Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
Uploaded by
Sarem JamilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- RS80 EVO Reference Manual En-UsDocument292 pagesRS80 EVO Reference Manual En-UskarenNo ratings yet
- Acls Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesAcls Cheat Sheet PDFDarren Dawkins100% (4)
- Ecart MedsDocument5 pagesEcart Medsしゃいな ふかみNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAdvanced Cardiac ArrestDebbie MeyerNo ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021ay254No ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Joana JohnNo ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Jose Francisco Zamora ScottNo ratings yet
- QRH 3-10 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 June 2023Document1 pageQRH 3-10 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 June 2023ReddyNo ratings yet
- Adult CardDocument1 pageAdult CardIvan MoralesNo ratings yet
- Guideline Management Severe Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 2010 ArchivedDocument3 pagesGuideline Management Severe Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 2010 ArchivedSamuel CruzNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Anaphylactoid ReactionDocument8 pagesAnaphylaxis Anaphylactoid Reactionsringeri2No ratings yet
- Syok Anafilaksis 1Document4 pagesSyok Anafilaksis 1Mariatun Zahro NasutionNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2018Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2018simranNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Core Case 1 Upper Airway Case Scenario Cardspdf Respiratory CoreDocument25 pagesRespiratory Core Case 1 Upper Airway Case Scenario Cardspdf Respiratory CoreVitor HugoNo ratings yet
- Algorithms of AHA 2020Document23 pagesAlgorithms of AHA 2020Emirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- BronkospasmeDocument1 pageBronkospasmeHeru Fajar SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Management of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009Document6 pagesManagement of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009leviosagalNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- ECART-Drug studyDocument38 pagesECART-Drug studyESTEPHANIENo ratings yet
- OctaplexDocument3 pagesOctaplexraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- FerroussulfatedsDocument2 pagesFerroussulfatedsDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument34 pagesCesarean SectionAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- ASCIA Acute Management of Anaphylaxis Guidelines 2015Document4 pagesASCIA Acute Management of Anaphylaxis Guidelines 2015tom8989No ratings yet
- ASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFDocument8 pagesASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFAyu WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Aymane El KandoussiNo ratings yet
- SOP (DrAsma Basharat) SnakebiteDocument4 pagesSOP (DrAsma Basharat) SnakebitesmnoumandogarNo ratings yet
- Wardclasspptbt 120819085632 Phpapp01Document26 pagesWardclasspptbt 120819085632 Phpapp01Ryan-Jay AbolenciaNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument1 pageIsosorbide Dinitrate202110439No ratings yet
- ASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2019Document8 pagesASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2019Asadulla KhanNo ratings yet
- Complication Spinal EpiduralDocument26 pagesComplication Spinal EpiduraldennyramdhanNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Document79 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Deepa BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- CC Opioid OverdoseDocument1 pageCC Opioid Overdosestarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- Algorithm Hypertension Sci PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithm Hypertension Sci PDFGustavo CabanasNo ratings yet
- Emergency GuidelinesDocument11 pagesEmergency GuidelineswinstonappsNo ratings yet
- AnafilaksisDocument27 pagesAnafilaksisAhmad ZakiNo ratings yet
- Emergency MedsDocument12 pagesEmergency MedsAnne Ruth OlinNo ratings yet
- PALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockDocument64 pagesPALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockGlen LazarusNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic EmergenciesDocument11 pagesAnaesthetic EmergenciesSivasankaryNo ratings yet
- MILVv 10 N2Document3 pagesMILVv 10 N2garywall.ukNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section CASEDocument32 pagesCesarean Section CASEjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument31 pagesCesarean Sectionjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Adr Enaline (Epinephrine) 1mg/ml (1:1000) : Paediatric Cardiac Arrest AlgorhytmDocument13 pagesAdr Enaline (Epinephrine) 1mg/ml (1:1000) : Paediatric Cardiac Arrest AlgorhytmwawaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia ProtocolsDocument15 pagesAnesthesia Protocolslaljadeff12No ratings yet
- Vancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - LexicompDocument1 pageVancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - Lexicompsalmanul farisNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Transfusion Practice and Quality Control PDFDocument17 pages1 Blood Transfusion Practice and Quality Control PDFWenz MacuteNo ratings yet
- Contrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall ChartDocument1 pageContrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall Chartapi-358179847No ratings yet
- Sezure ProtocolDocument7 pagesSezure ProtocolRahel GrunderNo ratings yet
- Keep The Airway Open: Head-DownDocument1 pageKeep The Airway Open: Head-DownzenalNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis - DR Dina MDocument31 pagesAnaphylaxis - DR Dina MimamNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Document55 pagesCardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Ahmad AzharNo ratings yet
- AnaphylaxisDocument1 pageAnaphylaxisMazo KhanNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics PracticalDocument75 pagesPaediatrics Practicalmeadwaiet1999No ratings yet
- Allergy - 2021 - Sargant - Refractory Anaphylaxis Treatment AlgorithmDocument3 pagesAllergy - 2021 - Sargant - Refractory Anaphylaxis Treatment AlgorithmMichelle Navarro ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Seven Ps For RSI BOARDDocument2 pagesSeven Ps For RSI BOARDJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Document1 pagePreparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Quality PmnhNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided Heart Failure - Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentDocument14 pagesLeft-Sided Heart Failure - Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentHanzala Safdar AliNo ratings yet
- (April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?Document1 page(April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?SNo ratings yet
- Angine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaDocument39 pagesAngine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaAlexandra Andreea100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - Manchester Students 23.11.2020Document27 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome - Manchester Students 23.11.2020Dalila ZildžićNo ratings yet
- Zoll M Series CCT Defibrillator BrochureDocument2 pagesZoll M Series CCT Defibrillator BrochureManigandan DhamodhiranNo ratings yet
- Shadow Dance - Final AssemblyDocument58 pagesShadow Dance - Final AssemblyKevin Mc CourtNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument3 pagesSchool of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaAj NavNo ratings yet
- MASTERY TEST IN HOPE 1 Week 1Document1 pageMASTERY TEST IN HOPE 1 Week 1Noel MesinaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II Lab: Life Sciences 241 LDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology II Lab: Life Sciences 241 LfuarudinrNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Albert Teo 091511196Document7 pagesJurnal Albert Teo 091511196Cah YaniNo ratings yet
- Re-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsDocument8 pagesRe-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsSunilDwivediNo ratings yet
- Tani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographyDocument7 pagesTani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographycesareNo ratings yet
- Microparticulas PvaDocument2 pagesMicroparticulas PvaJulio Cesar VarelaNo ratings yet
- Heart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andDocument3 pagesHeart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andZauzaNo ratings yet
- BP ChartDocument1 pageBP Chartabu ubaidahNo ratings yet
- Fi H 0840 004 ParDocument16 pagesFi H 0840 004 ParNathaniel Roi BalbarinoNo ratings yet
- Testsv - Final 26971 32528Document63 pagesTestsv - Final 26971 32528Iris BakerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Document35 pagesStroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Sitti Fatwan NisakNo ratings yet
- Resting 2-D Echocardiography / Doppler Echocardiography ReportDocument1 pageResting 2-D Echocardiography / Doppler Echocardiography ReportArmy Setia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Spring Fling Brochure 2022Document12 pagesSpring Fling Brochure 2022North Country EMSNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Idioventricular RhythymDocument4 pagesAccelerated Idioventricular RhythymtjelongNo ratings yet
- Transesophageal Echocardiography: M. Elizabeth Brickner, MDDocument9 pagesTransesophageal Echocardiography: M. Elizabeth Brickner, MDHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- Ten Answers To Key Questions For Fluid Management Inintensive CareDocument11 pagesTen Answers To Key Questions For Fluid Management Inintensive CareAndres RiveraNo ratings yet
- Decompensatio Cordis - IPDDocument8 pagesDecompensatio Cordis - IPDJuliva NandaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDaniel CiubatiiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFDocument9 pagesAbdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFFIA SlotNo ratings yet
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
Uploaded by
Sarem JamilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
2526 AAP RCUK Periop Anaphylaxis-8C
Uploaded by
Sarem JamilCopyright:
Available Formats
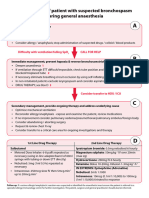
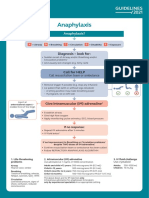
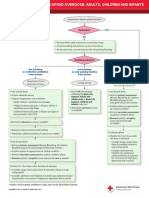
Peri-operative anaphylaxis A B = Airway/Breathing
For anaesthetists/intensivists Give 100% oxygen Ensure sustained ETCO2 trace.
Change to inhalational anaesthetic if appropriate.
Severe/persistent bronchospasm:
A = Airway B = Breathing C = Circulation D = Disability E = Exposure • Exclude oesophageal intubation
• Check patent airway and anaesthetic circuit
• Nebulised salbutamol and ipratropium
• Consider IV bronchodilator
Diagnosis – look for:
• Unexplained hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, bronchospasm (wheeze may be absent if severe)
• Unexpected cardiorespiratory arrest where other causes are excluded C = Circulation
• Skin signs are often absent in severe reactions Hypotension may be resistant, requiring prolonged
treatment with large volume resuscitation
• Give further fluid boluses, titrate to response
• Consider head-down table-tilt or elevating legs
Call for HELP • Establish invasive monitoring as soon as practical
Stop/remove non-essential surgery. Call for cardiac arrest trolley
IF REFRACTORY TO ADRENALINE INFUSION:
• Add a second vasopressor (noradrenaline or
vasopressin) in addition to adrenaline
Stop/remove suspected triggers if possible • Consider glucagon 1 mg IV in adults on beta-blockers
e.g. Antibiotics, NMBAs, dyes, colloids, chlorhexidine coated lines/catheters, lubricants , latex • Consider steroids for refractory reactions or shock
• Consider extracorporeal life support
Give initial IV bolus of adrenaline & Give rapid IV fluid bolus Immediate follow-up
Adult and child > 12 years: 50 micrograms IV Adult and child > 12 years: 500–1000 mL • Take blood (clotted) for serum tryptase once stable
(0.5 mL IV of 1 mg/10 mL [1:10,000]) • Request further samples 1–4 hours after onset of
Child < 12 years: 20 mL/kg symptoms, and at least 24 hours later
Child < 12 years: 1 microgram/kg, needs careful
• Complete allergy referral form: bit.ly/NAP6referral
dilution, titrate to effect • Multiple fluid boluses may be needed • If surgery is urgent or time-critical and patient is stable,
If no IV access: 10 micrograms/kg IM, (e.g. up to 3-5 L in adults, 60-100 mL/kg in children) proceed with surgery but avoid suspected triggers
(max 500 micrograms IM) of 1 mg/mL (1:1,000), and • Avoid colloid • Refer fatal cases to bit.ly/UKFAR
secure IV/IO access
If in doubt, give adrenaline *Use local protocol for adrenaline infusion
(Peripheral infusion recommended
if no central venous access)
If poor response to adrenaline boluses, start IV infusion* OR
Peripheral low-dose IV adrenaline infusion
Involve ICU team early (if no local protocol):
0.5 mg (0.5 mL of 1 mg/mL [1:1000]) in 50 mL
• In both adults and children, start at 0.5–1.0 mL/kg/hour,
If systolic BP < 50 mmHg or cardiac arrest, start CPR and titrate according to clinical response
• Continuous monitoring and observation is mandatory
You might also like
- RS80 EVO Reference Manual En-UsDocument292 pagesRS80 EVO Reference Manual En-UskarenNo ratings yet
- Acls Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesAcls Cheat Sheet PDFDarren Dawkins100% (4)
- Ecart MedsDocument5 pagesEcart Medsしゃいな ふかみNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAdvanced Cardiac ArrestDebbie MeyerNo ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021ay254No ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Joana JohnNo ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Jose Francisco Zamora ScottNo ratings yet
- QRH 3-10 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 June 2023Document1 pageQRH 3-10 Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 June 2023ReddyNo ratings yet
- Adult CardDocument1 pageAdult CardIvan MoralesNo ratings yet
- Guideline Management Severe Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 2010 ArchivedDocument3 pagesGuideline Management Severe Local Anaesthetic Toxicity v2 2010 ArchivedSamuel CruzNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Anaphylactoid ReactionDocument8 pagesAnaphylaxis Anaphylactoid Reactionsringeri2No ratings yet
- Syok Anafilaksis 1Document4 pagesSyok Anafilaksis 1Mariatun Zahro NasutionNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2018Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2018simranNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Core Case 1 Upper Airway Case Scenario Cardspdf Respiratory CoreDocument25 pagesRespiratory Core Case 1 Upper Airway Case Scenario Cardspdf Respiratory CoreVitor HugoNo ratings yet
- Algorithms of AHA 2020Document23 pagesAlgorithms of AHA 2020Emirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- BronkospasmeDocument1 pageBronkospasmeHeru Fajar SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Management of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009Document6 pagesManagement of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009leviosagalNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- ECART-Drug studyDocument38 pagesECART-Drug studyESTEPHANIENo ratings yet
- OctaplexDocument3 pagesOctaplexraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- FerroussulfatedsDocument2 pagesFerroussulfatedsDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument34 pagesCesarean SectionAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- ASCIA Acute Management of Anaphylaxis Guidelines 2015Document4 pagesASCIA Acute Management of Anaphylaxis Guidelines 2015tom8989No ratings yet
- ASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFDocument8 pagesASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFAyu WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Aymane El KandoussiNo ratings yet
- SOP (DrAsma Basharat) SnakebiteDocument4 pagesSOP (DrAsma Basharat) SnakebitesmnoumandogarNo ratings yet
- Wardclasspptbt 120819085632 Phpapp01Document26 pagesWardclasspptbt 120819085632 Phpapp01Ryan-Jay AbolenciaNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument1 pageIsosorbide Dinitrate202110439No ratings yet
- ASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2019Document8 pagesASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2019Asadulla KhanNo ratings yet
- Complication Spinal EpiduralDocument26 pagesComplication Spinal EpiduraldennyramdhanNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Document79 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Deepa BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document12 pagesPaediatric Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)zacklim_2000100% (1)
- CC Opioid OverdoseDocument1 pageCC Opioid Overdosestarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- Algorithm Hypertension Sci PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithm Hypertension Sci PDFGustavo CabanasNo ratings yet
- Emergency GuidelinesDocument11 pagesEmergency GuidelineswinstonappsNo ratings yet
- AnafilaksisDocument27 pagesAnafilaksisAhmad ZakiNo ratings yet
- Emergency MedsDocument12 pagesEmergency MedsAnne Ruth OlinNo ratings yet
- PALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockDocument64 pagesPALS Practice 1 Hypovolemic ShockGlen LazarusNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic EmergenciesDocument11 pagesAnaesthetic EmergenciesSivasankaryNo ratings yet
- MILVv 10 N2Document3 pagesMILVv 10 N2garywall.ukNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section CASEDocument32 pagesCesarean Section CASEjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument31 pagesCesarean Sectionjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Adr Enaline (Epinephrine) 1mg/ml (1:1000) : Paediatric Cardiac Arrest AlgorhytmDocument13 pagesAdr Enaline (Epinephrine) 1mg/ml (1:1000) : Paediatric Cardiac Arrest AlgorhytmwawaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia ProtocolsDocument15 pagesAnesthesia Protocolslaljadeff12No ratings yet
- Vancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - LexicompDocument1 pageVancomycin (Hospital Formulary) - Lexicompsalmanul farisNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood Transfusion Practice and Quality Control PDFDocument17 pages1 Blood Transfusion Practice and Quality Control PDFWenz MacuteNo ratings yet
- Contrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall ChartDocument1 pageContrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall Chartapi-358179847No ratings yet
- Sezure ProtocolDocument7 pagesSezure ProtocolRahel GrunderNo ratings yet
- Keep The Airway Open: Head-DownDocument1 pageKeep The Airway Open: Head-DownzenalNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis - DR Dina MDocument31 pagesAnaphylaxis - DR Dina MimamNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Document55 pagesCardiorespiratory Arrest (FS)Ahmad AzharNo ratings yet
- AnaphylaxisDocument1 pageAnaphylaxisMazo KhanNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics PracticalDocument75 pagesPaediatrics Practicalmeadwaiet1999No ratings yet
- Allergy - 2021 - Sargant - Refractory Anaphylaxis Treatment AlgorithmDocument3 pagesAllergy - 2021 - Sargant - Refractory Anaphylaxis Treatment AlgorithmMichelle Navarro ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Seven Ps For RSI BOARDDocument2 pagesSeven Ps For RSI BOARDJames BrownNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Document1 pagePreparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Quality PmnhNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided Heart Failure - Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentDocument14 pagesLeft-Sided Heart Failure - Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentHanzala Safdar AliNo ratings yet
- (April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?Document1 page(April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?SNo ratings yet
- Angine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaDocument39 pagesAngine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaAlexandra Andreea100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - Manchester Students 23.11.2020Document27 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome - Manchester Students 23.11.2020Dalila ZildžićNo ratings yet
- Zoll M Series CCT Defibrillator BrochureDocument2 pagesZoll M Series CCT Defibrillator BrochureManigandan DhamodhiranNo ratings yet
- Shadow Dance - Final AssemblyDocument58 pagesShadow Dance - Final AssemblyKevin Mc CourtNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument3 pagesSchool of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaAj NavNo ratings yet
- MASTERY TEST IN HOPE 1 Week 1Document1 pageMASTERY TEST IN HOPE 1 Week 1Noel MesinaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II Lab: Life Sciences 241 LDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology II Lab: Life Sciences 241 LfuarudinrNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Albert Teo 091511196Document7 pagesJurnal Albert Teo 091511196Cah YaniNo ratings yet
- Re-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsDocument8 pagesRe-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsSunilDwivediNo ratings yet
- Tani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographyDocument7 pagesTani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographycesareNo ratings yet
- Microparticulas PvaDocument2 pagesMicroparticulas PvaJulio Cesar VarelaNo ratings yet
- Heart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andDocument3 pagesHeart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andZauzaNo ratings yet
- BP ChartDocument1 pageBP Chartabu ubaidahNo ratings yet
- Fi H 0840 004 ParDocument16 pagesFi H 0840 004 ParNathaniel Roi BalbarinoNo ratings yet
- Testsv - Final 26971 32528Document63 pagesTestsv - Final 26971 32528Iris BakerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Document35 pagesStroke Hiperakut (Dr. Dedi Sutia, SP.N (K), FINA, MARS)Sitti Fatwan NisakNo ratings yet
- Resting 2-D Echocardiography / Doppler Echocardiography ReportDocument1 pageResting 2-D Echocardiography / Doppler Echocardiography ReportArmy Setia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Spring Fling Brochure 2022Document12 pagesSpring Fling Brochure 2022North Country EMSNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Idioventricular RhythymDocument4 pagesAccelerated Idioventricular RhythymtjelongNo ratings yet
- Transesophageal Echocardiography: M. Elizabeth Brickner, MDDocument9 pagesTransesophageal Echocardiography: M. Elizabeth Brickner, MDHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- Ten Answers To Key Questions For Fluid Management Inintensive CareDocument11 pagesTen Answers To Key Questions For Fluid Management Inintensive CareAndres RiveraNo ratings yet
- Decompensatio Cordis - IPDDocument8 pagesDecompensatio Cordis - IPDJuliva NandaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDaniel CiubatiiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFDocument9 pagesAbdominal Compartment Syndrome and Intra Abdominal.21 PDFFIA SlotNo ratings yet