Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MSP Schedule With Detailed Syllabus
MSP Schedule With Detailed Syllabus
Uploaded by
saumya khandelwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views25 pagesHow to prepare for mains
Original Title
MSP_Schedule_with_Detailed_Syllabus (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHow to prepare for mains
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views25 pagesMSP Schedule With Detailed Syllabus
MSP Schedule With Detailed Syllabus
Uploaded by
saumya khandelwalHow to prepare for mains
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 25
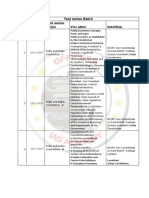
Schedule with Detailed Syllabus
Mains Support Programme (MSP) 2023
Phase – 1
Date Test Subject Topic Syllabus
Code
18.6.2023 PT-1 Polity Basic Concepts • Types of Constitution, Types of
(Salient Government, Parliamentary and
features of the Presidential System
Indian • Evolution of Indian Constitution:
Key Charter Acts, Government of
Constitution,
India Acts
Political
• Constituent Assembly:
Concepts and Composition, Features, and Key
Preamble), debates, Making of the
Constitution, Key Features of the
Indian Constitution
• Preamble: Ideals, Values, and
Objectives of the Indian
Constitution, Significance, and its
Fundamental
Amendability, Preamble as Part of
Rights the Constitution
• Federal and Unitary system of
Government, Federal and Unitary
Features of the Indian
Constitution
• Citizenship, provisions, Overseas
Citizens, Non-resident Indians,
Citizenship Amendment Acts etc.
• Union and its Territory, Formation
of States, Union Territories, Article
2 and Article 3 of the Constitution
• Amendment to the Constitution,
its procedure, Article 368 etc.
• Fundamental Rights: Evolution,
objectives and features,
philosophical dimension of Part
III, Meaning of state for Part III
and Part IV, Meaning and
importance of Fundamental
Rights, Rule of Law, Right to
Equality, Equality before law and
equal opportunity of law, up to
Article 18
25.6.2023 PT-2 Polity Fundamental • Fundamental Rights: Right to
Rights, Freedom, Right to life, Right
Fundamental against Exploitation, Right to
Freedom of Religion Cultural and
Duties,
Educational Rights, Article 32,
Directive Writs and their uses, Article 33-
Principle of 35, Procedure established by law
State Policy & and due process of law, Key SC
Doctrine of judgments, Amendments to the
Basic Structure Part III.
• Directive Principles of State
Policy: Evolution and Sources,
Basic features, Socialistic
Principles, Gandhian Principles,
Liberal-Intellectual Principles,
New
• Directives Principles, Criticism,
Relationship between FRs and
DPSPs: Key Judgments and
Current situation.
• Fundamental Duties: Evolution
and Features, Key duties,
Enforceability and justiciability,
Rights and Duties, Criticism and
Significance.
• Doctrine of Basic Structure, its
emergence, elements and
application.
2.7.2023 PT-3 Polity Legislature • Parliament: Organization and
(Parliament Composition, Powers and
and State Functions, Privileges of
Parliament and MPs, Sessions,
Legislature) Proceeding, Dissolution,
Prorogation, Effects on bills,
President’s address, Presiding
Officers of Parliament: Speaker,
Executive (State Deputy Speaker, Chairman,
and Central) Deputy Chairman of Rajya
Sabha, Leader of the House,
Union Territory Leader of Opposition. Rajya
Sabha: Composition, Election,
Lok Sabha: Composition,
Federalism Lawmaking Procedure, Motions,
Resolutions and Bills, Bills: Types
and procedure, Joint sitting,
Types of majorities, Parliamentary
Electoral committees, Separation of Power,
Politics Sovereignty of Parliament,
Constitutional Financial powers, office of profit,
and Non- Anti-defection Law
Constitutional • State Legislative Assemblies
bodies and Councils, Organization and
Composition, Powers and
Functions, Comparison of Rajya
Sabha and State Legislative
Councils etc.
• Parliamentary Committees,
Department-related Standing
committees, Joint Committees
etc.
• Union Executive: President:
Appointment, term of office,
qualification, Election procedure,
Presidential Powers,
Impeachment of the President,
Vice-President: Appointment,
term of office, qualification,
Election procedure, Removal,
Powers and Functions of Vice
President, Prime Minister: Powers
and role in a democracy
• Council of Ministers: Union and
States, Cabinet, Ministers
• State Executive: Governor,
Powers and Functions of
Governor, Chief Minister: Powers
and Functions
• Cabinet Committees,
Bureaucracy, Permanent
Executives.
• Union Territories and their
administration, Union Territory of
NCR and Puducherry, Central
Government's role, etc.
• Federalism: Centre-State
Relations: Legislative, Financial
and Administrative relations,
Taxation powers of both central
and state governments, and
Different Committees, like
Puncchi and Sarkaria
Commission.
• Broad features of judicial system
in India
• Representation of People Act,
1950 and 1951, Elections, Model
Code of Conduct, Political
Parties, Electoral System etc.
9.7.2023 PT-4 Polity Judiciary • Supreme Court: Composition
and Appointment of Judges,
Terms and Removal of Supreme
Court Judges, Independence of
Supreme Court, Jurisdiction of
SC
• High Courts: Appointment of
Local Self High Court Judges, Terms,
Government Removal, and Transfer of High
and Emergency Court Judges, Jurisdictions and
power of High Courts
Provisions
• Lower judiciary: Appointment,
Jurisdictions and Power
• Judicial Review, Judicial Activism,
Public Interest Litigation (PIL)
• Tribunals: Types, composition,
Law Commission of India, Bar
Constitutional Council of India, E-Courts, Tele-
law initiative, etc.
and non-
• Local Self Government:
constitutional Evolution of the third-tier
Bodies governance in India, 73rd and
74th Amendment Act,
Compulsory and Voluntary
Provisions, PESA Act, Types of
urban local bodies, Tenure and
Election of the Local bodies, XIth
and XIIth Schedules, Significance
and Problems associated Role of
State Election Commission, Role
of State Finance Commission
• Administration of Scheduled
Areas and Tribal Areas, 5th
Schedule and 6th Schedule
areas, Autonomous Councils,
Role of Governor and President
with respect to tribal areas,
Special Provisions for Some
States.
• Emergency Provisions: National
Emergency, President's Rule,
Financial Emergence and related
provisions.
• Constitutional and Non-
Constitutional Bodies: Election
Commission Finance
Commission Goods and Services
Tax Council National
Commissions for SCs, STs, BC
National Commission for Women
National Commission for
Minorities NITI Aayog, National
Human Rights Commission of
India(NHRC), State Human
Rights Commission (SHRC),
Central Information Commission,
State Information Commissions,
Central Vigilance Commission,
Central Bureau of Investigation
National Disaster Management
Authority National Investigation
Agency
16.7.2023 IR-1 International International • Bilateral, regional and global
Relations Relations groupings and agreements
involving India and/or affecting
India’s interests
• India and its neighbourhood-
relations
• Important International
institutions, agencies and fora,
their structure, mandate
• Effect of policies and politics of
developed and developing
countries on India’s interests
• Indian diaspora
23.7.2023 GT-1 Geography Physical • Geomorphology: Universe and
Geography Solar System;
• Earth- Latitude, Longitude,
Motion, Inclination, Time; Interior
of the earth - Sources of
information, Crust, Mantle and
Core; Various Discontinuity
Lithosphere; Magma Formation;
Rocks and Minerals;
• Continents and Ocean -
Continental Drift Theory, Sea
FloorSpreading, Convectional
Current Theory, Plate Tectonics
Theory; Plates Boundaries and its
types;
• Geomorphic Processes: Exogenic
and Endogenic; Earthquakes -
Causes, Types of Earthquakes,
Types of Waves, Shadow Zones;
Effects of Earthquake Waves;
Measuring Earthquakes;
Volcanoes- Types, Distribution,
Ring of fire, Volcanism;
• Landforms - Volcanic Landforms;
Erosional and Depositional
landforms of Wind, Water and
Glaciar; Mountains - Types and
Distribution.
• Oceanography: Oceans - Salinity-
Temperature pattern, Bottom
Reliefs, Various water
movements, Factors affecting
Ocean Water Movement; corals
reefs, other resources and
governance, Ocean Floor
mapping
• Atmosphere - Origin,
composition, Structure,
• Solar Radiation and Heat budget
- Insolation, Factors affecting the
Insolation at the surface of the
Earth, Reason of the season,
Heating and cooling of
atmosphere Terrestrial Radiation,
Shortwave Radiation, Longwave
Earth Radiation, Factors
controlling Temperature
distribution, Inversion of
Temperature.
• Circulations and the pressure
belts, Local winds- Precipitation,
Different types of weather,
Impact, Atmospheric Pressure,
Vertical variation of pressure,
Horizontal distribution of
pressure, World Distribution of
Sea Level Pressure, Factors
affecting the velocity and direction
of the Wind Atmospheric
Circulation and Weather Systems
• Latitudinal Variation of
Atmospheric Heating Pressure
Belts, Migration of Belts following
apparent Path of Sun Global
Circulation – Hadley Cell, Ferrel
Cell, Pattern of Planetary Winds
Seasonal Wind, Local Wind, Land
and Sea Breezes, Mountain and
Valley Winds;
• Air mass & fronts; Cyclones -
Temperate and Tropical (their
origin and distribution), etc.
Important Streams (Jets), Local
streams, and their impacts, El-
Nino, LA Nina, IOD, ENSO, Polar
Vortex;
• Water in the Atmosphere, Water
Vapour, variation, Humidity –
Absolute and Relative
Precipitation, Saturation Dew
Point, Evaporation and
Condensation Dew, Frost, Fog &
Mist, snowfall etc Clouds:
formation, types, Precipitation:
Rainfall, Snowfall, Sleet Hail;
• World Climatic classifications and
their features
30.7.2023 GT-2 Geography Indian • India - Location - Longitutde
Geography Latitudnal extent - Time zones,
Geographical extremes of India,
its Neighbors, Key Channels,
Straits of the Indian Ocean
• Physiography of India -
Geological Divisions,
Physiographic Divisions,
Historiography of Indian Plate
movement, Peninsular Block,
Formations of Himalayas;
Division of Himalayas- Peaks,
passes, glaciers Faults of
Himalayas
• Northern plains: features
Northern plains,
• Peninsular Plateau: Features
Peninsular Plateau, Division
Peninsular Plateau, Location,
peaks, pass, etc.
• Indian Desert - Features,
Division, Location, peaks etc.
• Coastal Plains - Features,
Division, Location, peaks etc.
• Islands of India - Features,
Division, Location, peaks etc
• Drainage System of India -
Evolution of drainage system of
the Himalayas and Peninsular
India, Indus River system, Ganga
River System, Brahmaputra River
system, other rivers of Northeast,
Peninsular Rivers Flowing
towards the East, Peninsular
Rivers Flowing towards the West
and their Tributaries, Central India
rivers, Rivers of West India,
Famous cities located on the
banks of these rivers.
• Climate - Seasonal rhythm,
Koppen’s Climatic classification,
Factors Determining the Climate
of India, Mechanism of Weather
in the Winter Season Mechanism
of Weather in the Summer
Season,
• Monsoon: Features, location,
extent, etc., Causative Factors,
Influencing Factors, Mechanism
of the South-West and Retreating
Monsoon, Distribution, variation
of Rainfall in India
• Impact of tropical cyclones on
India, Spatio-temporal Distribution
of Tropical Cyclone in India,
Impact of Temperate cyclones
and western disturbances on
India, Climatic Regions of India
• Impact of El-Nino and La-Nina -
Indian Droughts and Floods;
Landslides, glacial outbursts
• Monsoon and the Economic Life
in India
6.8.2023 GT-3 Geography Economic • Resources - Energy (Renewable
Geography and and non-renewable), water (Major
World Mapping Aquifers and fresh water and
brackish water) and minerals and
mining and their relation with
geological features, distribution -
the world and mappings.
Countries with the largest oil
reserves and production,
Countries with the largest coal
reserves and production India,
Energy resources Coal-bed
Methane, Gas Hydrates, Shale
Oil/ Shale Gas Biofuels, 2G
Ethanol Programme Electricity,
Generation, capacity Hydropower
projects, thermal projects
Renewable energy resources.
• Mineral resources: Iron of the
world Iron Resources in India and
production Bauxite Resources in
India and production Graphite,
and lithium Resources in India
and production etc.
• Rare Earth metals: features and
reserves in India and the world
Uranium and Thorium reserves in
India,
• Population - Demography and
migration, reasons,
consequences etc.
• Industries - Factors influencing
industrial locations, Industrial
Regions of the world, Some key
industries of India-Tertiary and
Quaternary Activities, quinary
activities; Transportation -
National highways, transport
corridors Railways of India Ports
of India National Waterways.
13.8.2023 ET-1 Environment Basic Ecology & • Biodiversity: Animal diversity-
Ecology & Concepts, Vertebrates-fish, amphibians,
Biodiversity Environment reptiles, birds, mammals.
Invertebrates-annelid, molluscs,
Pollution & Arthropods, Protozoa. Plants-
Degradation, Algae, fungi, Angiosperm,
Biodiversity gymnosperm, Thallophyta,
and Bryophyta, Pteridophyta Levels of
Conservation biodiversity-genetic, specific,
community, Measure of bio-
diversity- species richness,
species evenness, Services
provided by Biodiversity-
ecosystem, biological, social,
Causes of Biodiversity loss-
human-population pressure,
habitat destruction, mono-
cropping, man-animal conflict etc,
natural- cyclone, coral bleaching,
earthquake, etc. Biodiversity
Hotspots, Red Data book -
Classification of Vulnerability -
Critically Endangered,
Vulnerable, etc. Biogeographical
classification- 2 realms, 5 biomes,
10 biogeographic zones, 25
biogeographic provinces,
• Plant diversity (Mangrove,
medicinal, insectivore) marine
organism (plankton, sea grass,
seaweeds, corals).,
• Conservation: Strategy- Insitu
and Exsitu conservation,
Conservation Efforts in India-
National Park, wildlife sanctuary,
community reserve, Sacred
Groves, Coastal Protected Areas.
Project Tiger, Project Elephant,
Project Snow Leopard, Project
Hangul, Vulture Conservation
Program, MIKE sites, Global
Efforts- Man and Biosphere
Program, Biosphere Reserves,
World Heritage Sites, UNESCO
Global GeoParks, Aichi
Biodiversity Targets, Mangroves
for Future. CITES, TRAFFIC,
Bonn Convention.,
• Acts and Bodies: Biodiversity Act,
2002, Wildlife Act, 1972-
Schedule-1,2,3,4,5,6.
Environment Protection Act of
1982, The Protection of Plant
Variety and Farmers Right Act,
2001. National Board for Wildlife,
Central Zoo Authority, National
Tiger Conservation Authority,
wildlife crime control bureau.
Convention on Biological
Diversity, Cartagena, Nagoya,
Kigali, Basel, Rotterdam,
Svalbard seed vault, Ramsar
Convention. Convention to
Biodiversity (CBD)-COP-14, UN
OCEAN Conference- Blue Deal,
Glo-Litter, Marine Protected
Areas, Indo-Pacific Oceans
Initiative (IPOI), Kunming
Declaration, Kunming Biodiversity
Fund, International Fund for
Agricultural Development (IFAD),
Food and Agriculture
Organisation (FAO), International
Tropical Timber Organisation
(ITTO), United Nations Forum for
Forests (UNFF), Coalition Against
Wildlife Trafficking (CAWT),
Globally Important Agricultural
Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
• National: Environmental Laws:
Provisions in the Indian
Constitution towards
Environmental Protection Salient
Features of - Air (Prevention and
Control of Pollution) Act,1981;
Water (Prevention and Control of
Pollution) Act, 1974, Forest
Conservation Act I980, Wildlife
Protection Act,1972, Environment
(Protection) Act,1986, Public
Liability Insurance Act 1991, NGT
Act 2010, CAMPA Act 2016, Fly
Ash Utilization rule, 2016 with
recent amendments.
• Role of Government in
Environmental Protection:
Environment-related Institutions
and Organizations, Pollution
Control Boards, National Green
Tribunal; Forest Survey of India,
National Board for Wildlife; Land
Degradation Neutrality; Regional
Project on Stubble Burning,
National Afforestation Program,
National Air Quality Index (AQI),
National Action Programme to
Combat Desertification, Bharat
Stage Norms
• Schemes: National Mission for
Clean Ganga, India Signs Global
Environment Facility, Grant Wood
in Good Campaign. Boat Lab to
Study the Brahmaputra, National
River Conservation Plan National
Mission for Clean Ganga, Wildlife
Action Plan - SECURE
Himalayas, Strategic Plan for
Human-Elephant Conflict, Save
the Sparrow, Special Protection
Force for Rhinos; Biodiversity
Heritage Site - Ameenpur Lake,
Energy Conservation- Building
Code, Blue Flag Pilot Project,
Various waste management rules
- Hazardous waste management
rule 2008, Solid waste
management rule 2016,
Construction and demolition
waste management rule, 2018,
Bio-Medical Waste Management
Rules - 2016,
• International: UNFCCC, KYOTO
Protocol- Mechanism under
Kyoto-CDM, Global Environment
Facility, REDD+, Climate Smart
Agriculture, IPCC, TEEB,
Ecological footprint, Clean
Technology Fund, Green
environment Fund, C-40 Initiative,
Conservation International,
CCAC, Global Methane Initiative,
IRIS, CDRI. CoP3-Kyoto, CoP13-
Bali, CoP15-Copenhagen,
CoP16-Cancun, CoP19-warsaw,
CoP20-Lima, CoP21-Paris,
Cop22-Marrakesh, CoP23-Bonn
Cop26-Glasgow.
20.8.2023 ET-2 Environment Institutions/ • Conservation: Strategy- Insitu
Ecology & Policies/ Rules/ and Exsitu conservation,
Biodiversity Regulations/ Conservation Efforts in India-
National Park, wildlife sanctuary,
And Disaster International community reserve, Sacred
Management Institutions Groves, Coastal Protected Areas.
Climate Change Project Tiger, Project Elephant,
and Sustainable Project Snow Leopard, Project
Development, Hangul, Vulture Conservation
EIA and Program, MIKE sites, Global
Efforts- Man and Biosphere
Disaster Program, Biosphere Reserves,
Management World Heritage Sites, UNESCO
Global GeoParks, Aichi
Biodiversity Targets, Mangroves
for Future. CITES, TRAFFIC,
Bonn Convention.,
• Acts and Bodies: Biodiversity Act,
2002, Wildlife Act, 1972-
Schedule-1,2,3,4,5,6.
Environment Protection Act of
1982, The Protection of Plant
Variety and Farmers Right Act,
2001. National Board for Wildlife,
Central Zoo Authority, National
Tiger Conservation Authority,
wildlife crime control bureau.
Convention on Biological
Diversity, Cartagena, Nagoya,
Kigali, Basel, Rotterdam,
Svalbard seed vault, Ramsar
Convention. Convention to
Biodiversity (CBD)-COP-14, UN
OCEAN Conference- Blue Deal,
Glo-Litter, Marine Protected
Areas, Indo-Pacific Oceans
Initiative (IPOI), Kunming
Declaration, Kunming Biodiversity
Fund, International Fund for
Agricultural Development (IFAD),
Food and Agriculture
Organisation (FAO), International
Tropical Timber Organisation
(ITTO), United Nations Forum for
Forests (UNFF), Coalition Against
Wildlife Trafficking (CAWT),
Globally Important Agricultural
Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
• National: Environmental Laws:
Provisions in the Indian
Constitution towards
Environmental Protection Salient
Features of - Air (Prevention and
Control of Pollution) Act,1981;
Water (Prevention and Control of
Pollution) Act, 1974, Forest
Conservation Act I980, Wildlife
Protection Act,1972, Environment
(Protection) Act,1986, Public
Liability Insurance Act 1991, NGT
Act 2010, CAMPA Act 2016, Fly
Ash Utilization rule, 2016 with
recent amendments.
• Role of Government in
Environmental Protection:
Environment-related Institutions
and Organizations, Pollution
Control Boards, National Green
Tribunal; Forest Survey of India,
National Board for Wildlife; Land
Degradation Neutrality; Regional
Project on Stubble Burning,
National Afforestation Program,
National Air Quality Index (AQI),
National Action Programme to
Combat Desertification, Bharat
Stage Norms
• Schemes: National Mission for
Clean Ganga, India Signs Global
Environment Facility, Grant Wood
in Good Campaign. Boat Lab to
Study the Brahmaputra, National
River Conservation Plan National
Mission for Clean Ganga, Wildlife
Action Plan - SECURE
Himalayas, Strategic Plan for
Human-Elephant Conflict, Save
the Sparrow, Special Protection
Force for Rhinos; Biodiversity
Heritage Site - Ameenpur Lake,
Energy Conservation- Building
Code, Blue Flag Pilot Project,
Various waste management rules
- Hazardous waste management
rule 2008, Solid waste
management rule 2016,
Construction and demolition
waste management rule, 2018,
Bio-Medical Waste Management
Rules - 2016,
• International: UNFCCC, KYOTO
Protocol- Mechanism under
Kyoto-CDM, Global Environment
Facility, REDD+, Climate Smart
Agriculture, IPCC, TEEB,
Ecological footprint, Clean
Technology Fund, Green
environment Fund, C-40 Initiative,
Conservation International,
CCAC, Global Methane Initiative,
IRIS, CDRI. CoP3-Kyoto, CoP13-
Bali, CoP15-Copenhagen,
CoP16-Cancun, CoP19-warsaw,
CoP20-Lima, CoP21-Paris,
Cop22-Marrakesh, CoP23-Bonn
Cop26-Glasgow.
• Climate Change: Definition,
Global warming, Green House
Effect, Green House Gases-
CO2, NOx, SF6, Ch4, CFC.
Climate Forcings, Global warming
Potential, Blue Carbon, ozone
depletion. Anthropogenic-
Industry, Agriculture, Energy,
Deforestation, Transporation,
Consumerism., Glacial Retreat,
Ocean Acidification, Sea level
rise, Extreme climatic events,
heat waves, water insecurity,
threats to biodiversity, food
insecurity, Flash flood, Cloud
Burst;
• Mitigation Strategy- Carbon
Sequestration, Carbon sink,
Carbon Offsetting, Carbon Credit,
geo-engineering, alternate
sources of energy, afforestation,
lifestyle change. India's Position
at global fora, Climate Changes in
India, National Action Plan on
Climate Change, Natcom,
Panchamrit, Renewable Energy
Targets, ISA, LiFE, FAME,
GRIHA, NICRA, Bonn Challenge,
CAMPA, National clean energy
fund, Joint Forest Management.
• Sustainable Development:
Definition, Need of Sustainable
Development, History- Club of
Rome, Brundtland Commission,
Eco-Development, Principles of
Sustainability, Measure of
Sustainability, Role of
Stakeholders, MDG, SDG, Earth
summit, Sustainable development
In India, Programme and Action,
Challenges to sustainable
Development, Global sustainable
Development Report, Way
Forward. WSDS, Role of TERI.
• Environmental Impact
Assessment, Government Body
which Executes EIA,
Environmental Effects Analysed
under EIA Process
• Disaster and disaster
management
3.9.2023 ACT-1 Art and Indian • IVC- Various sites associated with
Culture Architecture, Architecture. Their significance
Sculpture and and location. Sculptures, figurines
& seals.
Pottery
• Mauryan Architecture- Ashokan
Pillars, Stupas, Cave
Architecture- Chaitiyas & Viharas,
Sculptures. Post Mauryan
Features of three schools of art-
Gandhara, Mathura, Amaravati.
Rock cut caves.
• Gupta period- Cave Architecture-
Ajanta, Ellora, Bagh, Nasik etc
Temple Architecture – Nagara
Style.
• Temple Architecture in South
India -Pallava style, Dravidian
Style- Chola temples, Vesara
Style, Nayaka school, Hoysala
Style, Pala school of temples.
• Medieval / Islamic Architecture-
Delhi Sultanate- Different
characteristics and introduction of
new features of various
dynasties- The Mamluks, Khiljis,
Lodhis.
• Mughal Architecture – Features
and important structures.
Provincial Styles- Bengal, Malwa,
Rajputana.
10.9.2023 ACT-2 Art and Religion and • Religions and Philosophies:
Culture Schools of Buddhism, Jainism, Lingayats,
Philosophy Sikhism, Sufi, Silsilah, Hinduism,
Schools of Philosophy, Samkhya,
Literature and Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Purva
Scholar Mimamsa, Uttara Mimamsa or
associated with Vedanta
Indian • Ancient India – Vedas,
Paintings Brahmanas, Aranyakas,
Upanishads, Ramayana,
Mahabharata, Puranas. Sanskrit
Literature - Prose, Drama &
Poetry - Works of court poets like
Indian Music Kalidasa, Sudraka, Bhasa of
(Folk and Ancient, Medival India.
Classical) • Pali & Prakrit Literature: Jain
Indian Dance texts- Angas, Upangas. Buddhist
Forms (Folk and – Canonical (Tripitakas) and non-
canonical (Jatakas).
Classical)
• Persian/Arabic Literature - Works
Indian of court historians of Delhi
Puppetry, Fairs Sultanate, Mughals, Bahminis.
and Festivals Ain-i-Akbari by Abul Fazl, Tarikh-i-
Cultural Firozshahi by Barauni
Institutions in • Indian Paintings: Prehistoric
India Paintings Cave paintings in
Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic,
Chacolithic periods. Their
location, colors, themes. Mural
Paintings- Ajanta, Ellora,
Sittanavasal etc. Miniature
paintings – Mughal Era Regional
Paintings Different Schools-
Rajasthani, Pahari, Kishangarh,
Bundi, Kangra, Basholi, Tanjore.
Folk Paintings Madhubani,
Pattachitra, Kalighat,Pattua,
Kalamkari, Warli etc..
• Indian Music: Classical Music-
Hindustani and Carnatic Forms-
Their features and styles. Folk
Music- Pandwani, Lavani,
Dandiya, Wanawan, Khonjom
Parwa etc.
• Dance Forms: Classical dance
forms- Bharatanatyam,
Kuchipudi, Mohiniyattam, Odissi,
Kathakali, Sattriya, Manipuri,
Kathak. Folk dances- Chauu,
Raslila, Garba, Dandiya,
Ghoomar, Padayani etc
• Indian Puppetry: String Puppets-
Kathputli, Bommalatam. Shadow
Puppets- RavanChayya, Togalu
Gombayetta. Rod puppets-Putul
Nautch, Yampuri.
• Fairs & Festivals: Important Tribal
and Northeast festivals. Ex-
Losar, Wangala, Bihu.
• Indian Theatre: Ritual theatres of
different traditions like Ankianat,
Ramlila. Entertainment theatre
forms- Tamasha, Nautanki,
Swang etc.
17.9.2023 SIPI-1 Social Social issues+ • Salient features of Indian Society,
Issues+Post Post Diversity of India.
independenc Independence • Role of Women and Women’s
Organization, Population and
e (for
Associated Issues, Poverty and
subjective Developmental issues,
test only) Urbanization, their problems and
their remedies.
• Effects of Globalization on Indian
society.
• Social Empowerment,
Communalism, Regionalism &
Secularism.
• Post Independence consolidation
and reorganization within the
country
1.10.2023 MIHT Modern Fall of Mughals • Social, Economic, and Political
-1 Indian and Advent of structure of the 18th and the first
History European half of the 19th Century India
Crisis of Mughal Empire, Nadir
Consolidation Shah Invasion, and Weakening of
of the British the North-West Succession
Empire in India states, Regional states, and new
Revolt of 1857 states of the 18th Century Advent
Early of Europeans in India.
Nationalist • British supremacy over other
colonial powers and Indian
Movements till
powers, British Expansion and
1884 Socio Consolidation in India: Carnatic
Religious Wars Rise and fall of Mysore,
Reform Anglo-Mysore Wars Rise,
Movements in Marathas, Anglo-Maratha Wars,
19th and 20th Conquest of Bengal: Battles of
Plassey and Buxar, Governor
century
Generals, Subsidiary Alliance,
and Doctrine of Lapse, British
Administration before 1857
• Revolt of 1857: Reasons,
Leaders, Important events,
Indian Freedom Consequences etc.
Struggle-1 • Early Nationalist Movements,
Factors in the Growth of Modern
Nationalism, Organisations like
Indian Association and their role
till 1884.
• Rise of Extremism during Indian
National Movement, Difference
between Moderates and
Extremists, Surat Split, Muslim
League, Morley Minto reforms,
Gadar Movement, Lucknow Pact,
Home Rule Leagues, August
Declaration of 1917, Montagu-
Chelmsford Reforms,
Revolutionary Nationalism and
Personalities, HRA, HSRA,
Bengal Armory Raid, etc.
• Beginning of Gandhian Era, Early
movements, Rowlatt Act and
Satyagraha, Jallianwala Bagh
massacre and Reactions.
• Congress-Khilafat Swaraj Party,
Simon Commission, Purna
Swaraj, Gandhi Irwin Pact,
Lahore Resolution, Karachi
Resolution, Civil Disobedience
Movement, Poona Pact.
• Social Reform Movements and
Personalities: Raja Rammohan
Roy and Brahmo Samaj,
Prarthana Samaj, Young Bengal
Movement and Henry Vivian
Derozio, Ishwar Chandra
Vidyasagar, Balshastri
Jambhekar, Paramahansa
Mandali, Satyashodhak Samaj
and Jyotiba or Jyotirao Phule,
Gopal Hari Deshmukh
‘Lokahitawadi’, Gopal Ganesh
Agarkar
• Important Organisations: The
Servants of India Society, Social
Service League, The
Ramakrishna Movement and
Swami Vivekananda, Dayananda
Saraswati and Arya Samaj, Social
Reforms movement in the south,
Caste Movements, Women
Rights etc.
8.10.2023 MIHT Modern Indian Freedom • Indian provincial elections of
-2 Indian Struggle-2 1937, Formation and Resignation
History + And World of Congress Ministries,
Nationalists’ response to the
World History History (for Second World War, Nehru Report
subjective test and Reactions, Government of
only) India Act, 1935.
• Important Events: August Offer,
Individual satyagraha, Cripps
Proposals, Quit India Movement,
Wavell Plan and Shimla
Conference, C R Formula,
Cabinet Mission Plan
• Important Personalities,
Governors-Generals and
Viceroys, Indian National Army,
INA trials and Reactions, Indian
Independence with Partition.
• Peasants and Tribal Movements
and Organizations, Important
Workers Movements and
Organizations
• Industrial revolution
• Colonization
• Decolonization
• World wars
• Redraw of national boundaries
• Political philosophies such as
capitalism, socialism,
communism, etc. – their forms
and consequences on society.
22.10.202 E-1 Ethics Ethics- • Ethics and Human Interface:
3 Philosophy Essence,
Determinants and Consequenc
es of Ethics in - Human Actions;
Dimensions of Ethics; Ethics - in
Private and Public
Relationships. Human Values -
Lessons from the Lives and
Teachings of Great Leaders,
Reformers and Administrators;
Role of Family Society and
Educational Institutions in
Inculcating Values.
• Attitude: Content, Structure,
Function; its Influence and
Relation with Thought and
Behaviour; Moral and Political
Attitudes; Social Influence and
Persuasion.
• Aptitude and Foundational
Values for Civil Service,
Integrity, Impartiality and Non-
partisanship, Objectivity,
Dedication to Public Service,
Empathy, Tolerance and
Compassion towards the
weaker-sections.
• Emotional Intelligence-
Concepts, and their Utilities and
Application in Administration
and Governance.
• Contributions of Moral Thinkers
and Philosophers from India and
World.
29.10.202 E-2 Ethics Ethics in • Public/Civil Service Values and
3 Governance Ethics in Public Administration:
Status and Problems; Ethical
Concerns and Dilemmas in
Government and Private
Institutions; Laws, Rules,
Regulations and Conscience as
Sources of Ethical Guidance;
Accountability and Ethical
Governance; Strengthening of
Ethical and Moral Values in
Governance; Ethical Issues in
International Relations and
Funding; Corporate Governance.
• Probity in Governance: Concept
of Public Service; Philosophical
Basis of Governance and Probity;
Information Sharing and
Transparency in Government,
Right to Information, Codes of
Ethics, Codes of Conduct,
Citizen’s Charters, Work Culture,
Quality of Service Delivery,
Utilization of Public Funds,
Challenges of Corruption.
5.11.2023 E-3 Ethics Case Studies • Comprising all the syllabus of E-1
and E-2
12.11.202 ET-1 Economy National • Introduction to macro-economics,
3 Income evolution, Types of goods like
Accounting, consumption, capital etc. Terms
like gross investment,
Macro and depreciation and their
Micro relationship, Meaning of GDP,
Economics and GNP etc, their comparison,
Terminology concepts like real and nominal
Money and GDP, Income, Value added and
Expenditure methods of GDP
Banking calculation, Recent changes in
methods and their analysis
• Micro-economics: Demand and
supply Choices, Preferences,
Utilities, Normal, Inferior, Luxury,
Giffen goods, Complement,
Substitute, Neutral goods;
Elasticity of demand, Types of
input market, Types of output
market, General equilibrium,
Market failure, Externalities,
Welfare Economy, Meaning,
important concepts-demand
curve, marginal cost of
production, opportunity cost, law
of diminishing return, substitution
effect, veblen goods
• Money: Types, functions,
evolution, demand; Demand:
Liquidity preference theory,
Liquidity trap, Money-supply,
Deposits (types- narrow, broad),
creation by banking system-
money multiplier terms, high
powered money, Bank Rate,
Factors affecting money supply,
Digital money, digital payment
system, Cryptocurrency,
Blockchain Technology, etc.
Central bank digital currency;
• Development of the Banking
System in India, Types of banks
in India, RBI Act 1934, RBI and its
functions, Banking Regulation
Act, Bank Nationalization, Basel
norms, non-banking financial
Institutions, Banking reforms,
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code,
• Monetary Policy - Evolution of
Monetary policy in India, Role of
RBI in monetary policy,
Instruments of Monetary Policy
and their impacts, Key Interest
Rates, Policy Rates and Reserve
Ratios, Role of RBI in Debt
Management, Monetary Policy
Committee and Inflation
Targeting.
19.11.202 ET-2 Economy Financial Sector • Concept and functions of financial
3 and Inflation markets, Instruments of money
Fiscal Policy/ market, Types of the capital
market, Distinguish between
Public Finance/ capital market and money market,
Budget/ Types and Examples of Bond and
Economic securities, Stock Exchanges of
survey India, Role of SEBI
• Insurance Industry - Insurance
Industry and Reforms, Role of
regulators viz. IRDA etc.
• Inflation - Deflator, difference of
core and non-core sectors,
Instruments to measure prices
like CPI, WPI and IIP etc.
• Public Finance and Budgeting:
Definition, Types, Terminologies,
Processes, etc. Gender
budgeting, Green budgeting,
Zero-based budgeting, etc.,
Receipts and expenditure,
Deficits: Fiscal, Revenue,
Effective Revenue, Primary,
Monetized, etc., Deficit Financing-
FRBM Act and amendments
Fiscal Policy
• Taxation System in India:
Classification, tax rate, effects,
Various other dimensions of
Taxation: methods (Progressive,
Regressive, proportional, etc.),
Fiscal reforms, Fiscal drag, Fiscal
consolidation, Direct Tax Code,
problems in implementation GST
and various dimensions, National
Anti-Profiteering Authority,
Subsidies: Dimensions and
Rationalization, Financial Stability
and Development Council
(FSDC), Financial Stability
Report, Public Debt Management
Cell, Base Erosion and Profit
Shifting, Global Minimum
Corporate Tax, Tax Buoyancy, Tax
Avoidance, GAAR, Financial Data
Management Centre, Public
Financial Management System,
Recent trends in Fiscal policy.
26.11.202 ET-3 Economy Balance of • Open economy- leakage, degree
3 Payment and of openness etc., Balance of
International Payments- current and capital
account (Surplus and Deficit-
Institutions trade deficits (current and
Planning/ capital), Transactions
Infrastructure/ (autonomous and
Industry accommodating), Foreign
Exchange Market (terms-
exchange and nominal rate,
purchasing power parity, NEER
and REER, exchange rate
determination-evolution (from
fixed - gold standard to
managed)-fixed, flexible and
floating, capital account
convertibility, relation of trade
deficit with saving and
investment. International
Institutions - WTO, Bretten
Woods Institutions - World Bank
Group (IBRD, IDA, MIGA, IFC
and ICSID) and IMF etc.
• Role of planning, Objectives of
planning, Criticism of planning
system in India., Role of NITI
Aayog, Meaning of resource
mobilisation and its components
like Savings -Public and Private,
FDI and FII, Types of investors
like angel investors, venture
capital, and the significance of
international financial institutions
like WB, IMF, AIIB, and New
Development bank, Keynesian
Model of economic growth, Major
trends and historical record in
India's growth (especially
comparison between pre-reform
and post-reform performances) of
various sectors of the economy,
Growth, Employment and Labour
Reforms, Technology and
Innovation, Industry. Economic
inequality in India after economic
reforms.
• Infrastructure- Roads, Aviation,
Railways, Inland waterways,
UDAN, SAGARMALA, NHAI, etc.
Industrial policy reforms, Trade
policy reforms, public sector
reforms, financial sector reforms,
capital market reforms and their
effects on industrial growth,
Evolution of PPP in India, BOT,
BOOT, EPC, ETC, HAM, FDI vs
FII.
3.12.2023 ET-4 Economy Human • Human Development and its
Resources and index, Inclusion: education, health
Development management system, skill
development, nutrition, India's
"Agricultural demographic transition and socio-
Inputs economic factors impacting it.
Agriculture Issues regarding employment:
land reforms trends in employment (structure
and Important and distribution of employment),
crops Labour reforms, etc.
• Unemployment: Definition and
Types, Causes of unemployment
in India, Measurement of
Unemployment in India,
Unemployment Trends in India.
• Poverty- Concept and dimensions
of Poverty, Measurement and
Methodologies to estimate
Poverty Line in India, Types and
Causes of Poverty, Hunger,
Malnutrition, Stunting, etc.
Multidimensional Poverty in India;
Characteristics of a developing
country: like lower levels of living,
productivity, human capital, high
population growth, dependency
burden, rural to urban migration,
inequality and absolute poverty,
dependence on agriculture and
low level of Industrialisation etc.
• Agricultural zones in India, Crop
and its Classification, Tillage,
Cropping System and Pattern,
Farming System, Sustainable
Agriculture, Organic Farming,
Integrated Farming System, Soil,
Seeds, Credit structure, Irrigation,
etc. Minimum Support Price
Agricultural Subsidies Crop
Insurance in India, Agricultural
Outputs: Infrastructure.
• Market reforms, Harvesting, etc.
Agriculture Price Policy (APP) in
India, Agri-Market Infrastructure
Fund, Agriculture Extension FCI,
NABARD, etc. Food security in
India, Public Distribution System,
Food processing, Mega Food
Park.
• Important crops: Rice (including
Plantation methods) Wheat,
Maize, Millets, Jowar, Bajra, Ragi,
Barley, Pulses, Cotton, Jute,
Sugarcane, Tobacco, Oilseeds,
Groundnut, Palm, Oil, Tea,
Coffee, Rubber etc.
10.12.202 ST-1 Science and Biology, • History and Origin of Life,
3 Technology Biotechnology Chemical Building Blocks of Life,
and IPR Health Diversity of Living Things-
Classification and Domains of
and Diseases Life, Viruses, Prokaryotes,
Eukaryotes Protists, Plants,
Nanotechnolog • Genetic engineering - process
y and Nuclear and application, Genomics,
Technology, Proteomics, RNA types and
Space technology Genome sequencing
and its applications, Genome
Technology
India Project,
Information Xenotransplantation, Biorrap
Technology, Portal, Heterologous Booster
Emerging Vaccine, CAR T Cells, GRAM-
Technology, Negative Bacteria, TZIELD,
Communication TROPONIN, GENE Drive,
, Defence • Biotechnology and its Application
in Environment- Bio composting,
Bioremediation, Microbial
remediation, Carbon capture
Technology,
• Plant biotechnology - Transgenic
plants, Methods and application
of Plant biotechnology; Animal
Biotechnology - Transgenic
animals, Methods and application
of Animal biotechnology
• Application of Biotechnology in
the Food and beverage industry-
Bio-processing, Biosafety
protocols IPR in Biotechnology,
Recent trends in biotechnology
and applied biotechnology;
• Human Immune System
(Difference of Antibodies,
Antigens & Why Vaccination-
Current Affairs),LUPUS; Diseases
- its Source (Bacteria or Virus or
fungi) , Mode of Transmission
(Water, Air or Sexually
Transmitted) & its Vectors
(Mosquito or bat or Worms),
Disease – Symptoms & its effects
on humans, Tomato Flu, SIDS,
Respiratory Synctial Virus(RSV),
Retinoblastoma, Poliovirus,
Ancovax, Ramsay Hunt
Syndrome, Lumpy Skin Disease,
Heterologous Booster Vaccine,
Aneurysm, Serotonin, Myositis,
Marburg Virus Disease,
Wolbachia, Sickle Cell Disease,
Langya Henipavirus, Lassa
Fever, Legionellosis, Black Death,
Anti-Microbial resistance or Anti
Biotic Resistance, National Policy
for Rare Diseases; World
Zoonoses Day,
• Nanotechnology: carbon
nanotubes, and related
developments, Very Large-Scale
Integration (VLSI), Photonic
Crystals, Cordy Gold
Nanoparticles (COR-AUNPS).
• Nuclear Technology: Types of
nuclear reactions, Nuclear Energy
and its application - Civil and
military applications, Nuclear
fuels and centrifugation Nuclear
Reactor; Nuclear Policy of India,
Nuclear Radiation and its impact,
Radioactive Waste, Nuclear &
Radiological Disasters,
Institutions involved in nuclear
energy Development, Department
of Atomic Energy, Atomic Energy
Regulatory Board, Bhabha Atomic
Research Centre, Indira Gandhi
Centre for Atomic Research;
Becquerel, Gray, Sievert, Gamma
Ray Bursts (GRB).
• Space: Types of Launch Vehicles
and application Space missions
of key space agencies NASA,
ISRO, ESA, ROSCOSMOS,
JAXA, CNSA; ISRO and its role in
national development, Private
sector in space Public-private
partnership in space sector,
MARSQUAKE, SGRA Black Hole
in Milky Way, Cosmic
Cannibalism, ILMT, GAIA Space
Mission, GSAT-24, POEM
platform, Autonomous Flying
Wing Technology, Aryabhat -1,
James Webb Space
Telescope(JWST), Lux-Zeplin
(LZ), AZAADISAT, Danuri-Lunar
Orbiter, Hayabusa-2, Exo-Moon,
Formation of Moon, Space
Situational Awareness
Observatory (SSA), TIANGONG,
Artemis-1 Lunar Mission, Inflated
Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD),
QIMINGXING-50, DART Mission,
Rashid Rover, DARK SKY
Reserve, KUAFU-1, Next-Gen
Launch Vehicle (NGLV),
Sampurnanand Telescope, EMIT
Mission, Coronal Holes, Long
March 5B Rocket, Falcon Heavy
Rocket, Vikram-S, Challenger
Spaceship Disaster, Polluted
White Dwarf Stars, Oceansat-3
Earth Observation Satellite-6,
• Computers- Generation of
computers Computer,
terminologies, Supercomputer
and its applications, Cloud
computing, Information
technology Components of IT, IT
enabled services, Application of
IT; Artificial Intelligence (AI), True
Random Number Generator
(TRNG) Device, PARAM Porul
Supercomputer, RFID
Technology, D2M Technology,
CRYSXPP, PARAM ANANTA,
WEB 5.0, LAMDA, Fiberisation,
Long Range Radio (LORA),
Quantum Entanglement,
BlueBugging,
• Display technologies: Cathode
ray, LCD, LED, Plasma Monitors,
OLED, AMOLED, Mobile
generations - Smartphone; Net
Neutrality, Internet of Things;
• India and global collaboration in
science projects Deepfakes, Web
3.0, Indian Space Association;
• DRDO, Important Missiles, Tech
Components (SPI), Vehicles,
ABHYAS, INS Sindhudhvaj,
Chinook Helicopter, Minuteman
III, VSHORADS Missile, LCH
Prachand, Kamikaze Drone,
Rustom-2, Hawk Air Defence,
Dirty Bomb, Anti-Radiation
Missile,
• Recent technological
developments, emerging
technologies, Deep Sea Mission,
Desalination plants.
17.12.202 IS- 1 Internal Internal • Role of external state and non-
3 Security Security state actors in creating
challenges to internal security.
• Linkages between development
and spread of extremism.
• Challenges to internal security
through communication networks,
the role of media and social
networking sites in internal
security challenges, basics of
cybersecurity; money-laundering
and its prevention
• Various Security forces and
agencies and their mandate
• Security challenges and their
management in border areas;
linkages of organized crime with
terrorism
24.12.202 SJG-1 Social Justice Social Justice+ • Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable
3 And Governance Sections of the population by the
Governance Centre and States and the
Performance of these Schemes;
Mechanisms, Laws,
Institutions and Bodies
constituted for the Protection and
Betterment of these Vulnerable
Sections.
• Issues Relating to Development
and Management of Social
Sector/Services relating to
Health, Education, Human
Resources.
• Issues relating to Poverty and
Hunger.
• Development processes and the
development industry the role
of NGOs, SHGs, various groups
and associations, donors,
charities, institutional and other
stakeholders
• Issues relating to the
development and management of
Social Sector/Services relating
to Health, Education, Human
Resources.
• Important aspects of governance,
transparency, and accountability,
e-governance – applications,
models, successes, limitations,
and potential; citizens charters,
transparency & accountability and
institutional and other measures
• Issues relating to poverty and
hunger
• Role of civil services in a
democracy
31.12.202 FLT-1 GS-1 General Studies • Complete syllabus of GS Paper-1
3 Paper-1
7.1.2024 FLT-2 GS-2 General Studies • Complete syllabus of GS Paper-2
Paper-2
21.1.2024 FLT-3 GS-3 General Studies • Complete syllabus of GS Paper-3
Paper-3
28.1.2024 FLT-4 GS-4 General Studies • Complete syllabus of GS Paper-4
Paper-4
You might also like
- AIM Detailed ScheduleDocument36 pagesAIM Detailed Scheduleragkavya85No ratings yet
- ILP-Decoding Prelims Syllabus: About The DocumentDocument29 pagesILP-Decoding Prelims Syllabus: About The DocumentUr AmanNo ratings yet
- indian-polity-syllabus-for-upsc-791035a7Document8 pagesindian-polity-syllabus-for-upsc-791035a7mehtanamita80No ratings yet
- Prelims CAMP Schedule and Detailed Syllabus-1 PDFDocument17 pagesPrelims CAMP Schedule and Detailed Syllabus-1 PDFsivank yoNo ratings yet
- 09 Schema PolityDocument7 pages09 Schema PolityCse 2025No ratings yet
- Indian Polity Constitution Governance TOCDocument7 pagesIndian Polity Constitution Governance TOCHritika MeenaNo ratings yet
- Law4101 Constitutional-Law - I Eth 1.0 0 Law 4101 Constitutional Law-1Document4 pagesLaw4101 Constitutional-Law - I Eth 1.0 0 Law 4101 Constitutional Law-1Karthik ShivaNo ratings yet
- Political Science (852) : Class XiiDocument5 pagesPolitical Science (852) : Class XiiMariamNo ratings yet
- ILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusDocument5 pagesILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusAryanNo ratings yet
- Test Series Batch Test No: Date Test Series Batch Syll Abus MaterialDocument7 pagesTest Series Batch Test No: Date Test Series Batch Syll Abus Material34_dineshkumarNo ratings yet
- ISC Political Science 040424 2025Document5 pagesISC Political Science 040424 2025hiruko1290No ratings yet
- Blue Simple Mind Map Graph A4 DocumentDocument1 pageBlue Simple Mind Map Graph A4 DocumentAarin ArynNo ratings yet
- Audit Course On Constitutional ClassDocument2 pagesAudit Course On Constitutional ClassecostarNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONAL VALUES JU (1)Document158 pagesCONSTITUTIONAL VALUES JU (1)PRAJWAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- UPSC EPFO 2020-21 Recruitment Test (RT) Syllabus: General EnglishDocument4 pagesUPSC EPFO 2020-21 Recruitment Test (RT) Syllabus: General EnglishBharat WasiNo ratings yet
- 3.-ISC Pol SCDocument5 pages3.-ISC Pol SCsiddhanganaNo ratings yet
- ILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusDocument46 pagesILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusDessaNo ratings yet
- Topic Listing Ilp 2020 IasbabaDocument46 pagesTopic Listing Ilp 2020 IasbabaKalyan valisetty100% (1)
- Theme 5 L2F Lyst3694Document28 pagesTheme 5 L2F Lyst3694RITURAJNo ratings yet
- Doctrineof Basic Structure, Fundamental Rightsand Indian ConstitutionDocument22 pagesDoctrineof Basic Structure, Fundamental Rightsand Indian Constitutionronsingtimung027No ratings yet
- Constitution of India: A 'Bag of Borrowings'Document13 pagesConstitution of India: A 'Bag of Borrowings'kushagra prabalNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India, Law and Engineering QuantumDocument143 pagesConstitution of India, Law and Engineering QuantumKnowledge Factory83% (6)
- CBSE Syllabus For Class 8 Social and Political Life 2023 24Document3 pagesCBSE Syllabus For Class 8 Social and Political Life 2023 24h84144891No ratings yet
- Prelims ScheduleDocument25 pagesPrelims ScheduleKumar mangalamNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - Rights in The Indian Constitution NotesDocument32 pagesPadhle 11th - Rights in The Indian Constitution NotesAafia100% (2)
- Ballb Sem 5 ScheduleDocument3 pagesBallb Sem 5 ScheduleAkansha DwivediNo ratings yet
- Government of Karnataka Department of Collegiate and Technical EducationDocument2 pagesGovernment of Karnataka Department of Collegiate and Technical EducationGPT149 NBANo ratings yet
- TGPSC Group-2 45 Days Plan 2024 - English ScheduleDocument12 pagesTGPSC Group-2 45 Days Plan 2024 - English ScheduleVanam RakeshNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India - B.Tech Coursn e V & VI Semester 2020-21 4th AugustDocument1 pageConstitution of India - B.Tech Coursn e V & VI Semester 2020-21 4th AugustAADITYA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India Law and Engineering QuantumDocument142 pagesConstitution of India Law and Engineering Quantumanandjaiswalanandjaiswal6No ratings yet
- Gs 2Document5 pagesGs 2Narendra KumawatNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Syllabus For APPSC GII ExamDocument1 pageIndian Constitution Syllabus For APPSC GII ExamNoor MohammadNo ratings yet
- Upsc Gs 2 Syllabus PDF 30Document15 pagesUpsc Gs 2 Syllabus PDF 30kaushikgaurav190No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law IDocument2 pagesConstitutional Law IAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of 5 Semester, 3 Year, LL.B. 2020-21 Constitutional Law - IDocument2 pagesSyllabus of 5 Semester, 3 Year, LL.B. 2020-21 Constitutional Law - IPIYUSH SHARMANo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction 301684114945148Document59 pages1 Introduction 301684114945148imsatakshisrivastav21No ratings yet
- LegalStudies SrSec 2022-23Document13 pagesLegalStudies SrSec 2022-23S. Giri Narayanan NarayananNo ratings yet
- ISC Political ScienceDocument6 pagesISC Political ScienceVISHVESH JUNEJANo ratings yet
- 3 Polity Theme 1 Basics, Key Terms, Important Concepts Theme 1 LecDocument11 pages3 Polity Theme 1 Basics, Key Terms, Important Concepts Theme 1 LecanilkumarosmeNo ratings yet
- ILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusDocument1 pageILP 2022 Decoding Prelims SyllabusAryanNo ratings yet
- TOPIC II ASalient Features of The Constitution - 1717420761Document6 pagesTOPIC II ASalient Features of The Constitution - 171742076121bdr15No ratings yet
- Legal StudiesDocument13 pagesLegal StudiesAditi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument4 pagesConstitutionkaswavaishnaviNo ratings yet
- 3sem Political Science (General) Syllabus Calcutta University.Document1 page3sem Political Science (General) Syllabus Calcutta University.Pritilata RoyNo ratings yet
- Schedule - EKLAVYA Integrated Pre Cum Mains - B1Document28 pagesSchedule - EKLAVYA Integrated Pre Cum Mains - B1Tejas GuptaNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument35 pagesConstitutionAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- MAN18R002 Indian Constitution - SyllabusDocument1 pageMAN18R002 Indian Constitution - Syllabussarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- Mains Mains-Syllabus General-studies-II Print ManuallyDocument9 pagesMains Mains-Syllabus General-studies-II Print ManuallyhoqueparvizulNo ratings yet
- Practice Mains Answer Writing 2023-24Document5 pagesPractice Mains Answer Writing 2023-24rahulNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 8 Syllabus For Civics Embibe 5 8Document4 pagesCbse Class 8 Syllabus For Civics Embibe 5 8NILANCHALNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 12 Political Science Syllabus 2023 24Document6 pagesISC Class 12 Political Science Syllabus 2023 24madhurya909No ratings yet
- UPSC GS II SyllabusDocument10 pagesUPSC GS II SyllabusGhouse cyber cafeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus2fgeneral Studies Ii2fprinDocument9 pagesSyllabus2fgeneral Studies Ii2fprinsaurabhs32112No ratings yet
- August 04 DNA Complete CADocument21 pagesAugust 04 DNA Complete CAVijay NairNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document2 pagesPaper 3Sonu SihmarNo ratings yet
- Mains Mains-Syllabus General-Studies-Ii Print ManuallyDocument9 pagesMains Mains-Syllabus General-Studies-Ii Print ManuallySiddhesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- POLITY & Governance Class 1 - 44. (Synopsis) PDFDocument215 pagesPOLITY & Governance Class 1 - 44. (Synopsis) PDFSayalee ParateNo ratings yet
- Upsc Mains GS Paper 2 SyllabusDocument10 pagesUpsc Mains GS Paper 2 SyllabusNaveenNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Function of the Office of Government EthicsFrom EverandUnderstanding the Function of the Office of Government EthicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Modul Kelas Xi 2020-2021Document12 pagesModul Kelas Xi 2020-2021adilNo ratings yet
- Mayon and Taal VolcanoDocument6 pagesMayon and Taal VolcanoYhazmin Iris IlustrisimoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: Structure IsomersDocument2 pagesReviewer in Science: Structure IsomersSharlaine TandinganNo ratings yet
- Ujian Semester Ganjil 2016Document8 pagesUjian Semester Ganjil 2016khofifahNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument16 pagesDRRRAlexa Feliz De PedroNo ratings yet
- Geologi - Stratigrafi Gunung Api PDFDocument155 pagesGeologi - Stratigrafi Gunung Api PDFDavid Halomoan100% (1)
- BELLEZAS NSTP Accomplishment Report With CRADocument8 pagesBELLEZAS NSTP Accomplishment Report With CRAbellezasheena02No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureSheana LopezNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan of Science Grade 10 2nd Set - 1st Quarter: Notre Dame of TabawanDocument3 pagesLearning Plan of Science Grade 10 2nd Set - 1st Quarter: Notre Dame of TabawanEsha HadjulaNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination Grade 9 GeographyDocument5 pagesAnnual Examination Grade 9 GeographybjdevhervehroheghghbhbhotbhhortbhNo ratings yet
- STEM11 - Earth Science NotesDocument28 pagesSTEM11 - Earth Science NotesPatricia Gabriell MulaNo ratings yet
- San Enrique Polytechnic Academy - Docx 4TH QuarterDocument9 pagesSan Enrique Polytechnic Academy - Docx 4TH QuarterUnibelle Joy LachicaNo ratings yet
- 3144 01 MS 3RP AFP tcm143-665873Document12 pages3144 01 MS 3RP AFP tcm143-665873Geeta Aswani100% (2)
- G10 Q1 Module 1Document31 pagesG10 Q1 Module 1Mikaela FabrosNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 ScienceDocument46 pagesCot 2 ScienceShrun ShrunNo ratings yet
- Dinosaurs 123Document25 pagesDinosaurs 123Caturya Windy Cita MaellyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 2272 Humanities Geography Elective AnswersDocument9 pages2018 2272 Humanities Geography Elective AnswersjackhelmanNo ratings yet
- Jonalyn New 11Document4 pagesJonalyn New 11Elvira CuestaNo ratings yet
- Makkah Is The Center of The EarthDocument9 pagesMakkah Is The Center of The EarthWaris Husain100% (1)
- Unit 3 Module 1 Volcano Summative TestDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Module 1 Volcano Summative TestJosaiah De Guzman40% (5)
- Unpacked Melc Science 9Document1 pageUnpacked Melc Science 9Marjorie Brondo100% (1)
- NCERT - Class 7 Geog - GistDocument53 pagesNCERT - Class 7 Geog - GistAjith AjNo ratings yet
- English Mid-Term Exam/Semester 1/2018-2019 24 OCTOBER 201 Answer SheetDocument8 pagesEnglish Mid-Term Exam/Semester 1/2018-2019 24 OCTOBER 201 Answer SheetJang FanNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Criminal Law and Procedure 8th Edition Scheb Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Criminal Law and Procedure 8th Edition Scheb Solutions Manual PDFborderertorn2leu100% (22)
- Volcanoes Sub-topic:Volcanic EruptionDocument16 pagesVolcanoes Sub-topic:Volcanic EruptionVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Igneous Petrology Andri's Lecture NoteDocument84 pagesIgneous Petrology Andri's Lecture Notesuryadi100% (2)
- Text 1Document12 pagesText 1RizkiAmeliaHeryantoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Auditing Assurance Services and Ethics in Australia 9th Edition Arens Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Auditing Assurance Services and Ethics in Australia 9th Edition Arens Solutions Manualpickersgillvandapro100% (32)
- Geothermal Surface Exploration Approach - Case Study of Menengai Geothermal Field, Kenya OyedeleDocument10 pagesGeothermal Surface Exploration Approach - Case Study of Menengai Geothermal Field, Kenya Oyedeleahmad_adenijiNo ratings yet
- Sim DRRM Melc Q2 Week 8 L36 37Document22 pagesSim DRRM Melc Q2 Week 8 L36 37Myrah BurbosNo ratings yet