Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromag Ans
Electromag Ans
Uploaded by
Joseph KamauCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 9103 Reaffirmed 2018 PDFDocument17 pages9103 Reaffirmed 2018 PDFIndira Banerjee100% (2)
- Data-Sheet Drum Brake RT - 200220 - enDocument1 pageData-Sheet Drum Brake RT - 200220 - enRFTNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics NotesDocument3 pagesA2 Physics NotesZain ImranNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Magnetic Circuitsxenohjb100% (1)
- Physics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionBen100% (4)
- Chapter 1 Faradays LawDocument53 pagesChapter 1 Faradays LawYSheng ChanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument20 pagesElectricity and MagnetismMido YoussefNo ratings yet
- EMT 2 MarksDocument11 pagesEMT 2 Markssarahpraveen212No ratings yet
- Conductors, Dielectrics, and CapacitanceDocument23 pagesConductors, Dielectrics, and Capacitanceepsilonnaught100% (2)
- Be Emtl MaterialDocument57 pagesBe Emtl Materialsravan_451No ratings yet
- DC Machine AssignmentDocument10 pagesDC Machine AssignmentMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument29 pagespdf24 Merged16naveenkannaaNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory (Ee-1203) : Short Questions and Answers Semester IIIDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Theory (Ee-1203) : Short Questions and Answers Semester IIIM A InayathullaahNo ratings yet
- Physics of Semiconductor DevicesDocument8 pagesPhysics of Semiconductor DevicesZohaib Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- EMT Two MarksDocument23 pagesEMT Two MarksRamesh KamathNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Electromagnetic - Theory PDFDocument10 pages2 Marks Electromagnetic - Theory PDFYerramsetty SreekanthNo ratings yet
- 290 Module IIIDocument31 pages290 Module IIIchicknaliaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 NotesDocument83 pagesModule 2 Notesstudentmaterial321No ratings yet
- Lorentz ForceDocument19 pagesLorentz ForcesreekarwNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1 MagnetismDocument30 pages6.2.1 Magnetismtomas garciaNo ratings yet
- PHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - MagnetostaticsDocument49 pagesPHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - Magnetostaticsنور وائلNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument7 pagesElectric FieldMark Abordo LabiosNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Applications in Electricity and MagnetismDocument6 pagesVector Calculus Applications in Electricity and MagnetismSadeep MadhushanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesElectromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document10 pagesGroup 1feugueng john francis kingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Online ClassDocument8 pagesLecture 2 Online ClassFaria Sultana MimiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Electromagnetic WavesDocument45 pagesModule 2 Electromagnetic WavesArnav AryaNo ratings yet
- Ec T36 EeDocument16 pagesEc T36 Eelakshmigajendran100% (2)
- Currents and Conductors Currents and ConductorsDocument27 pagesCurrents and Conductors Currents and ConductorsHasanNo ratings yet
- Half EffectDocument10 pagesHalf EffectAbubakar ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- EMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerDocument21 pagesEMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerFLOWERNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ForceDocument9 pagesMagnetic ForceReuben John AbalayanNo ratings yet
- State Coulomb's LawDocument6 pagesState Coulomb's Lawinfotechedge10No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentsardar aliNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics DaDocument7 pagesOptoelectronics DaZarif HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Electrostatics & MagnetismDocument64 pagesChapter 5 - Electrostatics & MagnetismiitrboyNo ratings yet
- HALL EFFECT PresentationDocument63 pagesHALL EFFECT Presentationkarthikk2001krishnanNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's EquationDocument9 pagesMaxwell's EquationRudra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Determination of Mobility: Hall EffectDocument2 pagesExperimental Determination of Mobility: Hall EffectShady SakrNo ratings yet
- Section VI 25 Charged ParticlesDocument11 pagesSection VI 25 Charged Particlesdanwilliams85No ratings yet
- BPHY101L-Module2-Lectureppt-Electromagnetic WavesDocument42 pagesBPHY101L-Module2-Lectureppt-Electromagnetic WavesLakshminaarayanan VsNo ratings yet
- 25 EM Induction Student BookletDocument40 pages25 EM Induction Student BookletLoïc DarrieumerlouNo ratings yet
- Motion of Charged Particles in Electric and Magnetic FieldsxDocument33 pagesMotion of Charged Particles in Electric and Magnetic FieldsxRam Krishna100% (1)
- Short 2Document3 pagesShort 2K Pawan Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 2aDocument37 pagesChapter 2aLøvēly ChakriNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Electric Current Electric Field Charge PermeabilityDocument1 pageMagnetic Field Electric Current Electric Field Charge PermeabilitysyulmnmdNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Class BEE 1A/1BDocument40 pagesApplied Physics: Class BEE 1A/1BPeace of HeartNo ratings yet
- Section V 22 ElectromagnetismDocument19 pagesSection V 22 Electromagnetismdanwilliams85No ratings yet
- Hall Effect Final ManualDocument9 pagesHall Effect Final ManualhrishikaeshapratapsarkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical MachinesDocument32 pagesBasic Electrical MachinesIrene AtienoNo ratings yet
- Biot SavardDocument4 pagesBiot SavardrasajatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Magnetostatics FieldDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - Magnetostatics FieldMrmouzinhoNo ratings yet
- 206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksDocument22 pages206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces, Fields, and Faraday's LawDocument49 pagesMagnetic Forces, Fields, and Faraday's LawIan Ark E. ColarteNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics PDFDocument63 pagesMagnetostatics PDFShashank KrrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project ElectromagnetismDocument24 pagesPhysics Project Electromagnetismaman100% (2)
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument4 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsAishwarya NaiduNo ratings yet
- Theory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeDocument8 pagesTheory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeAbrahamRubioNo ratings yet
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleFrom EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Gas StoichiometryDocument22 pagesGas Stoichiometrykenot100% (1)
- Types of Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesTypes of Differential EquationsAliph Hamzah100% (1)
- TOK EssayDocument5 pagesTOK EssayShankar MutnejaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: SciencedirectDocument2 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: SciencedirectLekane nelsonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22khalidbashirchandioNo ratings yet
- Controller For Operation of Evaporator On Water Chiller: EKC 316ADocument16 pagesController For Operation of Evaporator On Water Chiller: EKC 316AHendra SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersCarlos Evangelista SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Signal Processing of Acoustic GunshotDocument6 pagesModeling and Signal Processing of Acoustic Gunshotaamirnadeem2009No ratings yet
- Differential Protection: Document byDocument26 pagesDifferential Protection: Document byS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Effective Nuclear Charge, Penetration, Orbital Energy PDFDocument6 pagesEffective Nuclear Charge, Penetration, Orbital Energy PDFAtul Gautam100% (1)
- 30RAP-6T - Check ListDocument2 pages30RAP-6T - Check ListGaray Valdovinos AlanNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument46 pagesProjectile MotionRaymund EspinoNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions Manualgraphitehamous.22x7100% (55)
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- E MAX TIR Trip Indication Relay 2015Document4 pagesE MAX TIR Trip Indication Relay 2015Ryan McMaster0% (1)
- ERICO Seismic Sway Bracing SeminarDocument129 pagesERICO Seismic Sway Bracing Seminarmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- RE18325-03 Solenoid Valve With Feedback OD15051841YZDocument4 pagesRE18325-03 Solenoid Valve With Feedback OD15051841YZMujahidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Document90 pagesSulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Jack Lali100% (1)
- Mitsu C004e-I Solid End MillsDocument358 pagesMitsu C004e-I Solid End MillskatomegumioncrackNo ratings yet
- C) Isolated System:: Unit-6Document16 pagesC) Isolated System:: Unit-6MUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- 4x10 1Cx70 MergedDocument10 pages4x10 1Cx70 MergedJalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- MTHL Scope of WorkDocument12 pagesMTHL Scope of Worktariq1987No ratings yet
- In-Plane and Out-Of Plane Response of Currently Constructed Masonry InfillsDocument14 pagesIn-Plane and Out-Of Plane Response of Currently Constructed Masonry InfillsVasilikiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5, 6 and 7Document9 pagesLab 5, 6 and 7SARANG ABBASINo ratings yet
- Demisters & Tower Packings CatalogueDocument28 pagesDemisters & Tower Packings CatalogueVioleta ArabadzhievaNo ratings yet
- JIS G3106-SM400 - SM490 - SM520 - SM570 Structural Steel PlateDocument7 pagesJIS G3106-SM400 - SM490 - SM520 - SM570 Structural Steel PlateAbhishek BhargavNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryDocument12 pagesPurpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryGauri ThakurNo ratings yet
- Light Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel GroupDocument33 pagesLight Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel Groupalvise30No ratings yet
Electromag Ans
Electromag Ans
Uploaded by
Joseph KamauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromag Ans
Electromag Ans
Uploaded by
Joseph KamauCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromag
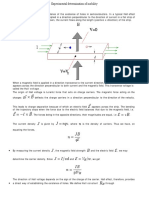
The Lorentz force equation describes the force experienced by a charged particle moving in an
electromagnetic field. the force exerted on a charged particle q moving with velocity v through an
electric field E and magnetic field B F=q(E+v×B)
Conduction current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire or a metallic
structure. It is caused by the movement of electrons in response to an electric field. displacement
current is associated with changing electric fields in dielectric materials where there are no mobile
charge carriers. t is associated with the rate of change of electric flux in a region of space
A scalar quantity is a physical quantity that only has magnitude and no direction. A scalar field is a
function that associates a scalar value with every point in a space or region.eg temperature distribution
in a room.
At the boundary between any two dielectrics, the tangential components of the electric field are
continuous, and the normal components are discontinuous and equal to the surface charge density.
A vector quantity is a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector field is a
function that associates a vector with every point in a space or region.
The divergence of a vector field describes the rate at which the vector field's vectors spread out or
converge at a given point. he curl of a vector field provides valuable information about the rotational
behavior of the field.
Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that a current is induced in a conductor which is in a
changing magnetic field.
The law of BiotSavart1 then states that at any point P the magnitude of the magnetic field intensity
produced by the differential element is proportional to the product of the current, the magnitude of the
differential length, and the sine of the angle lying between the filament and a line connecting the
filament to the point P at which the field is desired; also, the magnitude of the magnetic field intensity is
inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the differential element to the point P
Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of H about any closed path is exactly equal to the
direct current enclosed by that path,
Divergence theorem: The integral of the normal component of any vector field over a closed surface is
equal to the integral of the divergence of this vector field throughout the volume enclosed by the closed
surface.
State three factors that affect Coulomb’s Force
1. Magnitude of the Charges (�1q1 and �2q2)
2. Distance Between the Charges (�r)
3. Permittivity of the Medium
You might also like
- 9103 Reaffirmed 2018 PDFDocument17 pages9103 Reaffirmed 2018 PDFIndira Banerjee100% (2)
- Data-Sheet Drum Brake RT - 200220 - enDocument1 pageData-Sheet Drum Brake RT - 200220 - enRFTNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics NotesDocument3 pagesA2 Physics NotesZain ImranNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Magnetic Circuitsxenohjb100% (1)
- Physics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionBen100% (4)
- Chapter 1 Faradays LawDocument53 pagesChapter 1 Faradays LawYSheng ChanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument20 pagesElectricity and MagnetismMido YoussefNo ratings yet
- EMT 2 MarksDocument11 pagesEMT 2 Markssarahpraveen212No ratings yet
- Conductors, Dielectrics, and CapacitanceDocument23 pagesConductors, Dielectrics, and Capacitanceepsilonnaught100% (2)
- Be Emtl MaterialDocument57 pagesBe Emtl Materialsravan_451No ratings yet
- DC Machine AssignmentDocument10 pagesDC Machine AssignmentMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument29 pagespdf24 Merged16naveenkannaaNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument28 pagesA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory (Ee-1203) : Short Questions and Answers Semester IIIDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Theory (Ee-1203) : Short Questions and Answers Semester IIIM A InayathullaahNo ratings yet
- Physics of Semiconductor DevicesDocument8 pagesPhysics of Semiconductor DevicesZohaib Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- EMT Two MarksDocument23 pagesEMT Two MarksRamesh KamathNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Electromagnetic - Theory PDFDocument10 pages2 Marks Electromagnetic - Theory PDFYerramsetty SreekanthNo ratings yet
- 290 Module IIIDocument31 pages290 Module IIIchicknaliaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 NotesDocument83 pagesModule 2 Notesstudentmaterial321No ratings yet
- Lorentz ForceDocument19 pagesLorentz ForcesreekarwNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1 MagnetismDocument30 pages6.2.1 Magnetismtomas garciaNo ratings yet
- PHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - MagnetostaticsDocument49 pagesPHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - Magnetostaticsنور وائلNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument7 pagesElectric FieldMark Abordo LabiosNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Applications in Electricity and MagnetismDocument6 pagesVector Calculus Applications in Electricity and MagnetismSadeep MadhushanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesElectromagnetic Waves, Circuits and ApplicationsMayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document10 pagesGroup 1feugueng john francis kingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Online ClassDocument8 pagesLecture 2 Online ClassFaria Sultana MimiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Electromagnetic WavesDocument45 pagesModule 2 Electromagnetic WavesArnav AryaNo ratings yet
- Ec T36 EeDocument16 pagesEc T36 Eelakshmigajendran100% (2)
- Currents and Conductors Currents and ConductorsDocument27 pagesCurrents and Conductors Currents and ConductorsHasanNo ratings yet
- Half EffectDocument10 pagesHalf EffectAbubakar ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- EMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerDocument21 pagesEMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerFLOWERNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ForceDocument9 pagesMagnetic ForceReuben John AbalayanNo ratings yet
- State Coulomb's LawDocument6 pagesState Coulomb's Lawinfotechedge10No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentsardar aliNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics DaDocument7 pagesOptoelectronics DaZarif HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Electrostatics & MagnetismDocument64 pagesChapter 5 - Electrostatics & MagnetismiitrboyNo ratings yet
- HALL EFFECT PresentationDocument63 pagesHALL EFFECT Presentationkarthikk2001krishnanNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's EquationDocument9 pagesMaxwell's EquationRudra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Determination of Mobility: Hall EffectDocument2 pagesExperimental Determination of Mobility: Hall EffectShady SakrNo ratings yet
- Section VI 25 Charged ParticlesDocument11 pagesSection VI 25 Charged Particlesdanwilliams85No ratings yet
- BPHY101L-Module2-Lectureppt-Electromagnetic WavesDocument42 pagesBPHY101L-Module2-Lectureppt-Electromagnetic WavesLakshminaarayanan VsNo ratings yet
- 25 EM Induction Student BookletDocument40 pages25 EM Induction Student BookletLoïc DarrieumerlouNo ratings yet
- Motion of Charged Particles in Electric and Magnetic FieldsxDocument33 pagesMotion of Charged Particles in Electric and Magnetic FieldsxRam Krishna100% (1)
- Short 2Document3 pagesShort 2K Pawan Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 2aDocument37 pagesChapter 2aLøvēly ChakriNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Electric Current Electric Field Charge PermeabilityDocument1 pageMagnetic Field Electric Current Electric Field Charge PermeabilitysyulmnmdNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Class BEE 1A/1BDocument40 pagesApplied Physics: Class BEE 1A/1BPeace of HeartNo ratings yet
- Section V 22 ElectromagnetismDocument19 pagesSection V 22 Electromagnetismdanwilliams85No ratings yet
- Hall Effect Final ManualDocument9 pagesHall Effect Final ManualhrishikaeshapratapsarkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical MachinesDocument32 pagesBasic Electrical MachinesIrene AtienoNo ratings yet
- Biot SavardDocument4 pagesBiot SavardrasajatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Magnetostatics FieldDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - Magnetostatics FieldMrmouzinhoNo ratings yet
- 206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksDocument22 pages206 - EE8391, EE6302 Electromagnetic Theory - 2marksBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces, Fields, and Faraday's LawDocument49 pagesMagnetic Forces, Fields, and Faraday's LawIan Ark E. ColarteNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics PDFDocument63 pagesMagnetostatics PDFShashank KrrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project ElectromagnetismDocument24 pagesPhysics Project Electromagnetismaman100% (2)
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument4 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsAishwarya NaiduNo ratings yet
- Theory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeDocument8 pagesTheory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeAbrahamRubioNo ratings yet
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleFrom EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Gas StoichiometryDocument22 pagesGas Stoichiometrykenot100% (1)
- Types of Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesTypes of Differential EquationsAliph Hamzah100% (1)
- TOK EssayDocument5 pagesTOK EssayShankar MutnejaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: SciencedirectDocument2 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: SciencedirectLekane nelsonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22khalidbashirchandioNo ratings yet
- Controller For Operation of Evaporator On Water Chiller: EKC 316ADocument16 pagesController For Operation of Evaporator On Water Chiller: EKC 316AHendra SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Fast Recovery RectifiersCarlos Evangelista SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Signal Processing of Acoustic GunshotDocument6 pagesModeling and Signal Processing of Acoustic Gunshotaamirnadeem2009No ratings yet
- Differential Protection: Document byDocument26 pagesDifferential Protection: Document byS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Effective Nuclear Charge, Penetration, Orbital Energy PDFDocument6 pagesEffective Nuclear Charge, Penetration, Orbital Energy PDFAtul Gautam100% (1)
- 30RAP-6T - Check ListDocument2 pages30RAP-6T - Check ListGaray Valdovinos AlanNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument46 pagesProjectile MotionRaymund EspinoNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Knight 3rd Edition Solutions Manualgraphitehamous.22x7100% (55)
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocument3 pagesEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNo ratings yet
- E MAX TIR Trip Indication Relay 2015Document4 pagesE MAX TIR Trip Indication Relay 2015Ryan McMaster0% (1)
- ERICO Seismic Sway Bracing SeminarDocument129 pagesERICO Seismic Sway Bracing Seminarmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- RE18325-03 Solenoid Valve With Feedback OD15051841YZDocument4 pagesRE18325-03 Solenoid Valve With Feedback OD15051841YZMujahidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Document90 pagesSulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Jack Lali100% (1)
- Mitsu C004e-I Solid End MillsDocument358 pagesMitsu C004e-I Solid End MillskatomegumioncrackNo ratings yet
- C) Isolated System:: Unit-6Document16 pagesC) Isolated System:: Unit-6MUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- 4x10 1Cx70 MergedDocument10 pages4x10 1Cx70 MergedJalal AlbadriNo ratings yet
- MTHL Scope of WorkDocument12 pagesMTHL Scope of Worktariq1987No ratings yet
- In-Plane and Out-Of Plane Response of Currently Constructed Masonry InfillsDocument14 pagesIn-Plane and Out-Of Plane Response of Currently Constructed Masonry InfillsVasilikiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5, 6 and 7Document9 pagesLab 5, 6 and 7SARANG ABBASINo ratings yet
- Demisters & Tower Packings CatalogueDocument28 pagesDemisters & Tower Packings CatalogueVioleta ArabadzhievaNo ratings yet
- JIS G3106-SM400 - SM490 - SM520 - SM570 Structural Steel PlateDocument7 pagesJIS G3106-SM400 - SM490 - SM520 - SM570 Structural Steel PlateAbhishek BhargavNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryDocument12 pagesPurpose of The Experiment: Modular Laboratory P in ChemistryGauri ThakurNo ratings yet
- Light Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel GroupDocument33 pagesLight Microscopy: Basic Principles and Concepts: Carlo Bevilacqua Prevedel Groupalvise30No ratings yet