Professional Documents
Culture Documents
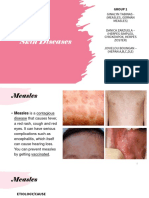
Communicable Diseases
Communicable Diseases
Uploaded by
ellixeronscp049Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communicable Diseases
Communicable Diseases
Uploaded by
ellixeronscp049Copyright:
Available Formats
Acute/Infectious/Communicable - In many people, it's marked by a severe
hacking cough followed by a high-pitched
Diseases intake of breath that sounds like "whoop."
Classified according to: - Before the vaccine was developed,
1. MODE of Transmission whooping cough was considered a
2. RANGE of Seriousness, Effect, Duration, Severity, childhood disease.
and Extent - Deaths associated with whooping cough
are rare but most commonly occur in
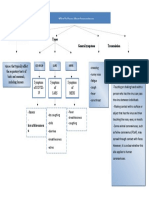
A. MODE of Transmission
infants.
1. Airborne Transmission
- That's why it's so important for pregnant
• SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME
women — and other people who will have
(SARS): CAUSED BY CORONAVIRUS
close contact with an infant — to be
• 774 DIED IN 2002
vaccinated against whooping cough.
• MENIGOCOCCEMIA: CAUSED BY NEISSERIA - Symptoms:
MENINGITIDIS ▪ Once you become infected with
whooping cough, it takes about
seven to 10 days for signs and
symptoms to appear, though it can
sometimes take longer.
▪ They're usually mild at first and
resemble those of a common cold:
• TUBERCULOSIS (MYCOBACTERIUM
▪ Runny nose
TUBERCULOSIS)
▪ Nasal congestion
• ALSO THROUGH DROPLETS
▪ Red, watery eyes
▪ Fever
▪ Cough
▪ After a week or two, signs and
symptoms worsen.
▪ Thick mucus accumulates inside
2. Droplet Transmission your airways, causing
• COMMON COLDS (RHINO VIRUS, CORONA uncontrollable coughing.
VIRUS, ETC.) ▪ Severe and prolonged coughing
attacks may:
➢ Provoke vomiting
➢ Result in a red or blue face
➢ Cause extreme fatigue
➢ End with a high-pitched
"whoop" sound during the
• WHOOPING COUGH (BORDETELLA next breath of air
PERTUSIS) ▪ Many people don't develop the
characteristic whoop.
▪ Sometimes, a persistent hacking
cough is the only sign that an
adolescent or adult has whooping
cough.
• MEASLES (RUBIOLA VIRUS) ▪ Infants may not cough at all.
Instead, they may struggle to
breathe, or they may even
temporarily stop breathing.
- Causes:
▪ Whooping cough is caused by a
type of bacteria called Bordetella
• Whooping Cough
pertussis.
- Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly
▪ When an infected person coughs
contagious respiratory tract infection.
or sneezes, tiny germ-laden
droplets are sprayed into the air • ENTEROBIASIS (ENTEROBIUS
and breathed into the lungs of VERMICULARIS)
anyone who happens to be nearby.
• GERMAN MEASLES (RUBELLA VIRUS)
• CHICKENPOX (VARICELLA)
• INFLUENZA (FLU VIRUS)
• POLIOMYELITIS (POLIO VIRUS)
• LEGIONNAIRE’S DISEASE: CAUSED BY
LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA - kung ma remove ang head sa worm, mamatay
• 34 DIED IN 1976 na ang worm
• (WATER DROPLETS)
ANIMAL RESERVOIR TRANSMISSION
• (AIRCON)
3. Intestinal Discharge Transmission • TAENIASIS / PORK OR BEEF TAPEWORM
• CHOLERA (VIBRIO CHOLERA) INFECTION
• DYSENTERY: AMOEBIC (ENTAMOEBA
HISTOLYTICA, BACILLARY OR BACTERIAL
(SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE)
• TYPHOID FEVER (SALMONELLA TYPHI)
• HEPATITIS A (HAV)
• GIARDIASIS (GIARDIA LAMBIA) • DIHYLLIDIASIS / DOG TAPEWORM
INFECTION
• ASCARIASIS (ASCARIS LUMBRICOIDES) • DIPHYLLOBOTHRIASIS / FISH TAPEWORM
INFECTION
4. Open Sores/Lesion Transmission
Male: curved end
• AIDS : HIV (SEX)
Female: pointed end
Embryonated egg: infectious
• TRICHURIASIS (TRICHURIS TRICHURA)
• HEPATITIS B & HEPATITIS C (SEX)
• CAPILLARIASIS (CAPILLARIA
PHILIPPINENSIS)
• LEPTOSPIROSIS: LEPTOSPIRA INTERROGANS
- naay striations sa cell wall
- peanut-shaped
• GONORRHEA (NEISSERIA GONORRHEA) B. CLASSIFICATION according to
(SEX)
RANGE
• Acute: ACUTE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT
INFECTION, ACUTE URINARY TRACT
INFECTION, ETC.
• Subacute: SUB-ACUTE BACTERIAL
ENDOCARDITIS (SABE)
• SYPHILLIS (TREPONEMA PALLIDUM) (SEX)
• Chronic: AIDS, TUBERCULOSIS, CANCER,
ETC.
Control/Eliminate PATHOGENS
A. PHYSICAL Methods:
1. Mechanical removal
2. Use of heat
3. Use of radiation
• SMALLPOX (VARIOLA VIRUS)
4. Filtration
5. Desiccation
6. Use of osmotic pressure
B. CHEMICAL Methods
1. Disinfection (except spores)
2. Sterilization (including spores)
5. Vector-Borne Transmission Common Disinfectants
• MOSQUITO: • Phenols
- MALARIA (ANOPHELES SPP.) • Halogens
- DENGUE FEVER (AEDES SPP.) • Alcohol
- YELLOW FEVER (AEDES SPP.) • Surface reactive agents
- FILARIASIS/ELEPHANTIASIS (ANOPHELES • Oxidizing agents
AND MANSONIA SPP.) • Gases
• TICK AND MITE (TYPHUS FEVER) • Aldehydes
• SANDFLY (LEISHMANIASIS) C. Use of DRUGS
• TSE TSE FLY, CONE-NOSED BUG 1. Antibiotics
(TRYPANOSOMIASIS) 2. Antifungal
3. Antiviral
4. Antihelmintics
ASEPSIS - It is the REDUCTION or ELIMINATION of
pathogenic microorganisms in areas where they can
6. Fomite Borne Transmission potentially grow and multiply.
• ANTHRAX ( BACILLUS ANTHRACIS)
Handwashing
- is a vigorous rubbing together of all surfaces
of lathered hands for about 10 to 20 seconds
followed by rinsing under a stream of water.
- most IMPORTANT and BASIC technique
- EASIEST and CHEAPEST form of aseptic
technique
• CHICKEN POX (VARICELLA VIRUS)
Types of handwashing:
1. Generic
2. Abbreviated
• COMMON COLDS (RHINO VIRUS, CORONA
VIRUS, ETC.)
• INFLUENZA (FLU VIRUS)
• MENINGITIS (NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS)
You might also like
- Biological Wastewater Treatment - Principles Modelling and DesignDocument103 pagesBiological Wastewater Treatment - Principles Modelling and DesignNguyen Phuc Pham78% (9)
- Community Health Nursing Notes SummaryDocument9 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Notes Summarysorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (28)
- Communicable Disease ActivityDocument1 pageCommunicable Disease ActivityMadelyn GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacy Practice and Simulation: PHAR456Document82 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacy Practice and Simulation: PHAR456Hassan El HajjNo ratings yet
- Nose Ears Throat CoughDocument82 pagesNose Ears Throat CoughHassan El HajjNo ratings yet
- 5 2-DeanDocument7 pages5 2-Deanfiel borataNo ratings yet
- Pertussis CHN OutputDocument24 pagesPertussis CHN OutputShannel J. DabalosNo ratings yet
- Causes of Morbidity and Mortality SirDocument97 pagesCauses of Morbidity and Mortality SirJoy Santiago VeneracionNo ratings yet
- Measles, Mumps, RubellaDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, RubellaRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Lecture Week 3 Notes PrelimsDocument6 pagesNCM 104 Lecture Week 3 Notes PrelimsVictor MurilloNo ratings yet
- Cough & ColdsDocument26 pagesCough & ColdsMarcelle DrukerNo ratings yet
- BBB - Respi&gi ReportsDocument11 pagesBBB - Respi&gi ReportsshesahNo ratings yet
- Medical Bulletin - ChickenpoxDocument1 pageMedical Bulletin - ChickenpoxMonaliza MoralesNo ratings yet
- Dengue, Malaria, Chic Ken Pox: By: Salome CarpioDocument30 pagesDengue, Malaria, Chic Ken Pox: By: Salome CarpioJu Lie AnnNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Respiratory Syncytial VirusDocument1 pageNursing CS Respiratory Syncytial VirusJazzmine GuraNo ratings yet
- Iii. Covid and PneumoniaDocument11 pagesIii. Covid and Pneumonialady birdNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lab MidtermsDocument29 pagesMicrobio Lab Midtermsate aiNo ratings yet
- Geron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Document29 pagesGeron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Potato TomatoNo ratings yet
- Covid PamphletDocument3 pagesCovid Pamphletapi-545056783No ratings yet
- CARIDocument3 pagesCARIFirenze FilNo ratings yet
- Measles (Rubeola) : Corynebacteriu M Diphtheria (Bacteria)Document2 pagesMeasles (Rubeola) : Corynebacteriu M Diphtheria (Bacteria)Mohammad AkkadNo ratings yet
- 1.1 COVID-19 Primer - Poster Colored English (30.48 X 45.72 CM)Document1 page1.1 COVID-19 Primer - Poster Colored English (30.48 X 45.72 CM)Rosalie T. Orbon-TamondongNo ratings yet
- Skin DiseseasesDocument161 pagesSkin DiseseasesDanica Lacopia ZarsuelaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument41 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionsmsichiliinnocent7No ratings yet
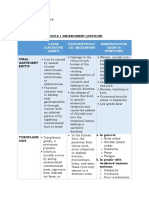
- Cause (Causative Agent) Pathophysiolo Gic Mechanism Manifestation (Signs & Symptoms)Document5 pagesCause (Causative Agent) Pathophysiolo Gic Mechanism Manifestation (Signs & Symptoms)Colene MoresNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Safety TrainingDocument9 pagesCOVID-19 Safety TrainingLucky OpenerNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease (COVID-19, Influenza, SARS, TB) - SlidesDocument16 pagesCommunicable Disease (COVID-19, Influenza, SARS, TB) - SlidesLENA ELINNA OLIN BINTI AMBROSENo ratings yet
- StemDocument6 pagesStemBellina DayaNo ratings yet
- Notes: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument4 pagesNotes: Mycobacterium TuberculosisAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Micropara Rev Ppt10Document12 pagesMicropara Rev Ppt10femmeclub coNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Cough - Colds, FeverDocument11 pagesPrevention and Control of Cough - Colds, FeverAriannaNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW 8.5 13 inDocument1 pageCOVID 19 EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW 8.5 13 inRheanna AbanillaNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Week 11Document49 pagesRESPIRATION Week 11Janelle Alyson De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- P ScriptDocument3 pagesP ScripttwnynyiskaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases PowerPoint - StudentDocument15 pagesCommunicable Diseases PowerPoint - StudentCruz YrNo ratings yet
- MS Respi DisorderDocument10 pagesMS Respi Disordersecondacvalo123No ratings yet
- Respiratory Block 2Document53 pagesRespiratory Block 2Maya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- SC - Nasal CongestionDocument2 pagesSC - Nasal Congestionyushalluuna bektiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocument150 pagesDiseases of The Respiratory SystemJanine AtesoraNo ratings yet
- Q3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableDocument35 pagesQ3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableJaeda EuclidNo ratings yet
- Covid 19: Dangerous On EarthDocument6 pagesCovid 19: Dangerous On Earthkartik kathuriaNo ratings yet
- Common Exanthems PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Exanthems PDFKaren Ivy BacsainNo ratings yet
- HC - Lec - Infectious DiseasesDocument10 pagesHC - Lec - Infectious DiseasesChelsea JaymaNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument7 pagesGerman MeaslesKath DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Whooping Cough and DiptheriaDocument25 pages3 - Whooping Cough and DiptheriaBa MulengaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Coronavirus? Types General Symptoms Transmission: What To Know About CoronavirusesDocument1 pageWhat Is A Coronavirus? Types General Symptoms Transmission: What To Know About CoronavirusesIntan Krisnia JuliatiiNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infections: Poltekkes Kemenkes DenpasarDocument5 pagesAcute Respiratory Infections: Poltekkes Kemenkes DenpasaremaaNo ratings yet
- RubellaDocument4 pagesRubellaDave ComstockNo ratings yet
- MENINGITISDocument5 pagesMENINGITISapi-3822433100% (1)
- Roseola PDFDocument1 pageRoseola PDFLili PredescuNo ratings yet
- Cause Agent Type of Agent MOT Signs and Symptoms Prevention and Control Treatment TuberculosisDocument6 pagesCause Agent Type of Agent MOT Signs and Symptoms Prevention and Control Treatment Tuberculosisvanessa patayonNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus and COVIDDocument14 pagesCoronavirus and COVIDMJ Villamor AquilloNo ratings yet
- NST P ReportingDocument19 pagesNST P Reportingmarielbatalona1No ratings yet
- UNHCR - Health Fact Sheet - Malaria Script DNDocument5 pagesUNHCR - Health Fact Sheet - Malaria Script DNcapitalNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu AdvisoryDocument3 pagesSwine Flu AdvisorykumarNo ratings yet
- Pedia Rotation CroupDocument2 pagesPedia Rotation CroupKaren ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection: Signs and SymptomsDocument51 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infection: Signs and SymptomsFatima GamalNo ratings yet
- Main Symptoms of Covid-19: Ways To Protect Yourself From Covid-19Document2 pagesMain Symptoms of Covid-19: Ways To Protect Yourself From Covid-19Anne Alery AlejandreNo ratings yet
- The Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Waste Incineration ArabicDocument36 pagesWaste Incineration ArabicAsala CosmeticsNo ratings yet
- Awareness of HPV and HPV Vaccines, Acceptance To VDocument6 pagesAwareness of HPV and HPV Vaccines, Acceptance To VMa. Isabel LadiaNo ratings yet
- MAX Employment Retention Based On Employment SatisfactionDocument104 pagesMAX Employment Retention Based On Employment SatisfactionMahnaz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Practices in WorkplaceDocument28 pagesInfection Control Practices in WorkplaceJames Patrick Dizon100% (1)
- Path To Improved Health: Physical Health - Taking Care of Your BodyDocument6 pagesPath To Improved Health: Physical Health - Taking Care of Your BodyMaria Katrinka Sophia MartiresNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Cohort StudiesDocument6 pages2.3 Cohort StudiesMiguel C. Dolot100% (1)
- Edu 214 Course SyllabusDocument6 pagesEdu 214 Course Syllabusapi-481214985No ratings yet
- DR Arif Azad: Public Health ProfessionalDocument5 pagesDR Arif Azad: Public Health ProfessionalAnonymous clKvKNaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional ValuesDocument20 pagesNutritional ValuesAngela Shane RayandayanNo ratings yet
- Infectious Agent Reservoir Portal of Exit Mode of Transmission Portal of Entry Susceptible HostDocument8 pagesInfectious Agent Reservoir Portal of Exit Mode of Transmission Portal of Entry Susceptible HostAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- Success Story About Water Pollution: by James SalzmanDocument2 pagesSuccess Story About Water Pollution: by James SalzmanThế Anh ĐoànNo ratings yet
- BING Paraphrase SAFIKADocument3 pagesBING Paraphrase SAFIKASafika Nur IzzahNo ratings yet
- Sop PGDocument2 pagesSop PGDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Infection Prevention & ControlDocument4 pagesInfection Prevention & ControlAmit HalderNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Antara Pola Makan Dan Kadar Glukosa Darah Sewaktu Pada Penderita Diabetes Melitus Tipe DuaDocument9 pagesHubungan Antara Pola Makan Dan Kadar Glukosa Darah Sewaktu Pada Penderita Diabetes Melitus Tipe DuaSuwai Batul Aslamiyah A Md KepNo ratings yet
- ID Identifikasi Wilayah Dengan PermasalahanDocument10 pagesID Identifikasi Wilayah Dengan PermasalahanDhery MursalNo ratings yet
- Conjuntivitis Folicular AgudaDocument3 pagesConjuntivitis Folicular AgudaMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Deemed Stray Vacancy Round Seats PG MD - Ms - DiplomaDocument39 pagesDeemed Stray Vacancy Round Seats PG MD - Ms - DiplomaManoj KashyapNo ratings yet
- Uganda National Health PolicyDocument19 pagesUganda National Health PolicyAlfred niyoNo ratings yet
- Skill 5th Sem SyllabusDocument3 pagesSkill 5th Sem SyllabusAdnan BandayNo ratings yet
- About Cyclosporiasis: On This PageDocument4 pagesAbout Cyclosporiasis: On This PageDennis NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Monthly Report: Municipal Nutrition CommitteeDocument6 pagesMonthly Report: Municipal Nutrition CommitteeMeriely BationNo ratings yet
- Rainwater Harvesting As An Alternative Water SourceDocument19 pagesRainwater Harvesting As An Alternative Water SourcekusumarukmiNo ratings yet
- Antenatal AssessmentDocument67 pagesAntenatal Assessmenthiral mistry100% (3)
- Application Form RSVCDocument1 pageApplication Form RSVCRey Christian Butalid ArendainNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Therapy: The Pneumonia PanaceaDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Therapy: The Pneumonia PanaceabobbyramakantNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids Thesis PDFDocument4 pagesHiv Aids Thesis PDFangiewillisjackson100% (4)
- Role of The Govt in HealthDocument4 pagesRole of The Govt in HealthaparnamadhuNo ratings yet