Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
Uploaded by
dkalavathimscsCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level Practice Exam QuestionsFrom EverandISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level Practice Exam QuestionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2 - Git Checklist (Light Theme)Document7 pages2 - Git Checklist (Light Theme)dymbv gNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity and Priority in Testing With Examples and DifferenceDocument29 pagesDefect Severity and Priority in Testing With Examples and DifferencelyleholstNo ratings yet
- Examples of Severity and PriorityDocument11 pagesExamples of Severity and PriorityEntertainment world wideNo ratings yet
- Test StrategyDocument8 pagesTest StrategyballavNo ratings yet
- Evaluation: Quality Assurance TestingDocument9 pagesEvaluation: Quality Assurance TestingUdeshika WanninayakeNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument123 pagesTestingEmy Saira thomasNo ratings yet
- Bug Defect Triage ProcessDocument20 pagesBug Defect Triage Processraulnq50% (2)
- Defect Life Cycle or A Bug Lifecycle in Software TestingDocument6 pagesDefect Life Cycle or A Bug Lifecycle in Software TestingKrish KumarNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity & Priority in Software TestingDocument10 pagesDefect Severity & Priority in Software TestingAnonymous S5fcPaNo ratings yet
- Defect MetricsDocument7 pagesDefect MetricsSaravanan RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- 15-Defect Classification-Defect Management Process-Defect Life Cycle-19-02-2024Document27 pages15-Defect Classification-Defect Management Process-Defect Life Cycle-19-02-2024KOTTURU KEERTHANA KeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Art of Defect Reporting v1.1Document28 pagesChapter 5 Art of Defect Reporting v1.1sai prathyushNo ratings yet
- Test ScenariosDocument17 pagesTest Scenariosiveraj100% (2)
- Defect Management Process in Software TestingDocument12 pagesDefect Management Process in Software TestingAamir AfzalNo ratings yet
- Bug Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationDocument52 pagesBug Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationMuhammadAfrizaNo ratings yet
- This Document Defines The DefectDocument5 pagesThis Document Defines The DefectPavan ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Empirical Report To Evaluate and Analysis Actual Defect of SystemDocument8 pagesEmpirical Report To Evaluate and Analysis Actual Defect of SystemTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- DefectsDocument2 pagesDefectsArshad RazaNo ratings yet
- Defect Management ProcessDocument6 pagesDefect Management ProcessMarius Alexandru IonNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity and Defect Priority With ExamplesDocument2 pagesDefect Severity and Defect Priority With ExamplesBalajiNRamalingam100% (1)
- What Is TestingDocument10 pagesWhat Is Testingapi-3833376No ratings yet
- Defect Management Board Questions With AnswerDocument18 pagesDefect Management Board Questions With AnswerNidhi PatilNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument30 pagesAnswerKaruna KiranNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and Fault: VerificationDocument4 pagesDifference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and Fault: VerificationAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Tips To Write AnswersDocument23 pagesTips To Write AnswersNEELAM RAWATNo ratings yet
- System DefecectDocument16 pagesSystem DefecectRsn786No ratings yet
- Software Metrics and ReliabilityDocument8 pagesSoftware Metrics and ReliabilityIssac TanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Manual Testing InterView Questions and AnswersDocument25 pages01 - Manual Testing InterView Questions and AnswersSiri VulisettyNo ratings yet
- Level Value Description: 1. Fault Type, Severity and StatusDocument36 pagesLevel Value Description: 1. Fault Type, Severity and Statusgoga1234No ratings yet
- 李鹏飞( Pengfei Li): Chapter 2 ConceptsDocument68 pages李鹏飞( Pengfei Li): Chapter 2 ConceptsMd Omar FaruqNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance - 1Document32 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance - 1bilalkhanpatricianNo ratings yet
- Bugtracking ToolsDocument18 pagesBugtracking ToolsMd shamimsorkarNo ratings yet
- BUGTRACKINGDocument6 pagesBUGTRACKINGapi-3756186No ratings yet
- 121 Manual Testing Interview Q A 1695364943Document36 pages121 Manual Testing Interview Q A 1695364943Maria IrlanNo ratings yet
- Manual Testing Interview Quesions and AnswersDocument35 pagesManual Testing Interview Quesions and AnswersGajapathi VJNo ratings yet
- Control and Sequence Bugs, Requirements Features Functionality BugsDocument44 pagesControl and Sequence Bugs, Requirements Features Functionality BugsAmarsammy VakaNo ratings yet
- STM Notes Unit1Document61 pagesSTM Notes Unit1vijaykannamalla100% (1)
- Software Testing ImpDocument52 pagesSoftware Testing ImpPinky ChandaNo ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument57 pagesManual TestingsoujanyaadaviNo ratings yet
- Defect & Test ManagementDocument12 pagesDefect & Test ManagementJU PMIT Sabuj0% (1)
- Basic Interview Questions For Manual TestingDocument21 pagesBasic Interview Questions For Manual TestingrajisgoodNo ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument11 pagesManual TestingsachinNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and FaultDocument28 pagesDifference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and FaultbhojanNo ratings yet
- Section A: D20MCA11140Document31 pagesSection A: D20MCA11140Anmol RaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1Document11 pagesLecture # 1Alina PariNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument32 pagesTestingmlnarayana12154470% (1)
- Defect Tracking - 2023Document19 pagesDefect Tracking - 2023Норт КорингNo ratings yet
- QA Preparation DocumentDocument17 pagesQA Preparation DocumentMuhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Principles of Software Testing: Satzinger, Jackson, and BurdDocument86 pagesPrinciples of Software Testing: Satzinger, Jackson, and BurdVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- 4.high, Midum, Low 4. High, Midum, Low: Severity PriorityDocument5 pages4.high, Midum, Low 4. High, Midum, Low: Severity PrioritySubhabrata MishraNo ratings yet
- Software/Web Testing Questions and AnswersDocument59 pagesSoftware/Web Testing Questions and AnswersamarlolageNo ratings yet
- Manual Testing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesManual Testing Interview Questions and AnswersRabindra P.SinghNo ratings yet
- Software Quality AssuranceDocument32 pagesSoftware Quality Assuranceshumail centerNo ratings yet
- Defect Template and ManagementDocument22 pagesDefect Template and ManagementMeenakshi BhattNo ratings yet
- $sotware TestingDocument26 pages$sotware TestingshushmitaNo ratings yet
- CH 1-SteDocument19 pagesCH 1-SteYash GavateNo ratings yet
- Example of Severity and PriorityDocument5 pagesExample of Severity and Prioritywillbark2day100% (1)
- Bug Report GuidelineDocument4 pagesBug Report GuidelineIgne NemeikaiteNo ratings yet
- Real-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsFrom EverandReal-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- APA 7th Referencing GuideDocument92 pagesAPA 7th Referencing GuideSandi WikramaNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-8-Performing An Advanced RHEL installation-en-USDocument166 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-8-Performing An Advanced RHEL installation-en-USDavidNo ratings yet
- SYLVANIA 40641 - 40641 LED15T8L48FGIS841SUBG9 25CS 1 - SKU - Rexel Atlantic PDFDocument1 pageSYLVANIA 40641 - 40641 LED15T8L48FGIS841SUBG9 25CS 1 - SKU - Rexel Atlantic PDFTGhareebNo ratings yet
- MODULE - 2 Digital Marketing EnvironmentDocument34 pagesMODULE - 2 Digital Marketing Environmentrajitha revannaNo ratings yet
- WKS046 Brenne PDFDocument19 pagesWKS046 Brenne PDFdavidguachalla10No ratings yet
- Fingerprint - Based Employee Attendance System - Free Source Code Projects and TutorialsDocument8 pagesFingerprint - Based Employee Attendance System - Free Source Code Projects and Tutorialswilson greenNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking - PrototypeDocument11 pagesDesign Thinking - PrototypeUtkarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Computernetwork UpdatedDocument19 pagesComputernetwork Updatedसुजन कार्कीNo ratings yet
- System Architecture Guide - Alcatel-Lucent 5620 SAMDocument22 pagesSystem Architecture Guide - Alcatel-Lucent 5620 SAMnur0% (1)
- Gmail - Intimation of Show Cause Notice For Suo Moto CancellationDocument1 pageGmail - Intimation of Show Cause Notice For Suo Moto Cancellationram kumarNo ratings yet
- Fine-Tuning Customer Segmentation in Financial Services WDocument20 pagesFine-Tuning Customer Segmentation in Financial Services WShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Controlpro Manual ENDocument29 pagesControlpro Manual ENstrimlakhNo ratings yet
- Et200s Im151 3 PN Fo Manual en-US en-USDocument68 pagesEt200s Im151 3 PN Fo Manual en-US en-USKinnari BhattNo ratings yet
- Bookmarks in Power BIDocument22 pagesBookmarks in Power BIChaitanya IT ReturnsNo ratings yet
- DataDocument11 pagesDataGauravRajNo ratings yet
- Manual LKPS 2019Document17 pagesManual LKPS 2019chan wai yinNo ratings yet
- Microsoft - Ucertify.az 104.exam - Prep.2024 Jan 06.by - Peter.209q.vceDocument13 pagesMicrosoft - Ucertify.az 104.exam - Prep.2024 Jan 06.by - Peter.209q.vceEric VelasquezNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Types of Computer Viruses and Other Malicious ProgramsDocument7 pages20 Common Types of Computer Viruses and Other Malicious ProgramsKavitha RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Espedeo Supra-5000 Projector - Manual - 11525Document187 pagesEspedeo Supra-5000 Projector - Manual - 11525Saša ŠoltićNo ratings yet
- GV300CAN @track Air Interface Protocol: GSM/GPRS/GNSS TrackerDocument444 pagesGV300CAN @track Air Interface Protocol: GSM/GPRS/GNSS TrackerNahuelNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 Answer SheetDocument4 pagesMod 3 Answer SheetFarah CarbonelNo ratings yet
- RAN Sharing 4gDocument195 pagesRAN Sharing 4gAhmedNo ratings yet
- Mail Server: Admin ManualDocument44 pagesMail Server: Admin Manualapi-19973860No ratings yet
- National Club-Ds SystemDocument1 pageNational Club-Ds Systemclarity withinNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Lab - CLI Automation With Python Using Netmiko - ILMDocument5 pages2.2 Lab - CLI Automation With Python Using Netmiko - ILMAlvaro Justiniano Valencia MunozNo ratings yet
- SDFC - Active DirectoryDocument82 pagesSDFC - Active DirectoryLouR2011No ratings yet
- Social Media Strategies For Choruses PresentationDocument84 pagesSocial Media Strategies For Choruses PresentationEveryman EleanyaNo ratings yet
- Google Group 7Document7 pagesGoogle Group 7Ritik MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- WHAT IS DIGITAL LITERACY - ReadingDocument5 pagesWHAT IS DIGITAL LITERACY - ReadingAybukeNo ratings yet
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
Uploaded by
dkalavathimscsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
CIGINITI-ETL Testing
Uploaded by
dkalavathimscsCopyright:
Available Formats
CIGINITI:
Select instr(‘CORPORATEFLOOR’,3,2) out put
What are the reasons when data not loaded in target?
Severity vs Priority
Below are the differences between severity and priority:
Features Severity Priority
Severity is a parameter to denote Priority is a parameter to decide
Definition the impact of a particular defect on the order in which defects should
the software. be fixed.
Severity means how severe the
Priority means how fast the
Purpose defect is affecting the
defect has to be fixed.
functionality.
Severity is related to the quality Priority is related to scheduling
Relation
standard. to resolve the problem.
Categories Severity is divided into 4 Priority is divided into 3
Features Severity Priority
categories:
categories:
Critical
Low
Major
Medium
Medium
High
Low
Who decides The testing engineer decides the The product manager decides the
defects? severity level of the defect. priorities of defects.
Value Its value is objective. Its value is subjective.
Its value doesn’t change from time Its value changes from time to
Value change
to time. time.
It is associated with functionality
Association It is associated with scheduling.
or standards.
It indicates the seriousness of the It indicates how soon the bug
Indication
bug in the product functionality. should be fixed.
Driving factor It is driven by functionality It is driven by business value.
It is based on the technical aspect It is based on the customer’s
Based On
of the product. requirements.
Examples of Priority and Severity Combination
There are possible combinations of priority and severity:
1. High Severity High Priority: Consider an example of a web application where the
if after filling in the login details, the user cannot click the login button then this is the
case of high severity and high priority.
High Severity: If the login button is not clickable then the whole application is
blocked and none of the functions can be accessed by the user
High Priority: If the login button is not clickable this means that the application is
not letting any user log in then what is the use of such an application? Such defects
are high-priority defects as the users will avoid such applications and businesses
will be impacted.
2. High Severity Low Priority: Consider the example of the application being used
on the older versions of Internet Explorer say IE8. This is a case of high severity and
low priority.
High Severity: The fault, in this case, is of high severity because when the
application is accessed on the older version, the page will not load properly and a
few fields and text will be overlapped thus whole application will be impacted.
Low Priority: The defect is of low priority because very few actual users use IE8
or older versions so the fix can wait.
3. Low Severity Low Priority: Consider the example of the help or faq section of the
website where the theme or font style of a section of the page does not match with that
of the rest of the page.
Low Severity: The defect is of low severity as the defect is not affecting the
website functionality.
Low Priority: The defect is of low priority as not many users will access this
particular section of the website so the fix can wait.
4. Low Severity High Priority: Consider the example when there is a typo on the
website. For example, the case of the school website where the ‘Admission Form’ is
misspelled as ‘Admission Form’.
Low Severity: The defect is of low severity because functionality-wise there is no
issue.
High Priority: The defect is of high priority since it is related to business and
needs to be fixed as soon as possible.
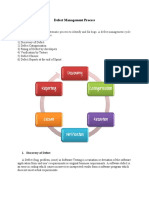
Defect Triage
Defect triage is the process where each defect is prioritized based on its severity,
frequency, risk, etc. The goal is to evaluate, prioritize, and assign the resolution of
defects. This is mainly used in agile project management. The defect triage meetings
frequency depends on a number of factors:
Project schedule.
Overall project health.
The number of bugs in the system.
Impact on schedules of team members’ availability.
The defect triage process can be summarized as:
1. Defect Review: This step involves reviewing all the defects including the defects
that were rejected by the team.
2. Defect Assessment: This step involves an initial assessment of the defects based
on the content and respective priority and severity settings.
3. Defect Assignment: This involves prioritizing the defects, and assigning the
defects to the correct release by the product manager.
You might also like
- ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level Practice Exam QuestionsFrom EverandISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level Practice Exam QuestionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2 - Git Checklist (Light Theme)Document7 pages2 - Git Checklist (Light Theme)dymbv gNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity and Priority in Testing With Examples and DifferenceDocument29 pagesDefect Severity and Priority in Testing With Examples and DifferencelyleholstNo ratings yet
- Examples of Severity and PriorityDocument11 pagesExamples of Severity and PriorityEntertainment world wideNo ratings yet
- Test StrategyDocument8 pagesTest StrategyballavNo ratings yet
- Evaluation: Quality Assurance TestingDocument9 pagesEvaluation: Quality Assurance TestingUdeshika WanninayakeNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument123 pagesTestingEmy Saira thomasNo ratings yet
- Bug Defect Triage ProcessDocument20 pagesBug Defect Triage Processraulnq50% (2)
- Defect Life Cycle or A Bug Lifecycle in Software TestingDocument6 pagesDefect Life Cycle or A Bug Lifecycle in Software TestingKrish KumarNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity & Priority in Software TestingDocument10 pagesDefect Severity & Priority in Software TestingAnonymous S5fcPaNo ratings yet
- Defect MetricsDocument7 pagesDefect MetricsSaravanan RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- 15-Defect Classification-Defect Management Process-Defect Life Cycle-19-02-2024Document27 pages15-Defect Classification-Defect Management Process-Defect Life Cycle-19-02-2024KOTTURU KEERTHANA KeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Art of Defect Reporting v1.1Document28 pagesChapter 5 Art of Defect Reporting v1.1sai prathyushNo ratings yet
- Test ScenariosDocument17 pagesTest Scenariosiveraj100% (2)
- Defect Management Process in Software TestingDocument12 pagesDefect Management Process in Software TestingAamir AfzalNo ratings yet
- Bug Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationDocument52 pagesBug Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationMuhammadAfrizaNo ratings yet
- This Document Defines The DefectDocument5 pagesThis Document Defines The DefectPavan ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Empirical Report To Evaluate and Analysis Actual Defect of SystemDocument8 pagesEmpirical Report To Evaluate and Analysis Actual Defect of SystemTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- DefectsDocument2 pagesDefectsArshad RazaNo ratings yet
- Defect Management ProcessDocument6 pagesDefect Management ProcessMarius Alexandru IonNo ratings yet
- Defect Severity and Defect Priority With ExamplesDocument2 pagesDefect Severity and Defect Priority With ExamplesBalajiNRamalingam100% (1)
- What Is TestingDocument10 pagesWhat Is Testingapi-3833376No ratings yet
- Defect Management Board Questions With AnswerDocument18 pagesDefect Management Board Questions With AnswerNidhi PatilNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument30 pagesAnswerKaruna KiranNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and Fault: VerificationDocument4 pagesDifference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and Fault: VerificationAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Tips To Write AnswersDocument23 pagesTips To Write AnswersNEELAM RAWATNo ratings yet
- System DefecectDocument16 pagesSystem DefecectRsn786No ratings yet
- Software Metrics and ReliabilityDocument8 pagesSoftware Metrics and ReliabilityIssac TanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Manual Testing InterView Questions and AnswersDocument25 pages01 - Manual Testing InterView Questions and AnswersSiri VulisettyNo ratings yet
- Level Value Description: 1. Fault Type, Severity and StatusDocument36 pagesLevel Value Description: 1. Fault Type, Severity and Statusgoga1234No ratings yet
- 李鹏飞( Pengfei Li): Chapter 2 ConceptsDocument68 pages李鹏飞( Pengfei Li): Chapter 2 ConceptsMd Omar FaruqNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance - 1Document32 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance - 1bilalkhanpatricianNo ratings yet
- Bugtracking ToolsDocument18 pagesBugtracking ToolsMd shamimsorkarNo ratings yet
- BUGTRACKINGDocument6 pagesBUGTRACKINGapi-3756186No ratings yet
- 121 Manual Testing Interview Q A 1695364943Document36 pages121 Manual Testing Interview Q A 1695364943Maria IrlanNo ratings yet
- Manual Testing Interview Quesions and AnswersDocument35 pagesManual Testing Interview Quesions and AnswersGajapathi VJNo ratings yet
- Control and Sequence Bugs, Requirements Features Functionality BugsDocument44 pagesControl and Sequence Bugs, Requirements Features Functionality BugsAmarsammy VakaNo ratings yet
- STM Notes Unit1Document61 pagesSTM Notes Unit1vijaykannamalla100% (1)
- Software Testing ImpDocument52 pagesSoftware Testing ImpPinky ChandaNo ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument57 pagesManual TestingsoujanyaadaviNo ratings yet
- Defect & Test ManagementDocument12 pagesDefect & Test ManagementJU PMIT Sabuj0% (1)
- Basic Interview Questions For Manual TestingDocument21 pagesBasic Interview Questions For Manual TestingrajisgoodNo ratings yet
- Manual TestingDocument11 pagesManual TestingsachinNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and FaultDocument28 pagesDifference Between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure and FaultbhojanNo ratings yet
- Section A: D20MCA11140Document31 pagesSection A: D20MCA11140Anmol RaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1Document11 pagesLecture # 1Alina PariNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument32 pagesTestingmlnarayana12154470% (1)
- Defect Tracking - 2023Document19 pagesDefect Tracking - 2023Норт КорингNo ratings yet
- QA Preparation DocumentDocument17 pagesQA Preparation DocumentMuhammad YousafNo ratings yet
- Principles of Software Testing: Satzinger, Jackson, and BurdDocument86 pagesPrinciples of Software Testing: Satzinger, Jackson, and BurdVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- 4.high, Midum, Low 4. High, Midum, Low: Severity PriorityDocument5 pages4.high, Midum, Low 4. High, Midum, Low: Severity PrioritySubhabrata MishraNo ratings yet
- Software/Web Testing Questions and AnswersDocument59 pagesSoftware/Web Testing Questions and AnswersamarlolageNo ratings yet
- Manual Testing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesManual Testing Interview Questions and AnswersRabindra P.SinghNo ratings yet
- Software Quality AssuranceDocument32 pagesSoftware Quality Assuranceshumail centerNo ratings yet
- Defect Template and ManagementDocument22 pagesDefect Template and ManagementMeenakshi BhattNo ratings yet
- $sotware TestingDocument26 pages$sotware TestingshushmitaNo ratings yet
- CH 1-SteDocument19 pagesCH 1-SteYash GavateNo ratings yet
- Example of Severity and PriorityDocument5 pagesExample of Severity and Prioritywillbark2day100% (1)
- Bug Report GuidelineDocument4 pagesBug Report GuidelineIgne NemeikaiteNo ratings yet
- Real-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsFrom EverandReal-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- APA 7th Referencing GuideDocument92 pagesAPA 7th Referencing GuideSandi WikramaNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-8-Performing An Advanced RHEL installation-en-USDocument166 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-8-Performing An Advanced RHEL installation-en-USDavidNo ratings yet
- SYLVANIA 40641 - 40641 LED15T8L48FGIS841SUBG9 25CS 1 - SKU - Rexel Atlantic PDFDocument1 pageSYLVANIA 40641 - 40641 LED15T8L48FGIS841SUBG9 25CS 1 - SKU - Rexel Atlantic PDFTGhareebNo ratings yet
- MODULE - 2 Digital Marketing EnvironmentDocument34 pagesMODULE - 2 Digital Marketing Environmentrajitha revannaNo ratings yet
- WKS046 Brenne PDFDocument19 pagesWKS046 Brenne PDFdavidguachalla10No ratings yet
- Fingerprint - Based Employee Attendance System - Free Source Code Projects and TutorialsDocument8 pagesFingerprint - Based Employee Attendance System - Free Source Code Projects and Tutorialswilson greenNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking - PrototypeDocument11 pagesDesign Thinking - PrototypeUtkarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Computernetwork UpdatedDocument19 pagesComputernetwork Updatedसुजन कार्कीNo ratings yet
- System Architecture Guide - Alcatel-Lucent 5620 SAMDocument22 pagesSystem Architecture Guide - Alcatel-Lucent 5620 SAMnur0% (1)
- Gmail - Intimation of Show Cause Notice For Suo Moto CancellationDocument1 pageGmail - Intimation of Show Cause Notice For Suo Moto Cancellationram kumarNo ratings yet
- Fine-Tuning Customer Segmentation in Financial Services WDocument20 pagesFine-Tuning Customer Segmentation in Financial Services WShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Controlpro Manual ENDocument29 pagesControlpro Manual ENstrimlakhNo ratings yet
- Et200s Im151 3 PN Fo Manual en-US en-USDocument68 pagesEt200s Im151 3 PN Fo Manual en-US en-USKinnari BhattNo ratings yet
- Bookmarks in Power BIDocument22 pagesBookmarks in Power BIChaitanya IT ReturnsNo ratings yet
- DataDocument11 pagesDataGauravRajNo ratings yet
- Manual LKPS 2019Document17 pagesManual LKPS 2019chan wai yinNo ratings yet
- Microsoft - Ucertify.az 104.exam - Prep.2024 Jan 06.by - Peter.209q.vceDocument13 pagesMicrosoft - Ucertify.az 104.exam - Prep.2024 Jan 06.by - Peter.209q.vceEric VelasquezNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Types of Computer Viruses and Other Malicious ProgramsDocument7 pages20 Common Types of Computer Viruses and Other Malicious ProgramsKavitha RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Espedeo Supra-5000 Projector - Manual - 11525Document187 pagesEspedeo Supra-5000 Projector - Manual - 11525Saša ŠoltićNo ratings yet
- GV300CAN @track Air Interface Protocol: GSM/GPRS/GNSS TrackerDocument444 pagesGV300CAN @track Air Interface Protocol: GSM/GPRS/GNSS TrackerNahuelNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 Answer SheetDocument4 pagesMod 3 Answer SheetFarah CarbonelNo ratings yet
- RAN Sharing 4gDocument195 pagesRAN Sharing 4gAhmedNo ratings yet
- Mail Server: Admin ManualDocument44 pagesMail Server: Admin Manualapi-19973860No ratings yet
- National Club-Ds SystemDocument1 pageNational Club-Ds Systemclarity withinNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Lab - CLI Automation With Python Using Netmiko - ILMDocument5 pages2.2 Lab - CLI Automation With Python Using Netmiko - ILMAlvaro Justiniano Valencia MunozNo ratings yet
- SDFC - Active DirectoryDocument82 pagesSDFC - Active DirectoryLouR2011No ratings yet
- Social Media Strategies For Choruses PresentationDocument84 pagesSocial Media Strategies For Choruses PresentationEveryman EleanyaNo ratings yet
- Google Group 7Document7 pagesGoogle Group 7Ritik MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- WHAT IS DIGITAL LITERACY - ReadingDocument5 pagesWHAT IS DIGITAL LITERACY - ReadingAybukeNo ratings yet