Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Division
Cell Division
Uploaded by
64u23dp4thCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Division
Cell Division
Uploaded by
64u23dp4thCopyright:
Available Formats
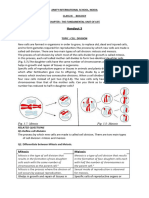
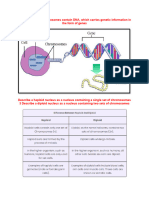
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more
daughter cells.
There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs in somatic cells and results
in two identical daughter cells.
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Meiosis is the type of cell division that occurs in germ cells and results in
four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The stages of meiosis are similar to mitosis but include two rounds of
division, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
Cell division is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
Errors in cell division can lead to genetic disorders and diseases, such as
cancer.
Regulation of cell division is controlled by checkpoints in the cell cycle,
which ensure that each stage is completed accurately before proceeding to the next
stage.)
You might also like
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsuckamaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell Divisionhm khanNo ratings yet
- Scitech 2Document2 pagesScitech 2remeceldo dagamacNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosisaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division.Document1 pageCell Cycle and Cell Division.ag8211729No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument18 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDar W. InNo ratings yet
- Charbel Matar BIO RESEARCHDocument5 pagesCharbel Matar BIO RESEARCH2eemmee eeccoolleeNo ratings yet
- Types of Cell DivisionDocument1 pageTypes of Cell Division8666r69rksNo ratings yet
- Mitosis DefinitionDocument19 pagesMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of CellsDocument1 pageReproduction of CellsruivaacobreadaNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis and Meiosis EssayDocument2 pagesBiology Mitosis and Meiosis Essayhammad133No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument38 pagesCell DivisionJane Marry IgnacioNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosishelenarivascNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Examination of Cell Structure and Function, Including Cellular Processes Like Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesCell Biology - Examination of Cell Structure and Function, Including Cellular Processes Like Mitosis and MeiosisbenildeshsfilesNo ratings yet
- Meiosis & MitosisDocument8 pagesMeiosis & MitosisAna Melisa DorueloNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesCell DivisionLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Group H Pathology PresentationDocument15 pagesGroup H Pathology PresentationdorsukendraNo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Process ProjectDocument2 pagesMitosis Process Projectapi-242679288No ratings yet
- Subhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentDocument8 pagesSubhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentHero PratikNo ratings yet
- Handout 3: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesHandout 3: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMisconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleVega, Charles Gabriel G.No ratings yet
- Bio Discussion 3Document2 pagesBio Discussion 3api-241205310No ratings yet
- Dokument Bez TytułuDocument2 pagesDokument Bez TytułuRozalia OttoNo ratings yet
- Biology - Mitosis & Meiosis SummaryDocument2 pagesBiology - Mitosis & Meiosis SummaryWei HouNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument24 pagesMitosisbrieNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell DivisionedukahonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1Abigail AbiadaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionHajie RosarioNo ratings yet
- Bio SciDocument3 pagesBio ScilowdicakesNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 6. The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 6. The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1Document3 pagesLearning Task 1rovicvaldenor97No ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Describe Mitosis and Meiosis and Compare These ProDocument1 pageDescribe Mitosis and Meiosis and Compare These ProlucyNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman Geslani100% (1)
- Mitosis and Meosis Nuclear Division NotesDocument11 pagesMitosis and Meosis Nuclear Division NotesEshan OmparkashNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsLakkiNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesCell Divisiontaranashamdasani0509No ratings yet
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- What Is MitosisDocument3 pagesWhat Is MitosisJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - Mitosis and Meiosis PDFDocument43 pagesCell Cycle - Mitosis and Meiosis PDFVEENA DEVINo ratings yet
- General Biology I Long Test ReviewerDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology I Long Test ReviewerJillian GarcilanNo ratings yet
- Pembelahan Sel Mitosis Dan Meiosis: Disarikan Oleh: Drs. Rd. Kurniawan, M.PfisDocument7 pagesPembelahan Sel Mitosis Dan Meiosis: Disarikan Oleh: Drs. Rd. Kurniawan, M.PfisMardiah DiahNo ratings yet
- Mitosis NotesDocument2 pagesMitosis Noteslevyan.alakesan9736No ratings yet
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesDifference Between Mitosis and MeiosisFabiola GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesMitosis and MeiosisSapnil VernekarNo ratings yet
- Understanding MitosisDocument1 pageUnderstanding MitosismicelforuniNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument1 pageMitosis64u23dp4thNo ratings yet
- Meoises NoteDocument1 pageMeoises NoteRIVALS〆toxicNo ratings yet
- Cell Division (2003) FinalDocument24 pagesCell Division (2003) FinalAnkita KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis: DR Michael Oku Department of Anatomy University of CalabarDocument18 pagesMitosis & Meiosis: DR Michael Oku Department of Anatomy University of CalabarchidimmaNo ratings yet
- Structure-of-Chromosomes-Cell-Cycle-and-Cell-DivisionDocument5 pagesStructure-of-Chromosomes-Cell-Cycle-and-Cell-DivisionKamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Class 10 NotesDocument11 pagesCell Division Class 10 NotesAbid HasanNo ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) MeiosisDocument4 pages(Biology Form 4) MeiosisUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Mitosis 1Document2 pagesMitosis 1alanoandrearistotleNo ratings yet