Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Transport Review KEY
Cell Transport Review KEY
Uploaded by
Thanh GáiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Transport Review KEY
Cell Transport Review KEY
Uploaded by
Thanh GáiCopyright:
Available Formats
Machine Translated by Google
________ Transport protein that changes shape when a
Cell Transport Review Worksheet
WOOD
particle binds with it
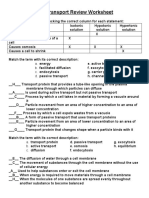
Complete the table by checking the correct column for each Match the term with its correct description:
statement:
statement Isotonic a. transport proteins e. osmosis
Hypotonic Hypertonic
solution solution solution b. active transport f. endocytosis c. diffusion
g. exocytosis
Causes a cell to
swell x d. passive transport h. equilibrium
Doesn't change
x E
_____ The diffusion of water through a cell membrane
the shape of a cell
Causes osmosis _____ The movement of substances through the cell
EASY
x x x
Causes a cell to membrane without the use of cellular energy
shrink x _____
A Used to help substances enter or exit the cell
membrane
_____ When energy is required to move materials through a
REMOVE
Match the term with its correct description: cell membrane
H
a. energy e. active transport _____ When the molecules of one substance are spread
b. facilitated diffusion f. exocytosis evenly throughout another substance to become
c. endocytosis g. carrier protein balanced
d. passive transport h. channel protein _____ A vacuole membrane fuses (becomes a part of) the
WOOD
cell membrane and the contents are released
H _____
F The cell membrane forms around another substance,
________ Transport protein that provides a tube-like opening
for example, how the amoeba gets its food
in the plasma membrane through which particles
can diffuse _____ When molecules move from areas of high
OLD
A concentration to areas of low concentration
________ Is used during active transport but not passive
transport
________ Process by which a cell takes in material by forming
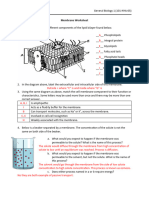
OLD Label the diagrams of cells using the following terms:
a vacuole around it diffusion, active transport, osmosis, equilibrium. The
________ Particle movement from an area of higher
EASY
arrows show the direction of transport. You may use
concentration to an area of lower concentration the terms more than once!
F
________ Process by which a cell expels wastes from
a vacuole
High
________ A form of passive transport that uses transport
REMOVE
8 H2O 2 H2O High
CO2
molecules molecules protein
proteins levels levels
E Particle movement from an area of lower
________
concentration to an area of higher concentration
Low CO2 levels 2 H2O molecules 2 H2O molecules Low protein levels
ACTIVE OSMOSIS EQUILIBRIUM ACTIVE
Machine Translated by Google
4. At which solution of concentration gradient is each cell
Osmosis Practice Activity diagram? (Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic)
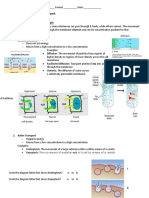
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration. Only water
moves in osmosis! The diagrams below show the concentration of
water and salt inside the cell and the concentration of water
and salt surrounding the cell. Complete the sentences below by
comparing the concentration of the water inside the cell and the
concentration outside the cell.
95% NaCl
first.
5% H2O
HYPOTONIC HYPERTONIC ISOTONIC
5% NaCl
95% H2O OUT OF THE CELL
a. Water will flow _____________________
(into the cell, out of the cell, in both 5. This diagram is moving from a high to a low concentration:
directions).
b. The cell will SHRINK
________________________________
(shrink, burst, stay the same). OSMOSIS (DIFFUSION OF WATER)
25% NaCl
2. 75% H2O
80% NaCl
20% H2O INTO THE CELL
a. Water will flow _____________________ 6. Using a transport protein to move
(into the cell, out of the cell, in both particles across the membrane:
directions). ___________________
FACILITATED DIFFUSION (HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION)
BURST
b. The cell will ________________________________
(shrink, burst, stay the same).
7. Describe the processes occurring in the following pictures:
3.
35% NaCl
35% NaCl 65% H2O
65% H2O IN BOTH DIRECTIONS
a. Water will flow _____________________
(into the cell, out of the cell, in both
directions).
STAY THE SAME
b. The cell will ________________________________
ENDOCYTOSIS EXOCYTOSIS ACTIVE TRANSPORT
(shrink, burst, stay the same).
You might also like
- Handout - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHandout - Cell Transport Review Worksheetapi-502781581No ratings yet
- BIO 230W Lab ReportDocument8 pagesBIO 230W Lab ReportAlaina WeinheimerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function: Main Idea DetailsDocument3 pagesCellular Structure and Function: Main Idea Detailsfatema buhussain0% (1)
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument5 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementMargie OpayNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheetapi-4218787360% (1)
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Transport WorksheetVictoria Niño D100% (1)
- Edited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportDocument2 pagesEdited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportTalha 1075% (4)
- Cell Transport QuizDocument2 pagesCell Transport QuizDoreen Khrystel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheetapi-422807575No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet 1Document4 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet 1api-4218765530% (3)
- 05 Guided Reading Activity AnswersDocument6 pages05 Guided Reading Activity AnswersArjay TiempoNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Transport - Study - Guide - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesCellular - Transport - Study - Guide - Answer KeyJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Indirect and Direct Methods of Gene TransferDocument4 pagesIndirect and Direct Methods of Gene TransferOrpita Das100% (2)
- General Biology 1 Second Quarter WorksheetDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Second Quarter WorksheetAlfer JaoNo ratings yet
- Oct 15Document3 pagesOct 15api-421717478No ratings yet
- 2 - Cell TransportDocument2 pages2 - Cell Transportwjatau28No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetsDocument8 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetsD50% (2)
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: A. B. C. DDocument2 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: A. B. C. DXavier BrownNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Worksheet g8Document4 pagesCell Transport Worksheet g8Ariane DionisioNo ratings yet
- Cellsummativereview AnswersDocument5 pagesCellsummativereview Answersapi-422802678No ratings yet
- TALAGTAG JOHN ANDREI Cell Transport Worksheet 1Document7 pagesTALAGTAG JOHN ANDREI Cell Transport Worksheet 1Malachi LamaNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Summative ReviewDocument5 pagesCell Summative Reviewapi-422959755100% (1)
- WORKSHEET NO. 3cell Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET NO. 3cell Transport WorksheetLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetsDocument6 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetsRyan De AlloNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument5 pagesPlasma Membrane Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementCarlosNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 BiologyDocument1 pageQuiz 2 BiologyAhmed NasrNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport ReviewDocument2 pagesCell Transport ReviewRizza MoradaNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport ActivityDocument2 pagesCell Transport ActivityascanobraverichmondNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport WorksheetJackielyn RavinaNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba Sisters5zhrbrtbwdNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetHessa Faisal0% (1)
- Worksheet: Cell Transport: Match The Term With Its Correct DescriptionDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Cell Transport: Match The Term With Its Correct DescriptionM WigginsNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument2 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementJaniya KellyNo ratings yet
- Cell Trasport Worksheet ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesCell Trasport Worksheet ANSWER KEYFatima Al sharifNo ratings yet
- Membrane Worksheet AnswerkeyDocument2 pagesMembrane Worksheet AnswerkeyretterateNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No.2 - Cell ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet No.2 - Cell ProcessesLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Bio1-Drill 1.3-5Document1 pageBio1-Drill 1.3-5Alec ArelaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substance Across The Plasma Membrane (Part 2)Document7 pagesMovement of Substance Across The Plasma Membrane (Part 2)LAKIESHANo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetЯн ЛомNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightDocument5 pagesCell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightJay-ann Reyes CabarongNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightDocument5 pagesCell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Study Guide PDFDocument4 pagesCellular Transport Study Guide PDFJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHANDOUT - Cell Transport Review Worksheet7qvxkqqhs7No ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDenis Martinez100% (1)
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 Chapter3Document1 pageGenBio1 Chapter3yahnie ًNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneDocument4 pagesCell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: H A C D F B E GDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: H A C D F B E GKimberly CullinaneNo ratings yet
- $R7VH3B1Document2 pages$R7VH3B1Hessa TotaNo ratings yet
- Guided NotesDocument4 pagesGuided NotesMahlodi LamolaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Cell Transport WorksheetDocument5 pages2015 Cell Transport Worksheetpaigemk1988No ratings yet
- Cy-Cell Transport ReviewttkDocument2 pagesCy-Cell Transport Reviewttkapi-2608174140% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDocument5 pagesAs-Level Biology Cell Membranes and Transport Worksheet: Name: - Class: XI SCIENCEDina Anggraini Pramitasari100% (2)
- Review For Quiz 3.1Document9 pagesReview For Quiz 3.1kyleighleehaadkins137No ratings yet
- Duma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Document3 pagesDuma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Cherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Cell - Transport Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesCell - Transport Chapter SummaryAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- 0 094855 Sheet5Document6 pages0 094855 Sheet5omar.hazembadawi2010No ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.5 Cell Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument4 pagesWorksheet 3.5 Cell Membrane and Transport MechanismsEunice LlamadoNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Analyzing Visual ImageryFrom EverandConvolutional Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Analyzing Visual ImageryNo ratings yet
- Do You Want To Alone or With Someone Else Explain Your Choice.Document9 pagesDo You Want To Alone or With Someone Else Explain Your Choice.Thanh GáiNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document13 pagesScience 1Thanh GáiNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 - Science-Part 1Document24 pagesGrade 4 - Science-Part 1Thanh GáiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 - ScienceDocument24 pagesGrade 3 - ScienceThanh GáiNo ratings yet
- Grade 2-ScienceDocument18 pagesGrade 2-ScienceThanh GáiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 2Document14 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 2Saroja Veeresh100% (2)
- 2-Substitution Matrices and Python - 2017Document65 pages2-Substitution Matrices and Python - 2017Areej ZafarNo ratings yet
- Sarthak Mechanism of Blood ClottingDocument42 pagesSarthak Mechanism of Blood ClottingVishal MishraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in SCIENCE 7-WPS OfficeBhea GasparNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2我穿白色的胖次No ratings yet
- Sds PageDocument11 pagesSds PageBantita Treepong100% (1)
- Jagendorf Andre PPDocument15 pagesJagendorf Andre PPNurlaila KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Hall+Collis Integron Review MolMic1995Document9 pagesHall+Collis Integron Review MolMic1995DrAhmedSalimNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Notes For Science and TechnologyDocument106 pagesSankalp Notes For Science and TechnologyKamal BhatiyaNo ratings yet
- 03 Enzyme KineticsDocument48 pages03 Enzyme KineticsCester Gale DucusinNo ratings yet
- ACTIVE TRANSPORT Vs PASSIVE TRANSPORTDocument6 pagesACTIVE TRANSPORT Vs PASSIVE TRANSPORTfelixnellyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle CheckpointsDocument17 pagesCell Cycle CheckpointsRetchel Cadayong NavalesNo ratings yet
- Life Chap 1 Part1Document16 pagesLife Chap 1 Part1Elhade ElbakushNo ratings yet
- Cerevisiae and Other Fungi: Principles of Gene Manipulation by Liuzengran Hebei University of Economics and BusinessDocument81 pagesCerevisiae and Other Fungi: Principles of Gene Manipulation by Liuzengran Hebei University of Economics and BusinessManuel DíazNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles DefinitionDocument40 pagesCell Organelles Definitionmuhammad aslam0% (1)
- Biotechnology - Igcse BiologyDocument4 pagesBiotechnology - Igcse BiologyTheStarNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Cycle 8.03Document47 pages1 Cell Cycle 8.03Rawbeena RamtelNo ratings yet
- Describe The Use of Recombinant DNA Technology in The Synthesis of Human Insulin by BacteriaDocument3 pagesDescribe The Use of Recombinant DNA Technology in The Synthesis of Human Insulin by BacteriaCleo PoulosNo ratings yet
- SMK Petaling Test Specification Table (Jsu) Biology Form 4 Paper 2Document2 pagesSMK Petaling Test Specification Table (Jsu) Biology Form 4 Paper 2Raidah AdhamNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument38 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organizationjake laraNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecules SS SSDocument15 pagesBiomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecule Biomolecules SS SSOm AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Adenoma Carcinoma SequenceDocument27 pagesAdenoma Carcinoma SequenceKhurshedul AlamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Basic Immunology 3rd Edition Abul K Abbas Full DownloadDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Basic Immunology 3rd Edition Abul K Abbas Full Downloadbrianbell06021999pfa100% (41)
- The Origin and Evolution of The Genetic Code 1th Anniversary Year of The Birth of Francis CrickDocument204 pagesThe Origin and Evolution of The Genetic Code 1th Anniversary Year of The Birth of Francis CrickOld Grumpy100% (1)
- Protein: Iloilo Doctor'S CollegeDocument27 pagesProtein: Iloilo Doctor'S Collegealthea vergaraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control of ProteinDocument43 pagesGenetic Control of ProteinGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Amino AcidDocument25 pagesChapter4 Amino Acidkidpu100% (2)
- 60 Assertion Reason MCQs by DR NK Sharma Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pages60 Assertion Reason MCQs by DR NK Sharma Molecular Basis of InheritanceDiNo ratings yet