Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Properties of Gases & Kinetic Molecular Theory
The Properties of Gases & Kinetic Molecular Theory
Uploaded by
parchrisj.ocampo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views17 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views17 pagesThe Properties of Gases & Kinetic Molecular Theory
The Properties of Gases & Kinetic Molecular Theory
Uploaded by
parchrisj.ocampoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
The Properties of Gases
Kinetic Molecular Theory
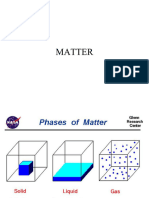
Characteristics of Gases
Gases fill their containers uniformly.
–random motion, no attraction
–undefined shape and volume
Characteristics of Gases
Gases are fluids.
–they are able to flow
Characteristics of Gases
Gases have very low densities.
– most of the volume occupied by a
gas is empty space
Characteristics of Gases
Gases are highly compressible.
– most of the volume occupied by a
gas is empty space
Characteristics of Gases
Gases undergo diffusion & effusion.
– random motion
• Diffusion – describes the movement of one
material through another
• Effusion – gas escapes through a tiny opening
Characteristics of Gases
Gases exert pressure.
– in all directions on the walls of
their containers
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
Ludwig Boltzmann, Rudolf Clausius, and James Maxwell
• The word kinetic refers to motion.
• Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its
motion.
• Kinetic Molecular Theory makes assumptions about:
– Size
– Motion
– Energy of gas particles
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Particles in an ideal gas…
– have no volume.
– have elastic collisions.
– are in constant, random, straight-line motion.
– don’t attract or repel each other.
– have an average KE directly related to Kelvin temperature.
Real Gases
• Particles in a REAL gas…
– have their own volume
– attract each other
• Gas behavior is most ideal…
– at low pressures
– at high temperatures
Properties of Gases
Gas properties can be modeled using math.
Model depends on:
V = volume of the gas (liters, L)
T = temperature (Kelvin, K)
P = pressure (atmospheres, atm)
n = amount (moles, mol)
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area
Gas pressure is the force exerted by a gas per
unit surface area of an object.
Atmospheric pressure (air pressure) results
from the collisions of air molecules with objects.
Measuring Pressure
• Barometer – an
instrument used to
measure
atmospheric
pressure
• Manometer – an
instrument used to
measure gas
pressure in a closed
container
Units of Pressure and STP
• Average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atm
• 1atm = 760 torr = 760 mmHg = 101.3 kPa
• STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure)
– 1 atm and 0oC or 1 atm and 273 K
Temperature
• Measured using a thermometer
• The average kinetic energy of an
object
• The greater the atomic and
molecular motion, the greater the
temperature is of a substance.
Temperature
• If all atomic and molecular motion
would stop, the temperature would
be at absolute zero (lowest
attainable temperature)
o
0 K or -273 C
• To convert Celsius to Kelvin
0
K = C + 273
You might also like
- Financial Policy at AppleDocument9 pagesFinancial Policy at AppleVamsiKrishnaKondapuram25% (4)
- Seniors and Housing-Ministerial Orders and PoliciesDocument300 pagesSeniors and Housing-Ministerial Orders and PoliciesUnited Conservative Party CaucusNo ratings yet
- List of Bloatware Apps Safe To Remove Samsung Galaxy S3 S2Document2 pagesList of Bloatware Apps Safe To Remove Samsung Galaxy S3 S2Dermelclésio Sousa100% (1)
- Jundicial Intern Starter KitDocument15 pagesJundicial Intern Starter KitRollOnFriday90% (10)
- Defense MemorandumDocument8 pagesDefense Memorandumramos.jjmrNo ratings yet
- Information Risk Assessment Handbook 0.05 PDFDocument11 pagesInformation Risk Assessment Handbook 0.05 PDFJose Carlos Laura RamirezNo ratings yet
- Gases Chem 111 Rev2022Document94 pagesGases Chem 111 Rev2022lily brownNo ratings yet
- Q1-M1-KMT and Gas Laws (BL)Document34 pagesQ1-M1-KMT and Gas Laws (BL)Jim AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument91 pagesThe Kinetic Theory of GasesEbony Edwards100% (1)
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument25 pagesKinetic Molecular Theoryroseanneflorete100% (1)
- The Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument90 pagesThe Kinetic Theory of GasestalhawasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: ChemistryDocument16 pagesChapter 9: ChemistrytausmanNo ratings yet
- CHP3 Hysical States of MatterDocument45 pagesCHP3 Hysical States of Matternasec38602No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory PPTDocument29 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory PPTNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument18 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument13 pagesGASESJUAN MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Lecture 17,18 Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument88 pagesLecture 17,18 Kinetic Theory of GasesHuraira AbidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 26 - Defining Ideal Gases 2Document25 pagesLesson 26 - Defining Ideal Gases 2Jenny YoonNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument14 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular TheoryGalindez CieloNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument29 pagesProperties of Gasesshanemariemanuba142833No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Brownian Motion and Absolute ZeroDocument22 pagesThermal Physics Brownian Motion and Absolute ZeroSaad BBNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument53 pagesThermodynamicsReuben GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument19 pagesProperties of Gasesjayzle bea libaoNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument12 pagesProperties of Gasesshasagail100% (1)
- Grade 10 - GasesDocument35 pagesGrade 10 - GasesVictoria Lowman0% (1)
- Chemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDocument58 pagesChemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Course: B.Tech Mechanical Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering Unit-1Document84 pagesCourse: B.Tech Mechanical Subject: Elements of Mechanical Engineering Unit-1Amogh VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Teori GasDocument58 pagesTeori GasmisykamieraNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument12 pagesProperties of GasesimarichrisdelosreyesNo ratings yet
- The Gaseous State of MatterDocument43 pagesThe Gaseous State of MatterGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesDocument24 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of GasesmaximofwwandaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Prelims ReviewerDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Prelims ReviewerSophia BrionesNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Properties of GasesDocument35 pagesGas Laws: Properties of GasesEyaNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument3 pagesIdeal Gasandyboi360No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDocument34 pagesChemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsrosellNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument28 pagesThermoclarkdustin1106No ratings yet
- Introduction To GasesDocument29 pagesIntroduction To GasesJitz BugoyNo ratings yet
- Kinetic-Molecular Theory: Ideal Gas Equation PV NRTDocument9 pagesKinetic-Molecular Theory: Ideal Gas Equation PV NRTVidhuPandey100% (1)
- 5 - States of Matter - Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages5 - States of Matter - Fluid Mechanicshesham.physicsNo ratings yet
- G12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument21 pagesG12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryThea NavarezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument66 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsMikaela Dela Cruz0% (1)
- 1 MEC118 IntroductionDocument39 pages1 MEC118 Introductionmikeclarke1500No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document20 pagesChapter 13Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas EquationDocument16 pagesIdeal Gas EquationPaul AckermannNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument4 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryJessrelle GumawaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Gas PropertiesDocument16 pagesLesson 4-Gas PropertiesLouise Yvonne ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Gas Laws and KMTDocument22 pagesChapter 05 - Gas Laws and KMTmijaggiNo ratings yet
- Phys Chem II Gas Laws Lecture Notes - 230727 - 114428Document71 pagesPhys Chem II Gas Laws Lecture Notes - 230727 - 114428Tshiamo MotaungNo ratings yet
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureDocument49 pagesG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonNo ratings yet
- BI 2 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument23 pagesBI 2 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryfihiNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Model TheoryDocument21 pagesKinetic Particle Model Theorytanvir.md.ahsanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document33 pagesThermodynamics 1Janicz Balderama0% (1)
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Sayed Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Modelling A GasDocument16 pages3.2 Modelling A GasTama MartinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1Kassandra PaculanNo ratings yet
- 4Q W1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases, Boyle's and Charles' LawsDocument54 pages4Q W1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases, Boyle's and Charles' Lawsjia aganaNo ratings yet
- Behaivior of GasesDocument12 pagesBehaivior of Gaseskanha kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Notes - 1Document55 pagesUnit 1 - Notes - 1Rishika PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document33 pagesLecture 5nnurman347No ratings yet
- Gas Laws and Ideal Gases 1Document34 pagesGas Laws and Ideal Gases 1brianbobbiNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Chap. 5Document34 pagesLecture of Chap. 5Supp PrakobkitNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4week1-2Document32 pagesScience10 Q4week1-2ClyzuhNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument23 pagesPhysical ChemistryabeerNo ratings yet
- CH 4 States of Matter I (Gases)Document30 pagesCH 4 States of Matter I (Gases)batazaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37From EverandPhysics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37No ratings yet
- Police and Military RanksDocument3 pagesPolice and Military RanksKoenToeMastaNo ratings yet
- Orcio FMD 08lab1.2Document54 pagesOrcio FMD 08lab1.2Rhea Joy OrcioNo ratings yet
- Nevada Reports 1914 (37 Nev.) PDFDocument369 pagesNevada Reports 1914 (37 Nev.) PDFthadzigsNo ratings yet
- 1 Financial Statements AnalysisDocument5 pages1 Financial Statements AnalysisMark Lawrence YusiNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Working in A Large Law FirmDocument5 pagesThe Benefits of Working in A Large Law Firmabhishek laddhaNo ratings yet
- Regulation No. 466 - 2012Document12 pagesRegulation No. 466 - 2012Wondimagegnehu AbebeNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Theory and Practice 15th Edition Brigham Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFinancial Management Theory and Practice 15th Edition Brigham Solutions Manualrappelpotherueo100% (35)
- HUAWEIDocument41 pagesHUAWEIAkshay100% (1)
- 1193 CaseDigest Berg V MagdalenaEstate Ainna FathiDocument2 pages1193 CaseDigest Berg V MagdalenaEstate Ainna FathiAinnaMacalosNo ratings yet
- JEEL Vol 10 Iss 1Document76 pagesJEEL Vol 10 Iss 1AkankshaNo ratings yet
- CALJ Volume VI Issue - Anurag BhaskarDocument31 pagesCALJ Volume VI Issue - Anurag BhaskarSiri HarishNo ratings yet
- How Do Dinos Say I 39 M Mad EnglishareDocument32 pagesHow Do Dinos Say I 39 M Mad EnglishareVesna DimcicNo ratings yet
- 27 PPT SocialismDocument14 pages27 PPT SocialismTeja TheegalaNo ratings yet
- Rosh and CompanyDocument2 pagesRosh and CompanyAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Stdyro 2022 54483Document2 pagesStdyro 2022 54483Ali Reza FaqirzadaNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTOR'S ALL RISKS - Claim FormDocument4 pagesCONTRACTOR'S ALL RISKS - Claim FormSudheer KumarNo ratings yet
- Criminals, Militias, and Insurgents: Organized Crime in IraqDocument293 pagesCriminals, Militias, and Insurgents: Organized Crime in IraqSSI-Strategic Studies Institute-US Army War CollegeNo ratings yet
- Position Paper-African UnionDocument2 pagesPosition Paper-African UnionanisaiprNo ratings yet
- Davao Light V CADocument7 pagesDavao Light V CAyasuren2No ratings yet
- Transfers Subject To Retained Right To Receive The Income or Designate The Income BeneficiaryDocument31 pagesTransfers Subject To Retained Right To Receive The Income or Designate The Income BeneficiaryAngelica AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 3Document58 pages08 Chapter 3Shiva Shankar Reddy NimmalaNo ratings yet
- The Arabic Parts in Astrology The Lost Key To PredictionDocument28 pagesThe Arabic Parts in Astrology The Lost Key To PredictionChristina Hu0% (1)
- July 14: SF Gangbusters Break Italian Black-Market RingDocument24 pagesJuly 14: SF Gangbusters Break Italian Black-Market Ringjohn obrienNo ratings yet
- Canada Immigration Forms: 5445EDocument13 pagesCanada Immigration Forms: 5445EOleksiy Kovyrin100% (1)