Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.3.3 Constraining A Sketch
1.3.3 Constraining A Sketch
Uploaded by
ehalko2007Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.3.3 Constraining A Sketch
1.3.3 Constraining A Sketch
Uploaded by
ehalko2007Copyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1.3.
3 Geometric Constraints
Introduction
A CAD model can quickly display an engineer’s ideas in a realistic way. And those
models can be used to generate technical drawings that can communicate the
information necessary to make the idea a reality. In order to generate a 3D model,
designs must start with sketches that are generated within the CAD program. These
computer generated sketches will appear resemble hand drawn sketches in
geometry (the combination of points, lines, and shapes), but have big advantages
over hand drawn sketches. One important difference between a freehand sketch and
a CAD sketch is accuracy. The lines of a CAD sketch can be drawn perfectly
straight, with start and end points that occur in exact locations in space. By using
numeric (dimensional) constraints a line may also be given precise length, placed a
specific distance from another sketch feature, or constrained to be oriented at a
specific angle from another straight line. By applying geometric constraints a line can
be made perfectly horizontal or vertical. If more than one line is being sketched, they
can be made perfectly parallel or perpendicular, collinear, or equal in length. Lines
can be constrained to be tangent to circles or arcs, and two circles can be
constrained to be concentric. In order to precisely model a part, the designer must
be able to use dimensional and geometric constraints within the CAD program.
You have already used linear dimensioning in earlier activities. In this activity, you
will learn about geometric constraints that are common to most CAD programs and
practice applying these constraints to CAD sketches.
Equipment
Computer with 3D CAD solid modeling program
CAD files
o Geometric Constraints
Procedure
1. Navigate to the Virtual Desktop on your computer. Find and open the folder
titled 1.3.3 Constraining a Sketch. Then open Drawing File for SWYK page.
Next open the attached file called 5.2.a.A.SR Geometric Constraints.idw.
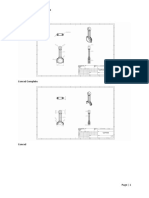
You must click on one of the images first to enter the sketch environment.
Read the instructions above each image in the file and use the Geometric
Constraint tools to complete each of the 12 exercises. Your completed sheet
should look similar to the sheet pictured.
2. Make the geometric constraints visible by choosing the Show Constraints tool
( ) in the Constrain panel under the Sketch tab.
3. Add your name to the bottom right corner of the sheet. You may use the Text
tool in the Draw panel under the Sketch tab to add text to a sketch.
© 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Introduction to Engineering Design Activity 5.2a Geometric Constraints – Page 1
4. Use the Snipping Tool to save an image of the completed drawing with
constraints visible. Paste the image directly onto this Word document. After
answering the conclusion questions, submit your work using the Submission
on Schoology for evaluation.
CAD file name and location:
Before
After
© 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Introduction to Engineering Design Activity 5.2a Geometric Constraints – Page 2
© 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Introduction to Engineering Design Activity 5.2a Geometric Constraints – Page 3
Conclusion
Answer the conclusion questions below, then save and submit in the Turn-
In section along with the .jpeg image of your constrained sketch.
1. What is a geometric constraint?
2. What are the different types of geometric constraints that are applied to sketches,
and what are their functions?
3. Define “tangent”.
a. Sketch a line tangent to two circles.
b. Sketch three circles such that all circles are tangent to the other two.
4. How is a geometric constraint different from a numeric constraint?
© 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Introduction to Engineering Design Activity 5.2a Geometric Constraints – Page 4
You might also like
- Manual de Sap Business One en EspañolDocument2 pagesManual de Sap Business One en EspañolJuan Villanueva Zamora0% (1)
- 5 2 A A Geometric Constraints 1Document3 pages5 2 A A Geometric Constraints 1api-248595624No ratings yet
- 5 2 A A Geometric Constraints LennonDocument2 pages5 2 A A Geometric Constraints Lennonapi-234212327No ratings yet
- 5 2 A A Geometric ConstraintsDocument4 pages5 2 A A Geometric Constraintsapi-283774592No ratings yet
- 5 5 A B Cadmodelfeatures Practice LennonDocument5 pages5 5 A B Cadmodelfeatures Practice Lennonapi-234212327No ratings yet
- A5 2 MakingSketchesAADDocument22 pagesA5 2 MakingSketchesAADMax2016No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Introduction To CADDocument280 pagesChapter 5 Introduction To CADNIK NURFATIN NATASHA BINTI AHMAD DAUD BK20110288No ratings yet
- Visual Graphic Design - VGD4: Computer Aided Design (CAD)Document14 pagesVisual Graphic Design - VGD4: Computer Aided Design (CAD)JD SalviejoNo ratings yet
- Advantages of CAD Over Conventional Drawing Techniques (Assignnet 1)Document9 pagesAdvantages of CAD Over Conventional Drawing Techniques (Assignnet 1)Firdaus Khan100% (1)
- Computer Aided DesignDocument14 pagesComputer Aided DesignthirumalaikumaranNo ratings yet
- CAD Part 1 2020-21Document17 pagesCAD Part 1 2020-21Ibrahim ImranNo ratings yet
- CAD Modeling in Construction PlanningDocument13 pagesCAD Modeling in Construction PlanningHaseebNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution System in AllDocument19 pagesElectrical Distribution System in Allkingston roseNo ratings yet
- 5 5 A B CadmodelfeaturesDocument12 pages5 5 A B Cadmodelfeaturesapi-312626334No ratings yet
- On AutocadDocument16 pagesOn Autocads bhadur singhNo ratings yet
- 5 2 B A IntroductiontocadmodelingskillsDocument15 pages5 2 B A Introductiontocadmodelingskillsapi-312666393No ratings yet
- CAD Part 2 - Parametric 2020-21Document22 pagesCAD Part 2 - Parametric 2020-21Ibrahim ImranNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Designing: Course Code: BTM 705 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveDocument1 pageComputer Aided Designing: Course Code: BTM 705 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveSanjay GomastaNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Machine DrawingDocument16 pagesComputer Aided Machine DrawingAmit Bhagure0% (1)
- How To Express Design Intent in Rhino 3D: White Paper November'09Document17 pagesHow To Express Design Intent in Rhino 3D: White Paper November'09fareed majeedNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam - Module 1Document85 pagesCad Cam - Module 1sibaprasad.behera2020No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Drawing and Graphics (ME 210) : Term 041Document12 pagesMechanical Engineering Drawing and Graphics (ME 210) : Term 041sigmasundarNo ratings yet
- CAD2Document34 pagesCAD2jahremade jahremadeNo ratings yet
- CATIA Full Book 2 Print - 2Document147 pagesCATIA Full Book 2 Print - 2Sum Sumne SumanthNo ratings yet
- Secrets Revealed For Construction Simulation in Navisworks ManageDocument40 pagesSecrets Revealed For Construction Simulation in Navisworks ManageGláuber LucasNo ratings yet
- Sushant Paper FinalDocument11 pagesSushant Paper FinalMaxGorilla MadCartelNo ratings yet
- CAD (MEng 2302)Document2 pagesCAD (MEng 2302)addisudagneNo ratings yet
- CADM Mod 2Document39 pagesCADM Mod 2Aswin MNo ratings yet
- v2 AC4772 Autocad ParametricsDocument36 pagesv2 AC4772 Autocad ParametricsLauro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I - Introduction To Cad/CamDocument73 pagesUnit - I - Introduction To Cad/CamPrakhar JainNo ratings yet
- The Design Process Ideation and Computer Aided Design PDFDocument11 pagesThe Design Process Ideation and Computer Aided Design PDFAmna EjazNo ratings yet
- ES 01-Handout No.1Document21 pagesES 01-Handout No.1Jonathan TambisNo ratings yet
- Cad/Cam: Chapter TwoDocument172 pagesCad/Cam: Chapter TwoMoathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CadDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Cadakshay_pundeNo ratings yet
- Catia v5 ReportDocument69 pagesCatia v5 ReportNeelkamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignmnt 2 Parametric Model LiningDocument15 pagesAssignmnt 2 Parametric Model LiningusamaumerNo ratings yet
- WindshieldDocument4 pagesWindshieldapi-269424168No ratings yet
- Cad System: Cad-Cam Unit IiDocument64 pagesCad System: Cad-Cam Unit IikoalaboiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper About AutocadDocument5 pagesResearch Paper About Autocadh039wf1t100% (1)
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing NotesDocument31 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing NotesKrishna kumarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Solid Modeling With AutocadDocument17 pagesTeaching Solid Modeling With AutocadCaurelou PitocNo ratings yet
- Irjet V9i7575Document7 pagesIrjet V9i7575shubs2226No ratings yet
- CADD MODULE Week 2Document7 pagesCADD MODULE Week 2John Robert DoloirasNo ratings yet
- CadDocument8 pagesCadLuck VelascoNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided DesignDocument7 pagesComputer Aided DesignRicardo AqpNo ratings yet
- 3.4.A LinearDimensionsDocument10 pages3.4.A LinearDimensionsitsmedd1No ratings yet
- 3D Cad - An Emergent Tool For Concept DesignDocument4 pages3D Cad - An Emergent Tool For Concept DesignAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Program in 2D & 3D DrawingDocument5 pagesAutoCAD Program in 2D & 3D Drawingaop4210No ratings yet
- WLDDG 501 Design and Communication GraphicsDocument99 pagesWLDDG 501 Design and Communication Graphicshagabimanajanvier897No ratings yet
- Section1 Module1 InstructorNotes r3Document19 pagesSection1 Module1 InstructorNotes r3asdfgdsfNo ratings yet
- Jamie Stafford - CAD PortfolioDocument6 pagesJamie Stafford - CAD Portfoliomaitham100No ratings yet
- Cadd 2d Module Complete 2021Document71 pagesCadd 2d Module Complete 2021Ged RichNo ratings yet
- Preface: Computer Aided Engineering Graphics (CAEG)Document183 pagesPreface: Computer Aided Engineering Graphics (CAEG)Josh Marshal Blessing MuchenjekwaNo ratings yet
- Creating and Editing Centerline Geometry 2020R1-03-01Document60 pagesCreating and Editing Centerline Geometry 2020R1-03-01Rutik PatelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Creative Tech. 7.4Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Creative Tech. 7.4Dan Abrenica100% (1)
- Introduction To CAD: Svcaet&Rs, Fae, Igkv, Raipur (C.G.)Document20 pagesIntroduction To CAD: Svcaet&Rs, Fae, Igkv, Raipur (C.G.)Jai JoshiNo ratings yet
- GD115-2 Rendering Part 2Document30 pagesGD115-2 Rendering Part 2Cynthia Bongar TablangNo ratings yet
- Geometric Modeling: Exploring Geometric Modeling in Computer VisionFrom EverandGeometric Modeling: Exploring Geometric Modeling in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Mniproject Report.Document22 pagesMniproject Report.add RomitNo ratings yet
- Ebook Adobe Indesign Classroom in A Book 2022 Release 1St Edition Kelly Anton Tina Dejarld Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Adobe Indesign Classroom in A Book 2022 Release 1St Edition Kelly Anton Tina Dejarld Online PDF All Chaptermirta.nixon211100% (13)
- Nikon - Download Center - NX StudioDocument4 pagesNikon - Download Center - NX StudioRaja Sekaran SajjaNo ratings yet
- Nile International Education System Certificate of Nile International Secondary Education Level 1Document12 pagesNile International Education System Certificate of Nile International Secondary Education Level 1ylakkaniNo ratings yet
- Sap Transactions Interview Questions: What Is A Transaction?Document18 pagesSap Transactions Interview Questions: What Is A Transaction?largemanNo ratings yet
- Key ShortcutsssDocument7 pagesKey ShortcutsssSreeSai SiddarthaNo ratings yet
- 7 - MS Word Mail Merging, Label, & Inserting ImageDocument24 pages7 - MS Word Mail Merging, Label, & Inserting ImageJosephVillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CoDeSys Version 3.5 First Steps Ver. 1Document74 pagesCoDeSys Version 3.5 First Steps Ver. 1Redenel SerquinaNo ratings yet
- MS836 User Manual PDFDocument139 pagesMS836 User Manual PDFSafik MukhasinNo ratings yet
- Art Gallery Management System: Department of Information TechnologyDocument12 pagesArt Gallery Management System: Department of Information TechnologyBushra ZahidNo ratings yet
- A Practical Introduction To Modern JavaScript (Zsolt Nagy)Document205 pagesA Practical Introduction To Modern JavaScript (Zsolt Nagy)Lawrence Lim100% (2)
- Mold enDocument12 pagesMold enCristinaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentAbeyMulugetaNo ratings yet
- JMP Help 1Document4 pagesJMP Help 1handsomepeeyushNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 PythonDocument21 pagesUnit-4 PythonDivyasri JeganNo ratings yet
- PASSWORD MANAGER PPT 2Document3 pagesPASSWORD MANAGER PPT 2FRUTI PATELNo ratings yet
- Instructions Update MVX Control System Via MVX-ControlDocument3 pagesInstructions Update MVX Control System Via MVX-ControlYorae AnggaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Rainbow TechnologyDocument25 pagesChapter - I: Rainbow Technologyl.maheshNo ratings yet
- 103what Is System Testing - Types & Definition With ExampleDocument4 pages103what Is System Testing - Types & Definition With ExampleFlorin ConduratNo ratings yet
- TM-1860 AVEVA Administration (1.4) Fundamentals Rev 2.0Document156 pagesTM-1860 AVEVA Administration (1.4) Fundamentals Rev 2.0praveen jangirNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Organization-Hardware-v3Document39 pagesComputer Systems Organization-Hardware-v3patrick rollodaNo ratings yet
- Creating An EbookDocument3 pagesCreating An EbookHarendranBalaNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Satellite-6.10-Content Management Guide-En-UsDocument119 pagesRed Hat Satellite-6.10-Content Management Guide-En-UsAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Introduction LinuxDocument10 pagesIntroduction LinuxKirubel LemmaNo ratings yet
- Flexpendant Application ManualDocument216 pagesFlexpendant Application ManualLuis Claudio RamosNo ratings yet
- The Guild 2 - Manual - PCDocument31 pagesThe Guild 2 - Manual - PCstraverso1230% (1)
- 10987C ENU PowerPoint Day 4Document79 pages10987C ENU PowerPoint Day 4rrNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Discrete Cosine and Wave Let TransformDocument6 pagesComparison Between Discrete Cosine and Wave Let TransformMichaelNo ratings yet
- Modbus TCP/IP Option Instruction Manual: s800v004, s801v003 and LowerDocument22 pagesModbus TCP/IP Option Instruction Manual: s800v004, s801v003 and Lowerindra lukmanNo ratings yet