Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Uploaded by
safwaanraqeeb786786Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 12 AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 12 AnswersBenecia odoguNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Klein 3rd Edition Chapter 7 NotesDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Klein 3rd Edition Chapter 7 NotesShenchu XieNo ratings yet
- Report On Paint MakingDocument31 pagesReport On Paint MakingModesola Shoroye100% (8)
- Mixed Questions AnswersDocument52 pagesMixed Questions Answersmunthalipeggy4No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones MSDocument11 pagesAldehydes and Ketones MSpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Why Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument4 pagesWhy Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukAmelia AkandeNo ratings yet
- Chem OrgDocument3 pagesChem OrgJonel C. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 6.2ionic Bonding MS - 2Document10 pages6.2ionic Bonding MS - 2Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSDocument3 pages2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSZHOU TIN YUI RICHARD G11G-34No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Test MsDocument6 pagesTopic 3 Test Ms576zkpmsp4No ratings yet
- Chem 20 Final ReviewDocument23 pagesChem 20 Final Review22-Rawan AdnanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 2.2 Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 2.2 Electrons, Bonding and StructureHazare 2004No ratings yet
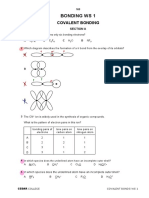
- 1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionDocument3 pages1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- Electrons Bonding and Structure MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument9 pagesElectrons Bonding and Structure MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementdeshanNo ratings yet
- C7 Practice AnswersDocument3 pagesC7 Practice AnswersMo KhNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Shri Pundlik Maharaj Mahavidyalaya Nandura Rly, Dist-BuldanaDocument93 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Shri Pundlik Maharaj Mahavidyalaya Nandura Rly, Dist-BuldanaHalala HajiNo ratings yet
- 1 Lesson 5 - Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument24 pages1 Lesson 5 - Nucleophilic SubstitutionShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesAQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeSarai AliNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument153 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistrydfafsasdNo ratings yet
- Scoring Key For The Sample QPDocument3 pagesScoring Key For The Sample QPSam MishraNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Document25 pagesRedox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Biggos businessNo ratings yet
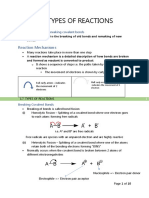
- 1.7. Types of ReactionsDocument10 pages1.7. Types of ReactionsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- (A) (I) M1 Initiation CL 2Cl - : Paddington AcademyDocument7 pages(A) (I) M1 Initiation CL 2Cl - : Paddington AcademyemiliaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25-Sep-2022Document20 pagesAdobe Scan 25-Sep-2022Sukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Chapter 13 2024Document38 pagesAS Chemistry Chapter 13 2024bbcdgg1234567No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument1 pageCarbon and Its CompoundsSK CreationsNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Ionic Bonding (1C) MSDocument10 pages6.1 Ionic Bonding (1C) MSsonnyNo ratings yet
- RXN Mech Otto Lect 5Document21 pagesRXN Mech Otto Lect 5P.No ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions 2 MSDocument5 pagesSubstitution Reactions 2 MSDaSubirNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2Document6 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- 03 Reaction Mechanism (Solution)Document7 pages03 Reaction Mechanism (Solution)Anup KNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2 MSDocument6 pagesIonic Bonding 2 MSshonshaju286No ratings yet
- HALOPP (Halogenoalkanes)Document19 pagesHALOPP (Halogenoalkanes)liofve X viNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document3 pagesChapter 05Thabisile MoyoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 4.2 Alcohols, Haloalkanes and AnalysisDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 4.2 Alcohols, Haloalkanes and AnalysisRizki HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- University Chemistry CH 3Document40 pagesUniversity Chemistry CH 3h911016No ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Document25 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Namrah ZakaNo ratings yet
- Number Answer Notes MarksDocument9 pagesNumber Answer Notes MarksAli FahmiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Note 1Document3 pagesChemical Bonding Note 1youservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- CHEM3220 - Chapter 5 - 2023-24Document22 pagesCHEM3220 - Chapter 5 - 2023-24am0企鵝No ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Document6 pagesAnswer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Tan JennyNo ratings yet
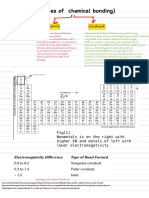
- Electronegativity QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectronegativity QuestionsThe ImmortalNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument8 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenesrajtarabap55No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: SynthesisDocument71 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: Synthesiskrystel pyneeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: What Holds Things Together?Document23 pagesChemical Bonding: What Holds Things Together?baabisoorajNo ratings yet
- As-Level Ap2 Paper 1 MsDocument8 pagesAs-Level Ap2 Paper 1 Msindiaisyourbae123No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Basesapi-3708473No ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Bonding and Structure MSDocument18 pages2.2.2 Bonding and Structure MSSir MannyNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chemistry Model Exam 2021 Ans Key Unoff Anoop ChandranDocument10 pagesHsslive Xi Chemistry Model Exam 2021 Ans Key Unoff Anoop Chandranകായംകുളം കൊച്ചുണ്ണിNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Answers To Examination Style Questions On Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3 Answers To Examination Style Questions On Chapter 3MOMINAH AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Hibridisasi, Reaksi Kimia Organik Dan Isomer: Oleh: Indah Hairunisa S.Farm., M.Biotech ., AptDocument37 pagesHibridisasi, Reaksi Kimia Organik Dan Isomer: Oleh: Indah Hairunisa S.Farm., M.Biotech ., AptRita AspiyantiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesAlkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsellachloedeeksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elimination RXNDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Elimination RXNmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases黃向廷No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ZZZDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry ZZZfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- 2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFDocument16 pages2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- Qn. No. Part - A MarksDocument13 pagesQn. No. Part - A MarkslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Addition by Electrophilic Reagents: BR BR BRDocument4 pagesAddition by Electrophilic Reagents: BR BR BRDaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical BondingmiddenmaeNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Alahazrat and His TaqwaDocument9 pagesAlahazrat and His Taqwasafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Questionssafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- How To Write Essays & Assignments UEL - (Introduction)Document12 pagesHow To Write Essays & Assignments UEL - (Introduction)safwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Task 2 - Student ExamplesDocument28 pagesTask 2 - Student Examplessafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bibliographysafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Anaphy MariebDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Anaphy MariebKeanna ZurriagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11.Document45 pagesChapter 11.HalaNo ratings yet
- Shree Dhootapapeshwar Standards: Ayush Kwath Dispersible TabletsDocument3 pagesShree Dhootapapeshwar Standards: Ayush Kwath Dispersible TabletssmartwaiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Nitrogen Fertilizer Encapsulated Urea Fertilizer in Process of Controlled Release Their Effect On Growth of Chinese Kale Brassica Alboglabra BaileyDocument10 pagesImpact of Nitrogen Fertilizer Encapsulated Urea Fertilizer in Process of Controlled Release Their Effect On Growth of Chinese Kale Brassica Alboglabra BaileyLeonardo EstradaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology in CartoonsDocument164 pagesBiotechnology in CartoonsMonica Zapata100% (1)
- No Title Available - 2013 - Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable PlasticsDocument16 pagesNo Title Available - 2013 - Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable PlasticsJiankun YangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document21 pagesChapter 12Suganthi AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- 152 809 2 PBDocument12 pages152 809 2 PBsujal jhaNo ratings yet
- 2020 GADSL Reference List ProdDocument220 pages2020 GADSL Reference List ProdParom WaikasikarnNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design and Scale Up of Lactic Acid Production From Fermentation-Derived Magnesium LactateDocument6 pagesConceptual Design and Scale Up of Lactic Acid Production From Fermentation-Derived Magnesium LactateNial HoerunNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of DNADocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of DNASamreen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Frictional and Optical PropertiesDocument28 pagesFrictional and Optical PropertiesJoselyn GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Homemade Organic Insecticide With The Use of Lemongrass Oil-ESDocument4 pagesHomemade Organic Insecticide With The Use of Lemongrass Oil-ESNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Chloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyDocument7 pagesChloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyChloe TroulanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 13&14Document9 pagesChemistry 13&14Jhonvic AllitorabNo ratings yet
- Bee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care: ReviewDocument17 pagesBee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care: ReviewwizuraihakimroyNo ratings yet
- Pollution: OllutionDocument7 pagesPollution: OllutionPhilobatir SamehNo ratings yet
- October 16, 2020 BS-Biology 1-2 Ej M. FerrerDocument3 pagesOctober 16, 2020 BS-Biology 1-2 Ej M. FerrerEj FerrerNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 2Document20 pagesCarboxylic Acid 2brettNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QO1-1Document3 pagesEjercicios QO1-1hector juarezNo ratings yet
- Are Nanoclay Containing Polymer Composites Safe For Food Packaging. 2019Document22 pagesAre Nanoclay Containing Polymer Composites Safe For Food Packaging. 2019yurinnelNo ratings yet
- Mesomeric Effect Et AlDocument7 pagesMesomeric Effect Et AlAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Q, S, U, V, W, X, Y, Z Januari 2021Document10 pagesQ, S, U, V, W, X, Y, Z Januari 2021Mutmainnah PeaceNo ratings yet
- Green Earth ProjectDocument9 pagesGreen Earth ProjectLouise DominguezNo ratings yet
- 6-IR Spectroscopy of Alkane, Alkene and Carbonyl CompoundsDocument8 pages6-IR Spectroscopy of Alkane, Alkene and Carbonyl Compoundsbloodhound13042005No ratings yet
- Desmodur Z 4470 BA - en - 04465350 12978466 13462745Document3 pagesDesmodur Z 4470 BA - en - 04465350 12978466 13462745RICHNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesOrganic-Chemistry Hydrocarbonsxyrruschloe06No ratings yet
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Sources Effects andDocument9 pagesEndocrine Disrupting Chemicals Sources Effects andgranapadanomonsterNo ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument36 pagesDna and RnaMoona MalikNo ratings yet
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Uploaded by
safwaanraqeeb786786Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Chapter 13 Exam Style Answers
Uploaded by
safwaanraqeeb786786Copyright:
Available Formats
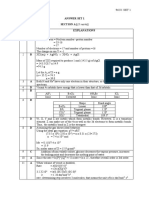
13 Halogenoalkanes
AQA Chemistry Exam-style mark scheme
Question
Answer Marks Guidance
number
1a Electron pair donor 1
OR
Species which uses a pair of electrons to form a co-
ordinate / covalent bond.
1b Replacement of the halogen (atom) (by the 1 They must describe the idea of
nucleophile) substitution in a halogenoalkane.
OR Penalise reference to ‘halogen
molecule’ and penalise the idea
The carbon–halogen bond / C–X breaks and a bond
forms with the nucleophile or between the carbon that the halogenoalkane contains
and the nucleophile. a halide.
1c Splitting molecules using / by water 1 NOT simply the reaction with
water or simply the addition of
OR
water.
breaking / splitting / dissociating (C–X) bond(s) /
Ignore ‘compound’.
using / by water.
1d Heat energy / enthalpy required / needed / absorbed 1 Ignore bond formation.
to break / split it / the carbon–halogen bond
OR
Heat energy / enthalpy required / needed / absorbed
Ignore ‘average’.
(at constant pressure) for homolysis of the (C–X /
the carbon–halogen) bond.
2ai 1 Insist on C–OH bond.
Do not allow 2-hydroxypropane.
1
propan-2-ol
2 a ii nucleophilic substitution 1 Both words needed for mark.
Do not allow SN1 or SN2.
2 Penalise incorrect polarity on
C–Br (M1).
If SN1, both marks possible.
2bi Elimination 1
2 b ii base OR proton acceptor 1 Do not accept nucleophile.
3ai An electron pair donor 1 Answer must refer to an electron
pair.
OR
‘Attracted’ does not equal
forms a covalent or co-ordinate or dative bond by
‘donated’.
donating a pair of electrons.
3 a ii Penalise M1, if covalent NaOH is
used.
Penalise M2 for formal charge on
C or incorrect partial charges.
M1 must show an arrow from the lone pair of
electrons on the oxygen atom of the negatively Penalise once only for a line and
charged hydroxide ion to the central C atom. 1 two dots to show a bond.
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 1
13 Halogenoalkanes
AQA Chemistry Exam-style mark scheme
Question
Answer Marks Guidance
number
M2 must show the movement of a pair of electrons Max 1 mark for the wrong
from the C–Br bond to the Br atom. Mark M2 reactant.
independently.
1 Award 1 mark only for C–Br bond
breakage, if an SN1 mechanism
is used.
Do not penalise the use of ‘sticks’.
3bi Structure of the tertiary carbocation (CH3)3C or 1 Insist on a full positive charge on
drawn out the central C atom.
Penalise a bond to the positive
charge.
3 b ii Tertiary carbocation / carbonium ion (from 2-bromo- 1 Ignore reference to the alleged
2-methylpropane) is more stable (than the primary relative stability of
carbocation / carbonium ion). halogenoalkanes.
OR
Primary carbocation / carbonium ion (from 2-bromo-
2-methylpropane) is less stable (than the tertiary
carbocation / carbonium ion).
4ai
1
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 2
13 Halogenoalkanes
AQA Chemistry Exam-style mark scheme
Question
Answer Marks Guidance
number
4 a ii 1
1
2-chloro-2-methylbutane
4bi Elimination 1
4 b ii Alkene A and B (in any order) 1
1
Alkene C
4 b iii Alkene C has a CC bond, but does not have two 1
different groups attached to the end carbon atom.
5 Mr of CF3CHBrCl 197.4 1
3.948 ´ 10–4 ´ 103
Moles of halothane
197.4
0.002 1
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 3
13 Halogenoalkanes
AQA Chemistry Exam-style mark scheme
Question
Answer Marks Guidance
number
Number of molecules 0.002 6.02 1023
1
1.204 1021
(1.204 ´ 1021 ´ 500 ´ 10–6 )
Molecules in 500 cm3
150 1
4.01 1015
6a 2-bromobutane 1
6b Elimination 1
Curly arrow from lone pair on oxygen of hydroxide
ion to H atom on correct C–H adjacent to C–Br. 1
Curly arrow from single bond of adjacent C–H to
adjacent single bond C–C. 1
Curly arrow from C–Br bond to side of Br atom. 1
6ci Structural isomers have the same molecular 1
formula, but different structural formulas / different
structures.
6 c ii Correct structure for but-1-ene: 1
7ai M1 Elimination 1 For M1, accept ‘Base elimination’,
but no other prefix.
1
Penalise M2, if covalent KOH.
1
Penalise M4 for formal charge on
1
C of C–Br OR incorrect partial
M2 must show an arrow from the lone pair on the charges on C–Br.
oxygen of a negatively-charged hydroxide ion to a
Ignore other partial charges.
correct H atom.
Penalise once only in any part of
M3 must show an arrow from a C–H bond adjacent
the mechanism for a line and two
to the C–Br bond towards the appropriate C–C
dots to show a bond.
bond. Only award if a reasonable attempt has been
made at the attack on the H atom of the appropriate Max any 2 of 3 marks for the
adjacent C–H. mechanism for wrong reactant (or
wrong product if shown).
M4 is independent, provided it is from their original
molecule.
Award full marks for an E1 mechanism in which M3
is on the correct carbocation.
7 a ii Structure for pent-1-ene: 1 Penalise C3H7.
CH3CH2CH2CHCH2
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 4
13 Halogenoalkanes
AQA Chemistry Exam-style mark scheme
Question
Answer Marks Guidance
number
7b M1 Electrophilic addition 1 For M1, both words required.
1 For the mechanism
1 M2 Ignore the partial negative
charge on the double bond.
1
M3 Penalise partial charges on
1
the Br–Br bond, if wrong way and
penalise formal charges.
M2 must show an arrow from the double bond Penalise once, only in any part of
towards the Br atom of the Br–Br molecule. the mechanism for a line and two
M3 must show the breaking of the Br–Br bond. dots to show a bond.
M4 is for the structure of the tertiary carbocation, Max any 3 of 4 marks for the
with Br on the correct carbon atom. mechanism for wrong organic
reactant or wrong organic produce
M5 must show an arrow from the lone pair of (if shown) or primary carbocation.
electrons on the negatively charged bromide ion
towards the positively charged carbon atom. If HBr is used, max 2 marks for
the mechanism.
7c M1 Nucleophilic substitution 1 For M1, both words required.
1 Penalise M2 if NH3 is negatively
charged.
1
Penalise M3 for formal charge on
1
C or incorrect partial charges.
1
The second mole of ammonia is
M2 must show an arrow from the lone pair of not essential for M5; therefore
electrons on the nitrogen atom of an ammonia ignore any species there.
molecule to the C atom.
Penalise once only for a line and
M3 must show the movement of a pair of electrons two dots to show a bond.
from the C–Br bond to the Br atom. M3 is
independent, provided it is from the original Max any 3 of 4 marks for the
molecule. mechanism for wrong organic
reactant (or wrong organic product
M4 is for the structure of the alkylammonium ion, if shown).
which could be a condensed formula. A positive
charge must be shown on / close to the N atom. Accept the correct use of ‘sticks’.
M5 is for an arrow from the N–H bond to the N atom.
Award full marks for an SN1 mechanism, in which
M2 is the attack of the ammonia on the intermediate
carbocation.
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 5
You might also like
- Chapter 12 AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 12 AnswersBenecia odoguNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Klein 3rd Edition Chapter 7 NotesDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Klein 3rd Edition Chapter 7 NotesShenchu XieNo ratings yet
- Report On Paint MakingDocument31 pagesReport On Paint MakingModesola Shoroye100% (8)
- Mixed Questions AnswersDocument52 pagesMixed Questions Answersmunthalipeggy4No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones MSDocument11 pagesAldehydes and Ketones MSpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Why Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument4 pagesWhy Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukAmelia AkandeNo ratings yet
- Chem OrgDocument3 pagesChem OrgJonel C. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 6.2ionic Bonding MS - 2Document10 pages6.2ionic Bonding MS - 2Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSDocument3 pages2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSZHOU TIN YUI RICHARD G11G-34No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Test MsDocument6 pagesTopic 3 Test Ms576zkpmsp4No ratings yet
- Chem 20 Final ReviewDocument23 pagesChem 20 Final Review22-Rawan AdnanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 2.2 Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 2.2 Electrons, Bonding and StructureHazare 2004No ratings yet
- 1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionDocument3 pages1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- Electrons Bonding and Structure MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument9 pagesElectrons Bonding and Structure MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementdeshanNo ratings yet
- C7 Practice AnswersDocument3 pagesC7 Practice AnswersMo KhNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Shri Pundlik Maharaj Mahavidyalaya Nandura Rly, Dist-BuldanaDocument93 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Shri Pundlik Maharaj Mahavidyalaya Nandura Rly, Dist-BuldanaHalala HajiNo ratings yet
- 1 Lesson 5 - Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument24 pages1 Lesson 5 - Nucleophilic SubstitutionShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesAQA Chemistry: 17 Thermodynamics Exam-Style Mark SchemeSarai AliNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument153 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistrydfafsasdNo ratings yet
- Scoring Key For The Sample QPDocument3 pagesScoring Key For The Sample QPSam MishraNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Document25 pagesRedox Reaction and Electrochemistry (C-Inpo)Biggos businessNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Types of ReactionsDocument10 pages1.7. Types of ReactionsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- (A) (I) M1 Initiation CL 2Cl - : Paddington AcademyDocument7 pages(A) (I) M1 Initiation CL 2Cl - : Paddington AcademyemiliaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25-Sep-2022Document20 pagesAdobe Scan 25-Sep-2022Sukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Chapter 13 2024Document38 pagesAS Chemistry Chapter 13 2024bbcdgg1234567No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument1 pageCarbon and Its CompoundsSK CreationsNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Ionic Bonding (1C) MSDocument10 pages6.1 Ionic Bonding (1C) MSsonnyNo ratings yet
- RXN Mech Otto Lect 5Document21 pagesRXN Mech Otto Lect 5P.No ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions 2 MSDocument5 pagesSubstitution Reactions 2 MSDaSubirNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2Document6 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- 03 Reaction Mechanism (Solution)Document7 pages03 Reaction Mechanism (Solution)Anup KNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2 MSDocument6 pagesIonic Bonding 2 MSshonshaju286No ratings yet
- HALOPP (Halogenoalkanes)Document19 pagesHALOPP (Halogenoalkanes)liofve X viNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document3 pagesChapter 05Thabisile MoyoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 4.2 Alcohols, Haloalkanes and AnalysisDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz 4.2 Alcohols, Haloalkanes and AnalysisRizki HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- University Chemistry CH 3Document40 pagesUniversity Chemistry CH 3h911016No ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Document25 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Namrah ZakaNo ratings yet
- Number Answer Notes MarksDocument9 pagesNumber Answer Notes MarksAli FahmiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Note 1Document3 pagesChemical Bonding Note 1youservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- CHEM3220 - Chapter 5 - 2023-24Document22 pagesCHEM3220 - Chapter 5 - 2023-24am0企鵝No ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Document6 pagesAnswer Scheme Chemistry P1 2022 Set 1Tan JennyNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectronegativity QuestionsThe ImmortalNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument8 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenesrajtarabap55No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: SynthesisDocument71 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: Synthesiskrystel pyneeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: What Holds Things Together?Document23 pagesChemical Bonding: What Holds Things Together?baabisoorajNo ratings yet
- As-Level Ap2 Paper 1 MsDocument8 pagesAs-Level Ap2 Paper 1 Msindiaisyourbae123No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and BasesDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Basesapi-3708473No ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Bonding and Structure MSDocument18 pages2.2.2 Bonding and Structure MSSir MannyNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chemistry Model Exam 2021 Ans Key Unoff Anoop ChandranDocument10 pagesHsslive Xi Chemistry Model Exam 2021 Ans Key Unoff Anoop Chandranകായംകുളം കൊച്ചുണ്ണിNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Answers To Examination Style Questions On Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3 Answers To Examination Style Questions On Chapter 3MOMINAH AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Hibridisasi, Reaksi Kimia Organik Dan Isomer: Oleh: Indah Hairunisa S.Farm., M.Biotech ., AptDocument37 pagesHibridisasi, Reaksi Kimia Organik Dan Isomer: Oleh: Indah Hairunisa S.Farm., M.Biotech ., AptRita AspiyantiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesAlkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsellachloedeeksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elimination RXNDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Elimination RXNmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases黃向廷No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ZZZDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry ZZZfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- 2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFDocument16 pages2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- Qn. No. Part - A MarksDocument13 pagesQn. No. Part - A MarkslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Addition by Electrophilic Reagents: BR BR BRDocument4 pagesAddition by Electrophilic Reagents: BR BR BRDaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical BondingmiddenmaeNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Alahazrat and His TaqwaDocument9 pagesAlahazrat and His Taqwasafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Questionssafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- How To Write Essays & Assignments UEL - (Introduction)Document12 pagesHow To Write Essays & Assignments UEL - (Introduction)safwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Task 2 - Student ExamplesDocument28 pagesTask 2 - Student Examplessafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument3 pagesAnnotated Bibliographysafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Anaphy MariebDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Anaphy MariebKeanna ZurriagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11.Document45 pagesChapter 11.HalaNo ratings yet
- Shree Dhootapapeshwar Standards: Ayush Kwath Dispersible TabletsDocument3 pagesShree Dhootapapeshwar Standards: Ayush Kwath Dispersible TabletssmartwaiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Nitrogen Fertilizer Encapsulated Urea Fertilizer in Process of Controlled Release Their Effect On Growth of Chinese Kale Brassica Alboglabra BaileyDocument10 pagesImpact of Nitrogen Fertilizer Encapsulated Urea Fertilizer in Process of Controlled Release Their Effect On Growth of Chinese Kale Brassica Alboglabra BaileyLeonardo EstradaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology in CartoonsDocument164 pagesBiotechnology in CartoonsMonica Zapata100% (1)
- No Title Available - 2013 - Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable PlasticsDocument16 pagesNo Title Available - 2013 - Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable PlasticsJiankun YangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document21 pagesChapter 12Suganthi AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- 152 809 2 PBDocument12 pages152 809 2 PBsujal jhaNo ratings yet
- 2020 GADSL Reference List ProdDocument220 pages2020 GADSL Reference List ProdParom WaikasikarnNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design and Scale Up of Lactic Acid Production From Fermentation-Derived Magnesium LactateDocument6 pagesConceptual Design and Scale Up of Lactic Acid Production From Fermentation-Derived Magnesium LactateNial HoerunNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of DNADocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of DNASamreen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Frictional and Optical PropertiesDocument28 pagesFrictional and Optical PropertiesJoselyn GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Homemade Organic Insecticide With The Use of Lemongrass Oil-ESDocument4 pagesHomemade Organic Insecticide With The Use of Lemongrass Oil-ESNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Chloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyDocument7 pagesChloetroulan - 03.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins - EssentialbiologyChloe TroulanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 13&14Document9 pagesChemistry 13&14Jhonvic AllitorabNo ratings yet
- Bee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care: ReviewDocument17 pagesBee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care: ReviewwizuraihakimroyNo ratings yet
- Pollution: OllutionDocument7 pagesPollution: OllutionPhilobatir SamehNo ratings yet
- October 16, 2020 BS-Biology 1-2 Ej M. FerrerDocument3 pagesOctober 16, 2020 BS-Biology 1-2 Ej M. FerrerEj FerrerNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 2Document20 pagesCarboxylic Acid 2brettNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QO1-1Document3 pagesEjercicios QO1-1hector juarezNo ratings yet
- Are Nanoclay Containing Polymer Composites Safe For Food Packaging. 2019Document22 pagesAre Nanoclay Containing Polymer Composites Safe For Food Packaging. 2019yurinnelNo ratings yet
- Mesomeric Effect Et AlDocument7 pagesMesomeric Effect Et AlAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Q, S, U, V, W, X, Y, Z Januari 2021Document10 pagesQ, S, U, V, W, X, Y, Z Januari 2021Mutmainnah PeaceNo ratings yet
- Green Earth ProjectDocument9 pagesGreen Earth ProjectLouise DominguezNo ratings yet
- 6-IR Spectroscopy of Alkane, Alkene and Carbonyl CompoundsDocument8 pages6-IR Spectroscopy of Alkane, Alkene and Carbonyl Compoundsbloodhound13042005No ratings yet
- Desmodur Z 4470 BA - en - 04465350 12978466 13462745Document3 pagesDesmodur Z 4470 BA - en - 04465350 12978466 13462745RICHNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesOrganic-Chemistry Hydrocarbonsxyrruschloe06No ratings yet
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Sources Effects andDocument9 pagesEndocrine Disrupting Chemicals Sources Effects andgranapadanomonsterNo ratings yet
- Dna and RnaDocument36 pagesDna and RnaMoona MalikNo ratings yet