower Lessonssmidhum7470100% (1)
- 60-Cell Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass Module (30mm Frame) JAM60D00 - BPDocument2 pages60-Cell Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass Module (30mm Frame) JAM60D00 - BPAlcides Araujo SantosNo ratings yet
- Question No 1-4 My School: 7. Eating - Like - Some - I-Cake in Good Sentence IsDocument4 pagesQuestion No 1-4 My School: 7. Eating - Like - Some - I-Cake in Good Sentence IsEl MinienNo ratings yet
- For Academic Council Meeting04052018Document28 pagesFor Academic Council Meeting04052018Anonymous PcPkRpAKD5No ratings yet
- Name:Fedrick Samuel W Reg No: 19MIS1112 Course: Machine Learning (SWE4012) Slot: L11 + L12 Faculty: Dr.M. PremalathaDocument30 pagesName:Fedrick Samuel W Reg No: 19MIS1112 Course: Machine Learning (SWE4012) Slot: L11 + L12 Faculty: Dr.M. PremalathaFèdríck SämùélNo ratings yet
- Manipulative Information and MediaDocument11 pagesManipulative Information and Mediamielin kaye villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Blss SSD FlyerDocument1 pageBlss SSD FlyerMARY JERICA OCUPENo ratings yet
- Lgko/Kgs: 1.1. Atis 1.2. Taxi ProceduresDocument22 pagesLgko/Kgs: 1.1. Atis 1.2. Taxi ProceduresMido ZezoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Internal Control)Document23 pagesAssignment 1 (Internal Control)Ali WaqarNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan FavorsDocument4 pages5e Lesson Plan Favorsapi-312673844No ratings yet
- TS90 B 2009Document813 pagesTS90 B 2009Yulius PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Florence Gilbao: ProfileDocument1 pageFlorence Gilbao: ProfileFLORENCE GILBAONo ratings yet
- Biologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryDocument25 pagesBiologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryAmee PatelNo ratings yet
- ISO 20022 Programme UHB SR2023 Final EditionDocument884 pagesISO 20022 Programme UHB SR2023 Final EditionSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa: Y/11DM Pneumatic Differential Pressure Transmitter User's ManualDocument5 pagesYokogawa: Y/11DM Pneumatic Differential Pressure Transmitter User's ManualRabah AmidiNo ratings yet
- Microseismic Monitoring. The Vision Is One of Process That Can Interpret Subsurface in Drilling Operation. FromDocument1 pageMicroseismic Monitoring. The Vision Is One of Process That Can Interpret Subsurface in Drilling Operation. FromDody Pratama GintingNo ratings yet
- Retrofitting of Reinforced ConDocument11 pagesRetrofitting of Reinforced ConForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- The Millerton News 12-3-15 PDFDocument34 pagesThe Millerton News 12-3-15 PDFLakeville JournalNo ratings yet
- BPO CultureDocument2 pagesBPO Cultureshashi1810No ratings yet
- Alufo Shutter ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAlufo Shutter ApplicationssmijusNo ratings yet