Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 3
Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Francisco, Antonette Jane A.Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Solutions: Solutions Manual For Photovoltaic Systems Engineering 4Th Edition MessengerDocument12 pagesSolutions: Solutions Manual For Photovoltaic Systems Engineering 4Th Edition MessengerMadaka Siva kumar50% (2)
- Chapter 2Document56 pagesChapter 2ajis sNo ratings yet
- Hopper DesignDocument37 pagesHopper DesignFeroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocument18 pages4-Computation of Average RainfallAafaque HussainNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Method)Document2 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Method)Via Lady Jee Garnacha100% (2)
- Descriptive HydrologyDocument49 pagesDescriptive HydrologyRomeo Baladad67% (3)
- Types of Presentation: InformativeDocument11 pagesTypes of Presentation: InformativeMd Sohanur Rahman100% (1)
- Interpretation of RainfallDocument31 pagesInterpretation of RainfallsavithaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Precipitation Lesson 1 PDFDocument67 pagesPart 3 - Precipitation Lesson 1 PDFJQNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY - Midterm ReviewerDocument4 pagesHYDROLOGY - Midterm ReviewerAvestruz ReginoNo ratings yet
- PRECIPITATIONDocument8 pagesPRECIPITATIONAljon LanguingNo ratings yet
- YT Session 4 Hydrology by Sandeep Jyani SSC JE 2023 STATE AE GATDocument26 pagesYT Session 4 Hydrology by Sandeep Jyani SSC JE 2023 STATE AE GATVìmäl VìhäänNo ratings yet
- PrecipitationDocument42 pagesPrecipitationKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Water Resources3Document26 pagesHydrology and Water Resources3Hazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Precipitation: Depth of Rain Volume of Rain Collected in CMDocument7 pagesMeasurement of Precipitation: Depth of Rain Volume of Rain Collected in CMAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Precipitation - Rain Guage NetworkDocument27 pagesPresentation - Precipitation - Rain Guage NetworkbobbyccwNo ratings yet
- U1 - L6 Optimum Number of Rain Gauge Stations PDFDocument3 pagesU1 - L6 Optimum Number of Rain Gauge Stations PDFishaq kazeemNo ratings yet
- CE143 - Module 3.1Document39 pagesCE143 - Module 3.1MaRc NoBlen D CNo ratings yet
- Lec - 3 - Engineering HydrologyDocument37 pagesLec - 3 - Engineering HydrologyZaTaSaraMeenaKomNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document20 pagesNull 3ayushkumarbhardwaj1562No ratings yet
- 4 Computationofaveragerainfall 170724064842Document17 pages4 Computationofaveragerainfall 170724064842Allecka GragasinNo ratings yet
- 04 Mean Precipitation Over An Area-1Document25 pages04 Mean Precipitation Over An Area-1antenorsarahmichelle7No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Type, Properties, and Behavior of PrecipitationDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting The Type, Properties, and Behavior of PrecipitationglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document16 pagesLecture 5AritroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document18 pagesLesson 3Hubert MoforNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Ch2 2Document30 pagesHydrology Ch2 2Zekariyas AbushaNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Precipitation and Rain GaugesDocument44 pagesFdocuments - in Precipitation and Rain GaugesSuvendu MajumderNo ratings yet
- Mean Precipitation Over An AreaDocument6 pagesMean Precipitation Over An AreaSonny Mae TuboNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data - Conversion of Point To Aerial RainfallDocument34 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data - Conversion of Point To Aerial Rainfallbernie romero50% (2)
- Hydrology Notes 2Document14 pagesHydrology Notes 2NzezwaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Dr. Shakil AhmadDocument14 pagesOutline: Dr. Shakil AhmadWaQar SaleemNo ratings yet
- 4) Chapter 3Document16 pages4) Chapter 3EricNo ratings yet
- Precipitation: ECW 557/431: Engineering HydrologyDocument61 pagesPrecipitation: ECW 557/431: Engineering HydrologyFariz SaniNo ratings yet
- Precipitation 2Document32 pagesPrecipitation 2Alexandra Shun MandrezaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Chapter 6 Part IDocument26 pagesHydrology Chapter 6 Part IspaudelNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Engineering Hydrology - pdf-68Document32 pagesShort Notes On Engineering Hydrology - pdf-68Nilesh AvhadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Precipitation (Part 2) : 1. Depth-Area-Duration RelationshipDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitation (Part 2) : 1. Depth-Area-Duration RelationshipzeyadNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument29 pagesChapter TwoyuusufmohamedhudleNo ratings yet
- Precipitation 09 11Document18 pagesPrecipitation 09 11Wanda FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Rainfallmeasurement 150312100947 Conversion Gate01Document21 pagesRainfallmeasurement 150312100947 Conversion Gate01DeepakNo ratings yet
- Precipitation: ET 1001 Introduction To HydrologyDocument32 pagesPrecipitation: ET 1001 Introduction To HydrologyK WATHSALANo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument24 pagesEngineering HydrologyPrince Vince100% (1)
- Mean Areal PrecipitationDocument6 pagesMean Areal PrecipitationHussam MurshedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Return Period Gautama - 235Document8 pagesJurnal Return Period Gautama - 235DayNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثالثة- الامطارDocument5 pagesالمحاضرة الثالثة- الامطارYM HMNo ratings yet
- Mean Precipitation Over An Area - Double Mass AnalysisDocument5 pagesMean Precipitation Over An Area - Double Mass AnalysisSonny Mae TuboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document11 pagesLecture 3AritroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Precipitation RevDocument27 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitation RevsmdunaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 2Document5 pagesHydrology 2ivyshamjuNo ratings yet
- Precipitationanditsestimation 150316012440 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument66 pagesPrecipitationanditsestimation 150316012440 Conversion Gate01 PDFMAKONo ratings yet
- K. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 62 PDFDocument1 pageK. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 62 PDFcivilengeeNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationDocument43 pagesLec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationumairNo ratings yet
- Outline: Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil AhmadDocument19 pagesOutline: Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil AhmadChaudryMuhammadHasnatNo ratings yet
- CHAP8-Probability and Statistical DistributionDocument46 pagesCHAP8-Probability and Statistical DistributionAisyah MustafaNo ratings yet
- Precipitation - Estimation of Missing DataDocument1 pagePrecipitation - Estimation of Missing DataRowena Pandan100% (1)
- WINSEM2023-24 BCLE306L TH VL2023240500550 2024-02-02 Reference-Material-IDocument57 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCLE306L TH VL2023240500550 2024-02-02 Reference-Material-Issinusingh123No ratings yet
- Manual SSHDocument12 pagesManual SSHAnonymous h5uTxGvcNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Mainly at Meteorological StationsDocument7 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Mainly at Meteorological StationsPruthaviraj BNo ratings yet
- Report HydrologyDocument56 pagesReport HydrologyKareem TaherNo ratings yet
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocument15 pages4-Computation of Average RainfallDarya Memon100% (9)
- Additional ES200Nconcept Notes For Water Resources EnggDocument12 pagesAdditional ES200Nconcept Notes For Water Resources EnggJoseph Neil TacataniNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 3, Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CDocument3 pagesSeatwork 3, Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Parliamentary Debate Judge InstructionsDocument2 pagesParliamentary Debate Judge InstructionsFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- BPdebateJudgingDocument2 pagesBPdebateJudgingFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Research PR 3Document23 pagesResearch PR 3Francisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- WHY RIZAL by Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CDocument1 pageWHY RIZAL by Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Activity CE103Document10 pagesActivity CE103Francisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Sample FS IntroductionDocument1 pageSample FS IntroductionFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Διατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήDocument1 pageΔιατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήjojogarciaNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 WEEK 11-20Document159 pagesChem 2 WEEK 11-20yagami50% (2)
- Analisis Rencana Kebutuhan Obat Di PuskesmasDocument13 pagesAnalisis Rencana Kebutuhan Obat Di Puskesmasigf kalselNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 For IELTS SummaryDocument32 pagesWriting Task 1 For IELTS SummarykarinamrzNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception Towards Green ProductsDocument9 pagesConsumer Perception Towards Green ProductsInternational Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Studies (IJAHSS)No ratings yet
- Graham Holton - UFOs and Religious CultsDocument23 pagesGraham Holton - UFOs and Religious CultsJorsant EdNo ratings yet
- Essential Academic English UHB20102: Week 2Document48 pagesEssential Academic English UHB20102: Week 2Muhammad Haikal Bin AmranNo ratings yet
- Research Works CitedDocument2 pagesResearch Works CitedSamual PauleyNo ratings yet
- Facts Versus OpinionDocument20 pagesFacts Versus OpinionIrish Ga-aNo ratings yet
- Complaint AffidavitDocument5 pagesComplaint AffidavitDarwin Charles ZamboNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsDocument36 pagesObjectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsOriLokisNo ratings yet
- Stephon Jackson - 10th Grade Registration For 2023-2024.xlsx - KamiDocument2 pagesStephon Jackson - 10th Grade Registration For 2023-2024.xlsx - KamiStephon JacksonNo ratings yet
- ch11 Inferences About Population VarianceDocument21 pagesch11 Inferences About Population VarianceGladys Oryz BerlianNo ratings yet
- Ejosed CFP 2024Document2 pagesEjosed CFP 2024jluis_jorgeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of WarfareDocument8 pagesEvolution of WarfareMatt LoweNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil Study in Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagesImportance of Soil Study in Civil EngineeringJack FosterNo ratings yet
- Highway Lab/ Asphalt Section: Asphalt Sample Preparation Data SheetDocument6 pagesHighway Lab/ Asphalt Section: Asphalt Sample Preparation Data SheetFiras BarrajNo ratings yet
- Bugreport Ginkgo PKQ1.190616.001 2020 01 28 08 03 18 Dumpstate - Log 15071Document23 pagesBugreport Ginkgo PKQ1.190616.001 2020 01 28 08 03 18 Dumpstate - Log 15071ErrinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 IR ModelsDocument43 pagesChapter 4 IR ModelsTolosa TafeseNo ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringDocument9 pagesMariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringJeisther Timothy GalanoNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus Bioavailability BiocharDocument15 pagesPhosphorus Bioavailability BiochartauqeermohsinNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document15 pagesGroup 4DORONILA, GUILLEN KLARHIZ P.No ratings yet
- Fire Is The Rapid Oxidation of A Material in The ExothermicDocument4 pagesFire Is The Rapid Oxidation of A Material in The ExothermicIllavarasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Statistical Analysis and Forecasting of Solar Energy (Intra-State)Document21 pagesAssignment 2 Statistical Analysis and Forecasting of Solar Energy (Intra-State)Chaitanya BalaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Math 623 Matrix Analysis: 1 Normal MatricesDocument9 pagesLecture Notes For Math 623 Matrix Analysis: 1 Normal MatricesCamilo Almandos CardonaNo ratings yet
- hjfb5m8w) 25 D HNDocument27 pageshjfb5m8w) 25 D HNSav OliNo ratings yet
- Critical Ischemia of LimbDocument12 pagesCritical Ischemia of LimbTomus ClaudiuNo ratings yet
Lesson 3
Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Francisco, Antonette Jane A.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3
Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Francisco, Antonette Jane A.Copyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3.3-3.
4 -Precipitation Σ A1 P 1
P AVE =
CHARACTERISTIC Σ A1
Isohyetal method—In this method, the
Depth-as it helps us understand the amount of point rainfalls are plotted on a suitable base
precipitation in a given area over a specific period. map
Duration-to the length of time rainfall occurs. Σ A1−2 P 1−2
P AVE =
Σ A1−2
Intensity- defined as the time rate of rainfall depth
and is commonly given in the units of millimeters
T WO POINT
per hour P1+ P 2
P1−2=
2
Frequency- specifically, the return period refers to
how often rainfall occurs Summation of two area is A
Lesson 3.6 missing data
Vertical Depth- that would accumulate on a level
surface if the precipitation remained where it fell. Causes of Missing Data
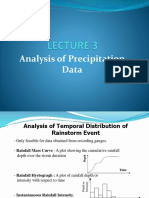
Hyetograph-a graphical representation of the Malfunctioning of precipitation gage
distribution of rainfall intensity over time. and/or related equipment
Effect of natural hazards
DIFFERENT TYPE OF RAIN GAUGES Sabotage (terrorism)
NON-RECORDING Human related problems
Symon’s rain gauge-It consists of a funnel with a METHONDS-
circular rim of 12.7 cm diameter and a glass bottle
statistical analysis
as a receiver.
time series analysis,
RECORDING neural networks,
spatial analysis, etc.
Tipping bucket rain gauge- This consists of a
Station-year method—records of two or
cylindrical receiver 30 cm diameter with a funnel
more stations
inside
PA Pb
Weighing type rain gauge.- when acertain weight =
a . a . r . A a . a .r .b
of rainfallis collected in a tank,
ARITHMETIC MEAN-According to the
Float type rain gauge.- as the rain is collected in arithmetic mean method, the missing
precipitation Px
a float chamber,
i=2
1
AUTOMATIC-RADIO-REPORTING RAIN-GAUGE- PX= ∑ P1
used in mountainous areas, which are not easily n i=1
accessible Normal ratio method- Where Px is the
missing precipitation for any storm at the
AUTOMATIC RAIN-GAUGE- observe rainfall
interpolation station x, “Pi”
amount every 10 minutes and automatically send i=2
1 N
the data to a collection server. PX= ∑ X P1
n i=1 N 1
RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)- useful in
locating precipitation and estimate its intensity and Lesson 3.7 DOUBLE MASS ANALYSIS
in determining the center of tropical cyclones.
Double mass analysis- This method compares the
cumulative annual (or alternatively, seasonal)
values of station X with those of a reference station.
LESSON 3.5 POINT RAINFALL
MEASUREMENTS Step 1: table (year, stn x, Stn Ave)
Step 2: Cumalative Stn. X and Stn. Ave (iplupls
POINT RAINFALL- It is the rainfall at a single
lang Y1 + Y2 +Y3…)
station.
Step 3: kunin ang ratio
Arithmetic average method—simply Sloper 1 = Given sa tapat ng year kung saan
averaging arithmetically the amounts of lumiko Cum Stn X– 0 / Given sa tapat ng year kung
rainfall saan lumiko Cum Stn X Ave -0
Sloper 2 = End - Given sa tapat ng year kung saan
Σ P1 lumiko Cum Stn X/ End- Given sa tapat ng year
P AVE = kung saan lumiko Cum Stn X Ave -0
n Ratio= Slope 2 / Slope 1
Thiessen polygon method—to allow for Step 4: adjust. stn X = original STN. X times Ratio
non-uniform distribution of gauges by Step 5: Cumulative of Adjusted STN X
providing a weighting factor for each gauge. plus the adj. Stn. X copy the Cum STn. Ave
Step 6: aarx = total of adj Stn. X over years
You might also like
- Solutions: Solutions Manual For Photovoltaic Systems Engineering 4Th Edition MessengerDocument12 pagesSolutions: Solutions Manual For Photovoltaic Systems Engineering 4Th Edition MessengerMadaka Siva kumar50% (2)
- Chapter 2Document56 pagesChapter 2ajis sNo ratings yet
- Hopper DesignDocument37 pagesHopper DesignFeroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocument18 pages4-Computation of Average RainfallAafaque HussainNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Method)Document2 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Method)Via Lady Jee Garnacha100% (2)
- Descriptive HydrologyDocument49 pagesDescriptive HydrologyRomeo Baladad67% (3)
- Types of Presentation: InformativeDocument11 pagesTypes of Presentation: InformativeMd Sohanur Rahman100% (1)
- Interpretation of RainfallDocument31 pagesInterpretation of RainfallsavithaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Precipitation Lesson 1 PDFDocument67 pagesPart 3 - Precipitation Lesson 1 PDFJQNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY - Midterm ReviewerDocument4 pagesHYDROLOGY - Midterm ReviewerAvestruz ReginoNo ratings yet
- PRECIPITATIONDocument8 pagesPRECIPITATIONAljon LanguingNo ratings yet
- YT Session 4 Hydrology by Sandeep Jyani SSC JE 2023 STATE AE GATDocument26 pagesYT Session 4 Hydrology by Sandeep Jyani SSC JE 2023 STATE AE GATVìmäl VìhäänNo ratings yet
- PrecipitationDocument42 pagesPrecipitationKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Water Resources3Document26 pagesHydrology and Water Resources3Hazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Precipitation: Depth of Rain Volume of Rain Collected in CMDocument7 pagesMeasurement of Precipitation: Depth of Rain Volume of Rain Collected in CMAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Precipitation - Rain Guage NetworkDocument27 pagesPresentation - Precipitation - Rain Guage NetworkbobbyccwNo ratings yet
- U1 - L6 Optimum Number of Rain Gauge Stations PDFDocument3 pagesU1 - L6 Optimum Number of Rain Gauge Stations PDFishaq kazeemNo ratings yet
- CE143 - Module 3.1Document39 pagesCE143 - Module 3.1MaRc NoBlen D CNo ratings yet
- Lec - 3 - Engineering HydrologyDocument37 pagesLec - 3 - Engineering HydrologyZaTaSaraMeenaKomNo ratings yet
- Null 3Document20 pagesNull 3ayushkumarbhardwaj1562No ratings yet
- 4 Computationofaveragerainfall 170724064842Document17 pages4 Computationofaveragerainfall 170724064842Allecka GragasinNo ratings yet
- 04 Mean Precipitation Over An Area-1Document25 pages04 Mean Precipitation Over An Area-1antenorsarahmichelle7No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Type, Properties, and Behavior of PrecipitationDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting The Type, Properties, and Behavior of PrecipitationglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document16 pagesLecture 5AritroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document18 pagesLesson 3Hubert MoforNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Ch2 2Document30 pagesHydrology Ch2 2Zekariyas AbushaNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Precipitation and Rain GaugesDocument44 pagesFdocuments - in Precipitation and Rain GaugesSuvendu MajumderNo ratings yet
- Mean Precipitation Over An AreaDocument6 pagesMean Precipitation Over An AreaSonny Mae TuboNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data - Conversion of Point To Aerial RainfallDocument34 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data - Conversion of Point To Aerial Rainfallbernie romero50% (2)
- Hydrology Notes 2Document14 pagesHydrology Notes 2NzezwaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Dr. Shakil AhmadDocument14 pagesOutline: Dr. Shakil AhmadWaQar SaleemNo ratings yet
- 4) Chapter 3Document16 pages4) Chapter 3EricNo ratings yet
- Precipitation: ECW 557/431: Engineering HydrologyDocument61 pagesPrecipitation: ECW 557/431: Engineering HydrologyFariz SaniNo ratings yet
- Precipitation 2Document32 pagesPrecipitation 2Alexandra Shun MandrezaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Chapter 6 Part IDocument26 pagesHydrology Chapter 6 Part IspaudelNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Engineering Hydrology - pdf-68Document32 pagesShort Notes On Engineering Hydrology - pdf-68Nilesh AvhadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Precipitation (Part 2) : 1. Depth-Area-Duration RelationshipDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitation (Part 2) : 1. Depth-Area-Duration RelationshipzeyadNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument29 pagesChapter TwoyuusufmohamedhudleNo ratings yet
- Precipitation 09 11Document18 pagesPrecipitation 09 11Wanda FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Rainfallmeasurement 150312100947 Conversion Gate01Document21 pagesRainfallmeasurement 150312100947 Conversion Gate01DeepakNo ratings yet
- Precipitation: ET 1001 Introduction To HydrologyDocument32 pagesPrecipitation: ET 1001 Introduction To HydrologyK WATHSALANo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument24 pagesEngineering HydrologyPrince Vince100% (1)
- Mean Areal PrecipitationDocument6 pagesMean Areal PrecipitationHussam MurshedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Return Period Gautama - 235Document8 pagesJurnal Return Period Gautama - 235DayNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثالثة- الامطارDocument5 pagesالمحاضرة الثالثة- الامطارYM HMNo ratings yet
- Mean Precipitation Over An Area - Double Mass AnalysisDocument5 pagesMean Precipitation Over An Area - Double Mass AnalysisSonny Mae TuboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document11 pagesLecture 3AritroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Precipitation RevDocument27 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitation RevsmdunaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 2Document5 pagesHydrology 2ivyshamjuNo ratings yet
- Precipitationanditsestimation 150316012440 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument66 pagesPrecipitationanditsestimation 150316012440 Conversion Gate01 PDFMAKONo ratings yet
- K. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 62 PDFDocument1 pageK. Subramanya - Engineering Hy-Hill Education (India) (2009) 62 PDFcivilengeeNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationDocument43 pagesLec 6 Analysis of PrecipitationumairNo ratings yet
- Outline: Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil AhmadDocument19 pagesOutline: Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil Ahmad Dr. Shakil AhmadChaudryMuhammadHasnatNo ratings yet
- CHAP8-Probability and Statistical DistributionDocument46 pagesCHAP8-Probability and Statistical DistributionAisyah MustafaNo ratings yet
- Precipitation - Estimation of Missing DataDocument1 pagePrecipitation - Estimation of Missing DataRowena Pandan100% (1)
- WINSEM2023-24 BCLE306L TH VL2023240500550 2024-02-02 Reference-Material-IDocument57 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCLE306L TH VL2023240500550 2024-02-02 Reference-Material-Issinusingh123No ratings yet
- Manual SSHDocument12 pagesManual SSHAnonymous h5uTxGvcNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Mainly at Meteorological StationsDocument7 pagesEstimation of Missing Rainfall Data: Mainly at Meteorological StationsPruthaviraj BNo ratings yet
- Report HydrologyDocument56 pagesReport HydrologyKareem TaherNo ratings yet
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocument15 pages4-Computation of Average RainfallDarya Memon100% (9)
- Additional ES200Nconcept Notes For Water Resources EnggDocument12 pagesAdditional ES200Nconcept Notes For Water Resources EnggJoseph Neil TacataniNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 3, Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CDocument3 pagesSeatwork 3, Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Parliamentary Debate Judge InstructionsDocument2 pagesParliamentary Debate Judge InstructionsFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- BPdebateJudgingDocument2 pagesBPdebateJudgingFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Research PR 3Document23 pagesResearch PR 3Francisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- WHY RIZAL by Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CDocument1 pageWHY RIZAL by Antonette Jane Francisco BSCE 3CFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Activity CE103Document10 pagesActivity CE103Francisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Sample FS IntroductionDocument1 pageSample FS IntroductionFrancisco, Antonette Jane A.No ratings yet
- Διατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήDocument1 pageΔιατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήjojogarciaNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 WEEK 11-20Document159 pagesChem 2 WEEK 11-20yagami50% (2)
- Analisis Rencana Kebutuhan Obat Di PuskesmasDocument13 pagesAnalisis Rencana Kebutuhan Obat Di Puskesmasigf kalselNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 For IELTS SummaryDocument32 pagesWriting Task 1 For IELTS SummarykarinamrzNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception Towards Green ProductsDocument9 pagesConsumer Perception Towards Green ProductsInternational Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Studies (IJAHSS)No ratings yet
- Graham Holton - UFOs and Religious CultsDocument23 pagesGraham Holton - UFOs and Religious CultsJorsant EdNo ratings yet
- Essential Academic English UHB20102: Week 2Document48 pagesEssential Academic English UHB20102: Week 2Muhammad Haikal Bin AmranNo ratings yet
- Research Works CitedDocument2 pagesResearch Works CitedSamual PauleyNo ratings yet
- Facts Versus OpinionDocument20 pagesFacts Versus OpinionIrish Ga-aNo ratings yet
- Complaint AffidavitDocument5 pagesComplaint AffidavitDarwin Charles ZamboNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsDocument36 pagesObjectives of Chapter Optoelectronic MaterialsOriLokisNo ratings yet
- Stephon Jackson - 10th Grade Registration For 2023-2024.xlsx - KamiDocument2 pagesStephon Jackson - 10th Grade Registration For 2023-2024.xlsx - KamiStephon JacksonNo ratings yet
- ch11 Inferences About Population VarianceDocument21 pagesch11 Inferences About Population VarianceGladys Oryz BerlianNo ratings yet
- Ejosed CFP 2024Document2 pagesEjosed CFP 2024jluis_jorgeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of WarfareDocument8 pagesEvolution of WarfareMatt LoweNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil Study in Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagesImportance of Soil Study in Civil EngineeringJack FosterNo ratings yet
- Highway Lab/ Asphalt Section: Asphalt Sample Preparation Data SheetDocument6 pagesHighway Lab/ Asphalt Section: Asphalt Sample Preparation Data SheetFiras BarrajNo ratings yet
- Bugreport Ginkgo PKQ1.190616.001 2020 01 28 08 03 18 Dumpstate - Log 15071Document23 pagesBugreport Ginkgo PKQ1.190616.001 2020 01 28 08 03 18 Dumpstate - Log 15071ErrinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 IR ModelsDocument43 pagesChapter 4 IR ModelsTolosa TafeseNo ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringDocument9 pagesMariano Marcos State University: College of EngineeringJeisther Timothy GalanoNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus Bioavailability BiocharDocument15 pagesPhosphorus Bioavailability BiochartauqeermohsinNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document15 pagesGroup 4DORONILA, GUILLEN KLARHIZ P.No ratings yet
- Fire Is The Rapid Oxidation of A Material in The ExothermicDocument4 pagesFire Is The Rapid Oxidation of A Material in The ExothermicIllavarasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Statistical Analysis and Forecasting of Solar Energy (Intra-State)Document21 pagesAssignment 2 Statistical Analysis and Forecasting of Solar Energy (Intra-State)Chaitanya BalaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Math 623 Matrix Analysis: 1 Normal MatricesDocument9 pagesLecture Notes For Math 623 Matrix Analysis: 1 Normal MatricesCamilo Almandos CardonaNo ratings yet
- hjfb5m8w) 25 D HNDocument27 pageshjfb5m8w) 25 D HNSav OliNo ratings yet
- Critical Ischemia of LimbDocument12 pagesCritical Ischemia of LimbTomus ClaudiuNo ratings yet