Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DrA Notes
DrA Notes
Uploaded by
panimalar madha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
DrA notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesDrA Notes
DrA Notes
Uploaded by
panimalar madhaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
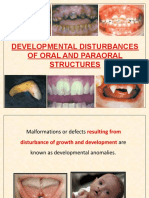
Extrinsic Staining of Teeth
*** Tobacco - Black or brown
*** Coffee, tea, and cola - Brown or black
** Chromogenic bacteria - Brown, black, green, or orange
** Chlorhexidine - Yellow-brown
Intrinsic Discoloration (“Staining”) of Teeth
*** Aging Yellow-brown; less translucency —
*** Death of pulp Gray-black; less translucency
** Fluorosis White; yellow-brown; brown; mottled
** Tetracycline Yellow-brown; yellow fluorescence
** Internal resorption “Pink tooth of Mummery”
* Calcific metamorphosis Yellow
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta Blue-gray; translucent
* Amelogenesis imperfecta Yellow-brown
* Congenital erythropoietic Yellow; brown-red; red fluorescence
* Erythroblastosis fetalis Yellow; green
Enlarged Pulp Chamber or Canal
** Internal resorption Secondary to caries or trauma
** Taurodontism Enlarged pulp chambers; shortened roots
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta “Shell teeth”
* Regional odontodysplasia “Ghost teeth”
* Vitamin D–resistant rickets High pulp horns
* Dentin dysplasia type II “Thistle-tube” pulps; pulp stone formation
Pulpal Calcification
*** Pulp stones Asymptomatic radiographic finding
*** Secondary dentin Response to caries
** Calcific metamorphosis Pulpal obliteration secondary to aging or
trauma
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta Pulpal obliteration by excess dentin
* Dentin dysplasia type I Pulpal obliteration by excess dentin;
“chevron”-shaped pulp chambers
* Dentin dysplasia type II Pulpal obliteration of primary teeth; pulp
stones in permanent teeth
Abnormally Shaped Roots
*** External root resorption Secondary to infection, cyst, tumor
*** Dilaceration Abnormal curvature
** Hypercementosis Excessive cementum production
** Concrescence Joining of teeth by cementum
** Taurodontism Enlarged pulp chambers; shortened roots
** Enamel pearl Ectopic enamel in furcation
* Benign cementoblastoma Tumor attached to root
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta Shortened roots; obliterated pulps
* Dentin dysplasia type I Shortened, pointed roots (“rootless teeth”)
obliterated pulps; periapical pathosis
Enamel Loss After Tooth Formation
*** Attrition Physiologic loss of tooth structure
*** Abrasion Pathologic loss of tooth structure
** Erosion Chemical loss of tooth structure
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta Hereditary defect in dentin formation;
poor junction between enamel and dentin
* Amelogenesis imperfecta Hereditary defect in enamel formation;
especially hypocalcified types
Extra Information
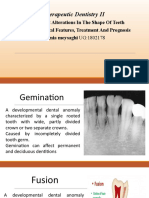
** Fusion or gemination “Double” tooth
** Fusion Joining of two tooth germs
** Gemination Incomplete splitting of a tooth germ
* Talon cusp Extra cusp on lingual of anterior tooth
* Dens evaginatus Extra cusp on occlusal of premolar tooth
* Amelogenesis imperfecta Hereditary defect in enamel formation
* Dentinogenesis imperfecta Fracturing away of enamel due to
hereditary defect in dentin formation; gray-yellow opalescent teeth;
calcified pulp chambers
** Mesiodens ( supernumeraries ) Cone-shaped teeth or microdont
** Enamel hypoplasia: high fever during tooth development
** Peg-shaped lateral incisors Cone-shaped teeth
** Dens invaginatus Cone-shaped teeth; tendency toward pulpal
death and periapical pathosis
*** Supernumerary teeth Mesiodens; fourth molars
Hyperdontia (Extra Teeth)
*** supernumerary Mesiodens, paramolar, distomolar teeth
** Cleft lip and palate Extra lateral incisor or canine 1
* Cleidocranial dysplasia Hypoplastic or missing clavicles; failure of
tooth eruption 576
Hypodontia (Missing Teeth)
*** hypodontia Missing third molars, lateral incisors 70
** Cleft lip and palate Missing lateral incisor or canine
DR\ A
دﻋواﺗﻛم ﻟﻲ وﻟﻛم ﺑﺎﻟﺗوﻓﯾق
This is my reference for all information - Oral and Maxillofacial
Pathology. Book
You might also like
- Final Bangus Value ChainDocument8 pagesFinal Bangus Value ChainSandy SandyNo ratings yet
- Nasm Study Guide PDF 2016 Nasm CPTDocument54 pagesNasm Study Guide PDF 2016 Nasm CPTAlonzo Mark100% (7)
- BPJPH - Current Status of Halal Policy and Regulation in IndonesiaDocument26 pagesBPJPH - Current Status of Halal Policy and Regulation in IndonesiaTeenagespirits100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - ESRDDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - ESRDheiyu100% (3)
- Dr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyDocument62 pagesDr. O.M Ogundana Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology/BiologyoladunniNo ratings yet
- Pedo2013 14Document189 pagesPedo2013 14Vladimir Argirovic100% (4)
- Development and Morphology of The Primary Teeth: Bagian IKGA Fakultas Kedokteran Gigi Maranatha 2017Document26 pagesDevelopment and Morphology of The Primary Teeth: Bagian IKGA Fakultas Kedokteran Gigi Maranatha 2017cella bentleyNo ratings yet
- Dental AnomaliesDocument62 pagesDental AnomaliesRanjanNo ratings yet
- Developemental Disturbances of Oral and Paraoral TissuesDocument209 pagesDevelopemental Disturbances of Oral and Paraoral TissuesMailoud AlnaileNo ratings yet
- Dental StainsDocument30 pagesDental StainsArtur Radvanszki100% (1)
- Teeth DefectsDocument32 pagesTeeth DefectsManoj NaiduNo ratings yet
- Developmental TeethDocument53 pagesDevelopmental Teethlyli Star AngeloNo ratings yet
- Dental Hard Tissue Discolouration - Etiology and TreatmentDocument48 pagesDental Hard Tissue Discolouration - Etiology and TreatmentMedic PresentNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument176 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPawan Kumar100% (5)
- Abnormalities in The Development of TeethDocument58 pagesAbnormalities in The Development of TeethAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANo ratings yet
- APznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17ZdDocument24 pagesAPznzabu1Ci9p9yRpxFqJSukJAe2 6rzeDQRKy GGsZNB1jUFPKmnLhAb3H17Zdclassybrands0No ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFDocument97 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Tooth PDFEmad AlriashyNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsDocument13 pagesEtiology of Malocclusion Local Factorsdrcharu860% (1)
- Etiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsDocument13 pagesEtiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsAshis BiswasNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of TeethDocument24 pagesAbnormalities of TeethRoshni ButalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Anomalies - LectureDocument10 pagesAnatomic Anomalies - LectureKhalid BhatNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations ShareDocument38 pagesOral Manifestations SharePrachi ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Perio Lec.6 Part 1 Dental StainsDocument37 pagesPerio Lec.6 Part 1 Dental StainsزينNo ratings yet
- Non-Caries Dental DiseaseDocument61 pagesNon-Caries Dental Diseaseapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of The ToothDocument14 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of The ToothAman Chowdhry100% (1)
- Classification of Anomaly2Document213 pagesClassification of Anomaly2samar yousif mohamed100% (1)
- Anamolies of Formation and Eruption For Class 22Document76 pagesAnamolies of Formation and Eruption For Class 22Nihaz 72No ratings yet
- Etiology of MalocclusionDocument46 pagesEtiology of MalocclusionMSA universityNo ratings yet
- Dental Anomalies: 2011/05/20 Hand Book of Pediatric DentistryDocument10 pagesDental Anomalies: 2011/05/20 Hand Book of Pediatric DentistryLesta Yang100% (1)
- Dev Dis ToothDocument92 pagesDev Dis ToothVaishnavi ThatiparthiNo ratings yet
- Lec 15, Anomalies of The Developing DentitionDocument45 pagesLec 15, Anomalies of The Developing DentitionAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders of TeethDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Disorders of TeethPatterson MachariaNo ratings yet
- Cawsons Chapter 2Document4 pagesCawsons Chapter 2Katie WithersNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument65 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of Teethisraa0dentist100% (4)
- Hypoplasia 1Document27 pagesHypoplasia 1Mohamed Khalil Khalil Ahmed Ellabban Ahmed EllabbanNo ratings yet
- Enamel Hypoplasia: SmijalDocument27 pagesEnamel Hypoplasia: Smijalbirjis fatimaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders and SyndromesDocument77 pagesGenetic Disorders and Syndromesفاطمة الجش.No ratings yet
- ORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensDocument24 pagesORAL PATHOLOGY Practical SpecimensPravin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of TeethDocument78 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TeethPauline Joy Cayago CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Is Malocclusion?Document24 pagesWhat Is Malocclusion?Bibek RajNo ratings yet
- 15 Anomalies of The Developing DentitionDocument15 pages15 Anomalies of The Developing DentitionScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologyDocument38 pagesDevelopmental Disorders: Dr. Chakshu Aggarwal (MDS) SNR Lecturer Oral PathologydrchakshuaggarwalNo ratings yet
- Classification of Tooth DiscolourationDocument14 pagesClassification of Tooth DiscolourationSARINAHNo ratings yet
- Armin HedayatDocument1 pageArmin HedayatarminhedayatNo ratings yet
- 7 Affection of TeethDocument38 pages7 Affection of TeethAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- 2 Un-Carious Defects of TeethDocument114 pages2 Un-Carious Defects of TeethFaraz Mohammed100% (1)
- Abnormalities of TeethDocument74 pagesAbnormalities of Teethzainab.yasinNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Tooth-Bleaching Techniques: Chemistry, Safety and EfficacyDocument22 pagesAn Overview of Tooth-Bleaching Techniques: Chemistry, Safety and EfficacyMuhammad AbazaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Dr. Rea CorpuzDocument114 pagesPrepared By: Dr. Rea CorpuzNaqiyah NoorbhaiNo ratings yet
- Etiology of MalocclusionDocument72 pagesEtiology of MalocclusionPavan PreethamNo ratings yet
- Armin HedayatDocument2 pagesArmin HedayatarminhedayatnetNo ratings yet
- Tooth Discolour at Ion PedoDocument28 pagesTooth Discolour at Ion PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of TeethDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of TeethSherin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Factors of MalocclusionDocument25 pagesEtiologic Factors of MalocclusionBibek RajNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic IIDocument11 pagesTherapeutic IIkimiaNo ratings yet
- Armin HedayatDocument1 pageArmin HedayatarminhedayatblogsNo ratings yet
- Tooth DiscolorationDocument73 pagesTooth DiscolorationAli AlsayedNo ratings yet
- AnamolisDocument11 pagesAnamolisAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Lec. 3 Dental Stain Dr. Ayser Najah: Colour and Colour PerceptionDocument17 pagesLec. 3 Dental Stain Dr. Ayser Najah: Colour and Colour Perceptionفاطمة فالح ضايف مزعلNo ratings yet
- Pathology Notes - GI SystemDocument55 pagesPathology Notes - GI Systems21514.laiNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Psychology Test 2 Practice QuestionsDocument15 pagesPsychology Test 2 Practice Questionsshamim3261100% (3)
- Case Study On Diabetis and AnemiaDocument21 pagesCase Study On Diabetis and AnemiaAfna SyedNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement PCDocument8 pagesMethod of Statement PCAbada SaadNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis, Stress and Adaptation - Ppt2aDocument154 pagesHomeostasis, Stress and Adaptation - Ppt2aV_RN100% (2)
- Restaurant Report Card: April 25, 2024Document8 pagesRestaurant Report Card: April 25, 2024KBTXNo ratings yet
- 566 PDFDocument6 pages566 PDFafrilya eka anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04: Laboratory Safety Test Bank: 1. A. B. C. D. Ans: ADocument7 pagesChapter 04: Laboratory Safety Test Bank: 1. A. B. C. D. Ans: AroeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Open Plant StructuresDocument6 pagesGuidelines For Open Plant StructuresIndrawNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Prof. Mona Abdelmoneim Mohamed AbdelmageedDocument19 pagesResearch Methodology: Prof. Mona Abdelmoneim Mohamed AbdelmageedBasil DomiNo ratings yet
- AVM School Admission FormDocument2 pagesAVM School Admission FormManoj DhakalNo ratings yet
- Msds For Skim CoatDocument8 pagesMsds For Skim Coatlovely palomaNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument8 pagesTable of ContentsEmmanuel BeresoNo ratings yet
- OSH Legislation FinalDocument54 pagesOSH Legislation FinalRaDaCa CabsNo ratings yet
- 11 кл 1 четверть 472Document54 pages11 кл 1 четверть 472Еркегуль ЖауенNo ratings yet
- Test NotesDocument6 pagesTest NotesharikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Oral CancerDocument12 pagesEpidemiology of Oral Cancerعدي عبدالالهNo ratings yet
- Applying Taguchi Methods To Health CareDocument12 pagesApplying Taguchi Methods To Health CarehamzaabdalameerNo ratings yet
- AFD Runs End JanuaryDocument3 pagesAFD Runs End Januarylarry_kelley_1No ratings yet
- May 2012 CFAR Newsletter - Stories of AIDSDocument2 pagesMay 2012 CFAR Newsletter - Stories of AIDSUNC CFARNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Nutritional SciencesDocument4 pagesRecent Advances in Nutritional SciencesSava1988No ratings yet
- W1 - Intro To Air Pollution EngineeringDocument26 pagesW1 - Intro To Air Pollution Engineeringevolution95No ratings yet
- PE 12 HOPE 3 Q2 Module 3 Lesson 6 7 by FarrahDocument33 pagesPE 12 HOPE 3 Q2 Module 3 Lesson 6 7 by Farrahricsha masanayNo ratings yet
- Decaf Coffee - Good or BadDocument5 pagesDecaf Coffee - Good or BadAdam70sdNo ratings yet
- 글리세린 R995F MSDS 영문Document9 pages글리세린 R995F MSDS 영문하은No ratings yet
- Why Do You Want To Become A Police Officer EssayDocument7 pagesWhy Do You Want To Become A Police Officer Essaytycheknbf100% (1)
- JBNJN - Docx ENGLISHDocument2 pagesJBNJN - Docx ENGLISHمحسن حدوان عليخانNo ratings yet